Answers
Related Questions
The initial rate of a reaction is 16 times greater as the concentration of one of the reactants is quadrupled. What is the order of this reactant?
Answers
If the initial rate of a reaction is 16 times greater as the concentration of one of the reactants is quadrupled, then the reaction is second order.
Second order reactionA second order reaction is one in which the rate law can be written as Rate = k[A]^2 where;
k = rate constant[A] = concentration of the reactantHence, when [A] is quadrupled, we will notice that the rate of reaction is increased by sixteen fold because; Rate = k[4A]^2 = 16.
Learn more about second order reaction: https://brainly.com/question/1195122
I need help with this fill in the blank question


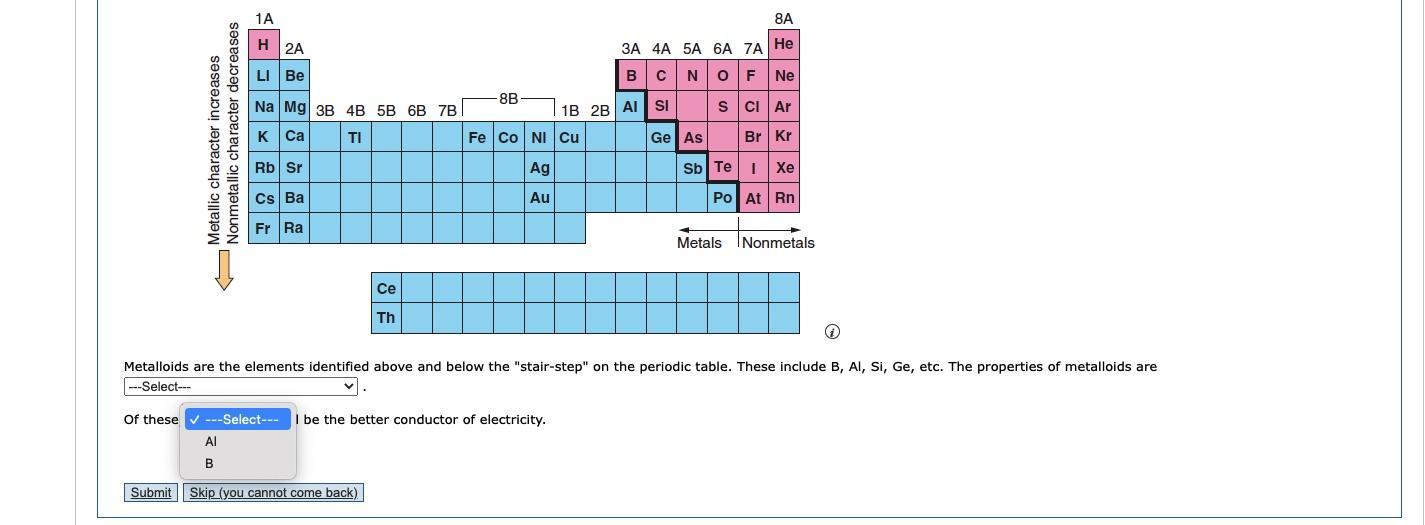
Answers
Answer: Most metalloids have some physical properties of metals and some of non-metals. So metalloids are similar to metals and non-metals.
Aluminium (Al) is a better conductor of electricity than Boron (B) which is a non-metal.
Magnesium hydroxide reacts with chlorine to form magnesium chloride,
magnesium chlorate and water. How many grams of magnesium hydroxide is
needed to yield 8.00 moles of magnesium chlorate?
77.8 g Mg(OH)2
9178.1 g Mg(OH)2
2799.6 g Mg(OH)2
.823 g Mg(OH)2
How many grams of sodium sulfato pro
Answers
The grams of magnesium hydroxide needed to yield 8.00 moles of magnesium chlorate is approximately 466.64 g. None of the options provided match the calculated value of 466.64 g.
To determine the grams of magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2) needed to yield 8.00 moles of magnesium chlorate (Mg(ClO3)2), we need to consider the balanced chemical equation for the reaction between magnesium hydroxide and chlorine.
The balanced equation is as follows:
2 Mg(OH)2 + 6 Cl2 → 2 Mg(ClO3)2 + 2 H2O
From the balanced equation, we can see that 2 moles of Mg(OH)2 react with 6 moles of Cl2 to produce 2 moles of Mg(ClO3)2.
Therefore, the stoichiometric ratio is 2 moles of Mg(OH)2 : 2 moles of Mg(ClO3)2.
To calculate the grams of Mg(OH)2 needed, we can use the stoichiometric ratio and the given moles of Mg(ClO3)2.
Given:
Moles of Mg(ClO3)2 = 8.00 moles
Using the stoichiometric ratio, we have:
8.00 moles Mg(ClO3)2 × (2 moles Mg(OH)2 / 2 moles Mg(ClO3)2) = 8.00 moles Mg(OH)2
To convert moles to grams, we need to multiply by the molar mass of Mg(OH)2.
The molar mass of Mg(OH)2 = (24.31 g/mol) + (2 * 16.00 g/mol) = 58.33 g/mol
Grams of Mg(OH)2 = 8.00 moles Mg(OH)2 × 58.33 g/mol = 466.64 g
Therefore, the grams of magnesium hydroxide needed to yield 8.00 moles of magnesium chlorate is approximately 466.64 g.
For more such questions on magnesium chlorate
https://brainly.com/question/12358640
#SPJ11
How was Bohr's atomic model different from those of previous scientists?
Answers
Answer:
Bohr placed the electrons in distinct energy levels. Rutherford described the atom as consisting of a tiny positive mass surrounded by a cloud of negative electrons. Bohr thought that electrons orbited the nucleus in quantized orbits. Also, rutherfords was just a hypothesis while Bhor took the time to make his an experiment
Which of these human activities is most likely to cause the excessive growth of phytoplankton in the world’s oceans? A.The use of chemical fertilizers that are carried by runoff into rivers B. The logging of old-growth forests, which results in erosion C. The spraying of chemical herbicides that reduce carbon dioxide in the air D. The mining of fossil fuels, which requires digging underground tunnels
Answers
The human activities which is most likely to cause the excessive growth of phytoplankton the use of chemical fertilizers that are carried by runoff into rivers.
What are phytoplankton?Phytoplanktons are the microalgae which is also known by the name microscopic marine algae, are generally found in the upper part of the water bodies.
These algaes are similar of terrestial plant. Growth of phytoplankton requires a suitable environment like sunlight and minerals. When the chemical fertilizers that we used in the soil will run off into the rivers due to any case like soil errosion, tsunami, etc.
Hence the use of chemical fertilizers that are carried by runoff into rivers.
To know more about phytoplankton, visit the below link:
https://brainly.com/question/844604
You are given 25.00 mL of an acetic acid solution of unknown concentration. You find it requires 35.75 mL of a 0.2750 M NaOH solution to exactly neutralize this sample (phenolphthalein was used as an indicator).
Required:
a. What is the molarity of the acetic acid solution?
b. What is the percentage of acetic acid in the solution?
Answers
Answer:
a. 0.393M CH₃COOH.
b. 2.360% of acetic acid in the solution
Explanation:
The reaction of acetic acid (CH₃COOH) with NaOH is:
CH₃COOH + NaOH → CH₃COO⁻ + H₂O + Na⁺
That means 1 mole of acid reacts per mole of NaOH.
Moles of NaOH to reach the equivalence point are:
35.75mL = 0.03575L × (0.2750mol / L) = 9.831x10⁻³ moles of NaOH
As 1 mole of acid reacts per mole of NaOH, moles of CH₃COOH in the acid solution are 9.831x10⁻³ moles.
a. As the volume of the acetic acid solution is 25.00mL = 0.02500L, the molarity of the solution is:
9.831x10⁻³ moles / 0.02500L =
0.393M CH₃COOHb. Molar mass of acetic acid is 60g/mol. The mass of 9.831x10⁻³ moles is:
9.831x10⁻³ moles ₓ (60g / mol) = 0.590g of CH₃COOH.
As volume of the solution is 25.00mL, the percentage of acetic acid is:
(0.590g CH₃COOH / 25.00mL) ₓ 100 =
2.360% of acetic acid in the solutionHow do the valence electrons of an atom affect chemical reactions?
Answers
Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell of an atom and are responsible for chemical reactions. In a chemical reaction, atoms gain or lose electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration, which is known as the octet rule. The number of valence electrons an atom has determines its chemical reactivity and how it will bond with other atoms. For example, atoms with only a few valence electrons, such as hydrogen, are highly reactive and will readily form chemical bonds, while atoms with many valence electrons, such as noble gases, are relatively unreactive and do not easily form chemical bonds.
What is the important conclusion of Henry Moseley's experiment? What is the importance of this conclusion in regard to periodic table ?
Answers
Henry Moseley was an English physicist who experimentally demonstrated that the major properties of an element are determined by the atomic number, not by the atomic weight, and established the relationship between atomic number and the charge of the atomic nucleus.
In 1914 Moseley published a paper in which he concluded that there were 3 unknown elements between Al and Au (there are, in fact, 4). He also concluded correctly that there were only 92 elements up to and including Uranium and 14 rare-earth elements.
You are working with a concentrated solution of ammonium hydroxide which place of safety equipment is most important to have on hand
Answers
Is lead a representative metal or transitional metal?
Answers
Answer:
It's a representative metal
Explanation: Transitional metals are metals of various chemical elements and have valence electrons—i.e., electrons that can participate in the formation of chemical bonds.
Starting with 0.3500 mol CO(g) and 0.05500 mol COCl2(g) in a 3.050 L flask at 668 K, how many moles of CI2(g) will be present at equilibrium?
CO(g) + Cl2(g)》COCl2(g)
Kc= 1.2 x 10^3 at 668 K
Answers
At equilibrium, the number of moles of \(Cl_2\) (g) will be 0.2025 mol.
1: Write the balanced chemical equation:
\(C_O\)(g) + \(Cl_2\)(g) ⟶ \(C_OCl_2\)(g)
2: Set up an ICE table to track the changes in moles of the substances involved in the reaction.
Initial:
\(C_O\)(g) = 0.3500 mol
\(Cl_2\)(g) = 0.05500 mol
\(C_OCl_2\)(g) = 0 mol
Change:
\(C_O\)(g) = -x
\(Cl_2\)(g) = -x
\(C_OCl_2\)(g) = +x
Equilibrium:
\(C_O\)(g) = 0.3500 - x mol
\(Cl_2\)(g) = 0.05500 - x mol
\(C_OCl_2\)(g) = x mol
3: Write the expression for the equilibrium constant (Kc) using the concentrations of the species involved:
Kc = [\(C_OCl_2\)(g)] / [\(C_O\)(g)] * [\(Cl_2\)(g)]
4: Substitute the given equilibrium constant (Kc) value into the expression:
1.2 x \(10^3\) = x / (0.3500 - x) * (0.05500 - x)
5: Solve the equation for x. Rearrange the equation to obtain a quadratic equation:
1.2 x \(10^3\) * (0.3500 - x) * (0.05500 - x) = x
6: Simplify and solve the quadratic equation. This can be done by multiplying out the terms, rearranging the equation to standard quadratic form, and then using the quadratic formula.
7: After solving the quadratic equation, you will find two possible values for x. However, since the number of moles cannot be negative, we discard the negative solution.
8: The positive value of x represents the number of moles of \(Cl_2\)(g) at equilibrium. Substitute the value of x into the expression for \(Cl_2\)(g):
\(Cl_2\)(g) = 0.05500 - x
9: Calculate the value of \(Cl_2\)(g) at equilibrium:
\(Cl_2\)(g) = 0.05500 - x
\(Cl_2\)(g) = 0.05500 - (positive value of x)
10: Calculate the final value of \(Cl_2\) (g) at equilibrium to get the answer.
Therefore, at equilibrium, the number of moles of \(Cl_2\) (g) will be 0.2025 mol.
For more such questions on equilibrium, click on:
https://brainly.com/question/517289
#SPJ8
1 mole of sulfur atoms has how much mass
Answers
Answer:
One atom of sulfur has a mass of 32.07 AMU; one mole of S atoms has a mass of 32.07 g.
Explanation:
Therefore, the answer should be 32.07 g
1. How are chemical bonds formed? *
Answers
Answer: Bonds form when atoms share or transfer valence electrons. Valence electrons are the electrons in the outer energy level of an atom that may be involved in chemical interactions. Valence electrons are the basis of all chemical bonds.
Explanation: Due to atoms and science ;)
Answer:
throught transferring or sharing an electron
Explanation:
a p e x :)))
A sample of nitrogen gas occupies a volume of 255 mL at 0.974 atm pressure. what volume will it occupy at 1.05 atm pressure?
Answers
The sample of nitrogen gas will occupy 236.54 mL of volume at 1.05 atm pressure.
Give a brief account on Boyle's Law.Boyle's law is the ideal law that defines the relationship between pressure and volume of gases. A law is given if the temperature is kept constant. Pressure and volume exhibit an inverse relationship.
The Boyle's Law is given as:
P₁V₁ = P₂V₂
Given,
Initial pressure (P₁) = 0.974 atm
Initial volume (V₁) = 255 mL
Final pressure (P₂) = 1.05 atm
Final volume = V₂
The final volume at 1.05 atm is calculated by substituting values in Boyle's Law as:
P₁V₁ = P₂V₂
0.974 × 255 = 1.05 V₂
V₂ = 248.37 ÷ 1.05
= 236.54 mL
To know more about Boyle's law, visit:
https://brainly.com/question/30367133
#SPJ1
Generally, systems move spontaneously in the direction of increasing entropy. TRUE FALSE
Answers
Answer:
true
Explanation:
Write and balance the equation for the neutralization reaction between phosphoric acid and
sodium hydroxide.
Answers
Answer: H3PO4(aq)+3NaOH(aq)→Na3PO4(aq)+3H2O(l)
Explanation:
please helppppp!!!
The Periodic Table is arranged by _______ properties:metals (mostly to the ____ of table,) metalloids(along the _____, and nonmetals) ( mostly to the ____ of table) . It is also arranged by chemical properties, including reactivity. Elements in the same vertical group have the same number of _____ electrons, and elements in the same horizontal period have the same number of _____ shells.
Answers
Explanation:
physicalleftmiddlerightouter mostelectron shellsExplain clearly in 2 ways each in which a soap and a detergent are similar and different.
Answers
Explanation:
the soap is the product made from a detergent
Does pb(no3)2 + Na3(PO4) = Pb3(PO4)2 + Na(NO3) have a precipitate?
Answers
Answer:
Yes, Pb3(PO4)2.
Explanation:
Hello there!
In this case, according to the given balanced chemical reaction, it is possible to use the attached solubility series, it is possible to see that NaNO3 is soluble for the Na^+ and NO3^- ions intercept but insoluble for the Pb^3+ and PO4^2- when intercepting these two. In such a way, we infer that such reaction forms a precipitate of Pb3(PO4)2, lead (II) phosphate.
Regards!

An aqueous solution of barium hydroxide is standardized by titration with a 0.170 M solution of nitric acid.
If 27.2 mL of base are required to neutralize 10.4 mL of the acid, what is the molarity of the barium hydroxide solution?
Answers
The molarity of the barium hydroxide solution is 0.065M.
How to calculate molarity?Molarity is the concentration of a substance in solution, expressed as the number moles of solute per litre of solution.
The molarity of a substance can be calculated using the following formula:
CaVa = CbVb
Where;
Ca = initial concentrationCb = final concentrationVa = initial volumeVb = final volumeAccording to this question, an aqueous solution of barium hydroxide is standardized by titration with a 0.170 M solution of nitric acid. If 27.2 mL of base are required to neutralize 10.4 mL of the acid, the molarity of the barium hydroxide solution can be calculated as follows:
0.170 × 10.4 = Cb × 27.2
1.768 = 27.2Cb
Cb = 0.065M
Therefore, 0.065M is the molarity of the barium hydroxide solution.
Learn more about molarity at: https://brainly.com/question/16727614
#SPJ1
Paulo is experimenting with H2O in its different states. He would like to present all the information he collected in one place. He thinks he should use a phase change diagram, but he isn't sure. What information could you give Paulo to encourage him to use a phase change diagram?
Answers
Paulo needs to use a phase diagram to show how much stable each of the various phases of water is.
What is the phase diagram?The phase diagram could be used to obtain the changes in a substance at different phases of matter. We know that water could exist as solid, liquid or gas. The state in which the water is a function of the pressure and the temperature of the system.
The phase diagram could be used to see the various conditions of temperature and pressure where we can trace to the liquid, solid and gaseous phases of the substance that is under study. On this phase diagram, we can also locate the triple point of water.
Given that the pressure and the temperature changes of water could be shown on a phase diagram, it then follows that Paulo needs to use a phase diagram to show the various phases of water.
Learn more about phase diagram:https://brainly.com/question/16945664?
#SPJ1
3. How many joules of heat are required to heat 20.5g of tin from 30°C to 230°C (Specific heat of tin = 0.213 J/g °C)
Answers
Which of the following could cause a change in state from a liquid to a solid?
Answers
Increases the pressure l
_____________________
Removing Energy l
How many moles of K+ & PO4^3- ions are present in 20.0 mL of a 0.015 M solution of potassium phosphate?
Answers
Answer:
9.0 × 10⁻⁴ mol of K⁺
3.0 × 10⁻⁴ mol of PO₄³⁻
Explanation:
Step 1: Calculate the moles of potassium phosphate in 20.0 mL of a 0.015 M solution
\(0.0200 L \times \frac{0.015mol}{L} = 3.0 \times 10^{-4} mol\)
Step 2: Write the balanced dissociation reaction
K₃PO₄(aq) ⇒ 3 K⁺(aq) + PO₄³⁻(aq)
Step 3: Calculate the moles of K⁺
The molar ratio of K₃PO₄ to K⁺ is 1:3. The moles of K⁺ are 3/1 × 3.0 × 10⁻⁴ mol = 9.0 × 10⁻⁴ mol
Step 4: Calculate the moles of PO₄³⁻
The molar ratio of K₃PO₄ to PO₄³⁻ is 1:1. The moles of PO₄³⁻ are 1/1 × 3.0 × 10⁻⁴ mol = 3.0 × 10⁻⁴ mol
calculate the number of zeptomoles (x 10-21 moles) of air trapped inside the container with the movable piston. use your first set of data (15 nm width) to do so
Answers
there are approximately 0.54 zeptomoles of air trapped inside the container with the movable piston.
To calculate the number of zeptomoles of air trapped inside the container with the movable piston, we first need to calculate the volume of the container.
Assuming the container is a rectangular prism with a length and height equal to the size of the graphene sheet (3 cm) and a width equal to the thickness of the spacer (15 nm), the volume of the container can be calculated as:
V = lwh = (3 cm)(3 cm)(15 nm) = 1.35 x 10^-5 cm^3
Next, we need to calculate the number of moles of air trapped inside the container. We can use the ideal gas law to do this:
PV = nRT
where P is the pressure, V is the volume, n is the number of moles, R is the ideal gas constant, and T is the temperature.
We know that the pressure inside the container is equal to atmospheric pressure, which is approximately 101325 Pa (or 1 atm). The temperature is not given, but we can assume it is room temperature, which is approximately 298 K. The ideal gas constant is 8.314 J/(mol*K).
Therefore, we can rearrange the ideal gas law to solve for n:
n = PV/RT
Substituting in the values we know:
n = (101325 Pa)(1.35 x 10^-5 cm^3)/(8.314 J/(mol*K) * 298 K)
n = 5.41 x 10^-28 mol
Finally, to convert this to zeptomoles, we multiply by 10^21:
n = 5.41 x 10^-7 zmol
Therefore, there are approximately 0.54 zeptomoles of air trapped inside the container with the movable piston.
To know more about zeptomoles, visit: brainly.com/question/13435684
#SPJ4
what volume of 0.300M would contain 1.5g
(H=1, S=32, O=16
Answers
To calculate the volume of 0.300M solution that contains 1.5g of the solute, we need to use the following formula:
moles of solute = mass of solute / molar mass of solute
moles of solute = (1.5g) / (1 x H + 1 x S + 3 x O) g/mol
moles of solute = (1.5g) / (1 + 32 + 3x16) g/mol
moles of solute = (1.5g) / 98 g/mol
moles of solute = 0.015306 moles
Now, we can use the following formula to calculate the volume of the solution:
moles of solute = molarity x volume (in liters)
0.015306 moles = 0.300 M x volume (in liters)
volume (in liters) = 0.015306 moles / 0.300 M
volume (in liters) = 0.05102 L
Finally, we can convert the volume from liters to milliliters (mL):
volume (in mL) = 0.05102 L x 1000 mL/L
volume (in mL) = 51.02 mL
Therefore, 51.02 mL of 0.300M solution would contain 1.5g of solute.
what statements best describe the work of marie and pierre curie? check all that apply
Answers
Answer:
Discovered two new radioactive elements They came up with the term radio activity.conducted experiments with uranium-containing
Explanation:
2.
Which mixture could be a useful buffer in a solution?
acetic acid (CH3CO2H) and hydrochloric acid (HCl)
sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and elemental sodium (Na)
ammonia (NH3) and ammonium chloride (NH4Cl)
acetic acid (CH3CO2H) and ammonia (NH3)
Pls answer quickly
Answers
Ammonia (\(NH_3\)) and ammonium chloride (\(NH_4Cl\)) mixture could be a useful buffer in a solution. Option C
A buffer is a solution that can resist changes in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added. It consists of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. The buffer system works by the principle of Le Chatelier's principle, where the equilibrium is shifted to counteract the changes caused by the addition of an acid or a base.
In option A, acetic acid (\(CH_3CO_2H\)) is a weak acid, but hydrochloric acid (HCl) is a strong acid. This combination does not form a buffer because HCl is completely dissociated in water and cannot provide a significant concentration of its conjugate base.
Option B consists of sodium hydroxide (NaOH), which is a strong base, and elemental sodium (Na), which is a metal. This combination does not form a buffer as there is no weak acid-base pair involved.
Option D contains acetic acid (\(CH_3CO_2H\)), a weak acid, and ammonia (\(NH_3\)), a weak base. Although they are weak acid and base, they do not form a buffer system together as they are both weak acids or bases and lack the required conjugate acid-base pair.
Option C, ammonia (\(NH_3\)), is a weak base, and ammonium chloride (\(NH_4Cl\)) is its conjugate acid. This combination can form a buffer system. When ammonia reacts with water, it forms ammonium ions (NH4+) and hydroxide ions (OH-).
The ammonium ions act as the weak acid, while the ammonia acts as the weak base. The addition of a small amount of acid will be counteracted by the ammonium ions, and the addition of a small amount of base will be counteracted by the ammonia, thus maintaining the pH of the solution relatively stable.
Therefore, option C, consisting of ammonia (\(NH_3\)) and ammonium chloride (\(NH_4Cl\)), is the suitable mixture that could be a useful buffer in a solution.
For more such question on buffer visit:
https://brainly.com/question/13076037
#SPJ8
Density is a common physical property of substances that can give insight into the structure of the substance on the atom or molecular level. You are attempting to measure the thickness of a rectangular piece of aluminum found at a crime scene, but it is too thin for your ruler. You know density has units of g/mL, and you recall mL is the same as cm?. Sooo...why not use the volume of the metal, the length and height? to find the volume by water displacement, you lower the sample into a graduated cylinder with an initial volume of water of 32.9 ml. the volume of water rises to 48.1 ml. you also mass the sample and determine it to be 20.28 g. finally, you measure the length of the solid to be 6.5 cm and the height to be 5.1 cm. from this information determine the thickness of the metal rectangular solid(mm).
Answers
The length of the solid to be 6.5 cm and the height to be 5.1 cm. the thickness of the metal rectangular solid(mm) is 4.58 mm.
given that :
height of solid = 5.1 cm
length of solid = 6.5 cm
the initial volume of graduated cylinder = 32.9 mL
the final volume of graduated cylinder = 48.1 mL
the volume of the solid = 48.1 - 32.9
= 15.2 mL = 15.2 cm³
the volume expression for the solid is given as :
volume = length × width × height
15.2 cm³ = 6.5 cm × width × 5.1
width = 15.2 / 33.15
Width = 0.458 cm = 4.58 mm
Thus, the thickness of metal = 4.58 mm
To learn more about graduated cylinder here
https://brainly.com/question/23122699
#SPJ4
Consider the following reaction:
2CH4(g)⇌C2H2(g)+3H2(g)
The reaction of CH4 is carried out at some temperature with an initial concentration of [CH4]=0.092M. At equilibrium, the concentration of H2 is 0.014 M.
Find the equilibrium constant at this temperature.
Answers
The equilibrium constant at this temperature is Kc= 4.17 x 10⁻⁶.
What is equilibrium?Since the equilibrium constant depends on the equilibrium concentration of both the reactants and the products of the chemical reaction.
Balanced reaction equation
2CH₄(g)⇌C₂H₂(g)+3H₂(g)
The initial concentration of the CH₄ = 0.093 M
The equilibrium concentration of the H = 0.017 M
Equilibrium constant = ?
Let's make the ice table
2CH₄(g) ⇌ C₂H₂(g) + 3H₂(g)
0.093 M 0 0
-2x +x +3x
0.093-2x x 0.017 M
3x = 0.017 M
Therefore, x =0.017 M /3 = 0.00567 M
Therefore, the equilibrium concentration of CH₄ =
0.093 M – 2x = 0.093 M – (2 x 0.00567 M) = 0.0817 M
Equilibrium concentration of the C₂H₄ = x = 0.00567 M
Let's write the equilibrium constant expression
Kc= [C₂H₄[H2]³/[CH₄]²
Let's put the values in the formula
Kc= [0.00567][0.017]³/[0.0817]²
Kc= 4.17 x 10⁻⁶
Therefore, the equilibrium constant is 4.17 x 10⁻⁶.
To learn more about equilibrium constant, refer to the link:
https://brainly.com/question/12971169
#SPJ9