Answers
The temperature of air as measured by a thermometer that is not insulated from radiation or moisture is known as the dry-bulb temperature (DBT).
The actual thermodynamic temperature is DBT, which is typically thought of as the air temperature. It measures the heat content of the atmosphere and relates the mean kinetic energy of the air molecules directly. Temperature is typically expressed in kelvins (K), degrees Fahrenheit (°F), or degrees Celsius.
Dry bulb temperature does not reflect the quantity of moisture in the air, in contrast to wet bulb temperature. It is crucial to take this into account when planning a building for a certain environment. One of the "most essential climate variables for human comfort," according to Nall
to know more about temperature , visit to
https://brainly.com/question/11464844
#SPJ4
Related Questions
27. The number of coils of wire through which a bar magnet is moved is increased. The
amount the needle on the meter is deflected
A. increases
B. decreases
C. shows no change
D. does not move at all
Answers
The amount the needle on the meter is deflected A. increases
This phenomenon can be explained by Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction. According to this law, when a magnetic field (created by the bar magnet) passes through a coil of wire, it induces an electric current in the wire. This induced current generates its own magnetic field, which interacts with the magnetic field of the bar magnet.
The deflection of the meter needle is a result of this induced current. When the number of coils of wire is increased, there is a greater number of wire loops for the magnetic field to pass through. This leads to a stronger induction of electric current, resulting in a larger deflection of the meter needle.
By increasing the number of coils, more magnetic flux is linked with the wire, resulting in a higher induced electromotive force (emf) and a greater current. This increased current produces a stronger magnetic field around the wire, leading to a larger deflection on the meter. Therefore, increasing the number of coils of wire enhances the magnetic field interaction, resulting in an increased deflection of the meter needle. Therefore, Option A is correct.
Know more about Faraday's law here:
https://brainly.com/question/1640558
#SPJ8
A geologist notices that a river is eroding its valley at a constant rate. Knowing the height of the valley walls, how could the geologist figure out when the river started carving the valley?
A.
Count growth rings of trees growing on the valley floor.
B.
Divide the height of the valley walls by the rate of erosion.
C.
Fill up the river valley with rocks, and time how long it takes the rocks to wash out.
D.
Sit and observe the river for a few hours until the valley walls double in height.
Answers
Answer:
B.
Divide the height of the valley walls by the rate of erosion.
Explanation:
There is a relationship between the rate of erosion and the hieght at which it is eroded according to Newton's law of motion. In the case of the scenario above, the best way to determine the time the river started carving the valley would be the division of the height of the valley walls by the rate of erosion.
If the internal energy of a system is decreased, which of the following is impossible?
a
Work done by the system is larger than heat
released.
b
Work done on the system is smaller than
heat released.
C
Work done by the system is larger than heat
absorbed.
d
Work done on the system is smaller than
heat absorbed.
Answers
Work done on the system is smaller than heat absorbed.
What happens when internal energy decreases?A cell's internal energy drops when it does work or expels heat. There won't be a net change in internal energy if the work performed by a cell matches the energy transferred in by heat or if the work performed on a cell matches the energy transported out by the heat.The energy within remains constant. The ideal gas law states that the temperature decreases according to the volume when a gas is compressed while maintaining a constant pressure. In this instance, more energy is lost as heat from the system is gained through work. Internal energy levels drop.Ideal gases' internal energy and enthalpy depend solely on temperature; neither volume nor pressure play a role. Using property relations, we may demonstrate these characteristics of ideal gases.
If the internal energy of a system is decreased, which of the following is impossible:
C) Work done on the system is smaller than heat absorbed.
To learn more about internal energy, refer to:
https://brainly.com/question/25737117
#SPJ9
A car initially traveling at a speed of 15.0 m/s accelerates uniformly to a speed of 20.0 m/s over a distance of 40.0 meters. What is the magnitude of the car's acceleration?
Answers:
1.1 m/s^2
2.0 m/s^2
2.2 m/s^2
9 m/s^2
Answers
Answer:
\(\boxed {\boxed {\sf 2.2 \ m/s^2}}\)
Explanation:
We are asked to solve for the magnitude of the car's acceleration.
We are given the initial speed, final speed, and distance, so we will use the following kinematic equation.
\({v_f}^2={v_i}^2+2ad\)
The car is initially traveling at 15.0 meters per second and accelerates to 20.0 meters per second over a distance of 40.0 meters. Therefore,
\(v_f\)= 20.0 m/s\(v_i\)= 15.0 m/s d= 40.0 mSubstitute the values into the formula.
\((20.0 \ m/s)^2= (15.0 \ m/s)^2 + 2 a (40.0 \ m)\)
Solve the exponents.
(20.0 m/s)² = 20.0 m/s * 20.0 m/s = 400.0 m²/s² (15.0 m/s)² = 15.0 m/s * 15.0 m/s = 225.0 m²/s²\(400.0 \ m^2/s^2 = 225.0 \ m^2/s^2 + 2 a(40.0 \ m)\)
Subtract 225.0 m²/s² from both sides of the equation.
\(400.0 \ m^2/s^2 - 225.0 m^2/s^2 = 225.0 \ m^2/s^2 -225 \ m^2/s^2 +2a(40.0 \ m)\)
\(400.0 \ m^2/s^2 - 225.0 m^2/s^2 = 2a(40.0 \ m)\)
\(175 \ m^2/s^2 = 2a(40.0 \ m)\)
Multiply on the right side of the equation.
\(175 \ m^2/s^2 =80.0 \ m *a\)
Divide both sides by 80.0 meters to isolate the variable a.
\(\frac {175 \ m^2/s^2}{80.0 \ m}= \frac{80.0 \ m *a}{80.0 \ m}\)
\(\frac {175 \ m^2/s^2}{80.0 \ m}=a\)
\(2.1875 \ m/s^2 =a\)
Round to the tenths place. The 8 in the hundredth place tells us to round the 1 up to a 2.
\(2.2 \ m/s^2=a\)
The magnitude of the car's acceleration is 2.2 meters per second squared.
To wait until the oncoming vehicle passes before completing a left turn is known as:
a)
b)
c)
IPDE strategy
Risk acceptance
Risk rejection
Inappropriate maneuver
Answers
Answer:
Risk rejection
Explanation:
There are several factors that contribute to the degree of driving risks and they include but not limited to the ability of the driver and the condition of a vehicle. Other factors are condition of the environment and the condition of the highway. When driving, a driver may wait until an oncoming vehicle passes before making a complete left turn as a risk rejection strategy. Left turns are more dangerous when making them because drivers tend to accelerate on to a left turn. The wider radius of a left turn is know to led to higher speeds and greater pedestrian exposure. A driver is advised to have more mental and physical efforts when making a left turn.
a double-decker london bus (figure 1) might be in danger of rolling over in a highway accident, but at the low speeds of its urban environment, it's plenty stable. the track width is 2.05 m. with no passengers, the height of the center of gravity is 1.45 m, rising to 1.73 m when the bus is loaded to capacity. What are the critical angles for both the unloaded and loaded bus?
Answers
When the bus is fully loaded, the center of gravity rises to 1.73 m, and the critical angles are 35.3 degrees for the unloaded bus and 30.6 degrees for the loaded bus, respectively.
Center of gravity: What is it?Theoretically, the body's total weight is concentrated at a location called the center of gravity.
What distinguishes the center of mass from the center of gravity?The main distinction between the centers of mass and gravity is that the center of gravity refers to the location where the total weight of the body is balanced, whereas the center of mass refers to the location where the body's complete mass is directed.
To learn more about gravity visit:
brainly.com/question/4014727
#SPJ4
Which of the following objects
transforms chemical energy into
mechanical energy?
A. Battery powered clock
B. Cell phone
C. Washing machine
D. Windmill
Answers
Battery-powered clocks and Washing machines are objects that transform chemical energy into mechanical energy.
What are chemical energy and mechanical energy?Chemical energy is a type of energy that is stored in the bonds of a chemical. It is converted into thermal energy when people burn wood or burn gasoline in the engine of a car. Mechanical energy is a type of energy that is stored in objects by tension. Compressed springs and stretched bands are examples of mechanical energy.
Mechanical energy i.e. kinetic energy or potential energy is the energy that is present in an object in motion or the energy that is stored in objects due to their position. Mechanical energy is a type of renewable energy.
So we can conclude that options A and C are the correct answers.
Learn more about energy here: https://brainly.com/question/13881533
#SPJ1
using an allowable shear stress of 50 mpa, determine the power that can be transmitted at 2000 rpm through a shaft with a 30-mm diameter.
Answers
The power that can be transmitted at 2000 rpm through a shaft with a 30-mm diameter is 55.5165kw.
Power=\(\frac{265.072*2*pi*2000}{60} = 55.5165kw\)
Resale rate upkeep (RPM) exists with a dealer specifying the minimal (or most) fee at which the product ought to be re-sold to clients. Context: From a competition policy viewpoint, specifying the minimal fee is of challenge.
Resale price upkeep Agreements (RPMs) are arrangements where resellers agree that they'll sell products or products at positive fees at or above charge ground (minimum RPM) or at or below a rate ceiling (most RPM). Early in the twentieth century RPM agreements were consistent with se illegal underneath federal antitrust regulation. Resale price protection (RPM) specifies the final fee that outlets fee purchasers. This roundtable targeted on using RPM for books, newspapers, and similar cultural merchandise. Resale price upkeep (RPM) exists with a dealer specifying the minimum (or maximum) rate at which the product must be re-sold to clients.
To learn more about RPM visit here:
brainly.com/question/29641749
#SPJ4
If the 4th harmonic in the diagram has a wavelength = 10 m,
find the wavelengths of the other three harmonics

Answers
The wavelengths are given as
firsts harmonic = 40 m
second harmonic = 20 m
third harmonic = 13.33 m
What is wavelengthsWavelength refers to the distance between two consecutive points of a wave that are in phase, or the distance it takes for a wave to complete one full cycle. It is commonly denoted by the Greek letter lambda (λ).
Using the wavelength of the fourth harmonics as reference, we have that the full scale is 20 m
firsts harmonic = 40 m (double of the full scale)
second harmonic = 20 m (covers the full scale)
third harmonic = 20 m * 2/3 = 13.33 m (covers 2/3 of the full scale)
Learn more about wavelengths at
https://brainly.com/question/10750459
#SPJ1
form a hypothesis to explain the shape of this graph

Answers
Answer:
the data change decreased and then increased. this went on repeatly but the decrease became less as the increase became more.
The two masses (mA
= 6.50 kg is hanging and mB
= 3.30 kg is on the floor) in the Atwood's machine shown in the figure below are released from rest, with mA
at a height of 0.865 m above the floor. When mA
hits the ground its speed is 1.89 m/s. The pulley is not massless and can be considered a solid disk with a moment of inertia of (1/2)mpr2
.
What is the total mechanical energy of the two blocks prior to being released from rest?
(Figure 1)
What is the total mechanical energy of the two blocks when mA
hits the ground?
Part C
What is the rotational kinetic energy of the pulley just before mA
hits the ground?
Part D
What is the mass of the pulley?
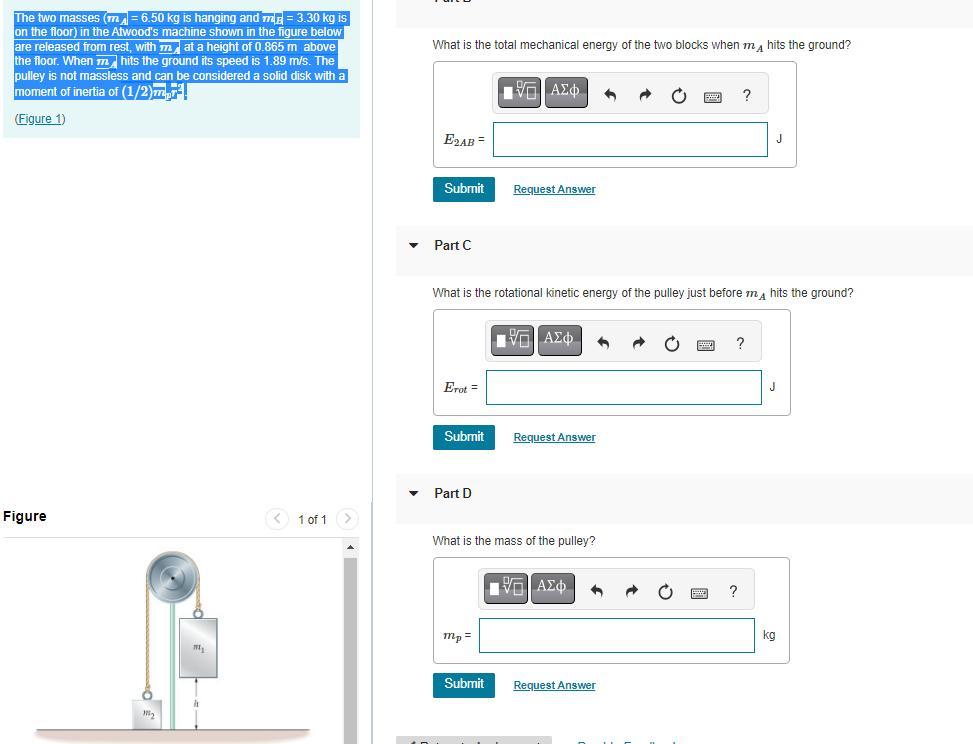
Answers
A)The total mechanical energy of the two blocks prior to being released from rest can be found by adding the gravitational potential energy of mA and the pulley to zero.
B).The gravitational potential energy of mB and the pulley is(3.30 kg + mp) × 9.81 m/s² × 0 m = 0 J,where mp is the mass of the pulley.The total mechanical energy of the two blocks prior to being released from rest is54.33 J + 0 J = 54.33 J
C) The rotational kinetic energy of the pulley just before mA hits the ground is(0.178 mp) J.
D) The mass of the pulley ismp = (1/2)mpr²/R² =(1/2)(0.020 kg)(0.100 m)²/(0.200 m)² = 0.001 kg = 1 g.r = (1/2)R.
The Atwood's machine shown in Figure 1 consists of two masses mA = 6.50 kg and mB = 3.30 kg. The height of mA above the floor is 0.865 m. When mA hits the floor, its velocity is 1.89 m/s. The pulley has a moment of inertia (1/2)mpr². We have to find the total mechanical energy of the two blocks before they are released, the total mechanical energy when mA hits the ground, the rotational kinetic energy of the pulley just before mA hits the ground, and the mass of the pulley. Let's solve these one by one. Part A The total mechanical energy of the two blocks prior to being released from rest can be found by adding the gravitational potential energy of mA and the pulley to zero.
The equation for gravitational potential energy is mgh. The gravitational potential energy of mA and mB is mAg(h-hB)where h is the height of mA above the floor and hB is the height of mB above the floor. Since the pulley is at the same height as mB, its gravitational potential energy ismBg(h-hB).The gravitational potential energy of mA is6.50 kg × 9.81 m/s² × 0.865 m = 54.33 J.The gravitational potential energy of mB and the pulley is(3.30 kg + mp) × 9.81 m/s² × 0 m = 0 J,where mp is the mass of the pulley.The total mechanical energy of the two blocks prior to being released from rest is54.33 J + 0 J = 54.33 J.Part BThe total mechanical energy of the two blocks when mA hits the ground can be found by adding the kinetic energy of mA, the kinetic energy of mB, and the rotational kinetic energy of the pulley to the gravitational potential energy of mB and the pulley. The equation for kinetic energy is (1/2)mv². The kinetic energy of mA is(1/2) × 6.50 kg × (1.89 m/s)² = 11.54 J.The kinetic energy of mB is(1/2) × 3.30 kg × 0 m/s² = 0 J, since it is at rest.The gravitational potential energy of mB and the pulley is(3.30 kg + mp) × 9.81 m/s² × 0 m = 0 J.The rotational kinetic energy of the pulley is(1/2) × (1/2)mp × R² × ω²,where R is the radius of the pulley and ω is its angular velocity just before mA hits the ground. We can use the fact that the linear speed of the rope is the same on both sides of the pulley to find ω. The equation for linear speed is v = Rω. When mA hits the ground, its speed is 1.89 m/s. The speed of mB is zero. Since the rope is inextensible, the speed of the rope is also 1.89 m/s.
Therefore, the speed of the pulley is also 1.89 m/s. We can find the angular velocity of the pulley by dividing the linear velocity by the radius.ω = v/R = 1.89 m/s ÷ (0.200 m/2) = 18.9 rad/s.The rotational kinetic energy of the pulley is(1/2) × (1/2)mp × R² × ω² =(1/4)mpR²ω² =(1/4)mp(0.200 m)²(18.9 rad/s)² =(0.178 mp) J.The total mechanical energy of the two blocks when mA hits the ground is11.54 J + 0 J + 0 J + (0.178 mp) J = 11.72 J + (0.178 mp) J.Part CThe rotational kinetic energy of the pulley just before mA hits the ground is(0.178 mp) J.Part DWe can find the mass of the pulley by using the moment of inertia of a disk and the mass of the pulley. The moment of inertia of a disk is (1/2)mr². Therefore,(1/2)mpR² = (1/2)mpr²,where R is the radius of the pulley and r is the radius of gyration of the pulley. The radius of gyration of a disk is (1/2)R.
for such more questions on mass
https://brainly.com/question/86444
#SPJ8
A river flows with a uniform velocity vr. A person in a motorboat travels 1.22 km upstream, at which time she passes a log floating by. Always with the same engine throttle setting, the boater continues to travel upstream for another 1.45 km, which takes her 69.1 min. She then turns the boat around and returns downstream to her starting point, which she reaches at the same time as the same log does. How much time does the boater spend traveling back downstream
Answers
Answer:
t ’= \(\frac{1450}{0.6499 + 2 v_r}\), v_r = 1 m/s t ’= 547.19 s
Explanation:
This is a relative velocity exercise in a dimesion, since the river and the boat are going in the same direction.
By the time the boat goes up the river
v_b - v_r = d / t
By the time the boat goes down the river
v_b + v_r = d '/ t'
let's subtract the equations
2 v_r = d ’/ t’ - d / t
d ’/ t’ = 2v_r + d / t
\(t' = \frac{d'}{ \frac{d}{t}+ 2 v_r }\)
In the exercise they tell us
d = 1.22 +1.45 = 2.67 km= 2.67 10³ m
d ’= 1.45 km= 1.45 1.³ m
at time t = 69.1 min (60 s / 1min) = 4146 s
the speed of river is v_r
t ’= \(\frac{1.45 \ 10^3}{ \frac{ 2670}{4146} \ + 2 \ v_r}\)
t ’= \(\frac{1450}{0.6499 + 2 v_r}\)
In order to complete the calculation, we must assume a river speed
v_r = 1 m / s
let's calculate
t ’= \(\frac{ 1450}{ 0.6499 + 2 \ 1}\)
t ’= 547.19 s
Which wave has high enough energy to cause damage to skin and sometimes cancer?
Answers
Answer: All UV can have harmful effects on biological matter (such as causing cancers) with the highest energies causing the most damage.
Explanation:
John drove a truck for one hour at a rate of 80 kilometers per hour (km/hr). The next hour, he drove at 100 km/hr. What was his average speed during those two hours?
km/hr
Answers
Please i have asked a.question please help.me
Explanation:
Please i have asked a question in math please help me
find the rms speed of a sample of oxygen at 30° C and having a molar mass of 16 g/mol.
Answers
At 30°C, the rms speed of a sample of oxygen with a molar mass of 16 g/mol is approximately 482.34 m/s.
The root mean square (rms) speed of a gas molecule is a measure of the average speed of the gas particles in a sample. It can be calculated using the formula:
vrms = √(3kT/m)
Where:
vrms is the rms speed
k is the Boltzmann constant (1.38 x 10^-23 J/K)
T is the temperature in Kelvin
m is the molar mass of the gas in kilograms
To calculate the rms speed of oxygen at 30°C (303 Kelvin) with a molar mass of 16 g/mol, we need to convert the molar mass to kilograms by dividing it by 1000:
m = 16 g/mol = 0.016 kg/mol
Substituting the values into the formula, we have:
vrms = √((3 * 1.38 x 10^-23 J/K * 303 K) / (0.016 kg/mol))
Calculating this expression yields the rms speed of the oxygen sample:
vrms ≈ 482.34 m/s
For such more questions on speed
https://brainly.com/question/31380575
#SPJ8
A television set is plugged into a 120 V outlet. The television circuit carries a current equal to 0.75 A. What is the overall resistance of the television set?
Answers
Answer:
R = 160 Ω
Explanation:
A television set is plugged into a 120 V outlet. The television circuit carries a current equal to 0.75 A. What is the overall resistance of the television set?
V = IR
120 volt = 0.75A * R
R = 160 Ω
The same amount of thermal energy was added to two equal masses of Aluminum and Iron. The specific heat of Aluminum is double the specific heat of iron. If the temperature of the Aluminum's mass changes by /\T, what is the change in the Iron's mass temperature?

Answers
Answer:
it is double the temperature change of iron
I will mark you brainlist! Use your own word
What is the weathering, erosion, and deposition?
Answers
Weathering is the breaking down or dissolving of rocks and minerals on Earths surface.
Erosion is the process by which the surface of the Earth gets worn down. Erosion can be caused by natural elements such as wind and glacial ice
Deposition is the dropping of sediment by wind, water, ice, or gravity.
Answer:
Weathering: refers to the process of breaking down and disintegrating rocks, minerals, soils, as well as several other materials.
Erosion: refers to the process of wearing down the surface of the earth due to glacial ice, wind and other natural elements.
Deposition: refers to the geological process, of sediments and soil, added to landforms due to wind, ice and other natural elements to build up layers od sediments.
Explanation:
What gases can CFC and HCFC refrigerants decompose into at high temperatures
Answers
Answer:
Hydrochloric and Hydrofluoric Acids.
4) Collision in which K.E and momentum of system remain same is called__________
(*)Elastic Collision
(*) Inelastic collision
(*) Conserved collision
(*) Linear collision
Answers
A collision that is elastic occurs when there is no net loss of kinetic energy in the system as a result of the collision. Kinetic energy and momentum are both conserved in elastic collisions.
Give an example of an elastic collision.When two balls collide at a pool table, that is an instance of an elastic collision. When you throw a ball on the ground and it bounces back into your hand, there is no net change in the kinetic energy, making it an elastic collision.
Give an illustration of what an elastic collision is.Two balls colliding at a pool table is an example of an elastic collision. When a ball is tossed to the ground and subsequently returns to your hand, there is no net change in the kinetic energy, making it an elastic collision.
To know more about collision visit:
brainly.com/question/12550364
#SPJ1
The greenhouse effect is
Answers
What is generally TRUE about diagnosing psychological disorders?
A.
High levels of neurotransmitters have been linked to depression.
B.
Diagnoses are not based on opinion or personal assessment.
C.
Doctors agree about what behaviors make up each disorder.
D.
Psychological disorders can be very difficult to diagnose.
Answers
The statement that says "Psychological disorders can be very difficult to diagnose" is true about diagnosing psychological disorders.
What are psychological disorders?Psychological disorders are those mental, behavioral, emotional and thinking conditions that interfere with the normal performance of the individual in society.
Mental disorders are psychiatric conditions that are expressed in a syndrome, verifiable from different diagnostic criteria.The steps to obtain a diagnosis include a medical history, physical examination, and possibly laboratory tests and a psychological evaluation.Therefore, we can conclude that a psychological disorder is an alteration in the mental balance of a person that requires specialized attention adapted to the characteristics of the dysfunction.
Learn more about psychological disorders here: https://brainly.com/question/6367767
2. A tank of water containing 2500 L of water is stored on the roof of a building. Find its potential energy with respect to the floor, which is 12.0m below the roof. b) Find its potential energy with respect to the basement, which is 4.0 m below the first floor (use g=10m/s²) Ans: a)3×105J b)4×105 60
Answers
The gravitational potential energies are 300 kJ and 400 kJ respectively
What is the gravitational potential energy?Gravitational potential energy is a form of potential energy that an object possesses due to its position relative to a reference point in a gravitational field. It is defined as the amount of work that must be done to move an object from its current position to a reference point, without changing its speed or direction.
The gravitational potential energy of an object can be calculated using the formula:
For the first case;
Note that the mass of 2500 L is 2500 Kg
With respect to the floor;
2500 Kg * 10 * 12 = 300 kJ
With respect to the basement;
2500 * 10 * 16 = 400 kJ
Learn more about energy:https://brainly.com/question/1932868
#SPJ1
A football player kicks a ball with a mass of 0.5 kg. The average acceleration of the football was 15 m/s/s. How much force did the kicker apply to the football?
Answers
Answer:
i think its 8.2
Explanation:
Which correctly describes a different evolutionary stage of a star like the sun
A) it’s forms from a cold, dusty molecular cloud
B) During a yellow giant stage, it burns carbon in its core and helium in the shell surrounding the core.
C) After leaving the main sequence, its core is stable due to electron degeneracy
D) It becomes a white dwarf after exploding as a supernova
E)During a red giant stage, its core contracts and cools
Answers
The statement that correctly defines an evolutionary stage of a star like the sun is that after leaving the main sequence, its core is stable due to electron degeneracy. That is option C.
What are the stage of life cycle of a star?The stages of the life cycle of a star include the following:
Giant Gas CloudProtostarT-Tauri PhaseMain SequenceRed GiantThe Fusion of Heavier ElementsSupernovae and Planetary NebulaeThe evolutionary stage is also called the main sequence stage of the life cycle of the star.
In this stage, the core temperature reaches the point for the fusion to occur whereby the protons of hydrogen are converted into atoms of helium. This leads to the stability of the core of the newly formed start due to electron degeneracy.
Learn more about star formation here:
https://brainly.com/question/29976256
#SPJ1
2 questions! most important one is the second one so answer that. only answer if the answer to the 2 question is yes. if you cant say yes to the second question then just dont answer
Answers
Please help me Thanks!

Answers
l will help and if you get it correctly I will say you are welcome
Two coils , held in fixed positions , have a mutual inductance of 100 mH . What is the peak emf in one coil when the current in the other coil is i ( t ) = 10 sin ( 1000 t ) , where is in amperes and t is in seconds ?
Answers
The peak emf in one coil at the given current in the other coil is 1,000 A.
What is mutual inductance?Mutual Inductance between the two coils is defined as the property of the coil due to which it opposes the change of current in the other coil.
The peak emf in one coil when the current in the other coil is i ( t ) = 10 sin ( 1000 t ) depends on the mutual inductance and the peak current.
The peak emf in one coil is calculated as follows;
emf₀ = M di/dt
where;
M is the mutual inductancedi/dt is the rate of change of currentdi/dt = (10 x 1000) cos (1000 t)
di/dt = 10,000 cos(1000 t)
The peak rate of change of current from the derivative of di/dt = 10,000 A/s
emf₀ = (100 x 10⁻³) x (10,000 A/s)
emf₀ = 1,000 V
Learn more about peak emf here: https://brainly.com/question/12943807
#SPJ1
Most scientific experiments are what type experiment, mostly because it is simpler and easier to test single variables? a) Natural experiment. b) Controlled experiment. c) Forced experiment. d) Redundant experiment.
Answers
Answer:
The correct answer is : option B. controlled experiments.
Explanation:
A scientific experiment which deals with a single variable at a time and compared the independent variable to a controlled variable after measuring the change in dependent variable.
It is a very simple and easy test for single variable. In these experiments subjects are divided in two groups one one, with independent variable and other variable.
Thus, the correct answer is : option B. controlled experiments.
The diameter of an atom is about 1 angstrom (10-10 m). In order to develop some intuition for the molecular scale of a gas, assume that you are considering 1 liter of air (mostly N2 and 02, with molar masses of 28 g/mol and 32 g/mol respectively) at room temperature and atmospheric pressure (about 105 Pa). As always, be sure to show your work and explain your reasoning.
a) Calculate the number of molecules in this sample of air.
b) Estimate the average spacing between the molecules.
c) Estimate the average speed of a molecule based on the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution. Convert your answer to miles per hour.
d) Suppose that we scale up the gas so that each atom is the size of a tennis ball. We also scale up the spaces between the atoms proportionally. Now what would be the average spacing between molecules? What would be the mass of a single molecule (assuming that the density of a molecule remains the same)?
Answers
Answer:
A) 2.5 * 10^22 molecules
B) 3.33 * 10^-9 m
C) 1134 miles/hour
D) average spacing = 2.1 m , New mass = 17 kg
Explanation:
Given data :
diameter of atom = 10^-10 m
volume of air = 1 liter
molar masses : 28 g/mol of N2, 32 g/mol of O2
atmospheric pressure = 10^5 Pa
attached below is the detailed solution

