A car traveling south is 200 kilometers from its starting point after 2 hours. What is the average velocity of the car? (OP A. 100 kilometers/hour south B. 200 kilometers/hour C. 200 kilometers/hour north 100 kilometers/hour
Answers
Answer:
A
Explanation:
take note that v=d/t (velocity is distance over(divided by) time, so in this case it would be 200 (distance) divided by 2 (time)
Related Questions
A plastic bottle partially filled with water floats on water, even though the density of the plastic (1.2 g/cc) is more than that of water. Why is that?
Answers
Answer:
True the plastic will float because of the principle of flotation or buoyancy
Explanation:
Buoyancy explains it all!!
Buoyancy is the upward force/upthrust experienced by a body immersed totally or partially in a liquid.
According to the principle of flotation:
"when a body is totally or partially immersed in liquid it experiences an upthrust which is equal to the volume of fluid displaced"
The plastic will float due to the fact the average density of the total volume of the plastic and the air inside it is less than the same volume of water it is floating in
average method and it reports the tollowing unit data tor the rorming department. Units completed in the torming department are transferred to the painting department. Production cost information for the forming department follows. . Calculate the equivalent units of production for both direct materials and conversion for the Forming department. o. Calculate the costs per equivalent unit of production for both direct materials and conversion for the Forming department c. Using the weighted average method, assign costs to the forming department's output-specifically, its units transferred to painting and its endina work in brocess inventorv. Calculate the costs per equivalent unit of production for both direct materials and conversion for the For Jsing the weighted average method, assign costs to the forming department's output-specifically, its 4 d its ending work in process inventory. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Calculate the equivalent units of production for both direct materials and conversion for the forming department. a. Calculate the equivalent units of production for both direct materials and conversion for the Forming departm b. Calculate the costs per equivalent unit of production for both direct materials and conversion for the Forming c. Using the weighted average method, assign costs to the forming department's output-specifically, its units tra and its ending work in process inventory. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Calculate the costs per equivalent unit of production for both direct materials and conversion for the forming department Required information Using the weighted average method, assign costs to the forming department's output-specifically, its units trar painting and its ending work in process inventory.
Answers
Given information: The average method reports the following unit data for the forming department. Units completed in the forming department are transferred to the painting department. Production cost information for the forming department follows.
Direct materials:
Units completed during the period = 45,000 units
Ending work in process inventory = 5,000 units
Direct materials cost = $202,500
Conversion costs:
Units completed during the period = 45,000 units
Ending work in process inventory = 5,000 units
Conversion cost = $189,000
a. Calculation of equivalent units of production for both direct materials and conversion for the forming department:
Equivalent units of production = Units completed during the period + (Ending work in process inventory * Degree of completion)
Direct materials:
Equivalent units of production = 45,000 + (5,000 * 50%) = 47,500 units
Conversion costs:
Equivalent units of production = 45,000 + (5,000 * 60%) = 48,000 units
b. Calculation of the cost per equivalent unit of production for both direct materials and conversion for the forming department:
Cost per equivalent unit of production = Total cost for the period / Equivalent units of production
Direct materials:
Cost per equivalent unit of production = $202,500 / 47,500 units = $4.26 per unit
Conversion costs:
Cost per equivalent unit of production = $189,000 / 48,000 units = $3.94 per unit
c. Calculation of the cost assigned to the forming department's output using the weighted average method:
Total cost = Cost of units transferred out + Cost of ending work in process inventory
Cost of units transferred out = Number of units transferred out * Cost per equivalent unit of production
Cost of ending work in process inventory = Number of units in ending work in process inventory * Cost per equivalent unit of production
Direct materials:
Cost of units transferred out = 40,000 * $4.26 per unit = $170,400
Cost of ending work in process inventory = 5,000 * $4.26 per unit = $21,300
Total cost = $170,400 + $21,300 = $191,700
Conversion costs:
Cost of units transferred out = 40,000 * $3.94 per unit = $157,600
Cost of ending work in process inventory = 5,000 * $3.94 per unit = $19,700
Total cost = $157,600 + $19,700 = $177,300
Learn more about unit data:
https://brainly.com/question/31181436
#SPJ11
A
is the order in which things are arranged.
O plan
sequence
O process
O goal

Answers
Answer:
sequence
Explanation:
sequences are the way in which things are ordered, for example: 1, 2, 3, 4 is a sequence:)
Do you think all substances can change into a solid,liquid or gas?
Answers
Answer:In short yes in long
Explanation:yes all substances can exist in any of these three states. In addition to existing in one of the three states, matter can also undergo a change of state. A change of state occurs when matter is converted from one state to another state for example when a liquid is converted to a gas or a solid is converted to a liquid.
Which Case clause will be true whenever the value of the selector in a Select Case blockis greater than or equal to 7?A. Case Is >7B. Case Is = 8C
Answers
The correct case clause would be A. Case Is >7.
In a Select Case block, the case clauses are used to check different conditions against a selector value. The selector value is compared with each case clause, and the first matching case clause is executed.
To determine which case clause will be true when the selector value is greater than or equal to 7, we need to consider the available options:
A. Case Is >7: This case clause will be true when the selector value is greater than 7.
B. Case Is = 8: This case clause will be true only when the selector value is exactly 8.
Since we are interested in finding the case clause that matches when the selector value is greater than or equal to 7, option A (Case Is >7) is the correct choice. It covers all values greater than 7, including 8 and any other number greater than 8.
For more questions like Selector click the link below:
https://brainly.com/question/28463976
#SPJ11
Marsha and Wes are trying to create an amusement park on Mars. What dimensions do they need to create their first attraction, the Crater Craze Climber?
Answers
Assuming they have identified a suitable location on Mars with sufficient space, they will need to determine the height, width, and depth of the attraction. Here are some potential dimensions they could consider:
Height: Depending on the target age group, the height of the Crater Craze Climber could vary. If it's intended for younger children, the maximum height should be around 10-12 feet (3-3.6 meters). For older children or adults, it could be taller, up to 20-30 feet (6-9 meters).Width: The width of the attraction will depend on the number of climbers they want to accommodate at one time. A width of 20-30 feet (6-9 meters) would be suitable for a small to medium-sized attraction, while a larger attraction could be up to 50-60 feet (15-18 meters) wide.Depth: The depth of the attraction will depend on the level of difficulty they want to achieve. A shallow depth of 5-10 feet (1.5-3 meters) would be suitable for younger children or beginners, while a deeper depth of 20-30 feet (6-9 meters) would provide a greater challenge for older children or experienced climbers.These dimensions are just suggestions, and Marsha and Wes will need to consider their specific goals and constraints in creating the Crater Craze Climber. Additionally, they should consult with experts in engineering and safety to ensure the attraction is structurally sound and safe for visitors.
Learn more about mars here:
https://brainly.com/question/644043
#SPJ1
Two identical balls are rolling toward one another, one from the left and the other from the right. The mass of each ball is 1.0 kg and the speed of each ball is 3.0 m/s. After an elastic collision, both balls roll away from one another at the same speed. What is the momentum of each ball before the collision and what is the total momentum of the two-ball system after the collision?
Answers
Each ball had a momentum of 3 kg m/s before the collision, and
the system of two balls had a total momentum of 0 kg m/s after the collision.
Given,
Each ball has a mass (m) of 1.0 kg.
Each ball moves at a speed (v) of 3.0 m/s.
Momentum (P) = Mass(m) x Velocity (v)
As a result of the identical mass and speed of both balls, the momentum of each ball before the collision would be:
P = mv
P = 1 * 3 kg m/s
P = 3 kg m/s
The momentum of each ball before the collision is 3 kg m/s.
When two identical balls roll in the opposite direction at the same speed with the same mass, their combined momentum would be as follows:
P = m₁v₁ - m₂v₂
P = 1 * 3 - 1 * 3
P = 3 - 3
P = 0 kg m/s
The collision is elastic, thus. The entire momentum before and after the collision is zero (0).
Visit the link below to learn more about the momentum:
brainly.com/question/13767949
How to integrate 1/ 1 + x2
Answers
The integral of 1/(1 + x²) is (1/2)ln|1 + x²| + C where C is the constant of integration.
Integration is a mathematical process of finding the antiderivative of a function. To integrate the given expression 1/(1 + x²), we will use the substitution method.
Let u = 1 + x², du/dx = 2x dx, then dx = du/2x and the integral becomes:
∫1/(1 + x²) dx = ∫1/u * (1/2x) du= (1/2)∫1/u du
The antiderivative of 1/u is ln|u| + C, where C is the constant of integration.
Therefore, the final solution of the integral is (1/2)ln|1 + x²| + C.
Let us work through the steps:
Step 1:Let u = 1 + x² and then differentiate both sides with respect to x to obtain du/dx. du/dx = 2x
Substitute 2x dx = du into the integral ∫1/(1 + x²) dx to get the integral in terms of u:∫1/u * (1/2x) du = (1/2) ∫1/u du
Step 2:Calculate the antiderivative of 1/u, which is ln|u|. Thus, the final solution is (1/2)ln|1 + x²| + C, where C is the constant of integration. The constant C will vary depending on the initial conditions of the problem.
for such more questions on integration
https://brainly.com/question/87852
#SPJ8
16/07/2021 23
question 9 of 10
homework
which movement will require the greatest amount of work to be
done?
this activity is
a force of 10n moving an object a distance of 3.0 m
b*
assessment
percentage
a force of 10n moving an object a distance of 5.0m
a force of 15n moving an object a distance of 3.0m
c attempts
a force of 15n moving an object a distance of 5.0m
Answers
D. The movement that will require the greatest amount of work to be
done is a force of 15n moving an object a distance of 5.0m (75 J).
What is work done?Work is said to be done when an applied force moves an object over a given distance.
W = Fd
where;
F is the applied forced is the displacement of the objectA force of 10n moving an object a distance of 3.0 mW = 10 x 3 = 30 J
A force of 10n moving an object a distance of 5.0mW = 10 x 5 = 50 J
A force of 15n moving an object a distance of 3.0mW = 15 x 3 = 45 J
A force of 15n moving an object a distance of 5.0mW = 15 x 5 = 75 J
Thus, the movement that will require the greatest amount of work to be
done is a force of 15n moving an object a distance of 5.0m (75 J).
Learn more about work done here: https://brainly.com/question/8119756
#SPJ1
PLEASE HELP!! ILL MARK BRAINLYEST!!
MORE THAN ONE
When an acid and a base are mixed, the excess ions:
A. combine to form water
B. increase
C. decrease
D. neutralize each other
Answers
Answer:
decrease and neutralize each other
Explanation:
as light travels from one medium to another, which of its properties change? (select all that apply.)
Answers
When light travels from one medium to another, its speed, direction, and wavelength can change, while its frequency remains constant. These changes are due to differences in the refractive indices of the two media.
As light travels from one medium to another, several of its properties change, including its speed, direction, and wavelength. The speed of light changes because the refractive index of each medium is different, which alters the velocity of the wave. The direction of the light may also change, a phenomenon known as refraction, as it enters a medium with a different refractive index. The amount of refraction depends on the angle of incidence, the angle between the incoming light and the normal line to the surface of the medium. Finally, the wavelength of the light may also change due to the refractive index of the medium, a phenomenon known as dispersion. This results in the separation of white light into its component colors when it passes through a prism or other refracting medium.
learn more about wavelength here:
https://brainly.com/question/13676179
#SPJ4
Determine the distance a 741.19 W crane lifts a crate in 57.59 s if it uses a force of 546,422.14 N.
Answers
The distance at which the crane lift a crate is 0.0781 m.
What is distance?Distnace is the lenght between two points.
To determine the distance the crane can lift the crate, we use the formula below.
Formula:
d = Pt/F.......................... Equation 1Where:
d = DistanceP = Powert = TimeF = ForceFrom the question,
Given:
P = 741.19 Wt = 57.59 sF = 546422.14 NSubstitute these values into equation 1
d = (741.19×57.59)/546422.14d = 0.0781 mHence, the distance is 0.0781 m.
Learn more about distance here: https://brainly.com/question/26550516
#SPJ1
4. A force of 185.6 N is being applied to a square of side length 3 m. Work out the
pressure on the square to 3 significant figures.
Answers
Answer:
\(p = f \div a\)
\(p = \frac{185.6}{ {3}^{2} } = \frac{185.6}{9} = 20.6pa\)
If You Increase The Distance Between The Plates Of A Capacitor, How Does The Capacitance Change? Not Sure Now Choose From One Of The Following Options Why? A. Doubling The Distance Between Capacitor Plates Will Reduce The Capacitance Four-Fold. B. Doubling The Distance Between Capacitor Plates Will Reduce The Capacitance Two-Fold. C. Doubling the distance between capacitor plates will increase the capacitance two times.
D. Doubling the distance between capacitor plates will increase the capacitance four times.
Answers
B. Doubling The Distance Between Capacitor Plates Will Reduce The Capacitance Two-Fold.
What is Capacitor?Capacitor is an electrical device used to store energy. It is composed of two conducting plates separated by an insulating material called the dielectric. When a voltage is applied to the two plates, an electric field forms between them, storing energy in the form of an electrical charge. Capacitors are used in a variety of applications, such as in filter circuits, timing circuits, and power supply circuits.
The capacitance of a capacitor is directly proportional to the area of the plates and inversely proportional to the distance between the plates. Therefore, when the distance between the plates is doubled, the capacitance is halved.
To learn more about Capacitor
https://brainly.com/question/27258294
#SPJ1
water near the surface of a tropical ocean has a temperature of 300 k while water 1000 m beneath the surface has a temperature of 270 k. it has been proposed that the warm water be used as the hot reservoir and the cool water as the cold reservoir of a heat engine. what is the maximum possible efficiency for such an engine?
Answers
A heat engine operates by converting thermal energy into mechanical energy. The efficiency of a heat engine is defined as the ratio of the useful work output to the heat absorbed from the hot reservoir.
It is given by:η = 1 - Tc/Thwhereη is the efficiency of the engine,Tc is the temperature of the cold reservoir, and The temperature of the hot reservoir.In this case, water near the surface of a tropical ocean has a temperature of 300 K while water 1000 m beneath the surface has a temperature of 270 K. It has been proposed that the warm water be used as the hot reservoir and the cool water as the cold reservoir of a heat engine.To find the maximum possible efficiency of such an engine, we substitute the given temperatures into the efficiency equation:η = 1 - Tc/Thη = 1 - 270/300η = 1 - 0.9η = 0.1 or 10%Therefore, the maximum possible efficiency for such an engine is 10%.
for more such question on thermal energy
https://brainly.com/question/28944987
#SPJ11
Arrange the following in order of increasing radius: O2-, F- , Ne ,Rb+ ,Br- Rb+ < F- < Br- < O2- < Ne Br- < Rb+ < Ne < F- < O2- Ne < F- < O2- < Rb+ < Br- O2- < F- < Ne < Rb+ < Br- O2- < Br- < F- < Ne < Rb + Br- < F- < O2- < Ne < Rb+ F- < O2- < Ne < Br- < Rb + Rb+ < F- < Br- < Ne
Answers
Radii is a vital feature of the elements, and it can be useful in determining the characteristics of elements in various chemical and physical processes. The radii of atoms and ions of the same element differ due to their various charge and mass characteristics.
Atomic and ionic radii increase as you move down a group on the periodic table, and decrease as you move across a period from left to right due to increased nuclear charge, making the electrons closer to the nucleus. The size of an atom and ion also changes due to the number of electrons charge, and electronic configuration.In order of increasing radius, the arrangement of \(Ne, F-, O2-, Br-, Rb\) is given as follows:
\(Ne < F- < O2- < Br- < Rb+\)
Rb+ has the smallest radius due to its large nuclear charge and fewer electrons in the valence shell.
As a result, they are larger than Rb+. O2- has more electrons than Ne and is the largest among the given ions and atoms. It is important to note that in certain conditions, the trends in radii may not be valid because of hybridization and other factors. Nonetheless, this arrangement is valid for the given ions and atoms.
To know more about nuclear charge visit :
https://brainly.com/question/18028941
#SPJ11
calculate the height (in m) of a cliff if it takes 2.32 s for a rock to hit the ground when it is thrown straight up from the cliff with an initial velocity of 8.19 m/s. 7.37 correct: your answer is correct. seenkey 7.37 m (b) how long (in s) would it take to reach the ground if it is thrown straight down with the same speed? 0.649 correct: your answer is correct. seenkey 0.649 s
Answers
To calculate the height of the cliff and the time it takes for the rock to reach the ground when thrown straight down, we can use the equations of motion.
(a) Height of the cliff:
When the rock is thrown straight up, it reaches its highest point before falling back down. The time it takes for the rock to reach its highest point is equal to the time it takes for the rock to fall back down to the ground.
Using the equation:
s = ut + (1/2)at^2
Where:
s is the distance traveled (height of the cliff),
u is the initial velocity (8.19 m/s),
t is the time (2.32 s),
a is the acceleration due to gravity (-9.8 m/s^2, taking downward direction as negative).
Rearranging the equation:
s = ut + (1/2)at^2
s = (8.19)(2.32) + (1/2)(-9.8)(2.32)^2
s = 19.004 - 25.798
s = -6.794 m
Since the height of a cliff cannot be negative, we take the absolute value of the result:
Height of the cliff = |s| = 6.794 m
So, the height of the cliff is approximately 6.794 meters.
(b) Time to reach the ground when thrown straight down:
When the rock is thrown straight down with the same speed, the initial velocity (u) is still 8.19 m/s, but the acceleration due to gravity (a) remains -9.8 m/s^2.
Using the equation:
s = ut + (1/2)at^2
Where:
s is the distance traveled (height of the cliff, which is now negative),
u is the initial velocity (8.19 m/s),
t is the time we want to find,
a is the acceleration due to gravity (-9.8 m/s^2, taking downward direction as negative).
Substituting the known values:
-6.794 = (8.19)t + (1/2)(-9.8)t^2
Rearranging the equation:
-6.794 = 8.19t - 4.9t^2
Rearranging further:
4.9t^2 - 8.19t - 6.794 = 0
Solving this quadratic equation, we find two possible values for t: 0.828 seconds and 1.303 seconds. Since we are considering the time it takes to reach the ground, the valid solution is t = 0.828 seconds.
Therefore, when the rock is thrown straight down, it takes approximately 0.828 seconds to reach the ground.
For more question motion
brainly.com/question/22021412
#SPJ11
Is it possible to use dimensional physical quantities in a way that results in a dimensionless physical quantity? Explain. ii. The eciency, (epsilon) of a heat engine is given by, = 1 − Qout Qin , where, Qin and Qout respectively are the heat given to the engine and the heat exhausted from the engine. a) Establish the dimensions of
Answers
Yes, it is possible to use dimensional physical quantities in a way that results in a dimensionless physical quantity. The process of combining physical quantities to obtain a dimensionless quantity is known as dimensional analysis, and it is widely used in the sciences to help simplify complex systems and equations.
The process of using the dimensions of physical quantities to determine the relationship between them is known as dimensional analysis. In other words, it's a mathematical technique that uses the dimensions of a physical quantity to determine how it relates to other physical quantities.Dimensions of the Efficiency of Heat EngineIn the case of the efficiency of a heat engine, the dimension of heat is [M L² T⁻²] and the dimensions of efficiency is dimensionless,
so it is given as:1 - [Qout/Qin]Therefore, the dimensional formula of efficiency will be: [M L² T⁻²] - [M L² T⁻²] / [M L² T⁻²] = [no dimension] Yes, it is possible to use dimensional physical quantities in a way that results in a dimensionless physical quantity. The process of combining physical quantities to obtain a dimensionless quantity is known as dimensional analysis, and it is widely used in the sciences to help simplify complex systems and equations.The efficiency of a heat engine is given by, = 1 − Qout/Qin, where Qin and Qout respectively are the heat given to the engine and the heat exhausted from the engine.a) Establish the dimensions of the efficiency of a heat engine.The dimension of heat is [M L² T⁻²] and the dimensions of efficiency is dimensionless, so it is given as:1 - [Qout/Qin]Therefore, the dimensional formula of efficiency will be: [M L² T⁻²] - [M L² T⁻²] / [M L² T⁻²] = [no dimension]Explanation:The dimensional analysis is used to simplify complex equations in science. In the case of heat engines, the efficiency is given by the ratio of the heat given to the engine (Qin) to the heat exhausted from the engine (Qout).
To know more about that dimensional visit:
https://brainly.com/question/14481294
#SPJ11
to examine a particular blood sample in biology lab, a student uses a compound microscope set to have a magnification of -4515. the objective and eyepiece are both attached to a tube which is 16 cm in length and the eyepiece has a focal length of 2.6 cm. the near point of the person using the microscope is 25.5 and you can assume she can view the image produced with a fully relaxed eye. 1)what is the focal length of the objective? f
Answers
The objective's focal length is roughly -15.31 cm. The converging lens objective is indicated by the negative sign.
The formula for compound microscope magnification can be used to get the focal length of the objective:
M = -(f₀ / fₑ)× (1 + d / f₀)
Where:
M = Magnification of the compound microscope = -4515 (negative sign indicates an inverted image)
f₀ = Focal length of the objective
fₑ = Focal length of the eyepiece = 2.6 cm
d = Distance between the objective and eyepiece = 16 cm
f₀ = -(M * fₑ) / (M + (d / fₑ))
Putting all the given values:
M = -4515
fₑ = 2.6 cm
d = 16 cm
f₀ = -((-4515) × 2.6) / (-4515 + (16 / 2.6))
f₀ ≈ -15.31 cm
Therefore, the objective's focal length would be roughly -15.31 cm and the converging lens objective will be indicated by the negative sign.
To know more about focal length
https://brainly.com/question/28197952
#SPJ4
what is anti-matter made of
Answers
HERE'S YOUR ANSWER
Explanation:
Antimatter is a material composed of so-called antiparticles. It is believed that every particle we know of has an antimatter companion that is virtually identical to itself, but with the opposite charge. For example, an electron has a negative charge.
A man stands in front of a vertical plane mirror which is fixed on a
wall as shown in the diagram below. The image formed by the
mirror is also shown.
The man looks at the image of his feet.
a. Complete the ray diagram to show how the man is able to see the
image of his feet in the mirror.
b. What is the purpose of the normal line in the diagram?
c. State which angle does x represent.
d. What's the type and direction of the image formed by the mirror?
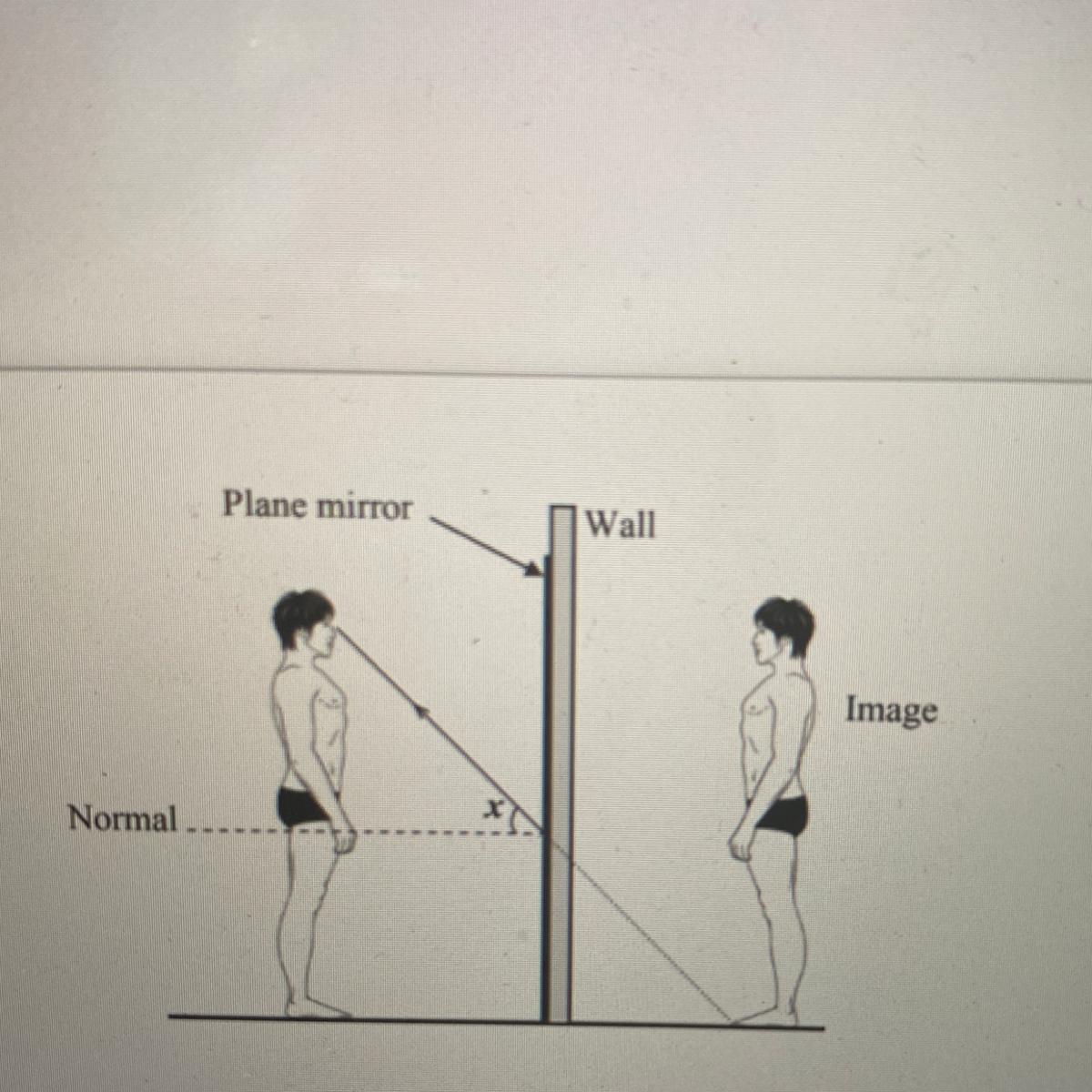
Answers
Answer:
a) ray horizontal and ray leaves his feet
b) The normal line respect to which the angles are measured,
c) The angle x is the reflected angle
d) virtual image, right image
Explanation:
a) To complete the rays, you must draw a horizontal ray at the height of the man's head, this ray touches the mirror perpendicularly, therefore it bounces in the same direction.
The other ray leaves his feet and touches the mirror at one point, it is reflected with the same angle, by the law of reflection and reaches the eyes of man, the brain creates an extension of this ray and at the point of the floor creates the image point.
b) The normal line is a line perpendicular to the surface with respect to which the angles are measured,
c) The angle x is the reflected angle, which is equal to the incident angle according to the law of reflection
d) The image is formed by the prolongation of the rays of light, therefore it is a virtual image and as it has the same direction of the man it is a right image
A 2.3-kg toy locomotive is pulling a 1.4-kg caboose. The frictional force of the track on the caboose is 0.46 N backward along the track. If the train is accelerating forward is 3.1 m/s2, what is the magnitude of the force exerted by the locomotive on the caboose
Answers
The net vertical force on the caboose (C) is
∑ F[v, C] = F[n, C] - (1.4 kg) g = 0
where F[n, C] is the magnitude of the normal force exerted by the track on the caboose; so we have
F[n, C] = (2.3 kg) g = 13.72 N
which means the coefficient of kinetic friction µ between the caboose and the track is
F[f, C] = 0.46 N = µ (13.72 N) ⇒ µ = (0.46 N) / (13.72 N) ≈ 0.034
and presumably the coefficient is the same for the locomotive.
The net vertical force on the locomotive (L) is
∑ F[v, L] = F[n, L] - (2.3 kg) g = 0
where F[n, L] is the magnitude of the normal on the locomotive, so that
F[n, L] = (2.3 kg) g = 22.54 N
and so the locomotive is opposed by a frictional force with magnitude
F[f, L] = µ (22.54 N) ≈ 0.76 N
Taking the locomotive and caboose together, the net horizontal force on the system is
∑ F[h] ≈ - F[f, C] - F[f, L] + F[engine] = (2.3 kg + 1.4 kg) (3.1 m/s²)
Solve for F[engine] :
F[engine] ≈ (3.7 kg) (3.1 m/s²) + 0.46 N + 0.76 N ≈ 13 N
A student travels on a motorcycle and moves at a constant speed of 80 k/h for 15 m, determine the distance traveled in that time
Answers
Uniform line movement
Data:
V = 80km/h
T = 15m = 0.25 h
d = ?
We perform a conversion from minutes to hours.
15 m * 1 h/60 m = 0.25 h
The formula for uniform motion is:
V = d/t
We clear for distance:
d = v * t
d = 80 km/h * 0.25 h
d = 20 km
The distance traveled in that time is 20 km.
If all objects have gravity, why do you think we don’t get pulled into the other objects around us all the time?
Answers
All objects do have gravity, but the gravitational force between two objects depends on their masses and the distance between them. The force of gravity between two objects decreases rapidly as the distance between them increases.
Gravity and ObjectsIt's also worth noting that objects need to be very massive and very close together for the gravitational force to become noticeable. For example, two people standing next to each other have a very small gravitational force between them, while two planets orbiting each other have a much stronger gravitational force.
In summary, while all objects have gravity, the gravitational force between objects depends on their masses and the distance between them, and the force of gravity between us and nearby objects is usually too small to have a noticeable effect. The force of gravity between us and the Earth is what keeps us in place and gives us weight.
Learn more about Gravity and Objects
https://brainly.com/question/557206
#SPJ1
Technician A says full time 4WD also allows the driver to select 2WD or 4WD. Technician B says part-time 4WD includes a differential or viscous coupling that allows the front and rear axles to rotate at different speeds. Which technician is correct?
A) Technician A only
B) Technician B only
C) Both Technicians A and B
D) Neither Technicians A nor B
Answers
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Because full time 4WD does not allows the driver to select 2WD or 4WD. And part-time 4WD does not includes a differential or viscous coupling that allows the front and rear axles to rotate at different speeds.
8-17 sound of frequency 2000 hz falls at normal incidence on a high wall in which there is a vertical gap,18 in.wide.a man is walking parallel to the wall at a distance of 50 ft from it on the far side.over what range of distance would he hear an intensity of sound more than 50% of the maximum value? more than 5%?
Answers
The man will hear an intensity of sound more than 50% of the maximum value over a range of distances greater than 5.5 ft from gap in the wall, and he will hear an intensity of sound more than 5% of maximum value over a range of distances greater than 1.9 ft from gap in the wall.
Assuming that sound of frequency 2000 Hz is emitted isotropically from a point source:
\(CI = P/(4\pi r^2)\)
The total distance traveled by the sound wave is:
\(D = (50 + x) + 1.5\)
Using the formula for the intensity of a sound wave:
\(I/I_{max} = [(50 + x) + 1.5]^2 / (50 + x)^2\)
For\(I/I_{max} > 0.05\), we have:
\([(50 + x) + 1.5]^2 / (50 + x)^2 > 0.5\)
\(x > 5.5 ft \ or \ x < -56.5 ft\)
Since x must be positive, the range of values of x for which\(I/I_{max} > 0.05\) :
\(x > 5.5 ft\)
\([(50 + x) + 1.5]^2 / (50 + x)^2 > 0.05\)
Solving for x, we get:
\(x > 1.9 ft \ or \ x < -52.9 ft\)
The range of values of x for which\(I/I_{max} > 0.05\) is:
\(x > 1.9 ft\)
To know more about sound wave, here
brainly.com/question/21995826
#SPJ4
What is the temperature profile for an atmosphere with uniform lapse rate γ,[ where γ≡−dT/dz] ? Find the corresponding pressure p(z) and density rho(z) profiles. Assume the atmosphere is an ideal gas in hydrostatic balance, with sea level temperature and pressure given by T
0
and p
0
, respectively.
Answers
The density profile is given by:
ρ(z) = p0 / (RT) - γz / (T)
These profiles provide the temperature, pressure, and density variation with height in an atmosphere with a uniform lapse rate γ, assuming hydrostatic balance and an ideal gas.
To find the temperature profile, pressure profile, and density profile for an atmosphere with a uniform lapse rate γ, we can use the ideal gas law and the hydrostatic balance equation. Let's derive these profiles step by step:
1. Temperature Profile:
Starting with the definition of lapse rate, γ ≡ -dT/dz, we have the following differential equation:
dT = -γ dz
Integrating both sides, we get:
∫dT = -γ ∫dz
T = -γz + C
Where C is the constant of integration. Since we have sea level temperature T0, we can substitute z = 0 and T = T0 into the equation:
T0 = C
Therefore, the temperature profile is given by:
T(z) = T0 - γz
2. Pressure Profile:
We can use the hydrostatic balance equation to derive the pressure profile. The equation states:
dp = -ρg dz
Where dp is the change in pressure, ρ is the density, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and dz is the change in height.
Let's assume the pressure at sea level is p0. Integrating both sides of the equation from p0 to p, and integrating from 0 to z for the height, we get:
∫dp = -∫ρg dz
p - p0 = -∫ρg dz
Since the density ρ is related to pressure by the ideal gas law, ρ = p / (RT), where R is the specific gas constant and T is the temperature, we can substitute this into the equation:
p - p0 = -∫(p / (RT)) g dz
p - p0 = -pg / RT ∫dz
p - p0 = -pgz / RT + C'
Where C' is the constant of integration. Substituting z = 0 and p = p0 into the equation:
p0 - p0 = C'
Therefore, the pressure profile is given by:
p(z) = p0 - pgz / RT
3. Density Profile:
We can use the ideal gas law to derive the density profile. The ideal gas law states:
p = ρRT
Rearranging the equation, we have:
ρ = p / (RT)
Substituting the expression for pressure from the pressure profile equation, we get:
ρ(z) = (p0 - pgz / RT) / (RT)
Simplifying further:
ρ(z) = p0 / (RT) - pgz / (RT^2)
So, the density profile is given by:
ρ(z) = p0 / (RT) - γz / (T)
These profiles provide the temperature, pressure, and density variation with height in an atmosphere with a uniform lapse rate γ, assuming hydrostatic balance and an ideal gas.
to learn more about density.
https://brainly.com/question/29775886
#SPJ11
The corresponding pressure p(z) and density rho(z) profiles as per the information given in question is p = e^(-(g/R)ln(T) + C) and ρ(z) = p0((T0 - γz)^(-g/R))/(R(T0 - γz)) respectively.
The temperature profile for an atmosphere with a uniform lapse rate γ is given by T(z) = T0 - γz, where T(z) is the temperature at altitude z, T0 is the temperature at sea level, and γ is the lapse rate defined as the negative derivative of temperature with respect to altitude, γ = -dT/dz.
To find the corresponding pressure profile p(z), we can use the hydrostatic balance equation, which states that the rate of change of pressure with altitude is equal to the product of the density of the gas, the acceleration due to gravity, and the negative derivative of temperature with respect to altitude.
Mathematically, this can be expressed as dp/dz = -ρg, where dp/dz is the rate of change of pressure with altitude, ρ is the density of the gas, and g is the acceleration due to gravity.
Since we have assumed the atmosphere to be an ideal gas, we can use the ideal gas law, which states that the pressure is directly proportional to the product of the density and the temperature.
Mathematically, this can be expressed as p = ρRT, where p is the pressure, ρ is the density, R is the specific gas constant for the gas, and T is the temperature.
Substituting this into the hydrostatic balance equation, we get dp/dz = -(p/R)(g/T)(dT/dz).
To solve this differential equation, we can separate the variables and integrate both sides.
∫dp/p = -∫(g/R)(dT/T)
ln(p) = -(g/R)ln(T) + C
where C is the constant of integration.
Exponentiating both sides, we get p = e^(-(g/R)ln(T) + C)
Using the properties of logarithms, we can simplify this expression as p = e^C(T^(-g/R))
Since T = T0 - γz, we can further simplify the expression as p = e^C((T0 - γz)^(-g/R))
To find the constant of integration C, we can use the sea level temperature and pressure given by T0 and p0, respectively.
At sea level, z = 0, and thus we have p0 = e^C(T0^(-g/R))
Simplifying, we get C = ln(p0/(T0^(-g/R)))
Substituting this value of C back into the expression for p, we get p(z) = p0((T0 - γz)^(-g/R))
Finally, to find the density profile ρ(z), we can use the ideal gas law.
ρ(z) = p(z)/(RT(z))
Substituting the expressions for p(z) and T(z), we get ρ(z) = p0((T0 - γz)^(-g/R))/(R(T0 - γz))
This gives us the density profile ρ(z) for an atmosphere with a uniform lapse rate γ.
Learn more about pressure from the link:
https://brainly.com/question/28012687
#SPJ11
1. An airplane flies with a constant speed of 720 km/h. How long will it take to travel a distance of 1500
kilometers?
Answers
Answer:
\(125\:\mathrm{minutes\: or\: }2.08\bar{3}\: \mathrm{hours}\)
Explanation:
Speed is given by \(s=\frac{d}{t}\), where \(d\) is distance travelled and \(t\) is time. Rearranging this equation, we have \(t=\frac{d}{s}\).
Plugging in our given information:
\(t=\frac{d}{s}=\frac{1500\:\mathrm{km}}{720\:\mathrm{km/h}}=2.08\bar{3}\: \mathrm{hours}\)
Thus, our answer is:
\(2.08\bar{3}\: \mathrm{hours}\cdot \frac{60\:\mathrm{minutes}}{1\:\mathrm{hour}}=\fbox{$125\:\mathrm{minutes}$}\)
can someone help me plz

Answers
Answer:
Positive I believe... because if you drop it it is negative so picking up a book means positive. thanks for the points though!
Explanation:
Can I have brainliest please? <3
A wave has a wavelength of 4.9 m and a velocity of 9.8 m/s. The medium through which this wave is traveling is then heated so that the velocity is doubled. If the frequency remains constant, what is the wavelength of the heated wave? 2.5 m 9.8 m 14.7 m 19.6 m
Answers
Answer:
the wavelength is 9.8 meters
Explanation:
We can use the relationship:
Velocity = wavelenght*frequency.
Initially we have:
wavelenght = 4.9m
velocity = 9.8m/s
then:
9.8m/s = 4.9m*f
f = 9.8m/s/4.9m = 2*1/s
now, if the velocity is doubled and the frequency remains the same, we have:
2*9.8m/s = wavelenght*2*1/s
wavelenght = (2*9.8m/s)*(1/2)s = 9.8 m
Answer:
9.8
Explanation: