Answers
Answer:
The resistivity of this wire is approximately \(2.1\times 10^{-7}\; \rm \Omega \cdot m\).
The conductivity of this wire is approximately \(4.7\times 10^6\; \rm (\Omega \cdot m)^{-1}\).
Assumption: the perpendicular cross-section of this wire is circular.
Explanation:
Convert all unit to standard ones:
Length of this wire: \(l = 100\; \rm cm = 1.00\; \rm m\).Diameter of this wire: \(0.3\; \rm mm = 3\times 10^{-4}\; \rm m\).Assume that a wire has a resistivity of \(\rho\), a length of \(l\), and a cross-section area of \(A\). The formula for the resistance of this wire would be:
\(R = \displaystyle \frac{\rho \cdot l}{A}\).
Rearrange this equation to find an expression for \(\rho\), the resistivity of this wire:
\(\displaystyle \rho = \frac{R\cdot A}{l}\).
For the wire in this question, both length \(l\) and resistance \(R\) are already given. However, the cross-section area \(A\) of this wire needs to be calculated from its diameter, \(d\):
\(A = \displaystyle \pi\, \left(\frac{d}{2}\right)^2 \approx 7.08\times 10^{-8}\; \rm m^2\).
Calculate the resistivity of this wire:
\(\displaystyle \rho = \frac{R\cdot A}{l} \approx \frac{3.0\; \Omega\times 7.08\times 10^{-8}\; \rm m^2}{1.00\; \rm m} \approx 2.1\times 10^{-7}\; \rm \Omega\cdot m\).
The conductivity of a material is the reciprocal of its resistivity:
\(\displaystyle C = \frac{1}{\rho} \approx \frac{1}{2.1\times 10^{-7}\; \Omega\cdot m}\approx 4.7\times 10^{6}\; \rm (\Omega \cdot m)^{-1}\).
Related Questions
Consider a system of two charges of magnitude 2 × 10-7 C and 4.5 × 10-7 C which is acted upon by a force of 0.1 N. What is the distance between the two charges?
Answers
To find the distance between two charges, we can use Coulomb's law, which states that the force between two charges is proportional to the product of their magnitudes and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
The formula for Coulomb's law is:
F = (k * |q1| * |q2|) / r^2
where:
F is the force between the charges,
k is the electrostatic constant (k = 8.99 × 10^9 N m^2/C^2),
|q1| and |q2| are the magnitudes of the charges, and
r is the distance between the charges.
Given:
|q1| = 2 × 10^-7 C
|q2| = 4.5 × 10^-7 C
F = 0.1 N
k = 8.99 × 10^9 N m^2/C^2
We can rearrange the equation to solve for r:
r^2 = (k * |q1| * |q2|) / F
Plugging in the values:
r^2 = (8.99 × 10^9 N m^2/C^2 * 2 × 10^-7 C * 4.5 × 10^-7 C) / 0.1 N
r^2 = (8.99 × 2 × 4.5) * (10^9 * 10^-7 * 10^-7) / 0.1
r^2 = 80.91 * (10^9 * 10^-7 * 10^-7) / 0.1
r^2 = 80.91 * 10^(-7 + 9 - 1)
r^2 = 80.91 * 10^1
r^2 = 809.1
Taking the square root of both sides:
r = √809.1
r ≈ 28.46
Therefore, the distance between the two charges is approximately 28.46 units.
Nowton's third law refers to 'action reaction forces*. These forces are
always:
Answers
equal in magnitude but opposite in direction
Experiment: Friction Investigation using a matchbox, pebbles, coins, string, small plastic bag, towel, small scale or balance
Answers
Below is an experiment investigating friction using a matchbox, pebbles, coins, string, small plastic bag, towel, small scale or balance.
Procedure:
Cut a piece of string that is long enough to wrap around the matchbox with some extra length to hold onto.Tie one end of the string to the matchbox.Put some pebbles or coins inside the small plastic bag.Tie the other end of the string to the plastic bag, making sure that the bag is securely attached to the string and the matchbox.Place the towel on a table or flat surface.Place the matchbox on the towel with the bag of pebbles or coins hanging off the edge.Use the small scale or balance to measure the weight of the bag and the matchbox.Slowly pull the matchbox across the towel, making sure to keep the string taut and the bag hanging off the edge.Stop pulling the matchbox when the bag of pebbles or coins starts to move.Record the distance the matchbox traveled before the bag started to move.Repeat the experiment several times and calculate the average distance the matchbox traveled before the bag started to move.Change one variable at a time (e.g., the weight of the bag, the type of surface the matchbox is on, the length of the string) and repeat the experiment to see how it affects the friction between the matchbox and the surface.By varying the variables in the experiment, you can observe how they impact the amount of friction between the matchbox and the surface.
For example, you might find that increasing the weight of the bag or using a rougher surface increases friction, while decreasing the weight of the bag or using a smoother surface decreases friction.
What is friction?Friction is a force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are in contact. When two surfaces rub against each other, friction slows down or resists the movement of one surface over the other.
Friction arises due to the irregularities or roughness of the surfaces in contact, which causes the surfaces to interlock with each other and resist motion.
Learn about friction here https://brainly.in/question/1182128
#SPJ1
A 6 kg blue ball rolls across the ground and collides with a stationary 1 kg red ball.
Before the collision the blue ball moved right with a speed of 4 m/s, and after the
collision it moved left with a speed of 1 m/s. If the red ball was not moving before the
collision, how fast is it moving after the collision?
Answers
The final velocity of the red ball is 18 m/s.
What is momentum?The term momentum has to do with the product of the mass and the velocity of an object We know that the momentum is always conserved in accordance with the Newton third law. Also it is clear that the momentum before collision is equal to the total momentum after collision and we are going to apply this principle here.
Then;
Mass of the blue ball = 6 kg
Mass of the red ball = 1 kg
Initial velocity of the blue ball = 4 m/s
Initial velocity of the red ball = 0 m/s
Final velocity of the red ball = ??
Final velocity of the blue ball = 1 m/s
We now have;
(6 * 4) + (1 * 0) = (1 * v) + (6 * 1)
24 = v + 6
v = 24 - 6
v = 18 m/s
Learn more about momentum:https://brainly.com/question/2193212
#SPJ1
Obtain the formula for the focal length of a lens in terms of object distance (u)
and magnification (m)
Answers
Answer:
m=image distance÷object distance
If the ratio of distance from the epicenter to S-P lag time is 10 to 1, what would the distance be if the S-P lag time is 23.2 minutes?
Answers
Calculate the magnitude of the electric field at one corner of a square 1.10 m on a side if the other three corners are occupied by 4.05×10−6 C charges. What is the direction of the electric field?
Answers
The direction of magnetic field is south-east and the magnitude is
\(23.66\) × \(10^{3} N/C\).
Here, the magnitude of CD and BC will be cancelled, as they both are in the opposite direction and equal to each other.
the magnitude, towards the diagonal AC will result in CP, which is the direction of the electric field.
magnitude of electric field can be defined as :- The force per charge on the test charge is a straight forward way to define the size of the electric field.
To find the magnitude of the electric field use the formula
\(E = kq/ r^{2}\)
inserting the values,
\(E = 9. 10^{9}\) × \(4.05\) × \(10^{-6} / 1.1 \sqrt{2}\)
\(E= 36.45\) × \(10^{3}\) / \(1.54\)
\(E = 23.66\) × \(10^{3}\) N/C
Learn more about calculating magnitude of the electric field at one corner here:-
https://brainly.com/question/14922532
#SPJ1

When Jose plays his guitar, the friction between his fingers and the strings allows him to pluck the strings. The friction creates some heat and the vibration of the strings creates the sound. The original amount of energy he applies to the strings is 1,000 joules. The energy of the vibrating strings is measured and is found to be 800 joules. Was Energy Lost?
Answers
Yes, energy was lost in this scenario. The original amount of energy applied to the strings by Jose was 1,000 joules. However, the measured energy of the vibrating strings is only 800 joules.
Yes, energy was lost in this scenario. The original amount of energy applied to the strings by Jose was 1,000 joules. However, the measured energy of the vibrating strings is only 800 joules. This discrepancy indicates that 200 joules of energy were lost. The energy loss can be attributed to various factors. Firstly, friction between Jose's fingers and the strings converts some of the applied energy into heat energy. This heat energy dissipates into the surrounding environment, resulting in a loss of energy from the system. Additionally, there may be other forms of energy loss involved, such as air resistance or sound energy radiated away from the vibrating strings. These energy losses contribute to the discrepancy between the original applied energy and the measured energy of the vibrating strings. Therefore, in this case, the difference between the initial and measured energy values indicates that some energy was lost in the form of heat, sound, or other forms of energy dissipation.
For more question on energy
https://brainly.com/question/13881533
#SPJ11
Water flows at a speed of 13 m/s through a pipe that has a diameter of 1.2 m. What is the
diameter of the smaller end of the pipe that the water comes out with a speed of 30 m/s?
Answers
The diameter of the smaller end of the pipe is approximately 0.78 meters.
To determine the diameter of the smaller end of the pipe, we can use the principle of conservation of mass. According to this principle, the mass flow rate of water should remain constant throughout the pipe.
The mass flow rate is given by the equation:
Mass flow rate = density of water * cross-sectional area * velocity
Since the density of the water remains constant, we can write:
Cross-sectional area1 * velocity1 = Cross-sectional area2 * velocity2
Given that the velocity1 is 13 m/s, the diameter1 is 1.2 m, and the velocity2 is 30 m/s, we can solve for the diameter2 using the equation:
(pi * (diameter1/2)^2) * velocity1 = (pi * (diameter2/2)^2) * velocity2
Simplifying the equation:
(1.2/2)^2 * 13 = (diameter2/2)^2 * 30
Calculating the equation:
(0.6)^2 * 13 = (diameter2/2)^2 * 30
0.36 * 13 = (diameter2/2)^2 * 30
4.68 = (diameter2/2)^2 * 30
Dividing both sides by 30:
0.156 = (diameter2/2)^2
Taking the square root of both sides:
0.39 = diameter2/2
Multiplying both sides by 2:
0.78 = diameter2
To learn more about diameter
https://brainly.com/question/32968193
#SPJ8
What is the average speed (in km/h) of Zhana, who runs to the store that is 4.0 km away in 30.0 minutes?
0.13 km/ h
8.0 km/h
2.0 km/h
Answers
Answer:
2.0km/h.
Explanation:
iiiiijjjjjij
Explanation:
Wwwww
ayuden ha resolver este ejercicio porfa

Answers
Answer:
un café y a seguir pensando porque no se la respuesta xd
Please Help!!
What is the potential energy of a spring that is compressed 0.75 m by a 25 kg block if the spring constant is 85 N/m?
24
34
87
797
Answers
Answer:
Potential energy of spring = 24 Joules.
Explanation:
Given the following data;
Spring constant = 85N/m
Extension, e = 0.75m
Mass = 25kg
To find the potential energy of a spring
Potential energy of a spring is given by the formula;
P.E = ½ke²
Substituting into the equation, we have
P.E = ½*85*0.75²
P.E = 42.5 * 0.5625
P.E = 23.91 ≈ 24 Joules
P.E = 24 Joules
Two billard balls with identical mass move toward each other, with the positive x-axis to the right. Assume that the collision between them is elastic. If the initial velocities of the balls are +40.0 cm/s and -30.0 cm/s, what are the velocities of the balls after the collision? Assume friction and rotation are unimprotant.
Answers
The velocities of the two balls after the collision are +70.0 cm/s to the right for both balls.
What is velocity?Velocity is described as the directional speed of an object in motion as an indication of its rate of change in position as observed from a particular frame of reference and as measured by a particular standard of time.
The initial momenta of the two balls are:
p1 = mv1 = m(+40.0 cm/s) = +40m
p2 = mv2 = m(-30.0 cm/s) = -30m
m= mass of each ball.
We know that by the conservation of momentum, the total momentum before the collision is equal to the total momentum after the collision.
p1 + p2 = mv1' + mv2'
mv1 + m(-v2) = mv1' + mv2'
We then Substitute the values for the momenta and solving for v1 and v2
v1 = (-v2) + v1 = (-(-30.0 cm/s)) + (+40.0 cm/s) = +70.0 cm/s
v2 = v1 - v2 = (+40.0 cm/s) - (-30.0 cm/s) = +70.0 cm/s
Learn more about velocity at:
https://brainly.com/question/80295
#SPJ1
Which point is labeled in the scatterplot below?
10
O
A.
10
A. (7,5)
B. (2,3)
C. (5,7)
D. (3, 2)

Answers
Answer:
B because you go to the left 2 then up 3 to get (2,3)
Answer:
D.(3,2)
Explanation:
Because the point "A" is 2 places right on the x axis and 3 places up on the y axis
kate is participating in a race.she ran 300 meters in 3 minutes.what is her average speed in m/min?
Answers
Answer:
Her average speed is: 100 m/min
Explanation:
Recall that the formula for average speed is given by:
Speed = Distance / time
Then in our case, this is
Speed = 300 m / 3 min = 100 m/min
What initial speed v is required if the blocks m1 =2.5 kg and m2=1.5 kg are to travel a distance d =7.0cm before coming to rest? Assume the coefficient of kinetic friction between m1 and the tabletop is ųk=0.21


Answers
Answer:
OPTRIMUM PRIDE URGH URGH URGH
Explanation:
AHHAAHAHAHAHA
A mixture of colloids, clay, silt, sand, pebbles, and cobbles is put into stream I at point A. The water
velocity at point A is 400 centimeters per second. A similar mixture of particles is put into stream II at
point A. The water velocity in stream II at point A is 80 centimeters per second.
Which statement best describes what happens when the particles are placed in the streams?
A) Stream I will move all particles that are added at point A.
B) Stream II will move all particles that are added at point A.
C) Stream I cannot move sand.
D) Stream II cannot move sand.
Answers
A combination of colloids, clay, silt, sand, pebbles, and cobbles is positioned into the move I at factor A. The water choice B) stream II will pass all debris that might be added at point A.
Circulation speed is the velocity of the water inside the flow. units are distance in step with time (e.g., meters in keeping with second or feet in keeping with second). movement speed is best in midstream close to the surface and is slowest alongside the movement mattress and banks due to friction.
Larger particles are much more likely to fall through the upward currents to the lowest, until the flow price increases, growing the turbulence on the streambed. in addition, suspended sediment will no longer always remain suspended if the drift charge slows.
Learn more about velocity here
https://brainly.com/question/24445340
#SPJ4
A leopard of mass 65 kg climbs 7 m up a tall tree. Calculate how much gravitational potential energy it gains. Assume g = 10 N/kg
Answers
The potential energy gained is 4550 J.
The potential energy that a huge item has in relation to another massive object due to gravity is known as gravitational energy or gravitational potential energy. When two objects descend toward one another, potential energy associated with the gravitational field is released.
The potential difference is given as:
U = mgh
Where U is the gravitational energy, m is the mass, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the height.
Now, we have
Leopard's mass, m = 65kg
The height of the tree, h = 7 m
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 10N/kg
Therefore,
U = mgh
U = 65 × 7 × 10
U = 65 × 70
U = 4550 J
Thus, the leopard will need 4550 J of gravitational potential energy to climb 7 meters.
Learn more about gravitational potential energy here:
https://brainly.com/question/15896499
#SPJ9
4.
How does the United Nations Development Program use its resources?
It provides health programs for mothers and children.
O It develops natural resources.
It works to eliminate poverty through development.
O It invests funds in industrialized nations.
Economic
Answers
Answer:
It develops natural resources.
It works to eliminate poverty through development.
Can someone explain how to do the algebra for this question? I know everything else, I just don’t know how to rearrange the question to solve for v.

Answers
Answer:
Refer to the step-by-step Explanation.
Step-by-step Explanation:
Simplify the equation with given substitutions,
Given Equation:
\(mgh+(1/2)mv^2+(1/2)I \omega^2=(1/2)mv_{_{0}}^2+(1/2)I \omega_{_{0}}^2\)
Given Substitutions:
\(\omega=v/R\\\\ \omega_{_{0}}=v_{_{0}}/R\\\\\ I=(2/5)mR^2\)\(\hrulefill\)
Start by substituting in the appropriate values: \(mgh+(1/2)mv^2+(1/2)I \omega^2=(1/2)mv_{_{0}}^2+(1/2)I \omega_{_{0}}^2 \\\\\\\\\Longrightarrow mgh+(1/2)mv^2+(1/2)\bold{[(2/5)mR^2]} \bold{[v/R]}^2=(1/2)mv_{_{0}}^2+(1/2)\bold{[(2/5)mR^2]}\bold{[v_{_{0}}/R]}^2\)
Adjusting the equation so it easier to work with.\(\Longrightarrow mgh+\dfrac{1}{2} mv^2+\dfrac{1}{2} \Big[\dfrac{2}{5} mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v}{R} \Big]^2=\dfrac12mv_{_{0}}^2+\dfrac12\Big[\dfrac25mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v_{_{0}}}{R}\Big]^2\)
\(\hrulefill\)
Simplifying the left-hand side of the equation:
\(mgh+\dfrac{1}{2} mv^2+\dfrac{1}{2} \Big[\dfrac{2}{5} mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v}{R} \Big]^2\)
Simplifying the third term.
\(\Longrightarrow mgh+\dfrac{1}{2} mv^2+\dfrac{1}{2} \Big[\dfrac{2}{5} mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v}{R} \Big]^2\\\\\\\\\Longrightarrow mgh+\dfrac{1}{2} mv^2+\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot \dfrac{2}{5} \Big[mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v}{R} \Big]^2\\\\\\\\\Longrightarrow mgh+\dfrac{1}{2} mv^2+\dfrac{1}{5} \Big[mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v}{R} \Big]^2\)
\(\\ \boxed{\left\begin{array}{ccc}\text{\Underline{Power of a Fraction Rule:}}\\\\\Big(\dfrac{a}{b}\Big)^2=\dfrac{a^2}{b^2} \end{array}\right }\)
\(\Longrightarrow mgh+\dfrac{1}{2} mv^2+\dfrac{1}{5} \Big[mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v^2}{R^2} \Big]\\\\\\\\\Longrightarrow mgh+\dfrac{1}{2} mv^2+\dfrac{1}{5} \Big[mR^2 \cdot\dfrac{v^2}{R^2} \Big]\)
"R²'s" cancel, we are left with:
\(\Longrightarrow mgh+\dfrac{1}{2} mv^2+\dfrac{1}{5} \Big[mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v^2}{R^2} \Big]\\\\\\\\\Longrightarrow mgh+\dfrac{1}{2} mv^2+\dfrac{1}{5}mv^2\)
We have like terms, combine them.
\(\Longrightarrow mgh+\dfrac{1}{2} mv^2+\dfrac{1}{5} \Big[mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v^2}{R^2} \Big]\\\\\\\\\Longrightarrow mgh+\dfrac{7}{10} mv^2\)
Each term has an "m" in common, factor it out.
\(\Longrightarrow m(gh+\dfrac{7}{10}v^2)\)
Now we have the following equation:
\(\Longrightarrow m(gh+\dfrac{7}{10}v^2)=\dfrac12mv_{_{0}}^2+\dfrac12\Big[\dfrac25mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v_{_{0}}}{R}\Big]^2\)
\(\hrulefill\)
Simplifying the right-hand side of the equation:
\(\Longrightarrow \dfrac12mv_{_{0}}^2+\dfrac12\cdot\dfrac25\Big[mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v_{_{0}}}{R}\Big]^2\\\\\\\\\Longrightarrow \dfrac12mv_{_{0}}^2+\dfrac15\Big[mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v_{_{0}}}{R}\Big]^2\\\\\\\\\Longrightarrow \dfrac12mv_{_{0}}^2+\dfrac15\Big[mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v_{_{0}}^2}{R^2}\Big]\\\\\\\\\Longrightarrow \dfrac12mv_{_{0}}^2+\dfrac15\Big[mR^2\cdot\dfrac{v_{_{0}}^2}{R^2}\Big]\\\\\\\\\Longrightarrow \dfrac12mv_{_{0}}^2+\dfrac15mv_{_{0}}^2\Big\\\\\\\\\)
\(\Longrightarrow \dfrac{7}{10}mv_{_{0}}^2\)
Now we have the equation:
\(\Longrightarrow m(gh+\dfrac{7}{10}v^2)=\dfrac{7}{10}mv_{_{0}}^2\)
\(\hrulefill\)
Now solving the equation for the variable "v":
\(m(gh+\dfrac{7}{10}v^2)=\dfrac{7}{10}mv_{_{0}}^2\)
Dividing each side by "m," this will cancel the "m" variable on each side.
\(\Longrightarrow gh+\dfrac{7}{10}v^2=\dfrac{7}{10}v_{_{0}}^2\)
Subtract the term "gh" from either side of the equation.
\(\Longrightarrow \dfrac{7}{10}v^2=\dfrac{7}{10}v_{_{0}}^2-gh\)
Multiply each side of the equation by "10/7."
\(\Longrightarrow v^2=\dfrac{10}{7}\cdot\dfrac{7}{10}v_{_{0}}^2-\dfrac{10}{7}gh\\\\\\\\\Longrightarrow v^2=v_{_{0}}^2-\dfrac{10}{7}gh\)
Now squaring both sides.
\(\Longrightarrow \boxed{\boxed{v=\sqrt{v_{_{0}}^2-\dfrac{10}{7}gh}}}\)
Thus, the simplified equation above matches the simplified equation that was given.
Whoever answers correctly gets brainlist!

Answers
Infared = used by police
gamma = short wavelength
radio = largest wavelength
visible = only ones we can see
Answer: police use infred waves,
radio waves have largest wave length, the
only part of the spectrum seen by humans is visible waves
gamma waves have shortest wave length
Explanation:
A 1.35 kg block is pulled across a flat, frictionless floor with a 3.07 n force at 32.0 above horizontal. What is the acceleration of the block
Answers
1. Calculating the horizontal component of the applied force:
Horizontal component = 3.07 N * cos(32.0°)
Horizontal component ≈ 2.597 N
2. Calculating the acceleration of the block:
Acceleration = Horizontal component / Mass
Acceleration = 2.597 N / 1.35 kg
Acceleration ≈ 1.925 m/s²
Therefore, the acceleration of the block is approximately 1.925 m/s².
In which of the following scenarios is the left hemisphere of the brain primarily needed?
Answers
The left hemisphere of the brain is primarily needed in scenario, Solving a complex mathematical problem. Option a is correct.
The brain is divided into two hemispheres, left and right, and they are specialized for different cognitive functions. The left hemisphere of the brain is primarily responsible for language processing, logical reasoning, and analytical thinking. Solving a complex mathematical problem involves logical reasoning, analytical thinking, and the use of language, all of which are primarily controlled by the left hemisphere of the brain.
Mathematical problems often require precise calculations, sequencing of steps, and the use of symbols and formulas, all of which require a strong left-brain function. In contrast, appreciating a work of art, listening to music, and recognizing facial expressions are all more complex perceptual and emotional processes that involve the right hemisphere of the brain. Option a is correct.
To know more about brain, here
brainly.com/question/11950231
#SPJ1
--The complete question is, In which of the following scenarios is the left hemisphere of the brain primarily needed?
a. Solving a complex mathematical problem.
b. Appreciating a work of art
c. Listening to music
d. Recognizing facial expressions.--
a. When throwing a ball vertically upward, my hand moves through a distance of about 1.0 m before the ball leaves my hand. The 0.80 kg ball reaches a maximum height of about 20 m above my hand. while the ball is in my hand after the ball leaves my hand
Answers
The required, it experiences a downward force due to gravity and a force due to air resistance.
What is the projectile motion?Projectile motion is the movement of an entity projected into space. After the initial force that launches the object, it only experiences the force of gravity. The object is called a projectile, and its path is called its trajectory.
Here,
When throwing a ball vertically upward, there is a displacement of about 1.0 m from the initial position of the hand to the position where the ball leaves the hand. The mass of the ball is 0.80 kg and it reaches a maximum height of about 20 m above the initial position of the hand. While the ball is in the hand after it leaves, it experiences a downward force due to gravity and a force due to air resistance.
Learn more about projectile motion here:
brainly.com/question/11049671
#SPJ1
A snapshot of three racing cars is shown in the diagram. All three cars start the race at the same time, at the same place, and move along a straight track. As they approach the finish line, which car has the lowest average speed?
Answers
Answer:
The car furthest from the finish line: Car III (Choice C).
Explanation:
It's asking for lowest average speed throughout the entire race. Therefore, whoever is last technically has the lowest average speed.
Car III is far behind Car I and Car II so Choice A and B aren't correct. Choice D is incorrect since the three cars aren't in the same position. Choice E is incorrect because there is enough information to see that Choice C has the lowest average speed.
Identify each setup and describe the difference in the magnetic field created by each.
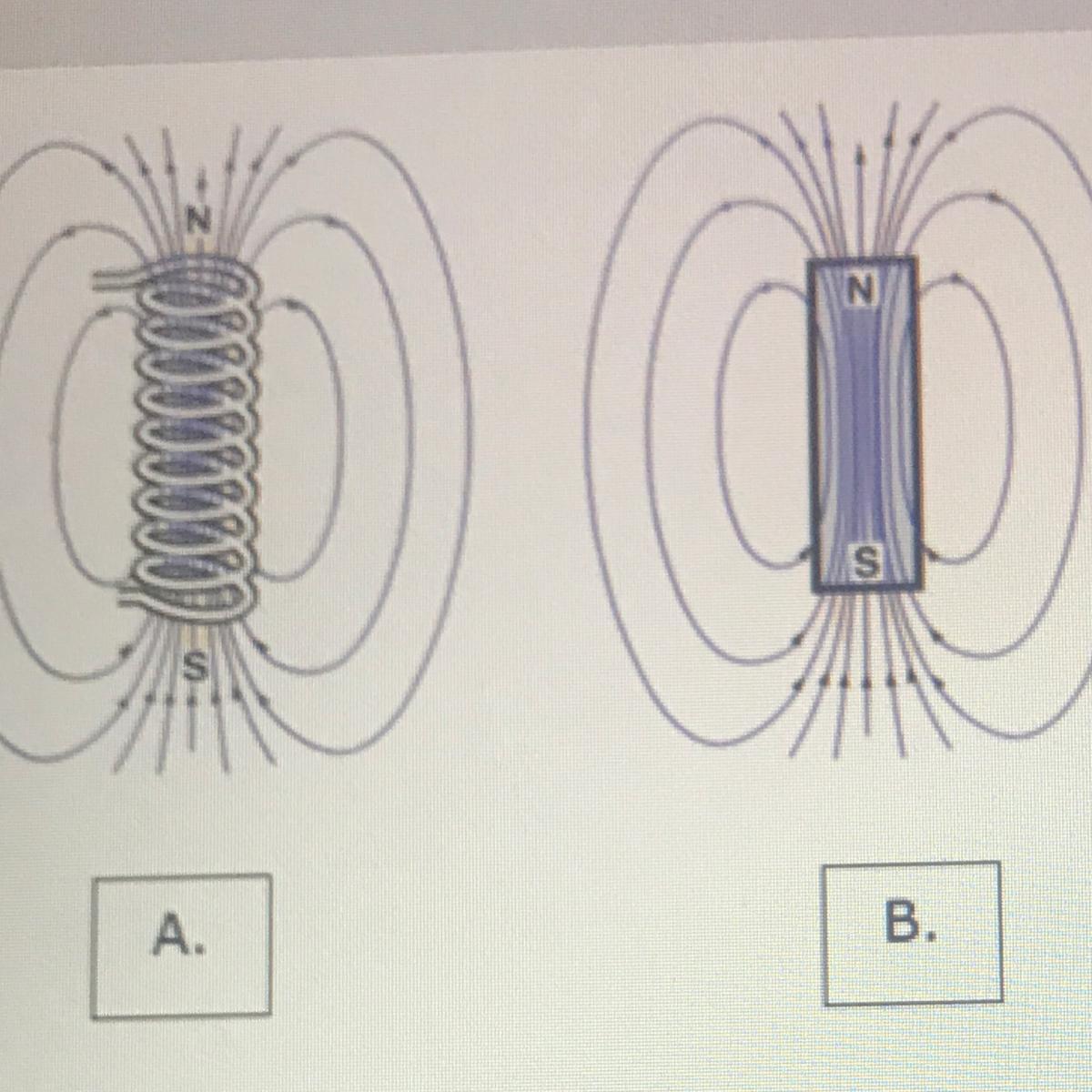
Answers
In A. we have a magnetic field created by a coil in physics, the term coil refers to a long, thin loop of wire, which produces a magnetic field when an electric current is passed through it. in this case, the core inside the coil is the air
In B. We have a magnetic field created by a magnet that is a piece of iron or other magnetic material that has its component with atoms so ordered that the material have properties of magnetism, such as attracting other iron-containing objects or aligning itself in an external magnetic field
In C. Also we have a coil but this time with a core of metal material, a core can increase the magnetic field to thousands of times the strength of the field of the coil alone.
A horizontal spring with a constant of 3000 N/m is compressed 4.0 cm from equilibrium. A 2.0 kg mass is placed on front of the compressed spring and then is released. The object drags on a flat surface with a coefficient of friction equal to .23 and eventually comes to rest. How far from the spring does the mass travel?
Answers
Regarding a spring-mass system's duration, the square root of the mass and the spring constant have opposing correlations. The length of spring will be longer and vice versa as the mass grows. Therefore, the mass influences spring.
What far from the spring does the mass travel?They swing back and forth around a stationary point. Classic examples of this type of vibrating motion are a simple pendulum and a mass on a spring.
Therefore, The use of motion detectors demonstrates that the vibrations of these objects have a sinusoidal nature, even if this is not obvious from plain viewing.
Learn more about spring here:
https://brainly.com/question/14670501
#SPJ1
hich of the following is a minimal sum-of-products (SOP) equation that implements the same logic as the equation f(a, b, c) = a(b + c') + ac a. f = ab + ac b. f = ab + ac' + be c. f=a d. f = b(a + d) e. f = a(b + b)(b + c)
Answers
The minimal SOP equation that implements the same logic as the given equation is f = ab + ac.
What is SOP?The sum of product (SOP) is a type of logic circuit used to represent a logical expression. It is also known as a canonical sum of products and is a type of canonical form. An SOP expression is composed of one or more product terms. Each product term is the logical AND of one or more literals and is separated from other product terms with a plus sign. The sum of product form of a logic expression is a sum of the product terms of the expression.
To know more about SOP
https://brainly.com/question/30386797
#SPJ1
Two tuning forks struck simultaneously produce a beat with a frequency of 2 Hz. The frequency of one fork is 364 Hz. What are the two possible frequencies of the other tuning fork?
Answers
Answer: If the other two frequencies are F and F1 then;
F-364=2
F=364+2
F=366Hz
364-F1=2
F1=364-2
F1=362Hz
Hence the two possible frequencies are 362Hz and 366Hz
Explanation:
Two tuning forks struck simultaneously produce a beat. The two possible frequencies of the other tuning fork are 366 Hz and 368 Hz.
What is beat frequency?Beat frequency is the difference between the frequencies of the two tones interacting with each other.
Given is the beat frequency of 2 Hz and the frequency of one fork is 364 Hz.
The frequency of other tuning fork will be
f2 -f1 = 2 Hz
f2 = 2 +364
f2 = 366 Hz
The other one is 366 +2 Hz = 368 Hz.
Therefore, the two possible frequencies of the other tuning fork are 366 Hz and 368 Hz.
Learn more about beat frequency.
https://brainly.com/question/14705053
#SPJ2
Ensuring that every contingency is planned for is an aspect of which of the following successful marketing plan requirements?
controllable
timely
fact based
flexible
Answers
Answer:
Fact based i think if not timely
Explanation: