(4x)
(2x + 6)°
What is the value of x?
Answers
Answer:
8\(x^{2} \\\) + 24x
Pls choose me as brainliest!
Related Questions
Suzy randomly picks marbles from a bag containing 13 identical marbles. How many possible outcomes are there if she selects 9 marbles
Answers
Suzy randomly picks marbles from a bag containing 13 identical marbles. The possible outcomes of the given probability if she selects 9 marbles is:
259,459,200.
What is random?Randomness is commonly used to refer to an event's apparent or actual lack of pattern or predictability. Random events, symbols, or steps frequently occur in no particular order and do not adhere to any recognizable pattern or combination.
Germanic in origin, Randon is a name for boys. With a name that means "wolf shield," you can inspire baby Randon to embrace their sense of adventure. something or someone that is suspiciously out of the ordinary, unidentified, or unknown. a peculiar or erratic individual or thing. Something that is random lacks structure, direction, or intent. Like the random selection of lottery numbers or unplanned random events, it occurs entirely by chance.
To learn more about probability refer to:
https://brainly.com/question/9793303
#SPJ4
Container A has 200 L of water, and is being filled at a rate of 6 liters per minute. Container B has 500 L of water, and is being drained at 6 liters per minute. How many minutes, m, will it take for the two containers to have the same amount of water?
Answers
It will take 25 minutes for the two containers to have the same amount of water .
In the question ,
it is given that ,
water present in container A = 200L
water present in container B = 500L
rate at which the water is filling in container A= 6 liter/minute
rate at which the water is draining in container B = 6 liter/minute
let the time taken = m minutes ,
So , According to the question ,
the equation representing the situation is
200 + 6m = 500 - 6m
Simplifying further , we get
6m + 6m = 500 - 200
12m = 300
m = 300/12
m = 25
Therefore , It will take 25 minutes for the two containers to have the same amount of water .
Learn more about Equations here
https://brainly.com/question/13304287
#SPJ1
what is 28.5 inches in height?
Answers
What is the HOL blocking issue in HTTP 1.1? How does HTTP 2 attempt to solve it?
Answers
HOL blocking issue in HTTP 1.1 HOL stands for "Head of Line" and is the term for what happens when a network pipeline receives requests from multiple connections and the first request needs to be processed before the next request can be processed.
As a result, if a single request takes longer to process, all other requests in the queue will be held up.
The problem that arises from this is known as the Head of Line (HOL) blocking issue.
HTTP/1.1 aims to solve the HOL blocking issue by reusing the same connection for multiple requests to avoid the connection setup overhead.
However, requests that are delayed for any reason, including server processing, network congestion, or latency, can create a bottleneck in the connection and cause subsequent requests to be blocked.
HTTP/2 approach to solve the HOL blocking issue
HTTP/2 attempts to solve the HOL blocking problem by introducing multiplexing, which is the ability to send multiple requests and responses simultaneously over a single connection.
With HTTP/2, the server can send several responses to the client for a single request in a non-blocking manner, avoiding the blocking problem that occurred with HTTP/1.1.
Another feature of HTTP/2 is that it enables server push, where the server can push data to the client before the client requests it, which can improve the performance of a web page.
To know more about HOL blocking issue visit:
https://brainly.com/question/33337854
#SPJ11
Greg is designing the lighting scheme for a building. He would like the lights to be randomly turned on to create an impression of activity. Which lighting scheme should he use
Answers
A random lighting scheme, where the lights are turned on and off in a non-predictable manner, would be the most suitable choice for Greg to create an impression of activity in the building.
To create an impression of activity, Greg should use a random lighting scheme where the lights are turned on and off randomly.
Now let's delve into the explanation. A random lighting scheme involves varying the on-off pattern of the lights in a way that does not follow a predictable sequence or pattern. This randomness creates an impression of activity by simulating the natural fluctuations of lighting that would occur in a busy environment.
By randomly turning the lights on and off, Greg can mimic the dynamic lighting conditions that would be observed in a building with people moving around and engaging in various activities. This can enhance the overall ambiance and perception of liveliness within the space.
Random lighting schemes also have practical benefits, as they can help conserve energy by avoiding the constant illumination of areas that are not in use. By randomly cycling the lights, Greg can achieve a balance between creating the desired impression of activity and ensuring efficient energy usage.
In summary, a random lighting scheme, where the lights are turned on and off in a non-predictable manner, would be the most suitable choice for Greg to create an impression of activity in the building.
Learn more about constant here:
https://brainly.com/question/27548709
#SPJ11
Find the length of the third side. If necessary, round to the nearest tenth
Pythagorean Theorem (Rounding)

Answers
Answer:
3.5
Step-by-step explanation:
Set up the Pythagorean Theorem (a^2 + b^2 = c^2) where the unknown side is x:
2^2 + x^2 = 4^2
4 + x^2 = 16
x^2 = 12
x = ± sqrt(12)
x ≈ 3.5
Note: '^' means "to the power of", so '^2' means "squared"
7 1/3 in its simplest form
Answers
Answer:
7 1/3
Step-by-step explanation:
7 1/3 is the simplest form, since you can't divide it anymore. However, if you're talking about improper fractions, then it would be 22/3.
Answer:
\(\frac{22}{3}\)
Step-by-step explanation:
Change 7 1/3 into a mixed number: 7 × 3 = 21, 21 + 1 = 22Put 22 over 3:\(\frac{22}{3}\)Abd and dbc are linear pairs, and abd and evc are vertical angles. if mabd = 5(2x + 1), mdbc= 3x + 6, and mebc = y+135/2, select all statements that are true
Answers
The following statements are true:
mabd + mdbc = 180 degrees
mabd = mevc
What are the true statements given that abd and dbc are linear pairs, abd and evc are vertical angles, and the measures are given?According to the definition of linear pairs, the two angles add up to 180 degrees. Therefore, mabd + mdbc = 180 degrees.
According to the definition of vertical angles, they have the same measure. Therefore, mabd = mevc.
Since abd and evc are vertical angles, and mabd = mevc, then mabd = mebc. Therefore, we can substitute mabd in the equation mebc = y+135/2 to get 5(2x + 1) = y+135/2.
We can solve for y to get y = 10x + 260.
Now we can substitute this value of y into the equation mebc = y+135/2 to get mebc = 10x + 347.5.
Therefore, none of the statements in the question that mention mebc are necessarily true or false, since we don't have enough information about the value of x to determine its measure.
Learn more about vertical angles
brainly.com/question/24460838
#SPJ11
A large population has mean 100 and standard deviation 16. What is the probability that the sample mean will be within plusminus 2 of the population mean if the sample size is n = 100? What is the probability that the sample mean will be within plusminus 2 of the population mean if the sample size is n = 400? What is the advantage of a larger sample size?
Answers
The probability that the sample mean will be within plus minus 2 of the population mean if the sample size is n = 100 between z-scores of 0 and 2.5 using a z-table.
The standard deviation of the sample distribution, commonly known as the standard error, can be computed using the formula given that the population mean is 100 and the standard deviation is 16:
Standard Error = Standard Deviation / sqrt(sample size)
Let's determine the likelihoods for sample sizes of n = 100 and n = 400:
For n = 100:
Standard Error = 16 / sqrt(100) = 16 / 10 = 1.6
We can determine the z-scores for the upper and lower boundaries to establish the likelihood that the sample mean will be within plus or minus 2 of the population mean:
Lower Bound z-score = (Sample Mean - Population Mean) / Standard Error
Lower Bound z-score = (100 - 100) / 1.6
Lower Bound z-score = 0
Upper Bound z-score = (Sample Mean - Population Mean) / Standard Error
Upper Bound z-score = (104 - 100) / 1.6
Upper Bound z-score = 4 / 1.6
Upper Bound z-score = 2.5
We can calculate the region under the normal distribution curve between z-scores of 0 and 2.5 using a z-table or statistical software. This shows the likelihood that the sample mean will be within +/- 2 standard deviations of the population mean.
For n = 400:
Standard Error = 16/√400
Standard Error = 16/20
Standard Error = 0.8
We determine the z-scores by following the same procedure as above:
Lower Bound z-score = (Sample Mean - Population Mean) / Standard Error
Lower Bound z-score = (100 - 100) / 0.8
Lower Bound z-score = 0
Upper Bound z-score = (Sample Mean - Population Mean) / Standard Error
Upper Bound z-score = (104 - 100) / 0.8
Upper Bound z-score = 4 / 0.8
Upper Bound z-score = 5
Once more, we may determine the region under the normal distribution curve between z-scores of 0 and 5 using a z-table or statistical software.
A larger sample size, like n = 400, has the benefit of a lower standard error. The sampling distribution of the sample mean will be more constrained and more closely resemble the population mean if the standard error is less.
As a result, there is a larger likelihood that the sample mean will be within +/- 2 of the population mean. In other words, the estimate of the population mean gets more accurate and dependable as the sample size grows.
To learn more about population mean link is here
brainly.com/question/30324262
#SPJ4
Learning Task 3 . Find the equation of the line. Do it in your notebook.
(a) In slope intercept form y = mx + b
(b) in standard form ax + by = c
1. The slope is 5 passing through (-1, 4).
2. The line passes through point (3, -4) and (-2, 2)
3. The slope is 3/4 and the y-intercept is (0,4)
4. The x intercept -3 and the y-intercept is 6
5. Passing through the points (-1, -2) and (5, 3)
Answers
Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
1. The slope is 5 passing through (-1, 4).
y=mx+b
y=5x+b [slope is 5]
4 = 5(-1) + b [Find b by solving for b with the given point]
b = 9
y=5x+9
2. The line passes through point (3, -4) and (-2, 2)
Calculate slope from the "rise" over the "run."
Rise = (-4 - 2) = -6
Run = (3-(-2)) = 5
Slope - Rise/Run = -6/5 or -1.2
y = -1.2x + b
Use either given point to find b.
y = -1.2x + b for (3,-4)
-4 = -1.2(3) + b
-4 = -3.6 + b
b = -0.4
y = -1.2x - 0.4
3. The slope is 3/4 and the y-intercept is (0,4)
y = mx + b
y = (3/4)x + b
The y-intercept is 4: b = 4
y = (3/4)x + 4
4. The x intercept -3 and the y-intercept is 6
The x-intercept can be written as (-3,0) and the y-intercept as (0,6).
Calculate the slope between these two points (Rise/Run). Rise= (6-0), or 6, Run= (0-(-3)), or 3. Rise/Run (Slope) = 6/3 or 2
y = 2x + b b = 6 (y-intercept is (0,6)
y = 2x + 6
5. Passing through the points (-1, -2) and (5, 3)
y = mx + b
Slope: Rise = (3-(-2)) = 5, Run = (5-(-1))= 6 Slope = Rise/Run Slope = (5/6)
y = (5/6)x + b
Calculate b:
y = (5/6)x + b for (-1,-2)
b = y-(5/6)x
b =-2-(5/6)*(-1)
b = -2 + (5/6)
b = (-12/6) + (5/6) = -(7/6)
y = (5/6)x - (7/6)
====
For each problem, rearrange the solution to the standard form ax + by = c
1. y=5x+9
-5x + y = 9
2. y = -1.2x - 0.4
1.2x + y = -0.4
3. y = (3/4)x + 4
-(3/4)x + y = 5
4. y = 2x + 6
-2x + y = 6
5. y = (5/6)x - (7/6)
-(5/6)x + y = -(7/6)
What’s is the answer for
5x + 15=
Answers
What is x equivalent to?
Question 6
2 pts
Two trains left a station at the same time. Train A traveled north at a certain speed and train B traveled south
at twice that speed. After 4 hours, the trains were 600 miles apart. How fast was each train traveling?
Train A was traveling
mph... (hint... this is the slower train)
Train B was traveling
mph.
Answers
Step-by-step explanation:
Train 1 speed be 'u'
Train 2 speed be 'v'
And v=2u
Speed=distance/time
Trains going in opposite directions
Relative speed= v-u (as train 1 I slower than train 2)
v-u=600/4
2u-u=150
u=150miles/hour
v=300miles/hour
find the measure of x. 65 x 57

Answers
Answer: 58
Step-by-step explanation: This is 58 because a triangle always equals 180 altogether so you take 180-65-57 and it is 58.
Show that the process X(t):=e t/2
cos(W(t)),0≤t≤T, is a martingale w.r.t. any filtration for Brownian motion and represent it as an Itô process on any time interval [0,T],T>0.
Answers
A stochastic process X(t) is called a martingale if the expected value of X(t) given all information available up to and including time s is equal to the value of X(s).
Thus, to show that the process X(t):=e^(t/2)cos(W(t)), 0 ≤ t ≤ T is a martingale w.r.t. any filtration for Brownian motion, we need to prove that E(X(t)|F_s) = X(s), where F_s is the sigma-algebra of all events up to time s.
As X(t) is of the form e^(t/2)cos(W(t)), we can use Itô's lemma to obtain the differential form:dX = e^(t/2)cos(W(t))dW - 1/2 e^(t/2)sin(W(t))dt
Taking the expectation on both sides of this equation gives:E(dX) = E(e^(t/2)cos(W(t))dW) - 1/2 E(e^(t/2)sin(W(t))dt)Now, as E(dW) = 0 and E(dW^2) = dt, the first term of the right-hand side vanishes.
For the second term, we can use the fact that sin(W(t)) is independent of F_s and therefore can be taken outside the conditional expectation:
E(dX) = - 1/2 E(e^(t/2)sin(W(t)))dt = 0Since dX is zero-mean, it follows that X(t) is a martingale w.r.t. any filtration for Brownian motion.
Now, let's represent X(t) as an Itô process on the interval [0,T]. Applying Itô's lemma to X(t) gives:
dX = e^(t/2)cos(W(t))dW - 1/2 e^(t/2)sin(W(t))dt= dM + 1/2 e^(t/2)sin(W(t))dt
where M is a martingale with M(0) = 0.
Thus, X(t) can be represented as an Itô process on [0,T] of the form:
X(t) = M(t) + ∫₀ᵗ 1/2 e^(s/2)sin(W(s))ds
Hence, we have shown that X(t) is a martingale w.r.t. any filtration for Brownian motion and represented it as an Itô process on any time interval [0,T], T > 0.
To know more about martingale visit:
brainly.com/question/32735198
#SPJ11
Solve the 19 problem. If no optimal solution exists because there is no Solution Set, enter fMirr. If no optimal solution exists becouse the region is unbounded, enter UNBOUNDEO. Note that an unbounded region can still have an optimal solution while a bounded region is guaranteed to have optimal solutions. HENT [See Example 1.] Maximize and minimize p=x+2y subject to x+y≥4x+y≤10x−y≤4x−y≥−4 Mrimums p=(α,y)=() Mavimam p=n)=()
Answers
The maximum value of the objective function is 4 at the vertex (4, 0), and the minimum value is -8 at the vertex (0, -4). The optimal solutions for the given LP problem are Maximum: p = 4 at x = 4 and y = 0 and Minimum: p = -8 at x = 0 and y = -4.
Maximize and minimize p = x + 2y
subject to:
x + y ≥ 4
x + y ≤ 10
x - y ≤ 4
x - y ≥ -4
First, let's graph the feasible region defined by the given constraints:
Plotting the lines:
x + y = 4 (solid line)
x + y = 10 (solid line)
x - y = 4 (solid line)
x - y = -4 (solid line)
The feasible region is the area that satisfies all the constraints and is bounded by the lines on the graph.
Upon examining the feasible region, we can observe that it is a bounded region.
To find the optimal solution, we need to evaluate the objective function p = x + 2y at the vertices (corner points) of the feasible region.
Now, let's find the vertices of the feasible region by solving the intersection points of the lines:
1. Intersection of x + y = 4 and x + y = 10:
Subtracting the equations, we get 0 = 6, which is not possible. No intersection point exists for these lines.
2. Intersection of x + y = 4 and x - y = 4:
Adding the equations, we get 2x = 8, x = 4. Substituting x = 4 into x + y = 4, we get 4 + y = 4, y = 0. The first vertex is (4, 0).
3. Intersection of x - y = 4 and x - y = -4:
Adding the equations, we get 2x = 0, x = 0. Substituting x = 0 into x - y = 4, we get -y = 4, y = -4. The second vertex is (0, -4).
Now, we evaluate the objective function at each vertex:
p(4, 0) = 4 + 2(0) = 4
p(0, -4) = 0 + 2(-4) = -8
The maximum value of the objective function is 4 at the vertex (4, 0), and the minimum value is -8 at the vertex (0, -4).
Therefore, the optimal solutions for the given LP problem are Maximum: p = 4 at x = 4 and y = 0 and Minimum: p = -8 at x = 0 and y = -4.
Learn more about functions here:
https://brainly.com/question/31062578
#SPJ11
Is my answer on the photo correct?

Answers
Answer:
yes
Step-by-step explanation:
at a rehearsal dinner the night before a wedding, the bride and groom need to assign 10 people to two tables of five people. how many different groups of five can they form?
Answers
The bride and groom can form 252 different groups of five people from the total of 10 people at the rehearsal dinner, as they need to assign them to two tables of five people each.
To determine the number of different groups of five people that can be formed, we can use the concept of combinations. In this scenario, we have 10 people who need to be divided into two groups of five people each.
The number of ways to choose five people out of 10 can be calculated using the combination formula. The formula for combinations is given by:
C(n, r) = n! / (r! * (n - r)!)
Where n represents the total number of people and r represents the number of people to be chosen. In this case, n = 10 and r = 5.
Plugging these values into the formula, we get:
C(10, 5) = 10! / (5! * (10 - 5)!)
= (10 * 9 * 8 * 7 * 6 * 5!) / (5! * 5 * 4 * 3 * 2 * 1)
= (10 * 9 * 8 * 7 * 6) / (5 * 4 * 3 * 2 * 1)
= 252
Therefore, the bride and groom can form 252 different groups of five people from the total of 10 people at the rehearsal dinner. This means that there are 252 distinct ways to divide the 10 people into two tables of five people each, providing flexibility in creating diverse groups for the dinner.
Learn more about divide here:
https://brainly.com/question/15381501
#SPJ11
What is the area of the octagon, rounded to the nearest square inch? 88 in. 2 175 in. 2 332 in. 2 700 in. 2.
Answers
2 | k - 3 | = 18 absolute value
Answers
Answer:
bdjdkkdns nsm
nzihb;uuuyyyttty
personal health the type a personalilty has been identified as a psychological risk factor for
Answers
The Type A personality has been identified as a psychological risk factor for cardiovascular diseases and stress-related health issues.
Studies have shown that individuals with Type A personality traits, such as competitiveness, time urgency, and hostility, may be at a higher risk for developing certain health issues, such as heart disease, high blood pressure, and stroke. This may be due to the heightened stress levels that Type A individuals often experience, which can lead to negative physiological effects on the body over time. Additionally, Type A individuals may engage in unhealthy behaviors, such as smoking, drinking, and overeating, as a way to cope with their stress.
Therefore, it is important for individuals with Type A personality traits to manage their stress levels and engage in healthy behaviors in order to reduce their risk of developing health problems
To learn more about psychological risk here:
brainly.com/question/29980622#
#SPJ11
twenty three less than sum of forty nine and thirty seven what is the answer?
Answers
Answer:
63.
Step-by-step explanation:
49 plus 37 is 86. subtract that by 23 and you get 63.
Solve using the substitution method:
y = -2x - 7
y = 3x + 3
Answers
So, -2x-7 = 3x + 3
+2x. +2x
-7= 5x +3
-5x. -5x
-5x-7= 3
+7. +7
-5x= 10
Divide -5 on both sides and you get x= -2
Then substitute -2 in the first equation
-2(-2)-7
4-7
Y= -3
After 3 years, a $1,500 investment is worth $1,680. What is the interest rate on the investment?
0.04 percent
2.0 percent
4.0 percent
37.3 percent
Answers
Answer:
0.04
Step-by-step explanation:
1680=1500+1500x3xr
1680-1500=1500x3xr
r=180/4500
r=0.04
Answer:
The answer is 4.0 percent
Step-by-step explanation:
I just answered that question and got it right
Last week, it rained g inches. This week, the amount of rain decreased by 5%. Which expressions represent the amount of rain that fell this week? g - 0.05 g - 0.05g 0.95g 0.05g (1 - 0.05)g
Answers
Answer:
The correct answers are:
0.95g
g - 0.05g
(1 - 0.05)g
Step-by-step explanation:
Amount of last week's rain = g inches
this week = 5% decrease on last week's amount
5% of last week's amount = 5/100 × g = 0.05g
∴ This week's amount of rain = 0.05g decrease
∴ Amount of rain this week = (Amount of rain last week) - 0.05g
∴ Amount of rain this week = g - 0.05g
This can be simplified by factorizing the common term "g"
g - 0.05g = g(1 - 0.05) = 0.95g
What’s the answer to this problem I’m really confused ?

Answers
Answer:
C
Step-by-step explanation:
sin= opposite/hypotenuse
The US consumes an average of 5.25 million metric tons of bananas per year. There are 317 million people in the US and there are 1000 kg in 1 metric ton. It costs $2.10 per kilogram of bananas. And how much money will this be per person every day?
Answers
Consumption of Bananas per year = 5, 250, 000 metric tons
We know 1000 kg = 1 metric ton, so
Consumption of Bananas per year (in kg) = 5, 250, 000 x 1000 = 5, 250, 000, 000 kgs
Cost of Banana = $2.10 per kg
So,
Cost of all bananas = 5, 250, 000, 000 x 2.10 = $ 11,025,000,000 (per year)
Taking a year to be 365 days, let's find the cost for a day:
\(\frac{11,025,000,000}{365}=\$30,205,479.4521\)Since there are 317 million [317,000,000] people in the US, the cost per person every day is:
\(\frac{30,205,479.4521}{317,000,000}\approx\$0.0952854\)Rounding to the nearest cent,
$0.10So, the amount (in dollars) per person every day = $0.10Answer$0.10help asap!!
select the correct answer.
Given a prism with a right triangle base and the dimensions and what is a correct expression for the volume of the prism?
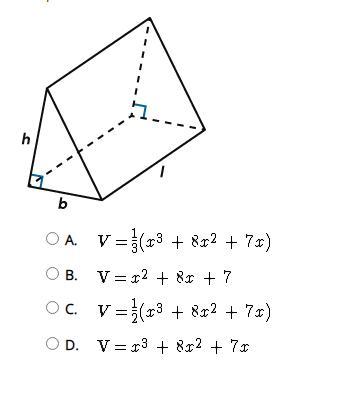
Answers
Answer:
It would be v=1/2(x^3+8x^2+7x)
Step-by-step explanation:
What is the mean absolute deviation of the following data: 61, 63, 64, 68, 70, 76 ROUND TO THE NEAREST HUNDREDTH Single line text.
Answers
Answer:
4.33 infinity.
Step-by-step explanation:
The infinity should just be a line over the 3's
Answer:
4.33
Step-by-step explanation:
First, find the mean value.
Mean = 67
61 - 67 = |-6| = 6
63 - 67 = |-4| = 4
64 - 67 = |-3| = 3
68 - 67 = 1
70 - 67 = 3
76 - 67 = 9
Add: 6 + 4 + 3 + 1 + 3 + 9/6 = 4.33333333333
4.33333333333 rounded to the nearest hundredth = 4.33
how to find the roots of a third degree polynomial
Answers
To find the roots of a third-degree polynomial, also known as a cubic polynomial, we can use a method called factoring or apply the cubic formula.
The first step is to check if there are any common factors that can be factored out. Next, we can use the rational root theorem to determine potential rational roots. By applying synthetic division or long division, we can divide the polynomial by the potential roots to see if they are indeed roots.
If a rational root is found, we can then use synthetic division to factor out the corresponding quadratic equation. Finally, we can solve the quadratic equation using methods like factoring, completing the square, or using the quadratic formula to find the remaining roots.
It's important to note that not all cubic polynomials can be easily factored or solved algebraically. In such cases, numerical methods or approximation techniques may be used to find the roots.
learn more about polynomial :
https://brainly.com/question/11536910
#SPJ4
To find the roots of a third degree polynomial, you can follow these steps: 1) Check for rational roots using the Rational Root Theorem. 2) Use synthetic division to divide the polynomial by a linear factor. 3) Factor the resulting quadratic equation. 4) Solve for the roots by setting each factor equal to zero.
To find the roots of a third degree polynomial, we can follow these steps:
First, check if there are any rational roots using the Rational Root Theorem. The Rational Root Theorem states that if a polynomial has a rational root, it will be of the form p/q, where p is a factor of the constant term and q is a factor of the leading coefficient.Use synthetic division to divide the polynomial by a linear factor. Synthetic division is a method used to divide a polynomial by a linear factor, which helps us find the remaining quadratic equation.Factor the quadratic equation obtained from synthetic division. This can be done by using the quadratic formula or by factoring further if possible.Once the quadratic equation is factored, we can find the roots by setting each factor equal to zero and solving for the variable.Remember, the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra states that every polynomial equation of degree n has exactly n complex roots, counting multiplicities.
Learn more:About find here:
https://brainly.com/question/22188924
#SPJ11
Please explain these sub headings in detail as possible . Minimum 7 pages.
3. Mathematics Modelling of Surfaces
• Discuss the term 'surface', in the context of Digital Terrain Modelling
Discuss the difference between '3D' and '2%D' Digital Terrain Models
Answers
Mathematical modeling of surfaces is the representation of two-dimensional manifolds using mathematical techniques, particularly in the context of Digital Terrain Modeling (DTM) where surfaces refer to the Earth's terrain or physical objects.
Mathematical modeling of surfaces plays a crucial role in various fields, including computer graphics, engineering, and geosciences. Surfaces are fundamental objects that can be represented and analyzed using mathematical techniques.
In this section, we will delve into the concept of surfaces, particularly in the context of Digital Terrain Modeling (DTM). Additionally, we will explore the distinction between 3D and 2D DTM.
1. The Concept of Surfaces:
In the realm of mathematics, a surface is defined as a two-dimensional manifold, meaning it is a topological space that locally resembles Euclidean space.
In simpler terms, a surface is a geometrical entity that can be thought of as a continuous collection of points, forming a boundary between a solid and its surrounding space. In the context of DTM, surfaces typically refer to the representation of the Earth's terrain or any other physical object using mathematical models.
2. Digital Terrain Modeling:
Digital Terrain Modeling involves the creation of digital representations of the Earth's surface or any specific region using computer algorithms. It serves as a crucial tool in various applications, such as urban planning, environmental analysis, and military simulations. DTM utilizes mathematical models to represent the terrain accurately, allowing for detailed analysis and visualization.
3. 3D Digital Terrain Models:
A 3D Digital Terrain Model (DTM) is a representation of the Earth's surface that captures three-dimensional information. It provides a detailed depiction of the terrain, including elevation data, contours, and topographical features.
3D DTMs are typically generated using techniques such as LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) or photogrammetry. These models enable precise analysis of the landscape, volumetric calculations, and visualization from different perspectives.
4. 2D Digital Terrain Models:
In contrast to 3D DTMs, 2D Digital Terrain Models represent the Earth's surface in two dimensions. They provide a simplified view of the terrain, focusing primarily on elevation data and contour lines. 2D DTMs are commonly used in cartography, where the terrain is represented on a flat surface, such as a map or a computer screen. While they lack the depth information of 3D DTMs, 2D models are still valuable for many applications, including geographic information systems (GIS) and land surveying.
5. Differences between 3D and 2D Digital Terrain Models:
The main distinction between 3D and 2D DTMs lies in the level of detail and the dimensionality of the representation. 3D DTMs provide a more comprehensive and realistic view of the terrain, capturing not only the elevation but also the shape, slopes, and other three-dimensional features. These models are highly suitable for applications that require a precise understanding of the terrain's topography, such as hydrological analysis or landscape design.
On the other hand, 2D DTMs offer a simplified representation of the terrain, primarily focusing on elevation data and contour lines. They are more commonly used for general visualization and analysis purposes where the third dimension is not critical. 2D DTMs are easier to create and process, making them more accessible for applications that do not require intricate three-dimensional modeling.
To know more about Mathematical modeling refer here:
https://brainly.com/question/10952874#
#SPJ11