Each segment of an oil pipeline is 30 feet long. If a segment of the pipeline leaks, repair workers reach the leak by opening the pipeline at the nearest end of the segment. The probability of a leak is distributed continuously and uniformly through each segment.
Required:
a. How far can repair workers expect to travel to reach a leak?
b. There is a 0.30 probability repair workers will travel between three feet and how many feet to reach a leak?
Answers
a) There is a 0.30 probability repair workers will travel between three feet and twelve feet to reach a leak.
b) The repair workers can expect to travel 15 feet to reach a leak because the leak can occur anywhere on the 30 feet long segment.
(a) Since each segment of an oil pipeline is 30 feet long. Hence, repair workers can expect to travel 15 feet to reach a leak because the leak can occur anywhere on the 30 feet long segment.
(b) Let X be the distance from one end of the pipe segment to the leak, then X follows a uniform distribution from 0 to 30.
Therefore, the PDF of X is given by `f(x) = 1/30` for `0 ≤ x ≤ 30`Now, P(3 ≤ X ≤ x) = 0.3
Since the distribution is uniform, the area of the shaded region is `0.3 × 30 = 9` square feet.
So, we have: `∫[3, x] f(t)
dt = 9/30` or `∫[3, x] 1/30
dt = 9/30`
Now, `∫[3, x] 1/30 dt = [t/30]_3^x = (x - 3)/30`
Hence, we can write as:`(x - 3)/30 = 0.3`
Solving for x, we get:x - 3 = 9 => x = 12 feet
Learn more about probability at:
https://brainly.com/question/32886316
#SPJ11
Related Questions
Ayuda por favor es para mañana
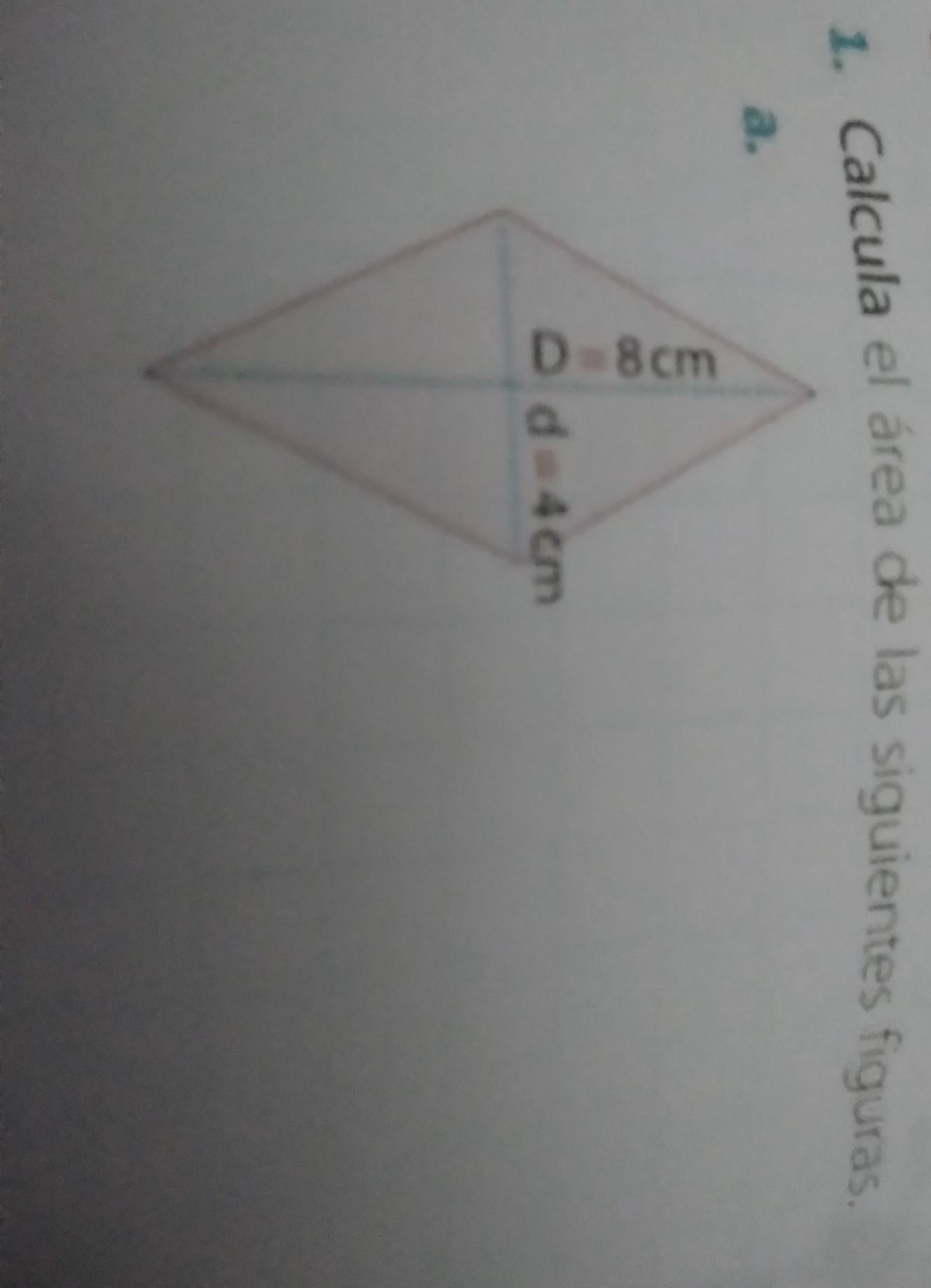
Answers
Answer:
16cm^2
Step-by-step explanation:
8*4=32
32/2 = 16
don conducted a survey of two groups (n subscript 1 equals 50 comma space n subscript 2 space end subscript equals 50 )of students that recently graduated from private and public colleges. he found that the mean debt for the students who attended private college was $26,600, while those who attended public colleges had a mean debt of $24,400. don wants to see if the difference in mean debt is statistically significant. what should don state for the null hypothesis?
Answers
Don's null hypothesis is that there is no statistically significant difference between the mean debt of students who attended private college and the mean debt of students who attended public colleges, represented as H₀: μ₁ - μ₂ = 0
The null hypothesis (H0) is a statement of "no difference" or "no effect" and is typically represented as "there is no statistically significant difference between the mean debt of students who attended private college and the mean debt of students who attended public colleges." Therefore, in this case, Don's null hypothesis can be stated as
H₀: μ₁ - μ₂ = 0
where μ₁ represents the population mean debt for students who attended private college, and μ₂ represents the population mean debt for students who attended public colleges.
Learn more about null hypothesis here
brainly.com/question/19263925
#SPJ4
consider a pi controller and the following feedback process what are the roots of the characteristic equation
Answers
The characteristic equation of a closed-loop control system with a proportional-integral (PI) controller is given by:
s^2 + (k_i/k_p)s + (1/k_p) = 0
where k_p is the proportional gain and k_i is the integral gain of the PI controller. To find the roots of the characteristic equation, we can use the quadratic formula:
s = (-b ± sqrt(b^2 - 4ac)) / 2a
where a, b, and c are the coefficients of the quadratic equation. Therefore, the roots of the characteristic equation depend on the values of k_p and k_i, which in turn depend on the specific feedback process being controlled.
Know more about closed-loop control system here:
https://brainly.com/question/30896173
#SPJ11
Kim works as a server in a restaurant. She is serving the table where a group of her friends are eating. Her friends always tip 15%. If the cost of the meal is $23.60, how much of a tip will Kim earn?
Answers
if the bill was $23.60, and the tip was 15%, kim will earn $3.54. the overall total of the meal would be $27.14 :)
Anwser will be $3.54
15% = .15 ( to convert percent to decimal, change the % to . and move the decimal two places to the left)
23.60 * .15 = 3.54
Use the figure to answer the question. Calculate GH is a=3 and b=20

Answers
Answer:
7.75
Step-by-step explanation:
By Geometric mean property:
\( GH = \sqrt {a \times b} \)
\( GH = \sqrt {3 \times 20} \)
\( GH = \sqrt {60} \)
\( GH = 7.74596669\)
\( GH \approx 7.75\)
In a standard deck of cards what is the probability of choosing a red king replacing it and then choosing and then a club.
Answers
Answer:
1/104
Step-by-step explanation:
The probability of choosing a red king is 2/52 since there are only two red kings in a deck of 52 cards...the probability of choosing a club would be 13/52 since there are 13 club cardsin a deck of 52 cards
Therefore the probability of choosing both by replacing the king would be 2/52 × 13/52 giving us 1/104
Why are there number in the middles I’m so confused

Answers
Step-by-step explanation:
The numbers between the squares are the possible answers.
For example, 2/3 ÷ 3/4 is either 1/2 or 8/9.
2/3 ÷ 3/4
2/3 × 4/3
8/9
The answer is 8/9, so you'll move up to the next square.
Solve 7x + 4 =- 3x - 26
Answers
Answer:
x=−3 is your answer :)
Step-by-step explanation:
Steps for Solving Linear Equation
7x+4=−3x−26
Add 3x to both sides.
7x+4+3x=−26
Combine 7x and 3x to get 10x.
10x+4=−26
Subtract 4 from both sides.
10x=−26−4
Subtract 4 from −26 to get −30.
10x=−30
Divide both sides by 10.
x=
10
−30
Divide −30 by 10 to get −3.
x=−3
How many sides do 5 dodecagons, 2 decagons, 5 nonagons, and 4 hexagons have in all? Tell me now
Answers
5*12 + 2*10 + 5*9 + 4*6
60 + 20 + 45 + 24
80 + 69
149 sides in total
3/4 < 4/9 *
1 point
True
False
Answers
Answer:
false
Step-by-step explanation:
4/9 is smaller than 3/4.
2(6k+8)-6k=4
What is the answer
Answers
Answer:
k=-2
Step-by-step explanation:
2(6k+8)-6k=4
12k+16-6k=4
6k+16=4
6k=-12
k=-2
what is (fxg)(x)
f(x)=x^3-4x+2
g(x)=x^2+2
Answers
Answer: x^6+6x^4+8x^2+2
Step-by-step explanation:
Since g comes after f then you will take g's equation and plug it into the f equation so it would turn out to be if you plugged it in
(x^2+2)^3-4(x^2+2)+2 which would equal x^6+6x^4+8x^2+2
what is limit definition of a derivative?
Answers
The limit definition of a derivative is a mathematical method used to calculate the instant rate of change of a characteristic at a particular point. it is based at the idea of the limit of a function because the input techniques a certain cost.
The limit definition of a derivative is expressed as follows:
\(f'(x) = lim (h → 0) [f(x + h) - f(x)] /h\)
Wherein f'(x) represents the derivative of the function f(x) at a particular factor x. The expression \(( f(x + h) - f(x)) / h\) represents the common price of alternate of the characteristic over a small interval of size h, focused at x. The limit of this expression as h approaches 0 represents the instant fee of change of the characteristic at x, or the slope of the tangent line to the function at that factor.
The limit definition of a derivative is a fundamental concept in calculus and is used to calculate the slopes of tangent lines, to find maximum and minimum factors, and to clear up optimization issues in a huge variety of packages.
Learn more about Limit definition of a derivative:-
https://brainly.com/question/30402318
#SPJ4
The area of a square is given by A=s2, where s is the length of each side of the square. If the area of a square room is 81 square meters, what is the length of one side of the room in meters?
Answers
Answer: The length of one side is 9m.
Step-by-step explanation:
If area is 81 square meters, that means A = 81 m^2.
Since A = s^2, we can substitute s^2 for A. Then
(s^2) = 81 m^2
Take the square root of both sides to solve for s:
(s^2)^(1/2) = (81 m^2)^(1/2)
s = 9 m
Someone plz help meh

Answers
Answer:
f( g ( - 2 ) ) = - 14
Step-by-step explanation:
f(x) = - 2x + 4
g(x) = 3x² - x - 5
f( g ( - 2 ) ) = ?
g( - 2 ) = 3( - 2 )² - ( - 2 ) - 5 = 12 + 2 - 5 = 9
f(9) = - 2 × 9 + 4 = - 14
f( g ( - 2 ) ) = - 14
HELP ASAP!!!!!! 34 ÷ (14 − 5) × 2
Answers
Answer:
B
Step-by-step explanation:
Answer:
14-5=9, then 34 / 9 x 2, 9x2=18, 34 / 18= 1.888888 orrrr 34 / 9= 3.7777 that x 2 = 7.55555554
(1 point) how many terms of the series do we need to add in order to find the sum to the indicated accuracy? ∑n=1[infinity](−1)n−1n2,error≤0.002.
Answers
To determine the number of terms we need to add in order to find the sum of the series with an error less than or equal to 0.002, we can use the concept of the Alternating Series Estimation Theorem.
The Alternating Series Estimation Theorem states that for an alternating series with terms decreasing in absolute value, the error in approximating the sum of the series by the sum of a finite number of terms is less than or equal to the absolute value of the next term.
In the given series, ∑n=1[infinity](−1)n−1n^2, the terms are decreasing in absolute value as n increases, so we can apply the Alternating Series Estimation Theorem.
The next term in the series, which determines the error, is given by (-1)^n * (n+1)^2. To ensure the error is less than or equal to 0.002, we need to find the smallest value of n such that:
|(-1)^n * (n+1)^2| ≤ 0.002
We can solve this inequality by testing values of n until we find the smallest value that satisfies it. Starting with n = 1:
|(-1)^1 * (1+1)^2| = 4 > 0.002
The inequality is not satisfied for n = 1.
Let's continue testing values of n:
|(-1)^2 * (2+1)^2| = 9 > 0.002
|(-1)^3 * (3+1)^2| = 16 > 0.002
|(-1)^4 * (4+1)^2| = 25 > 0.002
|(-1)^5 * (5+1)^2| = 36 > 0.002
|(-1)^6 * (6+1)^2| = 49 > 0.002
...
After testing a few values, we can see that the smallest value of n that satisfies the inequality is n = 9:
|(-1)^9 * (9+1)^2| = 100 > 0.002
Therefore, we need to add at least 9 terms in order to find the sum of the series with an error less than or equal to 0.002.
To learn more about Alternating Series Estimation Theorem. refer below
https://brainly.com/question/31418152
#SPJ11
the answer to the question.

Answers
Answer:
answer attached in pic ture

Answer:
1/16
Step-by-step explanation:
it is the same as
\(\frac{1}{8^\frac{4}{3}} = \frac{1}{ {(\sqrt[3]{8})}^4} = \frac{1}{2^4} = \frac{1}{16}\)
a variable is normally distributed with mean 15 and standard deviation 4 . a. find the percentage of all possible values of the variable that lie between and . b. find the percentage of all possible values of the variable that exceed . c. find the percentage of all possible values of the variable that are less than .
Answers
The percentage of all possible values of the variable that are less than 12 is 22.66%.
A variable is normally distributed with mean 15 and standard deviation 4 . a. find the percentage of all possible values of the variable that lie between and . b. find the percentage of all possible values of the variable that exceed . c. find the percentage of all possible values of the variable that are less than.Variables are unknown quantities that can take on different values.
In statistics, a variable can be a numeric or non-numeric value that can differ from one measurement to the next.A normal distribution is a type of probability distribution where the probability of each value of the variable is proportional to the distance of the value from the mean, and the distribution is symmetrical about the mean. The normal distribution is described by two parameters, the mean (μ) and the standard deviation (σ).a) To find the percentage of all possible values of the variable that lie between 10 and 20, first find the z-scores for 10 and 20.z-score for 10 = (10 - 15) / 4 = -1.25 z-score for 20 = (20 - 15) / 4 = 1.25 Using a standard normal distribution table, find the area between the z-scores of -1.25 and 1.25 Area = 0.7887 or 78.87%
Therefore, the percentage of all possible values of the variable that lie between 10 and 20 is 78.87%.b) To find the percentage of all possible values of the variable that exceed 22, first find the z-score for 22.z-score for 22 = (22 - 15) / 4 = 1.75 Using a standard normal distribution table, find the area to the right of the z-score of 1.75 Area = 0.0401 or 4.01%Therefore, the percentage of all possible values of the variable that exceed 22 is 4.01%.c) To find the percentage of all possible values of the variable that are less than 12, first find the z-score for 12.z-score for 12 = (12 - 15) / 4 = -0.75 Using a standard normal distribution table, find the area to the left of the z-score of -0.75 Area = 0.2266 or 22.66%Therefore, the percentage of all possible values of the variable that are less than 12 is 22.66%.
Learn more about Variable
brainly.com/question/17344045
#SPJ11
what is the answer 2+2=4-5/25
Answers
your phone plan charges you an initial fee of $50 plus $.25 per minute. if your bill last month was $225, how many minutes did you use? question 6 options: a) 725 minutes b) 700 minutes c) 650 minutes d) 600 minutes
Answers
To find the total number of minutes used, divide $175 by the $.25 per minute charge. This equals 650 minutes, meaning the user had used 650 minutes throughout the month.
$50 initial fee + $.25 per minute = $225
$225 - $50 = $175
$175 / $.25 = 650 minutes
The initial fee for the phone plan was $50, and for every minute used, an additional $.25 was charged. Last month's bill was $225, so subtracting the $50 initial fee from the total cost of the bill leaves $175, which is the cost of the minutes used. To find the total number of minutes used, divide $175 by the $.25 per minute charge. This equals 650 minutes.
The phone plan charges an initial fee of $50 for the month, as well as an additional $.25 for every minute used. Last month's bill was $225, so to find the total number of minutes used, subtract the $50 initial fee from the total cost of the bill. This results in $175, which is the cost of the minutes used. To find the total number of minutes used, divide $175 by the $.25 per minute charge. This equals 650 minutes, meaning the user had used 650 minutes throughout the month.
A user's phone plan last month costed $225, which included an initial fee of $50 plus $.25 for every minute used. After subtracting the initial fee from the total bill cost, $175 was left which was the cost of the minutes used. Dividing this number by the $.25 per minute charge reveals that the user had used 650 minutes.
learn more about number here
https://brainly.com/question/10547079
#SPJ4
what is the percent that it will land in the blue?
round to the nearest tenth of a percent.

Answers
Answer: 84.5%
==========================================================
Work Shown:
A = area of the smaller square
A = (5.98)^2
A = 35.7604 square cm which is exact
B = area of the larger square
B = (15.2)^2
B = 231.04 square cm which is exact
C = the chances of landing in the smaller square
C = A/B
C = 35.7604/231.04
C = 0.15478012465373 which is approximate
C = 0.154780
D = the chances of landing in the blue region
D = 1 - C
D = 1 - 0.154780
D = 0.84522
D = 84.522%
D = 84.5%
Write the equation of the line that passes through the point -3,4 and slope of 6
Answers
Explanation:
1. we first start with the equation y=Mx+b
2. Then we plug in the slope (6) into M
3. Now you have y=6x+b
4. Now you plug in your point (-3,4) into the y and the x values
5. You are now stuck with 4=6(-3)+b
6. Now multiply 6 and -3 which gets you -18
7. Your new equation is now 4=-18+b
8. Now add 18 to both sides of the equals sign
9. Now you have 4+18=b
10. Add 4+18 which gets you 22. B is 22
11. Plug b into the equation and turn the values of x and y back to those letters
12. You now have the answer of y=6x+22

can you plz help me??? Gwen wants to create a congruent shape to the one she made. Her regular pentagon has a perimeter of 24.2 cm. What is going to be the length of the sides in the shape that she creates? A. 4.84 cm B. 5.84 cm C. 9.68 cm D. 121 cm
Answers
Answer:
The answer is A) 4.84 cm :P
Step-by-step explanation:
Gwen wants to create a congruent shape, so, all the sides have to be the same size. And if its a pentagon like in your situation , a pentagon has 5 sides so you have to divide 24.2 cm because it's your regular pentagon by 5 (sides) (24.2 cm ÷ 5 sides = 4.84 cm )
I hope I helped you :P
Answer:
The answer is A.
Step-by-step explanation:
A simple random sample of 60 items resulted in a sample mean of 25. The population standard deviation is o = 7. (Round your answers to two decimal places.) (a) What is the standard error of the mean, 0-? (b) At 95% confidence, what is the margin of error?
Answers
a) The standard error of the mean is 0.90
b) The marginal error is 1.76
Given,
Number of samples in the population, n = 60
Sample mean of the population, μ = 25
Standard deviation of the population, σ = 7
We have to find the standard error of the mean and the margin of error at 95% confidence.
Here,
a) The standard error of the mean = Standard deviation / root of sample
= σ / √n
= 7/√60
= 0.90
b) The margin error;
Zₐ/₂ × σ / √n
= Zₐ/₂ × 7/√60
= 1.96 × 0.90
= 1.76
Therefore,
a) The standard error of the mean is 0.90
b) The marginal error is 1.76
Learn more about standard error and marginal error here;
https://brainly.com/question/17014419
#SPJ1
minimize f(x) = |x+3| + x^3 S.t. x sum [-2, 6]
Answers
Minimization of f(x) = |x+3| + x^3 at the endpoints (-2 and 6) the minimum value of the function is approximately 3.84, which occurs at x= \sqrt{1/3}
within the given interval.
To minimize the function subject to the constraint f(x) = |x+3| + x^3 that x lies in the interval [-2, 6], we need to find the value of x that minimizes f(x) within that interval.
First, let's analyze the function f(x). The absolute value term |x+3| can be rewritten as:
|x+3| =
x+3 if x+3 >= 0
-(x+3) if x+3 < 0
Since the interval [-2, 6] includes both positive and negative values of x+3, we need to consider both cases.
Case 1: x+3 >= 0
In this case, f(x) = (x+3) + x^3 = 2x + x^3 + 3
Case 2: x+3 < 0
In this case, f(x) = -(x+3) + x^3 = -2x + x^3 - 3
Now, we can find the minimum of f(x) within the given interval by evaluating the function at the endpoints (-2 and 6) and at any critical points within the interval.
Calculating the values of f(x) at x = -2, 6, and the critical points, we can determine the minimum value of f(x) and the corresponding value of x.
Since the equation involves both absolute value and a cubic term, it is not possible to find a closed-form solution or an exact minimum value without numerical methods or approximation techniques.
For more such questions on function
https://brainly.com/question/29631554
#SPJ8
Find the general solution of the system
dx1(t(/dt = 2x1(t)+2x2(t)+t
dx2(t)/dt = x1(t)+3x2(t)-2t
Answers
Given system is: dx1/dt = 2x1 + 2x2 + tdx2/dt = x1 + 3x2 - 2tNow we will use matrix notation, let X = [x1 x2] and A = [2 2; 1 3]. Then the given system can be written in the form of X' = AX + B, where B = [t - 2t] = [t, -2t].Now let D = |A - λI|, where λ is an eigenvalue of A and I is the identity matrix of order 2.
Then D = |(2 - λ) 2; 1 (3 - λ)|= (2 - λ)(3 - λ) - 2= λ² - 5λ + 4= (λ - 1)(λ - 4)Therefore, the eigenvalues of A are λ1 = 1 and λ2 = 4.Now let V1 and V2 be the eigenvectors of A corresponding to eigenvalues λ1 and λ2, respectively. Then AV1 = λ1V1 and AV2 = λ2V2. Therefore, V1 = [1 -1] and V2 = [2 1].Now let P = [V1 V2] = [1 2; -1 1]. Then the inverse of P is P⁻¹ = [1/3 2/3; -1/3 1/3]. Now we can find the matrix S(t) = e^(At) = P*diag(e^(λ1t), e^(λ2t))*P⁻¹, where diag is the diagonal matrix. Therefore,S(t) = [1 2; -1 1] * diag(e^(t), e^(4t)) * [1/3 2/3; -1/3 1/3])= [e^(t)/3 + 2e^(4t)/3, 2e^(t)/3 + e^(4t)/3; -e^(t)/3 + e^(4t)/3, -e^(t)/3 + e^(4t)/3].Now let Y = [y1 y2] = X - S(t).
Then the given system can be written in the form of Y' = AY, where A = [0 2; 1 1] and Y(0) = [x1(0) - (1/3)x2(0) - (e^t - e^4t)/3, x2(0) - (2/3)x1(0) - (2e^t - e^4t)/3].Now let λ1 and λ2 be the eigenvalues of A. Then D = |A - λI| = (λ - 1)(λ - 2). Therefore, the eigenvalues of A are λ1 = 1 and λ2 = 2.Now let V1 and V2 be the eigenvectors of A corresponding to eigenvalues λ1 and λ2, respectively. Therefore, V1 = [1 -1] and V2 = [2 1].Now let P = [V1 V2] = [1 2; -1 1]. Then the inverse of P is P⁻¹ = [1/3 2/3; -1/3 1/3]. Now we can find the matrix Y(t) = e^(At) * Y(0) = P*diag(e^(λ1t), e^(λ2t))*P⁻¹ * Y(0), where diag is the diagonal matrix. Therefore,Y(t) = [1 2; -1 1] * diag(e^(t), e^(2t)) * [1/3 2/3; -1/3 1/3]) * [x1(0) - (1/3)x2(0) - (e^t - e^4t)/3, x2(0) - (2/3)x1(0) - (2e^t - e^4t)/3]= [(e^t + 2e^(2t))/3*x1(0) + (2e^t - e^(2t))/3*x2(0) + (e^t - e^4t)/3, -(e^t - 2e^(2t))/3*x1(0) + (e^t + e^(2t))/3*x2(0) + (2e^t - e^4t)/3].Therefore, the general solution of the system is X(t) = S(t) + Y(t), where S(t) = [e^(t)/3 + 2e^(4t)/3, 2e^(t)/3 + e^(4t)/3; -e^(t)/3 + e^(4t)/3, -e^(t)/3 + e^(4t)/3] and Y(t) = [(e^t + 2e^(2t))/3*x1(0) + (2e^t - e^(2t))/3*x2(0) + (e^t - e^4t)/3, -(e^t - 2e^(2t))/3*x1(0) + (e^t + e^(2t))/3*x2(0) + (2e^t - e^4t)/3].
To know more about system visit :
https://brainly.com/question/30035551
#SPJ11
Which of the following number lines shows the correct sum of the number above and -5/2?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Answers
-4 2/3 as a decimal can't figure it out help!!!
Answers
Answer:
-4.6 Repeating
Step-by-step explanation:
This will be a repeating Decimal. :)
Answer:
0.6666
Step-by-step explanation:
you divide 2 by three and then you get your answer
Which inequality makes the statement below true? |-13 BLANK -13 O A. = O B. < OC. S O D. >
PLEASE HELP ME
Answers
Answer:
Hey there the best answer would be A.=
Step-by-step explanation: