Sodium easily combines with chorine is reactivity
Answers
answer
yes
Explanation:
Related Questions
2b. This same alpha amino group in the hydrophobic interior of the protein has the opportunity to form an ionic bond in that hydrophobic environment with a carboxylate group in the side chain of a charged Asp residue. Under these conditions, how would the pKa of this alpha amino group compare with the pKa of the alpha amino group in the hydrophobic interior of the protein without a nearby Asp residue to form this ionic bond?
Answers
The pKa of the α-amino group in the hydrophobic interior of the protein with a nearby Asp residue, would be lower compared to the pKa of the α-amino group in the hydrophobic interior without a nearby Asp residue.
In the hydrophobic interior of a protein, the α-amino group can form an ionic bond with a carboxylate group of a charged aspartic acid (Asp) residue. This interaction can significantly affect the pKa of the α-amino group compared to its pKa in the absence of the nearby Asp residue.
When the α-amino group forms an ionic bond with the Asp residue, it becomes positively charged by donating a proton to the carboxylate group. This ionic bond stabilizes the charged form of the α-amino group and facilitates the release of a proton, resulting in a lower pKa value. The presence of the ionic bond enhances the stability of the charged form of the α-amino group, making it more acidic and lowering its pKa value even further.
Therefore, the pKa of the α-amino group in the hydrophobic interior of the protein, when it forms an ionic bond with a nearby Asp residue, would be lower compared to the pKa of the α-amino group in the hydrophobic interior without a nearby Asp residue. The ionic bond formation enhances the acidity of the α-amino group, making it more likely to release a proton and lowering its pKa value.
Learn more about pKa here:
https://brainly.com/question/31588587
#SPJ11
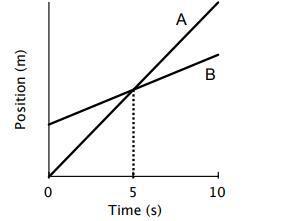
I) Do both the cyclists start at the same point? If not, who is ahead at the starting point? ii) At t = 7s, which cylclist is lagging behind? iii) Which cyclist – A or B would be travelling with greater speed? How can you justify?
Answers
Answer and Explanation:
Assuming the image attached is the distance/displacement-time graph of both cyclists A and B:
Cyclist B started at a position higher than 0 meters, whereas cyclist A started at 0 meters. Cyclist B started ahead.When t = 7, it s observed that cyclist A is at a higher position on the graph than cyclist B, and is therefor travelling faster. B is lagging behind.Cyclist A is travelling at a greater speed, because his distance covered is exponentially increased per time, whereas the Cyclist B only records marginal steady increase in distance covered.I hope this explanation was easy to understand and helpful.
what type of tests does a competent person need to perform in order to classify soil?
Answers
Here are some common tests performed by a competent person to classify soil; Visual Examination, Particle Size Analysis, Atterberg Limits Test, Organic Matter Content, and Chemical Analysis.
Visual Examination; This involves observing and describing the color, texture, structure, and other visible characteristics of the soil.
Particle Size Analysis; This test will determines the distribution of the particles size in the soil sample. It is usually done using sieves or sedimentation methods to classify soil into different size fractions such as gravel, sand, silt, and clay.
Atterberg Limits Test; This test will determines the moisture content at which the soil transitions between solid, plastic, as well as liquid states. It includes tests for liquid limit, plastic limit, and shrinkage limit, which help classify soil into different consistency states.
Organic Matter Content; Testing the organic matter content of soil helps classify it in terms of fertility, nutrient availability, and overall soil health. This is often done through laboratory analysis, such as loss-on-ignition or Walkley-Black methods.
Chemical Analysis; Soil may undergo chemical testing to determine its pH level, nutrient content, salinity, and presence of contaminants or pollutants. These tests can aid in classification for agricultural, environmental, or remediation purposes.
To know more about soil here
https://brainly.com/question/224605
#SPJ4
What is the relative humidity of the air when the dry-bulb temperature is 4°C and the dewpoint is 1°C?
Answers
The relative humidity of the air when the dry-bulb temperature is 4°C and the dewpoint is 1°C is approximately 87%.
The relative humidity is defined as the ratio of the partial pressure of water vapor in the air to the saturation vapor pressure at the same temperature, expressed as a percentage. The saturation vapor pressure is the maximum amount of water vapor that the air can hold at a particular temperature. When the air is cooled to the dewpoint temperature, the water vapor in the air begins to condense into liquid water. At this point, the air is saturated with water vapor, and the relative humidity is 100%. In this problem, the dewpoint is given as 1°C, which means that the air is almost saturated with water vapor. The dry-bulb temperature is given as 4°C, which is slightly higher than the dewpoint temperature. By using a psychrometric chart or an online calculator, we can determine that the relative humidity of the air is approximately 87%.
Learn more about partial pressure, below:
https://brainly.com/question/23841760
#SPJ11
A 21.5 L sample of gas at 107 kPa has a temperature of 27.2 °C. What is the pressure of the gas
if it is transferred to a 32.6L container at 44.1 °C?
Answers
Answer:
The right answer is "74.516 kPa".
Explanation:
The given values are:
V₁ = 21.5 L
V₂ = 32.6L
P₁ = 107 kPa
T₁ =27.2°C+273
T₂ = 44.1 °C+273
As we know,
⇒ \(\frac{P_1V_1}{T_1}= \frac{P_2V_2}{T_2}\)
then,
⇒ \(P_2=\frac{P_1V_1T_2}{T_1V_2}\)
On substituting the given values, we get
⇒ \(=\frac{107\times 21.5\times (44.1+273)}{(27.2+273)\times 32.6}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{107\times 21.5\times 317}{300.2\times 32.6}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{729258.5}{9786.52}\)
⇒ \(=74.516 \ kPa\)
An element “D” decays from 100g to 25g in 20 years. What is it’s half life?
Answers
An element “D” decays from 100g to 25g in 20 years. The half-life of element "D" is 10 years.
The half of-life of an detail is the time it takes for half of of the initial amount of the detail to decay. In this situation, the detail "D" decays from 100g to 25g in two decades.
To decide the 1/2-life, we want to discover the time it takes for the preliminary amount of the detail to lower to half of of its value.
Initial amount: 100g
Final amount (after one half-life): 50g
As it took 20 years for the amount to go down from 100g to 25g, we can assume that it took half of that time, or 10 years, for the amount to decrease from 100g to 50g.
Therefore, the half-life of element "D" is 10 years.
For more details regarding half-life, visit:
https://brainly.com/question/31666695
#SPJ1
For strong electrolytes, i = number of per mole of solute dissolved. CaCl dissolves yielding three ions, one Ca ion and two Clions, thus i = (NH. ),P dissolves yielding four ions, three NH' ions and one Pion, thus i = "Colligative Properties Study Guide" by Montgomery College is licensed under CC BY 4. 0
Answers
The statement you provided refers to the determination of the van't Hoff factor (i) for strong electrolytes. The van't Hoff factor represents the number of ions produced per mole of solute dissolved in a solution.
For example, when calcium chloride (CaCl2) dissolves, it dissociates into three ions: one Ca2+ ion and two Cl- ions. Therefore, the van't Hoff factor (i) for CaCl2 is 3 because it produces three ions per mole of solute dissolved.
Similarly, when ammonium phosphate (NH4)3PO4 dissolves, it dissociates into four ions: three NH4+ ions and one PO43- ion. Thus, the van't Hoff factor (i) for (NH4)3PO4 is 4 because it yields four ions per mole of solute dissolved.
The van't Hoff factor is essential in various calculations related to colligative properties, such as boiling point elevation and freezing point depression, where it is used to account for the number of particles in solution.
learn more about electrolytes here
https://brainly.com/question/32477009
#SPJ11
29. Identify which is a property of nonmetals *
good insulator
good conductor of electricity
have luster
Omalleable
(2 Points)
Answers
Answer:
Omalleable
Explanation:
Non-metals are very brittle, and cannot be rolled into wires or pounded into sheets. Conduction: They are poor conductors of heat and electricity. Luster: These have no metallic luster and do not reflect light.
1 question content area what is the total number of valence electrons in the lewis structure of sebr2o?
Answers
There are 24 valance electrons in the compound.
What are valence electrons?We know that the valence electrons are those that are found on the valence shell of an atom. There are four atoms that can be seen in the compound that is under consideration. The atoms are selenium, bromine (2 atoms) and oxygen.
Given that there are seven valence electrons in bromine and six valence electrons in oxygen and selenium. We have;
2(7 electrons of bromine) + 6 electrons of oxygen + 4 electrons of Se
= 24 electrons
Learn more about valence electrons:brainly.com/question/8906371
#SPJ1
Brainliest to first decent answer
What is the chemical formula for the molecule represented by the model?
CHO
C4H9O2
C4H8O
C3H8O2

Answers
The correct formula of the molecule is C4H9O2.
What is a model?The model of a compound is a representation of the molecule. It gives us an idea of what the molecule looks like as well as its molecular formula.
Looking at the structure of the compound as shown in the model in the question, the correct formula of the molecule is C4H9O2.
Learn more about molecular model:https://brainly.com/question/156574?
#SPJ1
Answer:C4H9O2.
Explanation:
iodine 131 has a half life of 8.1 days, polonium 214 has a half life of 1.5 x 10-4 s, if there are the same number of unstable nuclei in samples of both, which will have the larger activity?
Answers
Polonium has a shorter Half-Life time which means it will decay much faster than iodine which, so polonium will have larger activity.
Since both of the atoms would decay to the half of their quantity, as half-life means to do so the polonium has less time as the number of unstable nuclei is same in both the cases, so it's nucleus will do fission at a higher rate, resulting in higher activity as compared to that of Iodine which has a half-life of 8 days which means it does fission at a comparatively slow rate than polonium does.
To know more about Half-Life :
brainly.com/question/16387602
#SPJ4
Look at the reaction below and state which direction the reaction would shift:
A closed container of water and its vapor at equilibrium. Vapor is added to the system.
Water + Energy <=> Vapor
Answers
A system's equilibrium will move to the right, or toward the side of the products, in accordance with Le Chatelier's principle, if more reactants are added. ... The equilibrium will move to the left if we add more product to a system, producing more reactants.
What causes the rightward tilting of equilibrium?Solution: By increasing the number of reactants, the equilibrium moves to the right and in the direction of the products.
What causes the balance to tilt to the left?Thus, if a reactant is added, equilibrium shifts to the right, away from the reactant. Equilibrium shifts to the left, away from the product, when a product is added. If we take away the product, equilibrium returns and produces the product. Reactant is created if reactant is removed, breaking the equilibrium.
To know more about Le Chatelier's principle visit :-
https://brainly.com/question/29009512
#SPJ1
what colour would the methyl orange indicator be in the hydrochloric acid?
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
The methyl orange indicator is typically yellow in an acidic solution with a pH below 4. If the solution is a hydrochloric acid, the indicator will likely turn red, as hydrochloric acid has a pH of around 1. If the solution has a pH between 4 and 6, the methyl orange indicator will appear orange.
Use the description of a process to answer the question.
1. A person eats a candy bar.
2. The person's blood sugar rises.
3. The body produces insulin to reduce the person's blood sugar.
4. The person's blood sugar drops.
5. The person returns to a healthy level of blood sugar and remains there.
In which step of the process is the person most likely at chemical equilibrium?
A) in step 2 when the person's blood sugar rises
B) in step 5 when the person returns to a healthy level of blood
sugar and remains there
C) in step 4 when the person's blood sugar drops
D) in step 3 when the body produces insulin to reduce the
person's blood sugar
Answers
answer: in step 5 when the person returns to a healthy level of blood sugars and remains there
Explanation:
Answer:
Concentrations at Equilibrium Quick Check
1. The rate of the forward and backward reactions is equal.
2. No changes will be apparent, as the forward and reverse reactions continue.
3. The reactions that happen in baking are not reversible reactions.
4. The reaction mixture is not complete as reactants are still being added to the system.
5. in step 5 when the person returns to a healthy level of blood sugar and remains there
Explanation:
100% if you put these answers.
Question 25 points)
Obsidian is a glassy black igneous rock. A sample of obsidian is shown.
Which type of rock forms in a similar manner as obsidian but at a slower
rate?
Oa
Oь
Ос .
Od
schist, which forms under extreme heat and pressure
conglomerate, which forms when different-sized sediments cement together
gypsum, which forms when water evaporates and leaves behind minerals
granite, which forms as magma cools deep underground
Answers
Answer:
Granite
Explanation:
Answer:
Granite
Explanation:
Igneous forms when rock is cooled and hardens by Magma.
And the option granite, which forms as magma cools deep underground
Hope it helps have a Good Day
Calculate the standard reaction enthalpy for the reaction below:
3Fe2O3(s) → 2Fe3O4(s) + ½O2(g)
Answers
The standard reaction enthalpy for the given reaction is +235.8 kJ/mol.
What is the standard reaction enthalpy of reaction?The standard reaction enthalpy (ΔH°) for the given reaction is determined as follows:
Equation of reaction: 3 Fe₂O₃ (s) → 2 Fe₃O₄ (s) + ½ O₂ (g)
The standard enthalpy of formation values for Fe₂O₃ (s), Fe₃O₄(s), and O₂(g) is used to calculate the standard reaction enthalpy.
ΔH° = [2 × ΔH°f(Fe₂O₃)] + [½ × ΔH°f(O₂)] - [3 × ΔH°f(Fe₃O₄)]
where;
ΔH°f(Fe₂O₃) = -824.2 kJ/mol
ΔH°f(Fe₃O₄) = -1118.4 kJ/mol
ΔH°f(O₂) = 0 kJ/mol
ΔH° = [2 × (-1118.4 kJ/mol)] + [½ × 0 kJ/mol] - [3 × (-824.2 kJ/mol)]
ΔH° = -2236.8 kJ/mol + 0 kJ/mol + 2472.6 kJ/mol
ΔH° = 235.8 kJ/mol
Learn more about standard reaction enthalpy at: https://brainly.com/question/15174388
#SPJ1
In the diagram above, how many bonds are present between the carbons?
Select one:
- 1
- 2
- 6
- 3

Answers
Answer:
3
Explanation:
The compound here is ethyne, which belongs to the alkyne group. Here, there are three pairs of electrons shared between both carbons, so the number of bonds are 3.
Why is it impossible for a solution to become both more basic and more acidic at the same time?
A. An increase in H+ concentration will decrease OH- concentration.
B. H+ and OH- ions cannot exist in the same solution.
C. H+ and OH- react to form water (H2O).
D. Acids only release hydrogen ions in the presence of bases.
Answers
An increase in H+ concentration will decrease OH- concentration is the
reason why it's impossible.
What is an Acidic and Basic compound?An acidic compound has the presence of H+ ions in them while basic
compounds have the presence of OH- ions.
In a solution , as the number of Hydrogen ions increases, it leds to a
corresponding decrease in the Hydroxide ions which is the reason why
they can't coexist at the same time.
Read more about Acidic and basic compounds here https://brainly.com/question/4046668
A solution cannot be both acidic and basic at the same time because an increase in the H+ concentration will lead to a decrease in OH- concentration in the same solution.
What is pH?pH is the degree of acidity or alkalinity of a solution.
pH = -log [H+]
Also
pOH = -log [OH-]
Mathematically, pH + pOH = 14
Thus, for a given solution, as the pH increases, pOH decreases, and vice versa.
More on pH can be found here: https://brainly.com/question/491373
help pleasee! will
give brainliest +80 pts

Answers
Answer: type the compound into your search bar then it should tell you what it is for 3. you should look up "what is the formula for -----" same thing for #4
Explanation:
Answer:
2.a. germanium tetrahydride
2.b. dinitrogen tetrabromide
2.c. diphosphorus pentasulfide
2.d. selenium dioxide
2.e. nitrogen trihydride
2.f. silicon dioxide
3.a. PO3
3.b. SiCl4
3.c. N2O5
3.e. N2O4
3.f. CO
4.a CO2
4.b. SF6
4.c. N2Cl4
4.d. CI4
4.e. PF5
4.f. P2O5
****All numbers are subscripts, please do not write them as is, but to the bottom right of them like shown in the options from question 2.
Explanation:
To name covalent compounds (NM+NM), we use prefixes.
To name covalent compounds goes as follows:
First, name the first element in the formula the normal name it has (ex. Nitrogen, Oxygen). If the first element is present more than once shown by a subscript, use a prefix that will indicate how many there are present (ex. mono, di, tri).
Next, name the second element in the compound using prefixes aswell if present more than once. These elements though, will end with -ide instead of their original name (ex. monoxide, dibromide, trichloride).
Justin drives to school heading about 3 miles north from home and then head east for 1.5 miles. it takes him 45 minutes to get to school. what was his average speed/velocity?
Answers
If Justin drives 3 miles north and 1.5 miles to the east to get to school and takes him 45 minutes, his average speed/velocity is 6 miles/hour north east.
Speed is the amount of distance traveled by an object per unit of time. On the other hand, velocity is the amount of speed and the direction it is moving. Speed is a scalar quantity while velocity is a vector quantity.
To get the speed of Justin driving from home to his school, divide the distance he traveled by the amount it took him.
speed = (3 miles + 1.5 miles) / 45 minutes(1hr/60 minutes)
speed = 6 miles/hour
Taking note of the direction he traveled, the velocity will be:
velocity = 6 miles/hour north east
Learn more about velocity here: https://brainly.com/question/80295
#SPJ4
At 2500 K, Kp is equal to 20 for the reaction Cl2(g) + F2(g) ⇌ 2 CIF(g) An analysis of a reaction vessel at 2500 K reavealed the presence of 0.18 atm Cl2, 0.31 atm F2, and 0.92 atm CIF. What will tend to happen to CIF as the reaction pro- ceeds toward equilibrium?
Answers
CIF will tend to increase as the reaction proceeds toward equilibrium.
Given that Kp is equal to 20 at 2500 K, we can calculate the initial concentrations of CIF using the ideal gas law. Let's assume the initial volume is 1 liter for simplicity.
For Cl2:
P(Cl2) = 0.18 atm
n(Cl2) = P(Cl2) * V / (RT) = 0.18 mol
For F2:
P(F2) = 0.31 atm
n(F2) = P(F2) * V / (RT) = 0.31 mol
For CIF:
P(CIF) = 0.92 atm
n(CIF) = P(CIF) * V / (RT) = 0.92 mol
Based on the balanced equation, for every 1 mole of CIF, 1 mole of Cl2 and 1 mole of F2 are consumed. Therefore, the initial moles of CIF are equal to the initial moles of Cl2 and F2.
Since the initial concentrations of CIF, Cl2, and F2 are the same, and the reaction is not at equilibrium, we can conclude that CIF will tend to increase as the reaction proceeds toward equilibrium. This is because the reaction favors the formation of CIF, as indicated by the value of Kp. As CIF forms, the concentrations of Cl2 and F2 decrease, driving the reaction in the forward direction to restore equilibrium.
for more questions on CIF
https://brainly.com/question/28297792
#SPJ8
A chemist conducts an experiment in which 2. 00 l of hydrogen gas is collected over water at 1. 00 ATM and 298. 15 K. The phrase over water means that the gas was collected by bubbling it into an inversed bottle filled with water which is sitting in a water bath. However the gas collected is now saturated with water vapor. The partial pressure of water vapor at 298. 15 K is 0. 0 300 ATM. Using Dalton's law calculate the pressure of the hydrogen gas in ATM
Answers
Answer:According to Dalton's law of partial pressures, the total pressure is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of each gas. In equation form, this looks like this ...
Pt = P1 + P2 + ...
Pt = total pressure
P1 = partial pressure of gas 1
P2 = partial pressure of gas 2
Explanation:
How many electrons are in a chromium(III) ion, Cr3+?
Answers
Answer:
24 electrons
Explanation:
In order to write the Chromium electron configuration we first need to know the number of electrons for the Cr atom (there are 24 electrons). Once we have the configuration for Cr, the ions are simple.
I hope this is correct!
Consider the following electrochemical cell in, for which E o cell = 0.18 V at 80°C: Pt | H2(g) | HCl(aq) || AgCl(s) | Ag(s) H2(g) + 2AgCl(s) ⇌ 2H+(aq) + 2Cl−(aq) + 2Ag(s)
If pH = 1.27 in the anode compartment, and [Cl−] = 3.1 M in the cathode compartment, determine the partial pressure of H2 necessary in the anode compartment for the cell to be 0.27 V at 80°C
______atm
Please show all work step by step so I can understand what I'm doing wrong, thanks!
Answers
The partial pressure of H₂ necessary in the anode compartment for the cell to be 0.27 V at 80°C is approximately 0.011 atm.
To solve this problem, we can use the Nernst equation, which relates the cell potential to the concentrations (or partial pressures) of the species involved in the electrochemical reaction. The Nernst equation is given by:
Ecell = E°cell - (RT/nF) * ln(Q)
where:
Ecell is the cell potential under non-standard conditions
E°cell is the standard cell potential
R is the gas constant (8.314 J/mol K)
T is the temperature in Kelvin
n is the number of moles of electrons transferred in the balanced equation
F is the Faraday constant (96,485 C/mol)
ln is the natural logarithm
Q is the reaction quotient, which is the product of the concentrations (or partial pressures) of the species raised to their stoichiometric coefficients.
First, we need to write the balanced equation for the electrochemical cell and determine the number of moles of electrons transferred. The balanced equation is:
H₂(g) + 2AgCl(s) ⇌ 2H+(aq) + 2Cl⁻(aq) + 2Ag(s)
The number of moles of electrons transferred is 2 (two electrons are transferred per molecule of H₂ that is oxidized).
Now, we can use the Nernst equation to find the partial pressure of H₂ necessary in the anode compartment for the cell to be 0.27 V at 80°C.
The Nernst equation in this case becomes:
Ecell = E°cell - (RT/nF) * ln(Q)
Given:
E°cell = 0.18 V
Ecell = 0.27 V
pH = 1.27
[Cl−] = 3.1 M
We need to find the partial pressure of H₂(pH₂) in the anode compartment. Since we are dealing with a gas, we can express the concentration of H₂in terms of its partial pressure using the ideal gas law:
[H₂] = pH₂ / (RT)
The reaction quotient Q can be expressed using the concentrations of the species involved in the electrochemical reaction:
Q = ([H+]² * [Ag+]) / ([Cl-]² * pH₂²)
Now let's substitute the relevant values into the Nernst equation:
0.27 V = 0.18 V - (RT/(2F)) * ln(([H+]² * [Ag+]) / ([Cl-]² * pH2²))
To solve for the partial pressure of H2 (pH2), we rearrange the equation:
ln(([H+]² * [Ag+]) / ([Cl-]²* pH2²)) = (2F/RT) * (0.18 V - 0.27 V)
Taking the exponential of both sides:
([H+]² * [Ag+]) / ([Cl-]² * pH₂²) = exp((2F/RT) * (0.18 V - 0.27 V))
Now, let's substitute the values and solve for pH2:
pH₂ = √(([H+]² * [Ag+]) / ([Cl-]² * exp((2F/RT) * (0.18 V - 0.27 V))))
Substituting the given values:
pH₂ = √((10(-2*1.27))² * 3.1 / (3.1² * exp((2 * 96485) / (8.314 * (273 + 80)) * (0.18 - 0.27))))
The partial pressure of H₂(pH₂) is approximately 0.011 atm.
Learn more about electrochemical cell
brainly.com/question/29470878
#SPJ4
The elements of the group IA are termed as alkali metals, because their ___ are alkaline.
Answers
The answer is hydroxides.
The elements of the group IA are termed as alkali metals, because their hydroxides are alkaline.
what is the ph of 0.779 m ethylammonium chloride, c2h5nh3cl. the kb of ethylamine, c2h5nh2, is 4.3 x 10-4.
Answers
The pH of 0.779 M ethylammonium chloride (C2H5NH3Cl) is 10.08. What is ethylammonium chloride? Ethylammonium chloride is a chloride salt that is formed from the reaction between ethylamine and hydrochloric acid.
Ethylamine (C2H5NH2) is the primary component in the synthesis of ethylammonium chloride. When ethylamine is added to hydrochloric acid, a white solid is formed that has the chemical composition C2H5NH3Cl.How to find pH of ethylammonium chloride?The Kb value for ethylamine is given as 4.3 x 10^-4.
The reaction for ethylamine is:C2H5NH2(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ C2H5NH3+(aq) + OH-(aq)We can assume that ethylammonium chloride is completely ionized. So, we can write:C2H5NH3Cl → C2H5NH3+ + Cl-The hydrolysis of the ethylammonium ion is given by the following equation: C2H5NH3+ (aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ C2H5NH2(aq) + H3O+(aq)Therefore, Kb = [C2H5NH2][H3O+]/[C2H5NH3+]Let's assume x is the H3O+ ion concentration. Then [C2H5NH2] = [H3O+] and [C2H5NH3+] = 0.779 - x.Substituting these values in the above equation, we get the equation: 4.3 x 10^-4 = x^2 / (0.779 - x)By solving the above equation, we can get x, which is the H3O+ ion concentration. Once we get x, we can calculate the pH of the solution, which is given by the equation:pH = - log [H3O+]Finally, by substituting the value of [H3O+] we get the pH of the solution. PH of the solution is 10.08.
learn more about ph of ethylammonium chloride at: brainly.com/question/31096747
#SPJ11
4. What mass of ethanol that has a volume of 75.0 mL?
Answers
Mass of ethanol that has a volume of 75.0 mL is 591 g
Ethanol is used in the manufacture of drugs, plastics, lacquers, polishes, plasticizers, and cosmetics
Here given data is
Volume = 75.0 mL
Density = 789kg/m³
We have to calculate mass of ethanol = ?
So the formula is density = mass/volume
Mass = volume × density
Mass = 75.0 mL×789kg/m³
Mass = 591 g
Know more about mass
https://brainly.com/question/17371618
#SPJ1
What is ionization energy?

Answers
Answer:
b) The amount of energy required to eject an electron from an atom.
distillation could not be used to separate one of the following:
a. rubbing alcohol and water
b. motor oil and brake fluid
c. sand and gold
d. gasoline fractions
i’m not sure but i think it is c
Answers
Answer:
It's motor oil and brake fluid
Magnesium metal is placed in a solution of copper(II) nitrate. How many grams of the precipitate are formed if we start with 7 g of magnesium metal and 0.5 moles of copper(II) nitrate?
Answers
According to the stoichiometry of the chemical reaction between magnesium and copper nitrate 42.72 g of precipitate is formed if we start with 7 g of magnesium metal and 0.5 moles of copper(II) nitrate.
What is stoichiometry?It is the determination of proportions of elements or compounds in a chemical reaction. The related relations are based on law of conservation of mass and law of combining weights and volumes.
Stoichiometry is used in quantitative analysis for measuring concentrations of substances present in the sample.In the given reaction , 24.3 g magnesium gives 148.3 g magnesium nitrate thus, 7 g magnesium will give , 7×148.3/24.30=42.72 g
Thus, 42.72 g of precipitate is formed if we start with 7 g of magnesium metal and 0.5 moles of copper(II) nitrate.
Learn more about stoichiometry,here:
https://brainly.com/question/9743981
#SPJ1