What best describes electrons
Answers
Answer: A negatively charged particle that is found in atoms.
Related Questions
The particle, initially at rest, is acted upon only by the electric force and moves from point a to point b along the x axis, increasing its kinetic energy by 3. 20×10−19 J. In what direction and through what potential difference Vb−Va does the particle move?a. The particle moves to the left through a potential difference of Vb-Va = 0. 500 V. B. The particle moves to the left through a potential difference of Vb-Va = -0. 500 Vc. The particle moves to the right through a potential difference of Vb-Va = 0. 500 V. D. The particle moves to the right through a potential difference of Vb-Va = -0. 500 V. E. The particle moves to the left through a potential difference of Vb-Va = 5. 00 V. F. The particle moves to the right through a potential difference of Vb-Va = -5. 00 V
Answers
The particle moves to the right through a potential difference of Vb-Va = 3.20×10^-19 J / q.
The particle, initially at rest, is acted upon only by the electric force and moves from point a to point b along the x axis, increasing its kinetic energy by 3.20×10^-19 J. To determine the direction and potential difference through which the particle moves, we can use the relationship between electric potential difference (V) and electric force (F) on a charged particle.
The electric potential difference between two points is defined as the work done per unit charge to move a particle from one point to the other. The work done on a charged particle by an electric force is given by the equation
W = Fdcos(theta)
where F is the electric force, d is the distance moved by the particle, and theta is the angle between the direction of the force and the direction of the displacement.
In this case, since the particle is only acted upon by the electric force and moves along the x-axis, the angle between the direction of the force and the direction of the displacement is 0, and the work done by the electric force is given by W = Fdx.
Therefore, the potential difference between point a and point b is given by Vb - Va = W/q, where q is the charge of the particle.
Given that the particle's kinetic energy increases by 3.20×10^-19 J and the work-energy principle states that work done on a particle is equal to the change in kinetic energy, we can say that the work done on the particle is equal to 3.20×10^-19 J.
Now, the direction of the force can be determined by the sign of the potential difference, since the electric force is given by
F = -q(dV/dx).
Given that the potential difference is positive, the electric force is negative, meaning that the force is directed opposite to the direction of motion of the particle, therefore the direction of motion is to the right.
Therefore, the particle moves to the right through a potential difference of Vb-Va = 3.20×10^-19 J / q.
Learn more about potential difference at : https://brainly.com/question/12198573
#SPJ4
What is the elastic potential energy of a rubber band with a spring constant of 25.0 N/m if it is stretched by 10.0 cm from its original length?
Answers
Answer: 1,250 joules
Explanation: elastic potential energy is half of the spring constant multipied by extention squared so its 12.5 multiplied by 100 which is 1,250
tripling both the tension in a guitar string and its mass per unit length will result in changing the wave speed in the string by what factor?
Answers
There would be no change as the wave speed would be 1. Option B
What is the factor?According to the wave equation for a string, the wave speed (v) is given by the equation:
v = √(T/μ)
Tripling both the tension in a guitar string and its mass per unit length;
T₂ = 3T₁ (tripling the tension)
μ₂ = 3μ₁ (tripling the mass per unit length)
We have for the wave speed
v₂ = √(T₂/μ₂)
= √((3T₁)/(3μ₁))
= √(T₁/μ₁)
= v₁
We can see that based on the calculations that we have done in the problems. It is plane that there is no change in the wave speed.
Learn more about guitar string:https://brainly.com/question/30554638
#SPJ4

An object is thrown upward with an initial velocity of 32.1 m/s. When the object reaches it maximum height, it is true of the acceleration, a, and the velocity, v, that: Group of answer choices
Answers
Answer:
At all times the acceleration a = -9.80 m/s^2 assuming 32.1 is chosen positive
At the top the velocity will be zero because the object is turning around
a = (v2 - v1) / t = -v1 / t since the velocity at the top is zero
t = -v1 / a = -32.1 / -9/8 = 3.26 sec time to reach top
Hello~
Which of the following produces least friction?
(a) Sliding friction
(b) Rolling friction
(c) Composite friction
(d) Static friction
Answers
Answer:
Rolling friction
Explanation:
When a object rolls down the all sides of object comes contact to under surface for very low timeFor which the friction decreases .Option B is correct
Two men standing on the same side of wall and at the same distance from It, such that they are 4oom apart when one fires a gun the other hears the first report in 1.2s and the second in 0.5s after the first. calculate 1) Velocity of sound in air . 2)the perpendicular distance of the men from the wall.
Answers
Answer:
1. 571.43m/s
2. 142.9m and 342.9m
Explanation:
1.Take the difference in time.
1.2-0.7=0.7 seconds
Take the distance between them and divide with differnce in time.
400÷0.7=571.43 seconds.
2.Take the time of the two men and divide by two.
0.5÷2= 0.25 secs
1.2÷2= 0.6 secs
multiply each with the velocity.
0.25×571.43=142.9m
0.6×571.43=342.9m
Scientists have concluded that Earth is at risk of future impacts with meteoroids. What are some criteria that engineers consider when they try to design technology to detect meteoroids and prevent collisions?
Science
Answers
Explain step by step
Explanation:
Collisions with asteroids, comets and other stuff from space have been responsible for huge landmarks in our planet’s history: global shifts in climate, the creation of our moon, the reshuffling of our deepest geology, and the extinction of species.
Asteroid threats pop up in the news every now and then, but the buzz tends to fizzle away as the projectiles pass us by. Other times, as with the 2013 Chelyabinsk meteor in Russia, we don’t know they’re here until they’re here.
Perhaps most useful to remember is that when near-Earth objects (including asteroids, comets and meteoroids) enter the atmosphere, they’re called meteors; and if there’s anything left when they hit the ground, the resulting object is called a meteorite. We tend to focus on asteroids when talking about potential collisions, because they’re more likely to hit us than other stuff like comets, but still big enough to pose a threat.
By using optical and radio telescopes, the meteoroids are characterized and their shape, rotation and physical composition are determined.
Scientists have considered some criteria to detect the meteoroids and prevent collisions so that earth is protected from their impact. This includes finding the position and size of the meteoroids and so the orbit of the earth could be changed and thus there is possibility for preventing collision.
By using optical and radio telescopes, the meteoroids are characterized and their shape, rotation and physical composition are determined. With the early recognition of the meteoroid movement and their position, the evacuation of people from the particular areas of possible impact can be done.
To learn more about meteoroids, click:
https://brainly.com/question/1939309
#SPJ2
An airplane lands with an initial velocity of 70.0 m/s and then decelerates at 1.50 m/s2 for 40.0 s. What is its final velocity?
Answers
Answer:
10 m/s
Explanation:
vi = 70 m/s
a = -1.5 m/s²
t = 40 s
vf = vi + at
= 70 + (-1.5 x 40)
= 10 m/s
The final velocity will be "10 m/s".
Given:
Initial velocity,
\(v_i = 70 \ m/s\)Deceleration,
\(a = -1.50 \ m/s^2\)Time,
\(t = 40 \ s\)As we know,
→ Final velocity, \(v_f = v_i+at\)
By substituting the values, we get
\(= 70+(-1.5\times 40)\)
\(= 70+(-60)\)
\(= 70-60\)
\(= 10 \ m/s\)
Thus the above answer is appropriate.
Learn more:
https://brainly.com/question/18353887
i will give u brainliest!

Answers
Answer:
True
Explanation:
idk
Describe the energy of the skier at location W.*
At point W, potential energy is greatest and kinetic energy is least.
At point W, potential energy is least and kinetic energy is greatest.
At point W, potential energy and kinetic energy are the same.

Answers
Answer:
The description of the energy of the skier at point W is,
At point W, potential energy is greatest and kinetic energy is least
Explanation:
The given parameters are;
The highest point of the skier's path = Point W
The lowest point of the skier's path = Point X
The height of the peak after point X = Intermediate between point W and point X
The potential energy of the skier, P.E. = m·g·h
The kinetic energy of the skier, K.E. = 1/2·m·v²
The total mechanical energy of the skier, M.E. = P.E. + K.E.= Constant
Where;
m = The mass of the skier
g = The acceleration due to gravity = 9.8 m/s²
h = The height of the skier
v = The velocity of the skier
Therefore, the P.E. of the skier is highest at the highest point of the skier's path which is the point W, where h = Maximum
Similarly, the potential energy of the skier will be lowest at point X which is the lowest point on the skier's path
From P.E. + K.E. = constant, the kinetic energy will be least at point W, where the potential energy is highest.
Therefore, the description of the energy of the skier at point W is that the potential energy is greatest and kinetic energy is least.
Consider a double Atwood machine constructed as follows: A mass 4m is suspended from a string that passes over a massless pulley on frictionless bearings. The other end of this string supports a second similar pulley, over which passes a second string supporting a mass of 3m at one end and m at the other. Using two suitable generalized coordinates, set up the Lagrangian and use the Lagrange equations to find the acceleration of the mass 4m when the system is released. Explain why the top pulley rotates even though it carries equal weights on each side.
Answers
Two coils A and B are wound side by side. Coil A has 8120 turns and coil B has 11842 turns. 54% of flux produced by coil A links coil B. A current of 6 A in coil A produces 0.02 mWb, while the same current in coil B produces 0.078 mWb. a) Calculate the mutual inductance and the coupling coefficient. b) Calculate the emf induced in coil B when the current is reversed in 0.015 seconds.
Answers
a) Mutual inductance = 0.108 H; Coupling coefficient = 0.482. b) - 4.95 V.
a) Mutual inductance, M between coil A and coil B can be given as:
M = k√(L_AL_B) here, k is the coupling coefficient, L_A and L_B are the inductances of the coil A and coil B respectively. Since 54% of flux produced by coil A links coil B,
So, K = 0.54
L_A = N_A Φ/I_AL_A
= 8120 × 0.02/6
= 27.07 mH
L_B = N_B Φ/I_BL_B
= 11842 × 0.078/6
= 154.63 mH
M = k√(LALB) = 0.482 × √(27.07 × 0.15463) = 0.108 H
b) The emf induced in coil B can be given as:-
ε = M (dI_B/dt)/L_B
ε = 0.108 × (-6/0.015) / 0.15463 = -4.95 V
Thus, the emf induced in coil B when the current is reversed in 0.015 seconds is -4.95 V.
Learn more about inductances here:
https://brainly.com/question/29981117
#SPJ11
The form of energy stored in a stretched spring would be elastic kinetic energy intermolecular binding energy a mixture of elastic and mechanical transformational energy elastic potential energy The result of simultaneous application of two forces, facing away from each other on a spring, may be some shear in the spring some elongation in the spring some contraction in the spring some bending in the spring
Answers
The form of energy stored in a stretched spring is elastic potential energy. When a spring is stretched or compressed, it possesses potential energy due to the deformation of its structure.
This potential energy is called elastic potential energy because it is associated with the elasticity of the spring.
As the spring is stretched, work is done to overcome the forces within the spring that resist the change in its length. This work is converted into potential energy, which is stored in the spring. The amount of potential energy stored in the spring is directly proportional to the amount by which it is stretched or compressed.
When two forces are simultaneously applied to a spring in opposite directions, it may result in elongation or contraction of the spring, depending on the magnitude and direction of the forces. If the applied forces are strong enough to overcome the spring's elasticity, the spring will undergo deformation and exhibit elongation or contraction. This deformation is a manifestation of the stored elastic potential energy being converted into mechanical energy.
Shear, bending, and intermolecular binding energy are not directly related to the stretching of a spring.
To know more about inter molecular binding energy click this link-
https://brainly.com/question/30627196
#SPJ11
What is the biggest animal on land?
Answers
Answer:
elephant
Explanation:
Answer:
elephant
Explanation:
assuming you have a point charge in a powerful and constant electric field, what is the relationship between the electric field and the electric potential difference
Answers
Relationship between the electric field and the electric potential difference is that the potential difference is depending on the strength of the electric field and the distance over which it acts.
In the presence of a point charge in a powerful and constant electric field, there is a relationship between the electric field and the electric potential difference. The electric field is a measure of the force experienced by a charged particle placed in the field, per unit charge. It is a vector quantity, indicating both the magnitude and direction of the force. The electric potential difference, on the other hand, is a measure of the work done in moving a unit positive charge from one point to another in an electric field.
The relationship between the electric field (E) and the electric potential difference (V) can be described by the following equation:
V = E × d
Here, V represents the electric potential difference, E represents the electric field strength, and d represents the distance over which the potential difference is measured.
This equation indicates that the electric potential difference is directly proportional to the electric field strength and the distance over which the potential difference is measured. In other words, a stronger electric field will result in a larger potential difference, given the same distance. Similarly, a larger distance will result in a larger potential difference, given the same electric field strength.
Overall, the electric field and electric potential difference are related, with the potential difference depending on the strength of the electric field and the distance over which it acts.
For more such information: potential difference
https://brainly.com/question/14306881
#SPJ11
A ball was dropped and had a mass of .2 kg and was falling with a force of 2 N, what was its acceleration?
Answers
Answer:
10m/s I believe
Explanation:
F=MA
A=F/M
A=2/0.2
A=10m/s
much like a battery these generate electricity from chemical events
Answers
The term you are looking for is "chemical battery". Chemical batteries work by converting chemical energy into electrical energy through a series of chemical reactions. These reactions take place within the battery's cells, which are composed of two electrodes and an electrolyte.
When the battery is connected to a circuit, the chemical reactions produce an electrical current that can be used to power devices. Chemical batteries are widely used in many applications, including consumer electronics, electric vehicles, and renewable energy systems. They are a crucial component of our modern technological society, and ongoing research is focused on developing more efficient and sustainable battery technologies to meet growing energy demands.
To know more about electrical energy visit :-
https://brainly.com/question/16182853
#SPJ11
Question 9 of 10
April sits at rest on a skateboard. She has a mass of 55 kg. Her friend throws
her a watermelon (m= 2 kg) at a speed of 5 m/s. If she catches it, how fast
will she, the skateboard, and the watermelon move?
OA. 5 m/s
B. 0.18 m/s
C. 11 m/s
OD. 0.09 m/s
Answers
The final velocity of April, the skateboard, and the watermelon after the collision is 0.18 m/s.
What is the final velocity of the system?The final velocity of April, the skateboard, and the watermelon after the collision is calculated by applying the principle of conservation of linear momentum as shown below;
m1u1 + m2u2 = v (m1 + m2)
where;
m1 is mass of Aprilm2 is the mass of the ballu1 is the initial velocity of Aprilv is the final velocity of the system(55 x 0) + (2 x 5) = v (55 + 2)
10 = 57v
v = 10/57
v = 0.18 m/s
Learn more about linear momentum here: https://brainly.com/question/7538238
#SPJ1
Two point charges are placed at the following points on the x-axis. +2.0 C at
×=0, -3.0.C at 0.40m. Find the electric field strength at 1.20m?
Answers
The electric field strength at a distance of 1.20 m on the x-axis is -1.5 × 10⁴ N/C.
To find the electric field strength at a distance 1.20 m on the x-axis, we can use Coulomb's law:
\($$F=k\frac{q_1q_2}{r^2}$$\)
where F is the force between two charges, q1 and q2 are the magnitudes of the charges, r is the distance between the charges, and k is the Coulomb constant.For a single point charge q located at the origin of the x-axis, the electric field E at a distance r is given by:
\($$E=\frac{kq}{r^2}$$\) where k is the Coulomb constant.
So, let's calculate the electric field due to each charge separately and then add them up:
For the +2.0 C charge at x = 0, the electric field at a distance of 1.20 m is:\($$E_1=\frac{kq_1}{r^2}=\frac{(9\times10^9)(2.0)}{(1.2)^2}N/C$$\)
For the -3.0 C charge at x = 0.40 m, the electric field at a distance of 1.20 m is:
\($$E_2=\frac{kq_2}{r^2}\)
\(=\frac{(9\times10^9)(-3.0)}{(1.20-0.40)^2}N/C$$\)
The negative sign indicates that the direction of the electric field is opposite to that of the positive charge at x = 0.
To find the net electric field, we add the two electric fields\(:$$E_{net}=E_1+E_2$$\)
Substituting the values of E1 and E2:
\($$E_{net}=\frac{(9\times10^9)(2.0)}{(1.2)^2}-\frac{(9\times10^9)(3.0)}{(0.8)^2}N/C$$E\)
net comes out to be -1.5×10⁴ N/C.
Therefore, the electric field strength at a distance of 1.20 m on the x-axis is -1.5 × 10⁴ N/C.
Know more about electric field here:
https://brainly.com/question/19878202
#SPJ8
Air pressure decreases as elevation increases. Describe how the boiling point of
water on top of a mountain would be different from its boiling point at sea level.

Answers
Answer:
boiling point is directly proportional to air pressure. as the air pressure decreases due to increase in elevation, boiling point of the water on top of a mountain would be less than the boiling of water at sea level
Explanation:
if i weigh 741 n on earth and 5320 n on the surface of a nearby planet, what is the acceleration due to gravity on that planet? if i weigh 741 n on earth and 5320 n on the surface of a nearby planet, what is the acceleration due to gravity on that planet? 61.2 m/s2 70.4 m/s2 81.0 m/s2 51.4 m/s2
Answers
According to the given statement 70.4 m/s² is the acceleration due to gravity on that planet.
What is acceleration ?Acceleration is the rate of increase in a moving object's speed and direction over time. When something travels faster or slower, it is considered to be accelerating. Motion on a circle increases even while the speed remains constant because the direction is always shifting.
Briefing:W = 741 N is the weight of a person on Earth.
The formula below provides a person's weight as:
W = mg
The acceleration brought on by gravity is known as g.
m = W/m
m = 741/9.8
m = 75.61 kg
W' = 5320 N, where W' represents the weight of a person on the surface of a nearby planet.
The acceleration brought on by gravity on that planet is g'. So,
g' = W'/m
g' = 5320/75.61
g' = 70.4m/s²
To know more about Acceleration visit:
https://brainly.com/question/12550364
#SPJ4
what is physics?
in detail.....
Answers
Answer:
Physics is the study of the interactions between physical systems. The physicist attempts to describe the interaction with the most fundamental and general law or principle possible. ... All electrical phenomena involve the interaction between positive and negative charges.
Answer:
What is Physics at NTNU?
Physics is a natural science based on experiments, measurements and mathematical analysis with the purpose of finding quantitative physical laws for everything from the nanoworld of the microcosmos to the planets, solar systems and galaxies that occupy the macrocosmos.
The laws of nature can be used to predict the behaviour of the world and all kinds of machinery. Many of the everyday technological inventions that we now take for granted resulted from discoveries in physics. The basic laws in physics are universal, but physics in our time is such a vast field that many subfields are almost regarded as separate sciences.
The early Greeks established the first quantitative physical laws, such as Archimedes' descriptions of the principle of levers and the buoyancy of bodies in water. But they did not actually conduct experiments, and physics as science stagnated for many centuries. By the 17th century, however, Galileo Galilei and later Issac Newton helped pioneer the use of mathematics as a fundamental tool in physics, which led to advances in describing the motion of heavenly bodies, the laws of gravity and the three laws of motion.
The laws of electricity, magnetism and electromechanical waves were developed in the 1800s by Faraday and Maxwell, in particular, while many others contributed to our understanding of optics and thermodynamics.
Modern physics can be said to have started around the turn of the 20th century, with the discovery of X-rays (Röntgen 1895), radioactivity (Becquerel 1896), the quantum hypothesis (Planck 1900), relativity (Einstein 1905) and atomic theory (Bohr 1913).
Quantum mechanics (Heisenberg and Schrödinger), beginning in 1926, also gave scientists a better understanding of chemistry and solid state physics, which in turn has led to new materials and better electronic and optical components. Nuclear and elementary particle physics have become important fields, and particle physics is now the basis for astrophysics and cosmology.
To absorb the kinetic energy of the attached moving masses and thus provide protection at the end of a piston's travel, a pneumatic cylinder should be equipped with ____
Answers
To absorb the kinetic energy of the attached moving masses and thus provide protection at the end of a piston's travel, a pneumatic cylinder should be equipped with pneumatic valves.
For machines to operate, pneumatic systems use both potential and kinetic energy. Compressed air is used to store energy in pneumatic systems. When the potential compressed air is allowed to expand, kinetic energy (working energy/pressure) occurs. Pneumatic systems include a wide range of components that make them simple to use and very advantageous. To help consumers get the complete control they actually need, pneumatic timers, pneumatic valves, pneumatic controls, pneumatic cylinders, and pneumatic indicators are all available.
To learn more about kinetic energy:
https://brainly.com/question/1266955
#SPJ4
Use the particle model of matter to explain how a gas exerts pressure on the surfaces of its container.
Answers
The moving particles in a gas collide with each other and also with the walls of the container and as the collision increases, gases exert more pressure on the walls of the container.
What is kinetic theory of matter?Kinetic theory of matter states that “Matter is made up of those substances or particles which are constantly moving.” The energy level of the particles depends upon the temperature possessed by the matter. This helps us to determine whether that matter is in a solid, liquid, or gas state.
Thus, using the particle model of matter, we can how a gas exerts pressure on the surfaces of its container, and this occurs when the gas particles collides with one another. This collision of gas particles exert pressure on the surface of the container.
Learn more about kinetic theory here: https://brainly.com/question/8101588
#SPJ1
A resistor with a potential difference of 15.0 V develops a heat output of 327 W.
a) What is its resistance?
b) What is the current across the resistor?
Answers
Answer:
V = I * R voltage drop
P = I * V = I^2 * R power
I = P / V = 327 / 15 = 21.8 amps
b) I = 21.8 amps
a) R = P / I^2 = 327 / 21.8^2 = .69 ohms
Check:
V = I R = 21.8 * .69 = 15 Volts
Which is the hottest planet in our solar system and why?
Answers
Answer:
Venus is the hottest planet in our solar system. Its thick atmosphere is full of the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide, and it has clouds of sulfuric acid. The atmosphere traps heat, making it feel like a furnace on the surface. It's so hot on Venus, the metal lead would melt.
I HOPE IT HELPS YOU
PLEASE MARK ME BRAINLIEST :)each of the diagrams shows all the lines of complete destructive interference (dashed) and all the lines of maximum constructive interference (solid) due to two point sources. the wavelength, l, is the same in all three cases; the source separation is different. (the sources, which are not shown, lie along a horizontal line.) to help answer the question, label each nodal line and line of maximum constructive interference in the shaded region with the appropriate value of dd (in terms of l). for each case, determine the source separation (in terms of l). for any case(s) for which it is not possible to determine the source separation exactly, determine the source separation as closely as you can (e.g., by giving the smallest range into which the source separation must fall). (hint: you may find it helpful to first rank the cases by source separation.)
Answers
The main answer to the question is that the source separation and interference patterns in the given diagrams can be analyzed to determine the relationship between the source separation and the observed interference pattern.
How can we determine the source separation and interference pattern from the given diagrams?In the diagrams, the solid lines represent regions of maximum constructive interference, where the waves from the two sources reinforce each other, resulting in a higher amplitude. The dashed lines represent regions of complete destructive interference, where the waves from the two sources cancel each other out, resulting in a net amplitude of zero.
To determine the source separation, we can analyze the nodal lines and lines of maximum constructive interference in the shaded region. The nodal lines are regions of destructive interference where the wave amplitude is zero. By measuring the distance between adjacent nodal lines, we can determine the wavelength of the waves.
Next, we can measure the distance between the lines of maximum constructive interference, which will help us determine the source separation. The distance between adjacent lines of maximum constructive interference is equal to half the wavelength (l/2). By counting the number of these distances between the two sources, we can estimate the source separation.
Learn more about: source separation
brainly.com/question/31323663
#SPJ11
The value of the electric field at a distance of 28.8 m from a point charge is 68.3 N/C and is directed radially in toward the charge.
What is the charge? The Coulomb constant
is 8.98755 × 10⁹ Nm²/C².
Answer in units of C. Answer in units of
C.
Answers
To determine the charge, we can use the equation for the electric field due to a point charge:
E = k * q / r^2
Where E is the electric field, k is the Coulomb constant (8.98755 x 10^9 Nm^2/C^2), q is the charge, and r is the distance from the point charge.
We can rearrange this equation to solve for q:
q = E * r^2 / k
Plugging in the given values:
q = (68.3 N/C) * (28.8 m)^2 / (8.98755 x 10^9 Nm^2/C^2)
q = (68.3 N/C) * (826.24 m^2) / (8.98755 x 10^9 Nm^2/C^2)
q = (68.3 N/C) * (826.24 m^2/C^2)
q = (68.3 N/C) * (826.24 / 8.98755 x 10^9) C
q = (68.3 N/C) * (9.26 x 10^-9) C
q = 6.36 x 10^-7 C
The charge is approximately 6.36 x 10^-7 Coulombs.
Please help me. I have to submit this today.

Answers
Four satellites are in orbit around the Earth. The heights and the masses of
the four satellites are given in the table. For which satellite is the gravitational
pull of Earth the strongest?F= Gm1m2/r^2
A. Satellite A
B. Satellite B
C. Satellite C
D. Satellite D
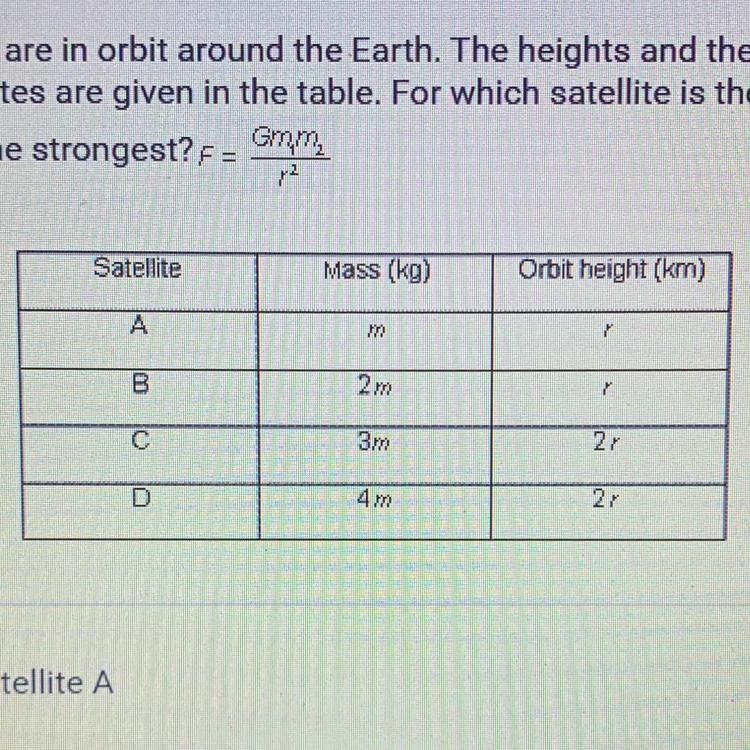
Answers
Answer:
satellite B
Explanation:
A .F= G (mM)/r²
B .F= G (2mM)/r² = 2G (Mm)r²
C .F= G (3mM)/(2r)² = ¾G (mM)/r²
D .F= G (4mM)/(2r)² = G (mM)/r²