Answers
The atmosphere is where the majority of the nitrogen on earth is found. 78% nitrogen gas makes it available to living things (N2).
What is nitrogen used for?The chemical industry depends on nitrogen. It is employed to create explosives, nylon, nitric acid, fertilizers, and colors. Nitrogen must be combined with hydrogen to create ammonia in order to create these products.
Is nitrogen harmful to humans?Individuals are killed every year by breathing "air" with insufficient oxygen. Several people believe nitrogen gas is safe since it makes up 78 percent of a air we breathe. Only when nitrogen is combined with the right amount of oxygen is it safe to breathe, though.
To know more about nitrogen visit:
brainly.com/question/16711904
#SPJ4
Related Questions
A sheet of aluminum foil has a volume of 0.555 cm3. If the foil measures 10.0 cm by 10.0 cm, what is the thickness of the foil?
Answers
Answer: B) 0.005 55 cm
Hope you have a blessed day!
Why do we monitor chinstrap penguins instead of krill?
Answers
Answer:Yes
Explanation:
Because Chinstrap penguins eat krills
3. A Wilkinson’s catalyst is widely used in the hydrogenation of alkenes. Show a catalytic cycle, including: i. chemical structure of the catalyst, with complete stereochemistry ii. molecular geometry of catalyst iii. type of reactions involved iv. the appropriate starting material, reagent and solvent v. major and minor end-products vi. all intermediates, for each reaction stated in (iii)
Answers
We can see here that the catalytic cycle for the hydrogenation of alkenes using Wilkinson's catalyst involves several steps.
What are the steps involved?Here's an overview of the catalytic cycle, including the necessary details:
i. Chemical structure of the catalyst:
Wilkinson's catalyst, also known as chloridotris(triphenylphosphine)rhodium(I), has the following chemical structure: [RhCl(PPh3)3]
ii. Molecular geometry of the catalyst:
The Wilkinson's catalyst has a trigonal bipyramidal geometry around the rhodium center. The three triphenylphosphine (PPh3) ligands occupy equatorial positions, while the chloride (Cl) ligand occupies an axial position.
iii. Type of reactions involved:
The catalytic cycle involves several reactions, including:
Oxidative addition: The rhodium center undergoes oxidative addition, reacting with molecular hydrogen (H2) to form a dihydride intermediate.Alkene coordination: The alkene substrate coordinates to the rhodium center, forming a π-complex.Hydrogenation: The coordinated alkene undergoes hydrogenation, resulting in the addition of hydrogen atoms to the double bond and formation of a metal-alkyl intermediate.Reoxidation: The metal-alkyl intermediate reacts with a hydrogen molecule to regenerate the rhodium dihydride species.iv. Starting material, reagent, and solvent:
The starting material is an alkene, and the reagent is Wilkinson's catalyst ([RhCl(PPh3)3]). The reaction is typically carried out in a suitable solvent, such as dichloromethane (CH2Cl2) or tetrahydrofuran (THF).
v. Major and minor end-products:
The major end-product of the hydrogenation reaction is the fully saturated alkane, resulting from the addition of hydrogen across the double bond. The minor end-product may include cis- or trans-configured alkanes if the original alkene substrate possesses geometric isomers.
vi. Intermediates:
The intermediates in the catalytic cycle include:
Rhodium dihydride complex: [RhH2(PPh3)3]Alkene-Rhodium π-complex: [Rh(η2-alkene)(PPh3)3]Metal-alkyl intermediate: [Rh(alkyl)(PPh3)3]These intermediates play a crucial role in facilitating the hydrogenation reaction and enabling the catalytic cycle to proceed.
Learn more about Wilkinson’s catalyst on https://brainly.com/question/31972308
#SPJ1
Which of these are effects of environmental change on populations? Check all that apply.
Answers
The statement "when a bottle of soda was opened, bubbles rapidly appeared in the liquid and were given off at the surface" can be categorized as an observation.
Observation refers to the act of noticing or perceiving something through the senses. In this case, the statement describes a specific event that was directly observed: the opening of a bottle of soda and the rapid appearance of bubbles in the liquid, which were then given off at the surface. This observation describes a phenomenon that can be witnessed and measured.
The appearance of bubbles when a bottle of soda is opened is a well-known and predictable occurrence. It can be explained by the principles of gas solubility and pressure.
The soda contains dissolved carbon dioxide (CO2) under high pressure, which is responsible for the carbonation. When the bottle is opened, the sudden release of pressure causes the dissolved CO2 to come out of solution, forming bubbles. These bubbles then rise to the surface and are released into the air.
While this statement captures an observed phenomenon, it does not propose a general principle or provide a comprehensive explanation of the underlying mechanisms. Therefore, it does not qualify as a law or theory, but rather as an observation based on direct sensory perception.
for such more questions on liquid
https://brainly.com/question/13116910
#SPJ8
Hello,
I am stuck on this: What is the de Broglie wavelength of a neutron (mass = 1.009 amu) moving at a velocity of 7.11 × 10⁶ meters per second?
I know the formula is wavelength= h/mv, but I keep getting the answer incorrect as: 4.67E-27
Answers
The de Broglie wavelength of the neutron moving at a velocity of 7.11×10⁶ m/s is 5.56×10¯¹⁴ m
de Broglie wavelength formulaλ = h /mv
Where
λ the de Broglie wavelengthh is the Planck's constantm is the massv is the velocityHow to determine the de Broglie wavelengthThe following data were obtained from the question:
Mass (m) = 1.009 amu = 1.009 × 1.661×10⁻²⁷ = 1.676×10⁻²⁷ KgVelocity (v) = 7.11×10⁶ m/sPlanck's constant (h) = 6.626×10¯³⁴ Jsde Broglie wavelength (λ) =?The de Broglie wavelength can be obtained as follow:
λ = h /mv
λ = 6.626×10¯³⁴ / (1.676×10⁻²⁷ × 7.11×10⁶)
λ = 5.56×10¯¹⁴ m
Learn more about de Broglie wavelength:
https://brainly.com/question/17438823
#SPJ1
I need help with question May someone help me? Thank yo

Answers
The question requires us to choose the best option regarding the bonds of nonmetal atoms.
Nonmetal atoms can form different types of bonds depending on the atom they are bonding to. They can participate in ionic bonds, where electrons are donated or received (exchanged electrons), usually when bonded to a metal (in this case, the metal usually "loses" the electron, while the nonmetal "gains" the electrons). They can also form covalent bonds when the electrons are shared with other nonmetals.
Regarding the options provided by the question, we can make the following comments:
- 1st option: the type of bond described, where electrons can move freely, is typical of metallic bonding;
- 2nd option: gaining electrons describe ionic bonding, while sharing electrons is related to covalent bonding;
- 3rd option: noble gases are the atoms with full valence orbitals.
- 4th option: losing valence electrons is also a description of ionic bonding.
Considering the information above, the best option to answer the question is the second one:
"Nonmetal atoms form bonds by gaining or sharing electrons".
(nonmetals participate in ionic bonds by donating electrons and in covalent bonds by sharing electrons).
8.0g of certain gas occupies 5.6 L at STP.
A) How many moles of gas are present?
B) What is the molar mass of the gas?
C) What is the common atmospheric gas was collected?
Answers
Answer:
A) Using the ideal gas law, we can calculate the number of moles of gas present:
```
PV = nRT
```
where:
* P = pressure (atm) = 1 atm
* V = volume (L) = 5.6 L
* n = number of moles of gas
* R = ideal gas constant = 0.08206 L atm / mol K
* T = temperature (K) = 273.15 K
Solving for n, we get:
```
n = (P * V) / RT
```
```
n = (1 atm * 5.6 L) / (0.08206 L atm / mol K * 273.15 K)
```
```
n = 0.25 mol
```
Therefore, there are 0.25 moles of gas present.
B) The molar mass of the gas can be calculated by dividing the mass of the gas (8.0 g) by the number of moles of gas (0.25 mol):
```
Molar mass = Mass / n
```
```
Molar mass = 8.0 g / 0.25 mol
```
```
Molar mass = 32 g/mol
```
The molar mass of the gas is 32 g/mol.
C) The common atmospheric gas with a molar mass of 32 g/mol is oxygen (O2). Therefore, the gas that was collected is oxygen.
Explanation:
A sample of an unknown compound is vaporized at 160 c . The gas produced has a volume of 2330 ml at a pressure of 1.00 atm ,and it weighs 2.10 g
Round answer to 3 significants digits

Answers
The molar mass is 3230.8 g/mol
How to determine the valueFirst, we need to know that the formula for the general gas law is represented as;
PV = nRT
such that the parameters are;
P is the pressureV is the volumen is the number of molesR is the gas constantT is the temperatureSubstitute the values
1 × 2.33 = n × 8.314 × 433.15
Multiply the values, we get;
n = 2.33/ 8.314 × 433.15
Divide the values
n = 6.5 × 10⁻⁴ moles
But, number of moles = mass/molar mass
Molar mass = 2.10/ 6.5 × 10⁻⁴
Molar mass = 3230.8 g/mol
Learn about ideal gas law at: https://brainly.com/question/25290815
#SPJ1
please help- science
1. - new
2. full
3. first quarter
4. last quarter

Answers
Answer:
2. Full
Explanation:
A lunar eclipse occurs at a full moon when Earth is directly between the moon and the sun. During a lunar eclipse, Earth blocks sunlight from reaching the moon.
Hope this helps!!
500.0 mL of a 0.205 M solution of LiBr is diluted to 700.0 mL. What is the new concentration of the solution?
Answers
Answer:
0.146 M
Explanation:
Use v1s1 = v2s2
here, v1 = 500 mL, v2 = 700 mL, s1 = 0.205 M & s2 = new concentration
please help it's already past due

Answers
Answer:
4 nitrogen, 2 oxygen, 2 nitrous oxide
Find the volume, in mL, of an object whose density is 400 g/mL and has a mass of 600
mg.
Answers
The volume of the object is 1.5ml.
What is the volume of an object?This refers to the space occupied within the boundaries of an object in three-dimensional space. It is also called the capacity of the object.
In the question:
ρ = 400 g/mL
m = 600 mg
v = ?
Formular for calculating density ρ:
ρ = m/v
Where,
ρ= Density of the object
m= Mass of the object
v = volume of the object
Were are given the values of density and mass in the question. We are to calculate the volume.
Makinig v subject of the formular we have:
v = m/ρ
v = 600 mg
400 g/mL
v = 1.5ml
Learn more about volume on
https://brainly.com/question/23937702
#SPJ1
18. What is the evidence and reasoning that supports the claim that Earth's magnetic field is
generated bt motion of liquid metal, and not a permanent, solid magnet deep inside Earth.
Answers
Answer:
The inside of the Earth is too hot to hold a solid magnet therefore, there is liquid metals within the mantle and deeper. These metals flow around causing volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, and Earth's magnetic field.
Explanation:
determine the molecular mass of the following compounds
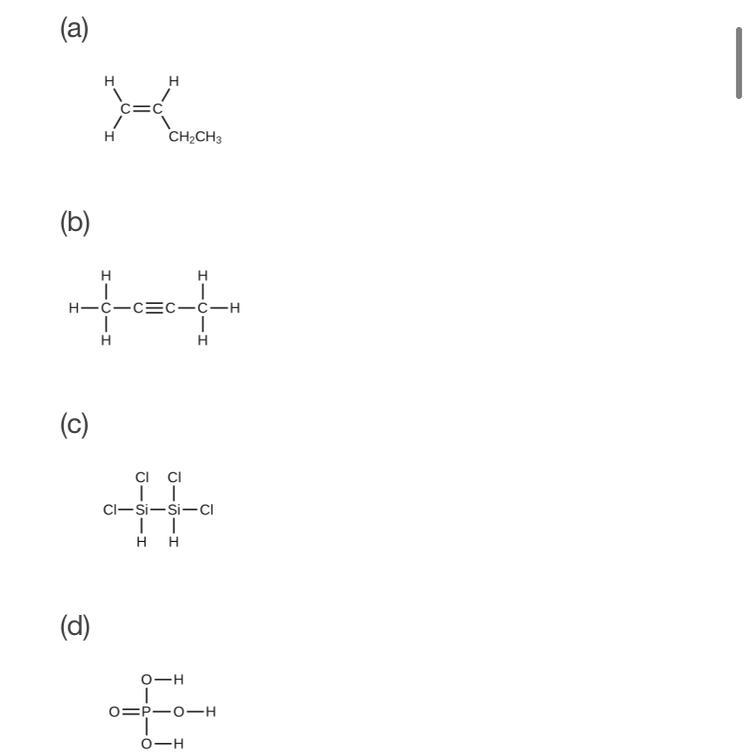
Answers
Answer:
(a).
(4 × C) + (8 × H)
= (4 × 12) + (8 × 1)
= 48+8
= 56 g
(b).
= (4 × C) + (6 × H)
= (4 × 12) + (6 × 1)
= ( 48+6 )
= 54 g
(c).
= ( 2 × Si ) + ( 4×Cl ) + (2×H)
= (2×28) + (4×35.5) + (2×1)
= 56 + 142 + 2
= 200 g
(d).
= (1×P) + (4×O) + (3×H)
= 31 + 64 + 3
= 98 g
What two processes can harm soil fertility
Answers
Over-tilling and Over farming are the two processes that can harm the fertility of the soil.
Over-tilling refers to the exceeding levels of tilling and levelling the soil which adversely affects the quality of the soil. This is because tillage fractures the soil, it disrupts soil structure, accelerating surface runoff and soil erosion. Tilling of soil also reduces crop residue, which help cushion the force of pounding raindrops.
Without crop residue, soil particles become more easily dislodged, being moved or 'splashed' away. The splashed particles clog soil pores, effectively sealing off the soil's surface, resulting in poor water infiltration and hence subsequently affects the soil fertility.
Similarly, the main effect of over-farming is soil depletion. When crops are grown in the same place year after year, the soil becomes depleted of the nutrients that the plants need to grow. This can lead to lower yields and poorer quality crops. In extreme cases, it can lead to desertification.
So, these two are the processes that can harm soil fertility.
To know more about soil erosion, click below:
https://brainly.com/question/17905503
#SPJ9
rank the following compounds from lowest to highest boiling point: sodium chloride, methane, methanol (ch4o), dimethyl ether (ch3och3). explain why
Answers
The increasing order from lowest to highest boiling point is,
Methane < Dimethyl ether < methanol < sodium chloride.
Boiling point of a substance is defined as the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the pressure surrounding the liquid and the liquid changes into a vapor. It is also called as saturation temperature. This temperature is the temperature for a corresponding saturation pressure at which a liquid boils into its vapor phase. Methanol is said to be a more polar molecule which can form hydrogen bonds between molecules. Methanol will have a much higher boiling point than methane due to the hydrogen bond present in it. The boiling point is dependent on the pressure. Due to the hydrogen bond sodium chloride has highest boiling point and methane has lowest boiling point. and It cannot be increased beyond the critical point. It decreases with decreasing pressure until the triple point is reached. It cannot be reduced below the triple point.
To learn more about Boiling point
https://brainly.com/question/40140
#SPJ4
10. When dissolved in water, most Group 1 metal salts can be described as
strong electrolytes.
strong acids.
weak electrolytes.
A
B
C
D
non-electrolytes.
(1)
Answers
When dissolved in water, most Group 1 metal salts can be described as strong electrolytes.
When Group 1 metal salts are dissolved in water, they can be described as strong electrolytes. This is because Group 1 metals, such as lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K), and so on, readily lose their outermost valence electron to form positive ions (cations). These cations then dissociate completely in water, separating from the anions to which they were originally bonded.
The dissociation of Group 1 metal salts in water results in the formation of positively charged metal ions and negatively charged non-metal ions (anions). These ions are free to move and conduct electric current, making the solution a good conductor of electricity. The complete dissociation of Group 1 metal salts in water and the presence of freely moving ions make them strong electrolytes.
Strong electrolytes are substances that ionize completely or almost completely in solution, producing a high concentration of ions. This is in contrast to weak electrolytes, which only partially ionize and produce a lower concentration of ions.
In summary, when Group 1 metal salts are dissolved in water, they form strong electrolytes due to their ability to dissociate completely into ions, leading to a high concentration of freely moving ions in the solution, thus enabling efficient electrical conductivity.
Know more about Group 1 metal salts here:
https://brainly.com/question/13277375
#SPJ8
I need to find the chemical equation

Answers
Answer:
2NaCN + CaCO3 --> Na2CO3 + Ca(CN)2
Explanation:
Knowing the names gets us: NaCN + CaCO3 --> Na2CO3 + Ca(CN)2
Balance: there are two sodiums and cyanides on the product side so add a 2 to the reactant side.
a water solution contains zn2 , ag , and al3 . which of the following compounds should be added to the solution to selectively remove the ag out of the solution, but not the other ions?
Answers
Only CuS will precipitate despite the solubility products of ZnS and CuS being 3 × 10⁻²² and 8 × 10³⁶, respectively.
What is meant by Hydrogen sulfide?A chemical substance having the formula H 2S is hydrogen sulfide. It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas that is toxic, caustic, and combustible. Trace concentrations of it in the ambient air have the distinct odor of rotten eggs.
The Occupational Health and Safety Administration reports that H2S is one of the main factors contributing to workplace gas inhalation fatalities in the United States.
The Bureau of Labor Statistics reports that between 2001 and 2010, hydrogen sulfide gas caused 60 worker fatalities.
Hydrogen sulfide, also known as H2S, sewer gas, swamp gas, stink damp, and sour damp, is a colorless gas that, in small quantities, has a strong rotten-egg odor. It is highly poisonous and highly flammable.
So, in a solution, only CuS will precipitate.
[CuS] = [Cu⁺² [ S⁻²] = 0.01 x 9.2 x 10⁻²² = 9.2 ₓ 10-⁻²⁴ > Ksp
[ZnS] = [Zn⁺² [ S⁻²] = 0.01 x 10⁻²² x 9.2 = 9.2 ₓ 10-⁻²⁴ < Ksp
To learn more about Hydrogen sulfide, refer to:
brainly.com/question/20714000
#SPJ4
The complete question is:
A solution contains 0.01 M Zn²⁺ and 0.01 M Cu²⁺ ions. It is saturated by passing H2 S gas in the solution. The S²⁻ ion concentration is 9.2 * 10^-22 M. The solubility products of ZnS and CuS are 3 * 10⁻²² and 8 * 10^-36 respectively. Which of the following is true?
A Cycle of Chemical Reactions of Copper PRE-LABORATORY ASSIGNMENT Finish the pre-laboratory assignments before the laboratory experiment. Read the manual of this experiment and complete the following questions. 1. a. Identify oxidation-reduction reactions in the copper cycle experiment. For each oxidation-reduction reaction, write half reactions to show what is oxidized and what is reduced. Identify acid-base reactions and precipitation reactions in the copper cycle experi- ment. Write equations for the corresponding reactions. b. How many mL of 3.0 M NAOH are required to neutralize 4.0 mL of 16.0 M HNO2? 2. 1N Copper. AplL tions and interpreting them in terms of chemical equations. You will also use a simple classification scheme for grouping chemical reactions by type. Finally, you will practice quantitative lab techniques by trying to recover the copper with minimal loss. AN OVERVIEW OF THE COPPER CYCLE One of the most fascinating aspects of laboratory experiments to new chemistry students is the variety of colors, odors, and textures encountered. The present experiment demonstrates that aspect by a sequence of striking changes in color, appearance, and bulk. By going through this experiment, students will develop laboratory techniques by the challenges of shepherding copper through all chemical changes with minimal loss. A schematic outline of the chemical reactions involved in the experiment is shown in Figure 5-1 HNO Cu(NO)2 Cu (1) NaOH (2) Zn (5) Cu(OH), 9VOA CUSO je() A (heat) 1000 Ht H,SO Cuo Figure 5-1. A schematic outline of the series of chemical reactions in the copper cycle. The overall copper cycle is then given as Cu(NO,)2(aq) Cu(s) Cu(OH)2(s) CuO(s) CUSO,(aq) Cu(s) The balanced equations corresponding to these steps are: Nitric acid is not only a strong acid but also a strong oxidizing agent, making it a very effective solvent for most metals. 1. (1) 4HNO,(aq)+ Cu(s) Cu(NOs)2(aq) + 2H20(l) + 2NO2(g) Many heavy metals form insoluble hydroxides which can be precipitated from solutions by sol- uble hydroxides such as NaOH. 2. (2) Cu(OH)2(s) + 2NANO,(aq) Cu(NO,)2laq) + 2NaOH(aq) Many transition metal hydroxides lose water upon heating, thus changing to oxides. For copper, this reaction happens at a relatively lower temperature and is accompanied by a striking color change, from blue to black. 3. (3) Cu(OH)2(s)Cu0(s) + H20(e) 4. Metal oxides, being base an hydrides, form salts with acids just as readily as do the bases themselves. CuO(s) + H,SO(aq) CuSO(aq) + H20(e) (4) 5. Chemically active metals, such as zinc, readily displace less active metals from their salts. CuSO&(aq) + Zn(s) Cu(s) + ZnSO(aq) (5) 6. The reaction used to remove excess Zn(s) left over from eq(5): Zn(s) +2H*(aq) Zn2t(aq) + H(g) (6) The last reaction is not explicitly shown in the cycle, but actually occurs twice. The first reaction is with H from excess HSO, as a side reaction during the reduction of CuSO and the second one is with HCL, as an intentional step for the removal of excess Zn remaining in solution after reduction of Cu2+ to Cu. Each equation, as given above, describes one of the colorful transformations, but it is easy to lose sight of their physical meaning if you merely look upon them as a bunch of symbols written on paper. To become more familiar with the chemical equations it is essential to try the following: Find out what the compounds, represented by the formulas, actually look like and what their chemical properties are. a. What class of compounds they belong to, e.g. acid, salt, etc., and what the generic properties of this class are, ie. what types of reactions they undergo. b. Similarly, try to categorize the equations (actually, the reactions they represent): oxidation- reduction (redox) reaction, acid-base reaction, precipitation reaction, replacement reaction, C. etc CLASSIFICATION OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS Precipitation In a precipitation reaction, two soluble substances react to form an insoluble compound, e.g. (7) CaCl2+ Na COs CaCO,(s) + 2NaCl CACO3 is insoluble in water so this salt will form a precipitate and fall out of the solution. 45 LAB 5: A CYCLE OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS OF COPPER
Answers
1 . a.
Solution :
a. The oxidation reduction reactio is
1. HNO₃ + Cu(3) --> Cu(NO₃)₂ + 2H₂O(l) + 2NO₂(g)
Half reaction
oxidation --> Cu(s) --> Cu(NO₃)₂(aq)
reduction --> HNO₃ -->NO₂
copper is oxidized and nitrogen is reduced
2 -> CuSO₄(aq) + zn(s) --> Cu(s) + ZnSO₄(aq)
Half reaction .
oxidation --> Zn(s) --> ZnSO4(aq)
Reduction --> CuSO₄ (aq) --> Cu(s)
zinc is oxidized and copper is reduced.
3 -> Zn(s) + 2H⁺(aq) --> Zn²⁺(aq) + H₂(g)
oxidation --> Zn(s) --> Zn²⁺(aq)
Reduction --> 2H⁺(aq) -->H₂(g)
Zinc is oxidized and hydrogen is reduced .
b . Acid - base reaction
CuO(s) + H₂SO₄(aq) -->CuSO₄(aq) + H₂O(l)
precipitation reaction
Cu(NO₃)₂(aq) + 2NAOH(aq) -->Cu(OH)₂ + 2NANO₃
2 . 21.33 mL of 3.0 M NAOH are required to neutralize 4.0 mL of 16.0 M HNO2
1 mole of NAOH required to neutralized the
1 mole of HNO₃
NAOH + HNO₃ --> H₂O +NANO₃
(M₁V₁)NAOH = (M₂V₂)HNO2
3 * V₁ = 4 * 16
V₁ = 64/3
V₁= 21.33 ml
The term oxidation was originally used to describe the reaction in which an element combines with oxygen.
Example: The reaction of magnesium metal with oxygen to form magnesium oxide involves the oxidation of magnesium.
The term reduction comes from the Latin root and means "to undo". So anything that goes back to magnesium metal is a reduction.
The reaction of magnesium oxide with carbon at 200°C to form magnesium metal and carbon monoxide is an example of the reduction of magnesium oxide to magnesium metal.
electrons were discovered, the chemist became convinced that redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons from one of his atoms to another.
Learn more about oxidation and reduction here : https://brainly.com/question/4222605
#SPJ4
Use your trendline equation to determine the gas pressure at 200 K and 400 K. (notice the temperature units) How many times greater is the pressure at 400 K in comparison to 200 K? Is this what you’d expect? Why?
Answers
Answer:
The pressure will be twice the initial pressure
Explanation:
Gay-Lussac's law states that the pressure of a gas is directely proportional to absolute temperature under constant volume. That is because vibrations of a gas increase when temperature increases, increasing the pressure of the gas.
That means if the temperature of a gas is doubled, the pressure will be twice the initial pressure.
The ideal gas constant R can be denoted as _______.
A. R = 9.315 (Pa × m3) / (mole × K)
B. R = 9.315 J / (mole × K)
C. R = 0.0821 (L × atm) / (mole × K)
D. All of the Above E. None of the Above
Answers
in the unit of J/(mole x K) and (Pa x m3)/ (mole x K) the value should be 8.314
5. Determine the effect
on the volume of a
basketball if the initial
volume is 6.4 L at
20°C and the ball is
taken outside to a
temperature of 27°C.
Answers
Answer: 6.25 L
Explanation:
Charles Law V1/T1 = V2/T2
Convert temperature to Kelvin by adding 273.15
V2 = V1T2/T1
V2= 6.4 X 293.15/300.15 = 6.25 L
Identify the type of reaction and predict the product: Calcium + water -->
Answers
Answer:
Exothermic Reaction
Product = Calcium hydroxide + hydrogen
Explanation:
Which statements are true about balancing chemical equations?
Check all that apply.
A. Balancing chemical equations does not involve trial and error.
B. Balancing chemical equations involves trial and error.
C. Atoms that are in only one of the reactants and only one of the
products should be done last.
D. Single atoms should be done last.
Answers
Answer:
statement C is the correct answer
Which of the following is an example of an optional deduction ? " a ) Medicare Ob ) Social Security c ) Retirement plan d ) State tax
Answers
Medicare
United states program for people who are older than 60
A chemical compound has a molecular weight of 89.05 g/mole. 1.400 grams of this compound underwent complete combustion under constant pressure conditions in a special calorimeter. This calorimeter had a heat capacity of 2980 J °C.1 (Note that the calorimeter was made of a metal shell, a water "substitute" - a special oil, and a thermocouple). The temperature went up by 11.95 degrees.
Required:
Calculate the molar heat of combustion of the compound.
Answers
Answer:
\(\Delta _{comb}H=-2,265\frac{kJ}{mol}\)
Explanation:
Hello!
In this case, for such calorimetry problem, we can notice that the combustion of the compound releases the heat which causes the increase of the temperature by 11.95 °C, it means that we can write:
\(Q _{comb}=-C_{calorimeter}\Delta T_{calorimeter}\)
In such a way, we can compute the total released heat due to the combustion considering the calorimeter specific heat and the temperature raise:
\(Q _{comb}=-2980\frac{J}{\°C} *11.95\°C\\\\Q _{comb}=-35,611J\)
Next, we compute the molar heat of combustion of the compound by dividing by the moles, considering 1.400 g were combusted:
\(n=1.400g*\frac{1mol}{89.05g} =0.01572mol\)
Thus, we obtain:
\(\Delta _{comb}H=\frac{Q_{comb}}{n}=\frac{-35,611J}{0.01572mol} \\\\\Delta _{comb}H=-2,265,331\frac{J}{mol}*\frac{1kJ}{1000J} \\\\\Delta _{comb}H=-2,265\frac{kJ}{mol}\)
Best regards!
I figured it out no problem
Answers
Answer:
good job ;0
Explanation:
Which best describes homeostasis?
A. altering the external environment to accommodate the body's needs
B. maintaining a relatively stable equilibrium by physiological processes.
C. keeping the body in a fixed and unaltered stated.
D. maintaining a constant internal environment.
Answers
Answer:
Yeah, it's B.
Explanation:
Homeostasis is when the body maintains a near constant internal environment.
what is the original pressure of a 750 ml sample of He at 0 degrees Celsius if it exerts 2 atm at 25 degrees Celsius and 500 ml
Answers
To determine the original pressure of a 750 ml sample of helium (He) at 0 degrees Celsius, we can use the combined gas law, which relates the initial and final conditions of a gas sample. The combined gas law equation is:
(P1 × V1) / (T1) = (P2 × V2) / (T2)
Where:
P1 and P2 are the initial and final pressures, respectively.
V1 and V2 are the initial and final volumes, respectively.
T1 and T2 are the initial and final temperatures, respectively.
Let's assign the given values:
P1 = unknown (original pressure)
V1 = 750 ml (initial volume)
T1 = 0 degrees Celsius (initial temperature)
P2 = 2 atm (final pressure)
V2 = 500 ml (final volume)
T2 = 25 degrees Celsius (final temperature)
Before using the combined gas law equation, we need to convert the temperatures to Kelvin scale by adding 273.15 to both T1 and T2:
T1 = 0 + 273.15 = 273.15 K
T2 = 25 + 273.15 = 298.15 K
Now we can plug in the values into the combined gas law equation:
(P1 × 750 ml) / (273.15 K) = (2 atm × 500 ml) / (298.15 K)
To solve for P1, we can cross multiply and rearrange the equation:
P1 = (2 atm × 500 ml × 273.15 K) / (750 ml × 298.15 K)
P1 = 0.924 atm
Therefore, the original pressure of the 750 ml sample of helium at 0 degrees Celsius is approximately 0.924 atm.