Answers
Let car A's starting position be the origin, so that its position at time t is
A: x = (40 m/s) t
and car B has position at time t of
B: x = 100 m - (60 m/s) t
They meet when their positions are equal:
(40 m/s) t = 100 m - (60 m/s) t
(100 m/s) t = 100 m
t = (100 m) / (100 m/s) = 1 s
so the cars meet 1 second after they start moving.
They are 100 m apart when the difference in their positions is equal to 100 m:
(40 m/s) t - (100 m - (60 m/s) t) = 100 m
(subtract car B's position from car A's position because we take car A's direction to be positive)
(100 m/s) t = 200 m
t = (200 m) / (100 m/s) = 2 s
so the cars are 100 m apart after 2 seconds.
Related Questions
The reliability or reproducibility of a measurement is its _____
Answers
The degree of data stability when the measurement is replicated under identical circumstances is known as reproducibility or reliability.
What exactly are repeatability and reproducibility?Reproducibility determines how an entire study an experiment can be replicated, whereas repeatability assesses the variation in data made by a single equipment or human under similar circumstances.
What makes repeatability crucial?Science needs reproducibility because it enables more in-depth investigation, and replication validates our findings. There are several investigations and experiments, which result in a wide range of variables, unforeseen, and things that are either outside your influence or you cannot guarantee.
To knw more about measurement visit:
https://brainly.com/question/2107310
#SPJ1
1. A Ograph A Ograph B Ograph c Which graph represents what happens to the pressure in a tire as air is added to the tire, assuming the temperature is constant?

Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
It's graph A because the pressure in the tire is increasing as the amount of air going into it increases. B says the pressure drops exponentially as air goes in, and C says that the pressure stays the same as air goes in. Pressure in a tire increases proportionally to the amount of air in it.
the earth's moon has a gravitational field strength of about 1.6 n/kg near its surface. the moon has a mass of 7.35x10^22 kg. what is the radius of the moon?
Answers
Given that,
The earth's moon has a gravitational field strength of about 1.6 n/kg
Mass of Moon, \(M=7.35\times 10^{22}\ kg\)
To find,
The radius of the Moon.
Solution,
The formula for the acceleration due to gravity is given by :
\(g=\dfrac{GM}{r^2}\)
r is radius of the Moon
\(r=\sqrt{\dfrac{GM}{g}} \\\\r=\sqrt{\dfrac{6.67\times 10^{-11}\times 7.35\times 10^{22}}{1.6}} \\\\r=1750437.44\ m\\\\r=1.75\times 10^6\ m\)
So, the radius of the Moon is \(1.75\times 10^6\ m\).
Your friend asks you for a glass of water and you bring her 5 millilitersof water. Is this more or less than what she was probably expecting?Explain your reasoning
Answers
Pulley system is marked wih a Mechanical Advantage of 2.5. A worker applies 450n to the pulley in an attempt to lift a sound system with a 1500n weight. Of this task we could say that:
Answers
The worker must apply 600N of force to lift the sound system. The mechanical advantage of 2.5 means that the worker only needs to apply 600N of force to lift the sound system.
What is Pulley system?We can employ pulley systems to provide ourselves a mechanical advantage by multiplying our input effort to apply more force to a load.
They can be used to apply tension within a system, such as in a Tensioned Line or Tyrolean, in addition to their traditional uses of hauling and lifting loads. The basic operating principles of pulley systems are explained on this page; for details on how to use them for hauling, check the topic on hauling systems.
The dynamic unit of Newtons is commonly used to express force, which is an impact that has both magnitude and direction (N). On this page, kilograms have been utilized for the sake of clarity.
Therefore, The worker must apply 600N of force to lift the sound system. The mechanical advantage of 2.5 means that the worker only needs to apply 600N of force to lift the sound system.
To learn more about Pulley, refer to the link:
https://brainly.com/question/13752440
#SPJ1
what is diffrence between damping and undamping?
Answers
Answer:
Oscillation whose amplitude reduce with time are called damped oscillation. This happen because of the friction. In oscillation if its amplitude doesn't change with time then they are called Undamped oscillation
Damped and undamped vibration refer to two different types of vibrations. The main difference between damped and undamped vibration is that undamped vibration refer to vibrations where energy of the vibrating object does not get dissipated to surroundings over time, whereas damped vibration refers to vibrations where the vibrating object loses its energy to the surroundings.
A rural, forested area receives a lot of rain in a short amount of time. What
would most likely cause potential flooding in the area?
A. If the surface aquifer has a high water table
B. If the area's soil is unsaturated
C. If the ground of the area is mostly sandy soil
D. If the area has an aquifer with a low water table
Answers
Answer: A. If the surface aquifer has a high water table
Explanation:
The water table refers to the water level underground. If it is high, it means that the water underground is close to the surface such that if a well was dug, it would not need to be dug too far for water to be seen.
When heavy rain falls, flooding is avoided if the water is either able to run off efficiently or if the ground is able to absorb the water. When the water table is high, it means that the ground will not be able to absorb much because the water is already close to the surface which means that should heavy rain fall, there will most likely be a flood.
What is the potential difference across the source?
60 V
220 V
440 V
120 V

Answers
Answer:
120 v
Explanation:
The two resistors have an equivalent of 20 * 30 /(20+30) = 12 ohms
10 amps of current in the circuit
v = ir
= 10 * 12 = 120 volts
Here is another way:
The two resistors are in prallel so the voltae across both is the same
use the one on the right v = ir = 4 x 30 = 120 v
what would the velocity time graph look like for this position time graph
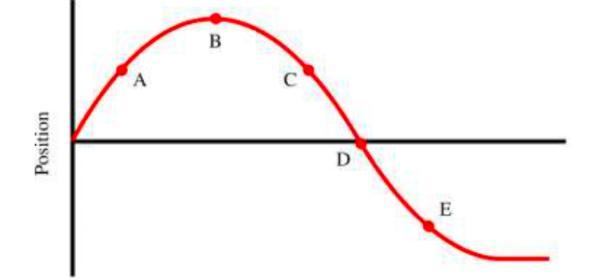
Answers
The velocity time graph would have the velocity used instead of the position in this position time graph.
What is Velocity time graph?This is referred to a plot between velocity and time and it helps to show the motion of the object that moves in a straight line.
We should note that the velocity-time graph reveals the speed of an object (and whether it is slowing down or speeding up), while the position-time graph describes the motion of an object over a period of time which is therefore why it was chosen as the correct choice.
Read more about Velocity time graph here https://brainly.com/question/24191409
#SPJ1
which if the following is the best example of a thermodynamiclly open system?
Answers
The following which is the best example of a thermodynamically open system is a cup of coffee and is therefore denoted as option A.
What is an Open system?This is referred to as the type of system in which matter and/or energy may enter and exit. There is also an exchange of both matter and energy with its surroundings.
An example is a cup of coffee because thermal energy is lost to the surrounding which is usually in the form of vapor. Other options such as our universe and insulated gas cylinder are closed system which is why there is usually no exchange of energy with external environment thereby making it the correct choice.
Read more about Open system here https://brainly.com/question/14266156
#SPJ1
The full question is:
which if the following is the best example of a thermodynamiclly open system?
A. a cup of coffee
B. our universe
C. a greenhouse
D. an insulated gas cylinder
write the dimensional formula of gravitational constant and specific heat capacity.
Answers
Answer:
SEE EXPLANATION
Explanation:
The dimensional formula of gravitational constant is given by,
M^-1 L^3 T^-2
Where,
M = Mass
L = Length
T = Time
Dimensional formula of Specific Heat Capacity =[ M^0L^2T^-2K^-1]
A 10kg object is 15 meters up a hill. Find its potential energy
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
Relative to an origin at the bottom of the hill,
PE = mgh = 10(9.8)(15) = 1470 J
The half-life of Silver-105 is 3.57 x 106 seconds. A sample contains 5.78 x 1017 nuclei. What is the decay constant for this decay?
Answers
Answer:
The decay constant, or "lambda" (λ), is the rate at which a radioactive isotope decays. It is usually measured in units of inverse time, such as seconds. In this case, the decay constant can be calculated as follows:
16:42
λ = (ln(2)/3.57 x 106) x (5.78 x 1017) = 0.
Explanation:
An 8.0 Kg mass is placed at = 3 where should a 10 Kg mass be placed along the − so that the center of mass will be located ay = 4.5?
Answers
Answer:
Therefore, the 10 kg mass should be placed at x = 5.7 m along the x-axis to achieve a center of mass located at y = 4.5 m.
Explanation:
To find the position along the x-axis where a 10 kg mass should be placed such that the center of mass is located at y = 4.5, we can use the formula for the center of mass:
x_cm = (m1 * x1 + m2 * x2) / (m1 + m2)
Here, m1 and x1 represent the mass and position of the 8 kg mass, respectively. m2 is the mass of the 10 kg mass, and we need to find x2, its position.
Given:
m1 = 8 kg
x1 = 3 m
x_cm = unknown (to be found)
m2 = 10 kg
y_cm = 4.5 m
Since the center of mass is at y = 4.5, we only need to consider the y-coordinate when calculating the center of mass position along the x-axis.
To solve for x2, we can rearrange the formula as follows:
x2 = (x_cm * (m1 + m2) - m1 * x1) / m2
Substituting the given values:
x2 = (x_cm * (8 kg + 10 kg) - 8 kg * 3 m) / 10 kg
Simplifying:
x2 = (x_cm * 18 kg - 24 kg*m) / 10 kg
Now, we can set the y-coordinate of the center of mass equal to 4.5 m and solve for x_cm:
4.5 m = (8 kg * 3 m + 10 kg * x2) / (8 kg + 10 kg)
Simplifying:
4.5 m = (24 kg + 10 kg * x2) / 18 kg
Multiplying both sides by 18 kg:
81 kg*m = 24 kg + 10 kg * x2
Subtracting 24 kg from both sides:
10 kg * x2 = 81 kg*m - 24 kg
Dividing both sides by 10 kg:
x2 = (81 kg*m - 24 kg) / 10 kg
Simplifying:
x2 = 8.1 m - 2.4 m
x2 = 5.7 m
(brainlest?) ples:(
Answer:
the 10 kg mass should be placed at x = -2.4 m to achieve a center of mass at y = 4.5 m.
Explanation:
To find the position along the x-axis where the 10 kg mass should be placed so that the center of mass is located at y = 4.5, we can use the principle of the center of mass.
The center of mass of a system is given by the equation:
x_cm = (m1x1 + m2x2) / (m1 + m2),
where x_cm is the x-coordinate of the center of mass, m1 and m2 are the masses, and x1 and x2 are the positions along the x-axis.
Given:
m1 = 8 kg,
x1 = 3 m,
m2 = 10 kg,
y_cm = 4.5 m.
To solve for x2, we need to find the x-coordinate of the center of mass (x_cm) by using the y-coordinate:
y_cm = (m1y1 + m2y2) / (m1 + m2),
where y1 and y2 are the positions along the y-axis.
Rearranging the equation and substituting the given values:
4.5 = (83 + 10y2) / (8 + 10).
Simplifying the equation:
4.5 = (24 + 10*y2) / 18.
Multiplying both sides by 18:
81 = 24 + 10*y2.
Rearranging the equation:
10*y2 = 81 - 24,
10*y2 = 57.
Dividing both sides by 10:
y2 = 5.7.
Therefore, the y-coordinate of the 10 kg mass should be 5.7 m.
To find the x-coordinate of the 10 kg mass, we can use the equation for the center of mass:
x_cm = (m1x1 + m2x2) / (m1 + m2).
Substituting the given values:
x_cm = (83 + 10x2) / (8 + 10).
Since the center of mass is at x_cm = 0 (the origin), we can solve for x2:
0 = (83 + 10x2) / (8 + 10).
Rearranging the equation:
83 + 10x2 = 0.
24 + 10*x2 = 0.
10*x2 = -24.
Dividing both sides by 10:
x2 = -2.4.
Which of the following biogeochemical cycles moves water through the atmosphere, surface, and crust of Earth?
A. Carbon cycle
B. Hydrologic cycle
C. Nitrogen cycle
D. Phosphorus cycle
Answers
Explanation: The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle, describes the continuous movement of water as it makes a circuit from the oceans to the atmosphere to the Earth and on again. Most of Earth's water is in the oceans. The sun, which drives the water cycle, heats water in the oceans.
Given a→=3i^+4j^-k^ and b→=i^-3j^+k^, find a unit vector n^ normal to the plane containing a→ and b→ such that a→, b→ and n^ in that order form a right-handed system.
Select one:
n^=i^-4j^+13k^186
n^=i^-4j^-13k^186
n^=i^+4j^-13k^186
n^=i^+4j^+13k^186
Answers
The unit vector normal to the plane is determined as (i - 4j - 13k) / √186.
Option B.
What is the unit vector n^ normal to the plane?The magnitude of the cross product of a→ and b→, is determined as follows;
|a→ × b→| = (3i +4j -k) × (i- 3j + k )
= [i j k]
[3 4 -1]
[1 -3 1]
The cross product of the vectors is calculated as follows;
= i (4 - 3) - j(3 - - 1) + k (-9 - 4)
= i - 4j - 13k
The magnitude of the vector is calculated as follows;
|n| = √ (1² + 4² + 13²)
|n| = √186
The unit vector normal to the plane is calculated as follows;
n = (i - 4j - 13k) / √186
Thus, the unit vector normal to the plane is determined as (i - 4j - 13k) / √186. The answer is B.
Learn more about unit vector here: https://brainly.com/question/17271641
#SPJ1
please help oooooooo

Answers
Answer: Can't see clearly.
Explanation:
A simple pendulum is used to measure gravity using the following theoretical equation,TT=2ππ�LL/gg ,where L is the length of the pendulum, g is gravity, andT is the period of pendulum.Twenty measurements of T give a mean of 1.823 seconds and a standard deviation of 0.0671 s. The device used to measure time has a resolution of 0.02 s. The pendulum length is measured once to be 0.823 m (with a scale having a resolution of 0.001 m). Determine the value of g and its uncertainty (assume 90% confidence where necessary). You may use any method of uncertainty propagation that we covered in class.
Answers
Answer:
g ±Δg = (9.8 ± 0.2) m / s²
Explanation:
For the calculation of the acceleration of gravity they indicate the equation of the simple pendulum to use
T = \(2\pi \sqrt{ \frac{L}{g} }\)
T² = \(4\pi ^2 \frac{L}{g}\)4pi2 L / g
g = \(4\pi ^2 \frac{L}{T^2}\)
They indicate the average time of 20 measurements 1,823 s, each with an oscillation
let's calculate the magnitude
g = \(4\pi ^2 \frac{0.823}{1.823^2}\)4 pi2 0.823 / 1.823 2
g = 9.7766 m / s²
now let's look for the uncertainty of gravity, as it was obtained from an equation we can use the following error propagation
for the period
T = t / n
ΔT = \(\frac{dT}{dt}\) Δt + \(\frac{dT}{dn}\) ΔDn
In general, the number of oscillations is small, so we can assume that there are no errors, in this case the number of oscillations of n = 1, consequently
ΔT = Δt / n
ΔT = Δt
now let's look for the uncertainty of g
Δg = \(\frac{dg}{dL}\) ΔL + \(\frac{dg}{dT}\) ΔT
Δg = \(4\pi ^2 \frac{1}{T2}\) ΔL + 4π²L (-2 T⁻³) ΔT
a more manageable way is with the relative error
\(\frac{\Delta g}{g} = \frac{\Delta L }{L} + \frac{1}{2} \frac{\Delta T}{T}\)
we substitute
Δg = g ( \frac{\Delta L }{L} + \frac{1}{2} \frac{\Delta T}{T}DL / L + ½ Dt / T)
the error in time give us the stanndard deviation
let's calculate
Δg = 9.7766 (\(\frac{0.001}{0.823} + \frac{1}{2} \ \frac{0.671}{1.823}\))
Δg = 9.7766 (0.001215 + 0.0184)
Δg = 0.19 m / s²
the absolute uncertainty must be true to a significant figure
Δg = 0.2 m / s2
therefore the correct result is
g ±Δg = (9.8 ± 0.2) m / s²
What is meant civilized?
Answers
Answer:
at an advanced stage of social and cultural development. "a civilized society"
Explanation:
polite and well-mannered "I went to talk to them and we had a very civilized conversation" hope this helps you :)
The radius of the circular path of an ion in a mass spectrometer is given by r=1/B √2Vaccelm/q. Use this equation to explain how a mass spectrometer is able to separate ions of different masses.

Answers
The mass spectrometer separates ions of different masses by utilizing the relationship between the strength of the magnetic field, the accelerating voltage, the charge-to-mass ratio of the ions, and the resulting radius of the circular path
What is the mass spectrometer?From the formula in the question;
B is a symbol for the magnetic field's intensity as it is applied to the mass spectrometer.
The accelerating voltage used to move the ions is called Vaccelm.
The charge of the ion, specifically its charge-to-mass ratio (q/m), is represented by the letter q.
The mass spectrometer may selectively alter the radius of the circular route for various ions by varying the magnetic field's intensity (B). This makes it possible to spatially segregate ions with various masses based on their various radii. The ions' locations and masses can then be measured using detectors placed along the journey.
Learn more about mass spectrometer:brainly.com/question/29217778
#SPJ1
for a projectile launched horizontally, which of the following best describes the horizontal component of a projectile's velocity? assume air resistance is negligible.
Answers
This means that the horizontal velocity of the projectile does not change and it continues to move at a constant speed in the horizontal direction.
What is projectile?The motion of an item hurled or projected into the air, subject to gravity's acceleration, is referred to as projectile motion. The item is known as a projectile, and its course is known as its trajectory. Throwing a ball straight up, kicking a ball at an angle to the horizontal, or simply dropping something and letting them fall are all instances of projectile motion. Gravity is the sole force acting on the item in projectile motion. A projectile is any item that, once projected or dropped, continues to move due to its own inertia and is solely impacted by gravity's downward pull. A projectile, by definition, has a single force that operates on the force of gravity.
Here,
The vertical component of the velocity, on the other hand, is influenced by gravity and changes continuously. The projectile slows down as it rises and speeds up as it falls. The total velocity of the projectile changes direction, but not magnitude.
So, in summary, the horizontal component of a projectile's velocity remains constant and the vertical component changes continuously due to the influence of gravity.
To know more about projectile,
https://brainly.com/question/21090110
#SPJ4
Complete question:
For a projectile launched horizontally, which of the following best describes the horizontal component of a projectile's velocity? Assume air resistance is negligible
The horizontal component of the projectile's velocity continually decreases.
The horizontal component of the projectile's velocity is zero.
The horizontal component of the projectile's velocity continually increases.
The horizontal component of the projectile's velocity initially decreases and then increases.
The horizontal component of the projectile's velocity remains a nonzero constant.
3. A car with a mass of 1600 kg has a kinetic energy of 125 000 J. How fast is it moving?
Answers
The car is moving at approximately 12.5 meters per second.
The kinetic energy (KE) of an object can be calculated using the formula:
KE = 1/2 * m * \(v^2\)
where
KE = kinetic energy,
m =Mass of the object, and
v = velocity.
In this case, we are given the mass (m) of the car as 1600 kg and the kinetic energy (KE) as 125,000 J. To find the velocity .
Substituting the values , we have:
125,000 J = 1/2 * 1600 kg *\(v^2\)
Now, we can solve for v by rearranging the equation:
\(v^2\) = (2 * 125,000 J) / 1600 kg
\(v^2\) = 156.25 \(m^2/s^2\)
Taking the square root, we find:
v = √156.25\(m^2/s^2\)
v ≈ 12.5 m/s
Therefore, the car is moving at approximately 12.5 meters per second.
Know more about kinetic energy here:
https://brainly.com/question/8101588
#SPJ8
A star near the visible edge of a galaxy travels in a uniform circular orbit. It is 41,200 ly (light-years) from the galactic center and has a speed of 275 km/s. Estimate the total mass of the galaxy based on the motion of the star.
Gravitational constant is 6.674×10−11 m3/(kg·s2) and mass of the Sun Ms=1.99 × 1030 kg.
*Answer in billion solar mass
Answers
The total mass of the galaxy is 443.4 Solar mass
Orbital velocity (\(v\)) = \(\sqrt{\frac{MG}{R} }\)
where M= weight of galaxy
G= gravitational constatnt = \(6.674*10^-^1^1\) (given)
R = distance from centre = \(41200\) Light years (given)= \(4.12*9.5*10^1^6\) km (1 ly= \(9.5*10^3\) billion km)
v= orbital velocity = \(275\) \(km/s\) (given)
∴ According to the formula
\((2.75*10^2)^2\) = \(\frac{M*6.674*10^-^1^1}{4.12*9.5*10^1^6}\)
⇒ \(7.56*10^4*4.12*9.5*10^1^6=M*6.674*10^-^1^1\) (cross multiplying and expanding)
⇒ \(29.59*10^2^1=M*6.674*10^-^1^1\)
⇒ \(\frac{29.59*10^2^1*10^1^1}{6.674}=M\)
⇒ \(4.434*10^3^2=M\)
1 solar mass = \(1.989*10^3^0 kg\)
⇒ Mass in solar mass =443.4 Solar mass
⇒ M = 443.4 Solar mass
Learn more about Orbital velocity here :
https://brainly.com/question/22247460
#SPJ10
explanations for energy transformations within a system of chemical energy of ice skating
Answers
During ice skating, there are several energy transformations that occur within the system, involving the chemical energy stored in the body and its conversion into other forms of energy.
The skater's body possesses chemical energy stored in the form of carbohydrates and fats obtained from food. This chemical energy is converted into mechanical energy as the skater's muscles contract and generate force to propel themselves forward on the ice. The chemical bonds in the molecules of carbohydrates and fats are broken, releasing energy that powers muscular movement.
As the skater glides on the ice, friction comes into play. The mechanical energy of the skater is transformed into thermal energy due to the interaction between the skate blades and the ice surface. Some of the mechanical energy is dissipated as heat due to friction, causing the ice to melt slightly beneath the blades.
This thermal energy contributes to the increase in the temperature of the ice and the surrounding environment. There may be sound energy produced as the skate blades interact with the ice. When the skater pushes off the ice or performs certain movements, vibrations are created, leading to the emission of sound waves.
know more about sound waves here:
https://brainly.com/question/1199084
#SPJ8
The velocity time graph of an object mass 50 g is shown in figure study graph and answer
1)calculate force acting on object in time interval 0-3 seconds
2)calculate the force acting on the object in the time interval 6-10 seconds
3)Is there any time interval in which no force acts on object.Justify

Answers
1) The force acting on the object during the time interval 0-3 seconds is 1/3 N.
2) The force acting on the object during the time interval 6-10 seconds is -0.5 N.
3) There is no time interval in which no force acts on the object.
(i) Force acting on the object in time interval 0-3 seconds. Force acting on the object is equal to the product of its mass and acceleration, i.e.,F = ma.
In the given velocity-time graph, the acceleration of the object can be determined by determining the slope of the velocity-time graph from 0 to 3 seconds.
Slope = (change in velocity) / (change in time)= (20-0) / (3-0) = 20/3 m/s^2
Acceleration, a = slope= 20/3 m/s^2
Mass of the object, m = 50 g = 0.05 kg
∴ Force acting on the object, F = ma= 0.05 × 20/3= 1/3 N.
Therefore, the force acting on the object during the time interval 0-3 seconds is 1/3 N.
(ii) Force acting on the object in time interval 6-10 seconds. Similar to the first question, the force acting on the object in time interval 6-10 seconds can be determined by determining the acceleration of the object during this time interval.
The slope of the velocity-time graph from 6 seconds to 10 seconds can be determined as follows:
Slope = (change in velocity) / (change in time)= (-20-20) / (10-6) = -40/4= -10 m/s^2 (negative sign indicates that the object is decelerating)
Mass of the object, m = 50 g = 0.05 kg
∴ Force acting on the object, F = ma= 0.05 × (-10)= -0.5 N.
Therefore, the force acting on the object during the time interval 6-10 seconds is -0.5 N.
(iii) Time interval in which no force acts on the object. There is no time interval in which no force acts on the object. This is because, as per Newton's first law of motion, an object will continue to remain in a state of rest or uniform motion along a straight line unless acted upon by an external unbalanced force.In other words, if the object is moving with a constant velocity, there must be a force acting on the object to maintain its motion.
Therefore, there is no time interval in which no force acts on the object.
For more such questions on force, click on:
https://brainly.com/question/12785175
#SPJ8
Voltages in series can be added together if the voltages are aiding each other.
a. True
b. False
Answers
You sever a volleyball with a mass of 2.0kg. The ball leaves your hand with a speed of 20 m/s. The ball has _____ energy. Calculate it show your work.
Answers
Answer:
400J
Explanation:
We can use the formula [ 1/2mv^2 ] to solve.
1/2(2)(20)^2
1/2(2)(400)
1/2(800)
400J
Best of Luck!
At t=0 a grinding wheel has an angular velocity of 25.0 rad/s. It has a constant angular acceleration of 26.0 rad/s2 until a circuit breaker trips at time t = 2.40 s. From then on, it turns through an angle 435 rad as it coasts to a stop at constant angular acceleration. Part APart complete Through what total angle did the wheel turn between t=0 and the time it stopped? Express your answer in radians. θ = 570 rad Previous Answers Correct Part B At what time did it stop? Express your answer in seconds. t = nothing s Request Answer Part C What was its acceleration as it slowed down? Express your answer in radians per second squared.
Answers
Answer:
a) The total angle of the grinding wheel is 569.88 radians, b) The grinding wheel stop at t = 12.354 seconds, c) The deceleration experimented by the grinding wheel was 8.780 radians per square second.
Explanation:
Since the grinding wheel accelerates and decelerates at constant rate, motion can be represented by the following kinematic equations:
\(\theta = \theta_{o} + \omega_{o}\cdot t + \frac{1}{2}\cdot \alpha \cdot t^{2}\)
\(\omega = \omega_{o} + \alpha \cdot t\)
\(\omega^{2} = \omega_{o}^{2} + 2 \cdot \alpha \cdot (\theta-\theta_{o})\)
Where:
\(\theta_{o}\), \(\theta\) - Initial and final angular position, measured in radians.
\(\omega_{o}\), \(\omega\) - Initial and final angular speed, measured in radians per second.
\(\alpha\) - Angular acceleration, measured in radians per square second.
\(t\) - Time, measured in seconds.
Likewise, the grinding wheel experiments two different regimes:
1) The grinding wheel accelerates during 2.40 seconds.
2) The grinding wheel decelerates until rest is reached.
a) The change in angular position during the Acceleration Stage can be obtained of the following expression:
\(\theta - \theta_{o} = \omega_{o}\cdot t + \frac{1}{2}\cdot \alpha \cdot t^{2}\)
If \(\omega_{o} = 25\,\frac{rad}{s}\), \(t = 2.40\,s\) and \(\alpha = 26\,\frac{rad}{s^{2}}\), then:
\(\theta-\theta_{o} = \left(25\,\frac{rad}{s} \right)\cdot (2.40\,s) + \frac{1}{2}\cdot \left(26\,\frac{rad}{s^{2}} \right)\cdot (2.40\,s)^{2}\)
\(\theta-\theta_{o} = 134.88\,rad\)
The final angular angular speed can be found by the equation:
\(\omega = \omega_{o} + \alpha \cdot t\)
If \(\omega_{o} = 25\,\frac{rad}{s}\), \(t = 2.40\,s\) and \(\alpha = 26\,\frac{rad}{s^{2}}\), then:
\(\omega = 25\,\frac{rad}{s} + \left(26\,\frac{rad}{s^{2}} \right)\cdot (2.40\,s)\)
\(\omega = 87.4\,\frac{rad}{s}\)
The total angle that grinding wheel did from t = 0 s and the time it stopped is:
\(\Delta \theta = 134.88\,rad + 435\,rad\)
\(\Delta \theta = 569.88\,rad\)
The total angle of the grinding wheel is 569.88 radians.
b) Before finding the instant when the grinding wheel stops, it is needed to find the value of angular deceleration, which can be determined from the following kinematic expression:
\(\omega^{2} = \omega_{o}^{2} + 2 \cdot \alpha \cdot (\theta-\theta_{o})\)
The angular acceleration is now cleared:
\(\alpha = \frac{\omega^{2}-\omega_{o}^{2}}{2\cdot (\theta-\theta_{o})}\)
Given that \(\omega_{o} = 87.4\,\frac{rad}{s}\), \(\omega = 0\,\frac{rad}{s}\) and \(\theta-\theta_{o} = 435\,rad\), the angular deceleration is:
\(\alpha = \frac{ \left(0\,\frac{rad}{s}\right)^{2}-\left(87.4\,\frac{rad}{s} \right)^{2}}{2\cdot \left(435\,rad\right)}\)
\(\alpha = -8.780\,\frac{rad}{s^{2}}\)
Now, the time interval of the Deceleration Phase is obtained from this formula:
\(\omega = \omega_{o} + \alpha \cdot t\)
\(t = \frac{\omega - \omega_{o}}{\alpha}\)
If \(\omega_{o} = 87.4\,\frac{rad}{s}\), \(\omega = 0\,\frac{rad}{s}\) and \(\alpha = -8.780\,\frac{rad}{s^{2}}\), the time interval is:
\(t = \frac{0\,\frac{rad}{s} - 87.4\,\frac{rad}{s} }{-8.780\,\frac{rad}{s^{2}} }\)
\(t = 9.954\,s\)
The total time needed for the grinding wheel before stopping is:
\(t_{T} = 2.40\,s + 9.954\,s\)
\(t_{T} = 12.354\,s\)
The grinding wheel stop at t = 12.354 seconds.
c) The deceleration experimented by the grinding wheel was 8.780 radians per square second.
Briefly explain why arterial injuries are more dangerous than damage to veins
or capillaries. Explanation should address structure and function of the
blood vessels.
IF YOU SEE THIS PLZ ANSWER RN
Answers
Answer:
Injury to a vein increases the risk of forming a blood clot.
Explanation:
hoped this helped
A ball is thrown upward with a speed of 12mls from the top of a building .how much later must a second ball be dropped .from the same starting point if it is to hit the ground at the same time as the first ball ? the initial position is 24m above the ground g= 10mls2
Answers
The second ball should be dropped 2.19 seconds after the first ball is thrown so that it hits the ground at the same time as the first ball.
What is the time of motion of the ball?
We can solve this problem using the kinematic equations of motion. Let's first find out how long it takes for the first ball to hit the ground.
Using the kinematic equation:
h = ut + 1/2 at^2
where;
h is the initial height of the ball (24m), u is the initial velocity (12 m/s), a is acceleration due to gravity (-10 m/s^2), and t is the time taken for the ball to reach the ground.Plugging in the values, we get:
-24 = 12t - 1/2 * 10 * t^2
Simplifying the equation:
5t^2 - 12t - 24 = 0
Using the quadratic formula:
t = 3.7 seconds
Therefore, the first ball takes 3.6 seconds to hit the ground.
Now, let's find out at what time the second ball should be dropped so that it hits the ground at the same time as the first ball.
Since the second ball is dropped from rest, its initial velocity (u) is 0. Using the same equation:
h = ut + 1/2 at^2
Plugging in the values, we get:
24 = 0t - 1/2 * 10 * t^2
Simplifying the equation:
5t^2 = 24
t^2 = 4.8
t = √(4.8)
t = 2.19 seconds (approx)
Learn more about time of motion here: https://brainly.com/question/2364404
#SPJ1