What is the [OH−] in 0.20 M oxalic acid, (COOH)2, solution?
a. 4.1 × 10−10 M
b. 7.4 × 10−11 M
c. 1.2 × 10−13 M
d. 3.2 × 10−12 M
e. 3.8 × 10−12 M
Answers
To find the [OH⁻] in a 0.20 M oxalic acid (COOH)₂ solution, we need to first determine the dissociation constant (Ka) of oxalic acid and calculate the [H⁺] concentration using the given molarity. Then, we can use the ion product constant of water (Kw) to find the [OH⁻] concentration.This value is closest to option (c), so the answer is c. 1.2 × 10⁻¹³ M
Oxalic acid is a weak diprotic acid with two dissociation steps. However, the first dissociation step contributes significantly more [H⁺] ions than the second step. Thus, we can focus on the first dissociation: (COOH)₂ → H⁺ + (COOH)⁻
The Ka for the first dissociation of oxalic acid is approximately 6.5 × 10⁻⁴. Using the given 0.20 M concentration, we can set up an equilibrium expression to solve for [H⁺]:
Ka = [H⁺][(COOH)⁻] / [(COOH)₂]
Assuming x is the concentration of [H⁺] and [COOH⁻], we get: 6.5 × 10⁻⁴ = x² / (0.20 - x)
Since x is small, we can approximate 0.20 - x ≈ 0.20, which gives: x ≈ √(6.5 × 10⁻⁴ × 0.20) ≈ 0.0113 M
Now that we have the [H⁺] concentration, we can use the ion product constant of water, Kw = 1.0 × 10⁻¹⁴, to find the [OH⁻] concentration: Kw = [H⁺][OH⁻] = 1.0 × 10⁻¹⁴ = (0.0113)([OH⁻])
[OH⁻] ≈ 8.85 × 10⁻¹³ M
To know more about oxalic acid
https://brainly.com/question/30635999
#SPJ11
Related Questions
Which BEST describes the role of mitochondiſa in maintaining homeostasis for the cell?
A Mitochondria control what crosses into and out of the cell.
B. Mitochondría manufacture and deliver proteins for the cell.
С.
Mitochondria aid in the movement of organelles around the cell.
D.
Mitochondria produce most of the energy that is used by the cell.
Answers
Answer: D
Explanation:
The mitochondria is the power house of the cell, remember power as energy
Which one is correct?

Answers
Answer:
The answer is a
Explanation:
the chemist added one of the four substances to one of the liquids and observed whether the substance floated or sank. by repeating this procedure with the other substances and liquids, she made a series of observations about the relative densities of the substances and the liquids. use the following selected observations to arrange the four unknown substances in order of increasing density. a. substance a sank in chloroform. b. substance b floated in water, but sank in toluene. c. substance c sank in water, but floated in chloroform and nitromethane. d. substance d sank in nitromethane, but did not sink as rapidly as substance a did in nitromethane.
Answers
Based on the observations provided, the order of increasing density for the four unknown substances is:
b < c < d < a
b. substance b floated in water, but sank in toluene.
c. substance c sank in water, but floated in chloroform and nitromethane.
d. substance d sank in nitromethane, but did not sink as rapidly as substance a did in nitromethane.
substance a sank in chloroform
Explanation of the chemical substances.Density is a physical property of matter that describes the amount of mass per unit volume of a substance. It is a measure of how tightly packed the particles in a substance are. The formula for density is:
Density = Mass / Volume
Substance b floated in water, but sank in toluene. This means that substance b is less dense than water but more dense than toluene.
Substance c sank in water, but floated in chloroform and nitromethane. This means that substance c is less dense than water but more dense than chloroform and nitromethane.
Substance d sank in nitromethane, but did not sink as rapidly as substance a did in nitromethane. This means that substance d is more dense than nitromethane, but less dense than substance a.
Substance a sank in chloroform. Since none of the other substances sank in chloroform, this means that substance a is the most dense of the four unknown substances.
Therefore, the more dense substances sank down compared to other with lower density.
Learn more about chemical substances below.
https://brainly.com/question/29108029
#SPJ1
A compound contains 79.3% tungsten (W) and 20.7 % oxygen. What is the empirical formula?
Answers
Answer:
To find the empirical formula of a compound, we need to determine the simplest whole number ratio of the atoms present in the compound. Let's assume we have 100 g of this compound. Then we have 79.3 g of tungsten and 20.7 g of oxygen. We can convert these masses to moles by dividing by their respective atomic masses: Number of moles of W = 79.3 g / 183.84 g/mol = 0.431 mol Number of moles of O = 20.7 g / 16.00 g/mol = 1.294 mol To get the simplest whole number ratio of the atoms, we need to divide both of these values by the smallest value, which is 0.431 mol: 0.431 mol W / 0.431 mol = 1 1.
Pilots of hot air balloons are able to steer them somewhat by moving them up or down to enter different air currents that move in different directions. Explain how the flame can be used to do that.
Answers
Answer:
To understand this first we must understand what is happening at the molecular level. When we heat any substance it changes its state of matter because its molecules get excited. For example, when we heat water it turns into gas so the molecules get excited. The hot air balloon will move faster if we add heat because the gas molecules will get excited and push against the balloon, making it faster. If we start removing heat, the balloon's acceleration will slow down because the molecules will get less excited.
Hot air balloons flies by means of it being lighter than air
The flame can be used to move the pilot to different directions by increasing the temperature of the air in the balloon and therefore, the volume, therefore, decreasing the density of the air which changes the elevation of the balloon to the appropriate elevation having winds moving in the desired direction
The principle by which the above process works is as follows:
According to Charles law, the volume of a mass of gas is directly proportional to its Kelvin temperature
V ∝ T
\(\dfrac{V_1}{T_1} = \dfrac{V_2}{T_2}\)
\(V_2 = T_2 \times \dfrac{V_1}{T_1}\)
\(Density, \rho = \dfrac{Mass, \ m}{Volume, \ V}\)
Therefore, as the temperature is increased, the volume occupied the mass gas increases, and therefore, the density decreases
The principle on which the hot air balloon operates on is the principle that hot air is less dense than and therefore, rises above cool air
Therefore, the pilot of an hot air balloon heats up the air in the balloon to allow the balloon to rise and the pilot switches off the burner so that the air in the balloon cools and the balloon looses altitude
The mechanism of the hot air balloon does not have a steering, and therefore, the wind direction is used to steer the balloon
The direction of the wind is different at different altitude, such that by obtaining the direction of the wind at a given altitude, the pilot can raise or lower the balloon up or down to the altitude having the desired wind direction, by increasing the temperature of the air in the balloon by switching on the burner to go to a higher altitude, or by switching off the burner so the air in the balloon cools and the balloon loses some of its altitude to reach the wind going in the direction of the pilot
Learn more about hot air balloon here:
https://brainly.com/question/21890581
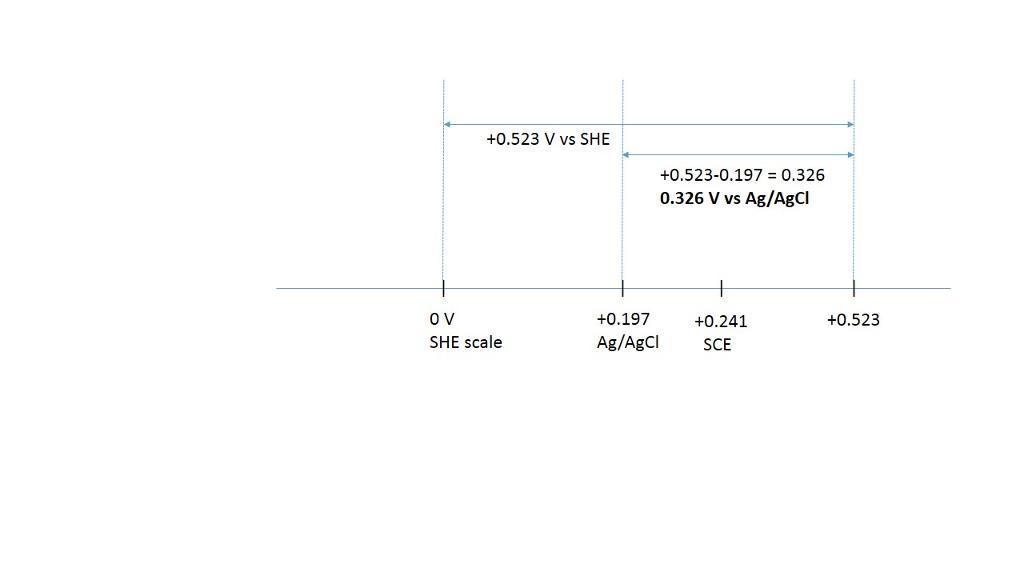
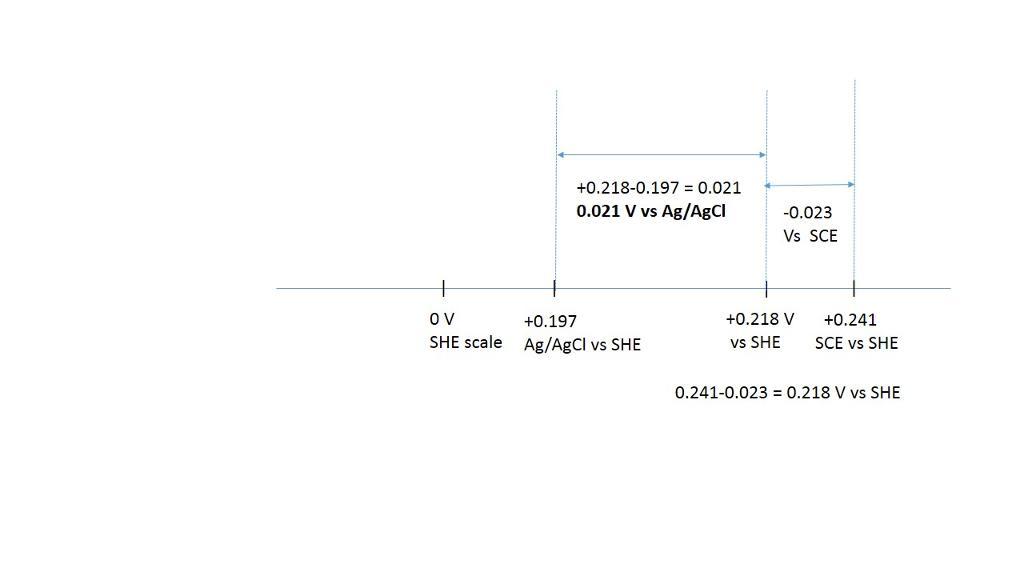
convert the following potentials. the ag | agcl and calomel reference electrodes are saturated with kcl. (a) 0.523 v versus s.h.e. ? versus ag | agcl (b) 0.111 v versus ag | agcl ? versus s.h.e. (c) 0.222 v versus s.c.e. ? versus s.h.e. (d) 0.023 v versus ag | agcl ? versus s.c.e. (e) 0.023 v versus s.c.e. ? versus ag | agcl
Answers
the ag | agcl and calomel reference electrodes are saturated with kcl.
a) +0.326 V vs Ag/AgCl for 0.523 V vs Ag/AgCl
+0.523- 0.197= 0.326
e) 0.021 V vs Ag/AgCl
+0.218-0.197= 0.0021
Calomel reference electrode is a salt electrode that is readily soluble in metals. It serves as a supplemental reference electrode to ascertain the electrode's standard potentials. Construction: The electrode is made of a glass tube with a bent side tube and another side tube, designated B.
Using a platinum wire contained in a glass tube and submerged in a layer of mercury, an external electrical contact is created. A salt bridge and the side tube come into touch electrically. The calomel electrode can act as either an anode or a cathode depending on the makeup of the other electrodes in the cell.
Learn more about Calomel reference electrode here:
https://brainly.com/question/17885489
#SPJ4
I need help with these questions

Answers
The definition of astronomic bodies are indicated below with the sentences defining them.
What are astronomic bodies?Astronomic bodies are celestial objects that occur naturally in space.
Here are their definitions below:
a. Supernova exhibits strong gravitational pull such that no light can escape
b. A nebula a large cloud of gas or dust in space.
c. A white dwarf is what a medium-mass star becomes at the end of it's life.
d. Protostar is the earliest stage of a star's life.
e. Black dwarf is a star left at the core of a planetary nebula.
f. Neutron stars are the remains of a high mass star.
g. A supernova is what occurs when a red supergiant star explodes.
Learn more about astronomic bodies at:
https://brainly.com/question/15434534
#SPJ1
the two electrodes of an electrolytic cell are placed in a sample of molten zinc iodide. after a time, reddish-brown i2(s) begins to form at one electrode while gray zn(s) deposits on the other.
Answers
In the given electrolytic cell setup having molten zinc iodide as the electrolyte, reduction of zinc ions to gray coloured zinc occurs at the cathode, whereas iodide ions get oxidized to reddish-brown iodine at the anode.
An electrolytic cell is a type of electrochemical cell that uses an external source of electrical energy to power a chemical process that would not occur otherwise. This contrasts with a galvanic cell, which serves as a power source and the cornerstone of a battery.
Any apparatus in which electrical energy is changed into chemical energy or vice versa is an electrolytic cell. Such a cell normally consists of two electrodes, which can be metallic or electronic conductors, kept apart from one another and in contact with an electrolyte, which is commonly an ionic substance that has been dissolved or fused.
In the given setup, the molten zinc iodide is the electrolyte, and the half reactions occurring at the two electrodes of the electrolytic cell are:
Half reaction at the cathode:
\(Zn^{2+} (l) + 2e^- \rightarrow Zn (s)\)
Half reaction at the anode:
\(2I^- (l) \rightarrow I_2 (s) + 2e^-\)
Learn more about Electrolytic cells here:
https://brainly.com/question/13361525
#SPJ4
Concentrated hydrochloric acid has 37.5% of HCl in mass and density of 1.2 g/cm
3
. What volume (in mL) of concentrated hydrochloric acid should be used to prepare 7 L of a 0.8 mol/L HCl(aq) concentration solution?
Answers
A 545 mL volume of concentrated hydrochloric acid should be used to prepare 7 L of a 0.8 mol/L HCl(aq) concentration solution.
How to Calculate Volume in a Chemical SolutionCalculate the number of moles of HCl required for the desired solution:
Moles of HCl = Concentration × Volume
= 0.8 mol/L × 7 L = 5.6 moles
Determine the mass of HCl required:
Mass of HCl = Moles of HCl × Molar Mass of HCl
The molar mass of HCl is approximately 36.46 g/mol.
Mass of HCl = 5.6 moles × 36.46 g/mol = 204.376 g
Calculate the mass of concentrated hydrochloric acid needed:
Concentrated hydrochloric acid has a concentration of 37.5% HCl in mass.
Mass of concentrated HCl = Mass of HCl / Percentage of HCl
Mass of concentrated HCl = 204.376 g / 0.375 = 545.003 g
Determine the volume of concentrated hydrochloric acid using its density:
Density = Mass / Volume
Volume = Mass / Density
Volume = 545.003 g / 1.2 g/cm³
As we want the volume in milliliters (mL), we need to convert cm³ to mL:
Volume = 545.003 mL / 1 cm³ = 545.003 mL
Therefore, approximately 545 mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid should be used to prepare 7 L of a 0.8 mol/L HCl(aq) concentration solution.
Learn more about chemical reaction here:
https://brainly.com/question/11231920
#SPJ1
Why is it less effective to wash an insoluble precipitate.
Answers
An insoluble precipitate is less effective to wash than a soluble precipitate. This is because insoluble precipitates are composed of particles that do not dissolve in water.
When a substance is insoluble, it cannot mix uniformly with water to form a solution.
As a result, when attempting to wash an insoluble precipitate, water can only clean the surface of the particles rather than reaching and cleansing the entire precipitate.
Consequently, the effectiveness of washing insoluble precipitates is diminished.
A precipitate refers to a solid substance that forms when two solutions are combined and a chemical reaction occurs, leading to the formation of an insoluble compound.
Precipitates can exist in two forms: soluble or insoluble, depending on the characteristics of the compound involved.
The process of washing a precipitate is important to eliminate any impurities or undesired substances that may be present.
To wash a precipitate, a wash solution is added to the mixture, which is typically a liquid capable of dissolving any soluble impurities or contaminants within the precipitate.
After the wash solution is added, the mixture is filtered to separate the precipitate, which is then dried and collected.
While soluble precipitates can be effectively washed by dissolving impurities, insoluble precipitates pose a challenge as they cannot dissolve in water, leading to limited cleansing of the precipitate particles.
To know more about Insoluble precipitate here: https://brainly.com/question/15415537
#SPJ11
Which description best characterizes the motion of particles in a solid?
slow but able to move past one another
fast and widely spaced
not moving
vibrating around fixed positions
Answers
Answer:
d
Explanation:
Answer:
D
Explanation:
IM JUST THAT DUDE
14. When weathering breaks down rocks with water, wears things away with wind, and scorches or freezes the earth
with temperature, it is called
weathering
15. In chemical weathering chemicals in the air mix with water to make
that eats
away at limestone rock Oxygen reacts with iron and forms
16. Erosion is the flow of water that moves rocks and sand, the push of the wind that carries sediments away and
even the movement of a
dropping pieces of rock at the bottoms of oceans and lakes.
Go onto brainpop.com and find the tutorial called Weathering. Login with sawgrassmid and poplearn.
and eventually
17. Weathering is the process that breaks down rocks into
18.
formation depends on sediments from weathering and those same bits make up sedimentary
rocks.

Answers
Answer:
14. Mechanical Weathering
15. & 16. I'm not sure
17. Smaller Pieces, Minerals I think
18. I can't remember
Explanation:
I'm not 100% sure about these but I hope they help. Sorry I couldn't do any more.
draw the higher energy chair conformation of cis-1,3-dimethylcyclohexane.
Answers
Here is the higher energy chair conformation of cis-1,3-dimethylcyclohexane:
CH3 H
| |
H--C--C--C--C--C--C--C--H
| |
CH3 H
In this conformation, the two methyl groups are in an axial position, which is less stable than the equatorial position. The hydrogen atoms on the same side of the ring as the methyl groups are also in axial positions, which contributes to the higher energy of this chair conformation.
A higher energy chair conformation is a specific arrangement of substituents on a cyclohexane ring that is less stable than the lowest energy or most stable chair conformation. In the higher energy chair conformation, one or more substituents are located in axial positions rather than equatorial positions, leading to destabilizing interactions with other groups or atoms in the molecule. This can result in an increase in potential energy, making the conformation less stable and more reactive than the most stable chair conformation.
To know more about higher energy chair conformation, please click on:
https://brainly.com/question/31727032
#SPJ11
In each sentence, choose the number that represents the correct answer. A. Under certain conditions, 6 units of hydrogen will burn in 1 second. This process releases energy at a rate of 286/572/1,716 kJ per second. B. Under the same conditions, 1 unit of ethanol will burn in 1 second. This process releases energy at a rate of 686 /1,371/8,226 kJ per second. C. Under these conditions, hydrogen / ethanol will release more energy in 1 second.
Answers
C. Under these conditions, hydrogen / ethanol will release more energy in 1 second is the correct answer.
The energy change that occurs when one mole of a compound is burnt in excess oxygen under standard conditions is called the standard enthalpy change of combustion. The standard enthalpy change of combustion of hydrogen is -286kJ/moL.Ethanol combustion is an exothermic process. The chemical reaction that occurs when ethanol burns releases a lot of heat and energy, 277.7 kJ per mole of ethanol, in addition to the creation of new compounds. In conclusion, ethanol burns by combining with oxygen to create carbon dioxide, water, and heat.The standard enthalpy change of combustion is the energy change that happens when one mole of a compound burns in excess oxygen under typical conditions. Enthalpy change for hydrogen combustion is typically -286kJ/moL.To know more about Hydrogen check the below link:
https://brainly.com/question/2079874
#SPJ1
I need help with chemistry (Wrong answer or answer just to take points and Nonsense will be reported)

Answers
Answer:28.411
Explanation: f1 m1+ f2 m2+ f3 m3
0.6628(28)+0.2634(29)+0.0738(30)=28.411
remember that for percentages you divide the number by 100 to get the decimal form.
The average atomic mass of the element given in the question above is 28.411 amu
How do I determine the average atomic mass?The average atomic mass of an element existing in various isotopic form can be obtained by using the following formula:
Average atomic mass = [(Mass of A × A%) / 100] + [(Mass of B × B%) / 100] + [(Mass of C × C%) / 100]
Where
A, B and C are the various isotopesA%, B% and C% are the abundance of each isotopesWith the above formula, we can obtain the average atomic mass as follow:
Mass of A = 28Abundance of A (A%) = 66.28%Mass of B = 29Abundance of B (B%) = 26.34%Mass of C = 30Abundance of C (C%) = 7.38%Average atomic mass =?Average atomic mass = [(Mass of A × A%) / 100] + [(Mass of B × B%) / 100] + [(Mass of C × C%) / 100]
Average atomic mass = [(28 × 66.28) / 100] + [(29 × 26.34) / 100] + [(30 × 7.38) / 100]
Average atomic mass = 18.5584 + 7.6386 + 2.214
Average atomic mass = 28.411 amu
Learn more about average atomic mass:
https://brainly.com/question/24185848
#SPJ1
Automobile airbags inflate due to the formation of nitrogen gas from the chemical reaction 2NaN3(s)—> 3N2(g)+2Na(s) Identify the number of each atom in the reactants and products for this balance reaction.
Answers
Number of atoms in reactants 2NaN3
Na - 2
N - 6
The 2 applies to the whole compound, multiple 2 by 3 for the nitrogen
Number of atoms in products 3N2 + 2Na
Na - 2
N - 6
What effect does the Earth's surface have on solar radiation?
Answers
Answer:
Thus, the proportion of Earth's surface that is covered by ice and snow affects how much of the Sun's solar radiation is absorbed, warming the planet, or reflected. Therefore, snow and ice which are covered in soot from pollution no longer reflect sunlight, but absorb it and so melting increases.
Answer:
Half of the solar radiation is absorbed and converted to infrared (heat).
Explanation:
PCI3 (g) + Cl2 (g) -> PCI5 (g)
An equilibrium mixture at 450 K contains contains 0.224 atm of PCIs, 0.284 atm of Cl. What is the pressure, in atm, of PCI3 knowing the Kp is 66.7 at this temperature.
Answers
The pressure of PCI₃ in the equilibrium mixture is approximately 0.000954 atm.
Understanding Pressure in a Chemical ReactionTo solve this problem, we can use the ideal gas law and the relationship between partial pressures and equilibrium constant (Kp) to find the pressure of PCI₃.
Given the balanced equation for the given reaction is:
PCI₃ (g) + Cl₂ (g) -> PCI₅ (g)
Let
P₁ = P(PCI₃) = equilibrium partial pressure of PCI₃
Given:
P(PCI₅) = 0.224 atm
P(Cl₂) = 0.284 atm,
Kp = equilibrium constant
Kp = [P(PCI₅) * P(Cl₂)) / (P(PCI₃)]
Substituting the given values:
66.7 = (0.224 atm * 0.284 atm) / P₁
Now we can solve for P₁:
P₁ = (0.224 atm * 0.284 atm) / 66.7
P₁ = 0.000954 atm
Learn more about pressure here:
https://brainly.com/question/30235826
#SPJ1
Naturally occurring rubidium consists of just two isotopes. One of the isotopes consists of atoms having a mass of 84.912 amu; the other of 86.901 amu. What is the percent natural abundance of the heavier isotope
Answers
Answer:
The percent natural abundance is 27.95% for the heavier isotope (86.901 amu)
Explanation:
The atomic mass of Rubidium (Rb) is 85.468.
To find the percent natural abundance, first we need to use the following equation:
84.912x + 86.901(1-x) = 85.468
x represents the percent natural abundance, in basic decimal form
In order to find x, we will use the distributive property, combine like terms and then move the constant to the other side to get x.
We are first finding the percent natural abundance of the first isotope to make this easier for us.
84.912x + 86.901(1-x) = 85.468
-> 84.912x + 86.901- 86.901x = 85.468
-> 86.901 - 1.989x = 85.458 (like terms were combined)
-> Subtract both sides by 86.901
-> Divide both sides by-1.989x
x = 0.720462544
Now turn this into a percent by multiplying by 100.
--> 72.05% for the first isotope (the one that contains 84.912 amu)
To find the natural abundance of the other isotope (the denser, heavier isotope), you could just subtract 72.05 from 100 to save time, but the usually desired way (the way that your teacher would probably want you to do) is down below:
We plug this decimal for the x-value into the parentheses from earlier:
(1 -x) ---> ( 1 - 0.720462544 ) = 0.279537456
Now we just need to convert this to a percent by multiplying by 100
0.279537456 * 100 = 27.95% of the heavier isotope (86.901 amu)
Who's the first person to reach the moon
Answers
Answer: Neil Armstrong
Explanation
On July 20, 1969, Neil Armstrong became the first human to step on the moon. He and Aldrin walked around for three hours. They did experiments. They picked up bits of moon dirt and rocksExplanation:
Answer:
In 1969, Neil Armstrong was the first person to reach the moon.
Explanation:
which statement concerning solutions is false? multiple choice solutions are homogeneous mixtures. solutes can be ionic or covalent. colloidal suspensions are solutions. solutions can have the solid, liquid, or gas state. solutions consist of solutes and solvents.
Answers
According to the given information Colloidal suspensions are solutions statement concerning solutions is false.
What are examples of colloidal suspensions?Milk, paint, and smoke are excellent illustrations of colloidal suspensions. As an illustration of a liquid colloidal in a liquid, the milk of cows, goat, and other creatures is a suspensions of granules in liquid water. Suspensions are nevertheless regarded as heterogeneous because, in the absence of vigorous mixing, the various components of the mixture won't stay uniformly dispersed.
What two varieties of colloidal suspension are there?Aerosols, that are dispersions comprising solids or liquids in a gas, and emulsified, which have been aerosols of one liquid in an another fluid in which it is immiscible, are two more significant types of colloids. The scattered particles in an emulsion are heterogeneous mixtures that are in size somewhere between that of a solution and.
To know more about Colloidal suspension visit:
https://brainly.com/question/29375084
#SPJ4
Which element is the most
reactive element in group one of the periodic
table
Answers
Answer:
Li
Explanation:
According to periodic table, lithium will be the most reactive element because reactivity decreases down the group
What was removed from the glucose molecules when they bonded to form maltose
Answers
Answer:
Two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom (water) was removed.
Explanation:
yw:))
Click oil basics and use the information to complete this passage that discusses how plastic production affects society.
the production of plastics makes life____, so it benefits society. on the other hand, the production of plastics causes land and water____, so it also harms society.
Answers
Easier and pollutuion are correct answer of this question . Click oil basics and use the information to complete this passage that discusses how plastic production affects society.
What is Pollution?
Pollution, also known as environmental pollution, is the addition of any material (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as heat, sound, or radioactivity) to the environment at a rate greater than it can be dispersed, diluted, decomposed, recycled, or stored in an innocuous form. The three basic sources of pollution—air, water, and land—are frequently categorised according to their effects on the ecosystem. Modern society is also concerned about certain types of pollution, such as plastic, light, and noise pollution. The environment, wildlife, and human health are all routinely negatively impacted by pollution of many forms.
Therefore, pollution can be defined simply as something that contaminates the environment. Pollution is the presence of dangerous compounds in the air, land, and water that can harm both living things and the environment. referring to dangerous substances that are released or brought into the environment, such as hazardous gases, liquids, or other poisonous materials. Pollutants, contaminants, or dangerous chemicals are other factors that contribute to the environment's unsuitability or safety, as are poisonous materials that contaminate the soil and the air. Pollution is another unavoidable side consequence of actions that disturb the ecosystem's biodiversity. Additionally, it jeopardises the environment's ability to endure.
Learn more about Pollution from given link
https://brainly.com/question/24704410
#SPJ4
Isopropanol is a solvent that is liquid at room temperature. How would isopropanol behave when poured out of its container onto a table
Answers
It needed to be 20 characters ignore this
In a combustion chamber, ethane (c2h6) is burned at a rate of 9 kg/h with air that enters the combustion chamber at a rate of 176 kg/h. determine the percentage of excess air used during this process
Answers
The percentage of excess air used during combustion process of ethane will be 37 %.
Burning, also known as combustion, would be a high-temperature highly exothermic chemical process that occurs when an oxidant, typically atmospheric oxygen, interacts with a fuel to generate oxidized, frequently gaseous products in a mixture known as smoke.
Calculation of percentage of air .
\(C_{2} H_{6} + (1-x)+a(O_{2} +3.76N_{2} )=bCO_{2} + cH_{2} O + axO_{2} + 3.76dN_{2} .\)
Mair=Mair/Rin
\(( MN)O_{2}\) + \((MN)N_{2}\)÷ \((MN)O_{2}\) + \((MN)N_{2}\) +\((MN)C_{2} H_{6} .\)
33 . 3.25(1-x) + 28 × 13.16(1-x) ÷ 33 × 3.25(1-x) + 28 × 13.16(1-x). + 30.1
= 176/176+8
X= 0.37
0.37 × 100
X= 37%
Therefore, the percentage of excess air used during combustion process of ethane will be 37 %.
To know more about combustion process
https://brainly.com/question/13153771
#SPJ4
True or False:
It's impossible for two electrons to occupy the
same 2s orbital because it is a violation of the Pauli
Exclusion Principle.
True
False
Answers
Answer:
True. If they're talking about the first orbital around the nucleus then yes, its true. The element will be unstable and die
Explanation:
10. Calcium sulfide (CaS) is insoluble in water: Why ? would positive because the ion-dipole interactions are If CaS were to dissolve. ΔH very weak compared to the ion-ion interactions being overcome. Salts containing Ca2+ are never soluble in water. The covalent bonds in CaS would require a great deal of energy to overcome upon dissolving. If CaS were to dissolve, ΔS would be negative because the possible arrangements for the water molecules would decrease.
Answers
The insolubility of calcium sulfide (CaS) in water is due to weak ion-dipole interactions, strong ion-ion interactions, the presence of covalent bonds, and a decrease in entropy upon dissolution.
These factors prevent CaS from dissolving in water and result in its insoluble nature. Calcium sulfide (CaS) is insoluble in water due to several reasons:
1. Ion-dipole interactions: When a salt dissolves in water, the positive ions are attracted to the negative end of water molecules (oxygen atom), and the negative ions are attracted to the positive end of water molecules (hydrogen atoms). However, in the case of calcium sulfide (CaS), the ion-dipole interactions between the calcium ions (Ca2+) and water molecules are very weak. This means that the attraction between the Ca2+ ions and water molecules is not strong enough to overcome the strong attraction between the Ca2+ ions and the sulfide ions (S2-), resulting in the insolubility of CaS in water.
2. Ion-ion interactions: In the case of salts containing Ca2+ ions, they are generally insoluble in water. This is because the ion-ion interactions between the Ca2+ and sulfide ions (S2-) are very strong. The attractive forces between these ions are much stronger than the attractive forces between the ions and water molecules. As a result, the Ca2+ and sulfide ions remain together as a solid rather than dissolving in water.
3. Covalent bonds: Another reason for the insolubility of CaS in water is the presence of covalent bonds in the compound. In CaS, the calcium and sulfur atoms are bonded together by covalent bonds. Covalent bonds are formed by the sharing of electrons between atoms. Breaking these covalent bonds requires a significant amount of energy. Therefore, for CaS to dissolve in water, the energy required to break the covalent bonds would be too high, making it unlikely for the compound to dissolve.
4. ΔS (change in entropy): When a substance dissolves in water, there is often an increase in the disorder or randomness of the system, which is indicated by a positive change in entropy (ΔS). However, in the case of CaS, the possible arrangements for water molecules would decrease upon dissolution, resulting in a negative change in entropy (ΔS). This decrease in entropy further contributes to the insolubility of CaS in water.
More on calcium sulfide: https://brainly.com/question/18566803
#SPJ11
Suppose a 22.092 g sample of a 1:1 mixture of acetylferrocene and ferrocene was separated by column chromatography, and the recovered fractions weighed 9.017 g (acetylferrocene) and 8.075 g (ferrocene), what was the percent recovery of acetylferrocene?
Answers
Answer:
81.6%
Explanation:
mass of acetylferrocene and ferrocene mixture = 22.092 g
mass ratio acetylferrocene and ferrocene mixture = 1 : 1
The sum of the ratios = 2, therefore the mass of each compound will be half the mass of the mixture
mass of each compound in the sample mixture = 1/2 * 22.09 2= 11.046 g
mass of recovered acetylferrocene = 9.017 g
percentage recovery = mass recovered/mass in sample * 100%
percentage recovery of acetylferrocene = (9.017 g / 11.046 g) * 100%
percentage recovery of acetylferrocene = 81.6%
At 2500 K, Kp is equal to 20 for the reaction Cl2(g) + F2(g) ⇌ 2 CIF(g) An analysis of a reaction vessel at 2500 K reavealed the presence of 0.18 atm Cl2, 0.31 atm F2, and 0.92 atm CIF. What will tend to happen to CIF as the reaction pro- ceeds toward equilibrium?
Answers
CIF will tend to increase as the reaction proceeds toward equilibrium.
Given that Kp is equal to 20 at 2500 K, we can calculate the initial concentrations of CIF using the ideal gas law. Let's assume the initial volume is 1 liter for simplicity.
For Cl2:
P(Cl2) = 0.18 atm
n(Cl2) = P(Cl2) * V / (RT) = 0.18 mol
For F2:
P(F2) = 0.31 atm
n(F2) = P(F2) * V / (RT) = 0.31 mol
For CIF:
P(CIF) = 0.92 atm
n(CIF) = P(CIF) * V / (RT) = 0.92 mol
Based on the balanced equation, for every 1 mole of CIF, 1 mole of Cl2 and 1 mole of F2 are consumed. Therefore, the initial moles of CIF are equal to the initial moles of Cl2 and F2.
Since the initial concentrations of CIF, Cl2, and F2 are the same, and the reaction is not at equilibrium, we can conclude that CIF will tend to increase as the reaction proceeds toward equilibrium. This is because the reaction favors the formation of CIF, as indicated by the value of Kp. As CIF forms, the concentrations of Cl2 and F2 decrease, driving the reaction in the forward direction to restore equilibrium.
for more questions on CIF
https://brainly.com/question/28297792
#SPJ8