Similar to Hippocrates, modern scientists who study etiology believe that
sickness is caused by spiritual events such as demons entering the body.
diseases come from natural causes such as bites from infected insects.
all diseases can be cured by the right combinations of different treatments.
the best treatment for a germ is a calming practice such as yoga or massage.
Answers
In Medicine, "etiology" means the origin or cause of a disease.
Similar to Hippocrates, modern scientists who study etiology believe that diseases come from natural causes such as bites from infected insects.
Answer:diseases come from natural causes such as bites from infected insects
Explanation: just took test
Related Questions
A marshmallow is fired from ground level with an initial speed of 41.5 m/s at an
angle of 33.5° above the horizontal. (a) Determine the maximum height reached
by the marshmallow. (b) Determine the horizontal range that the marshmallow
travels during its flight.
Answers
S=? t=2.34 a=0 u=41.5cos(33.5)
s= (41.5cos(33.5))(2.34)+1/2(0)
s=80.98 meters
this is the horizontal range

A car accelerates uniformly from rest tona speed of 30.0 mi/h in 12.0s. Find the distance the car travels during this time? Find the constant acceleration of the car?
Answers
Answer:
2.5 mi/s^2
Explanation:
please see paper for work!

RI, SI
-HALF-LIVES-
DIRECTIONS: Each circle represents the sample of parent and daughter material after
half-life. Shade the fraction of the circle that is pareat material. Write the fraction belom the
circle. The element that you are working with is a hypothetical and is called Brownlim. The
half-life of Brownism is 500 years.
оно
Ө 10
о
роз
о
010
Answers
If you need to shade the part of a circle indicative of parent material, these are the guidelines:
Start by drawing a circle that embodies the entire region under discussion.Assess the proportion of the circle illustrating the parent material. Suppose that the parent material comprises 60% of the total surface area; in this instance, you would have to fill in or darken 60% of the circle.How to explain the informationIt should be noted that to complete the shading process, employ techniques such as utilizing solid colors with pencils, markers, cross-hatching, or diagonal lines.
Ensure that you correctly portray the shaded fraction of the circle and provide clear contrasts between the unshaded segment.
Learn more about fractions on
https://brainly.com/question/78672
#SPJ1
In hiking, what fitness component is required of you
Answers
Can seem to get (c) correct. The one with the red x

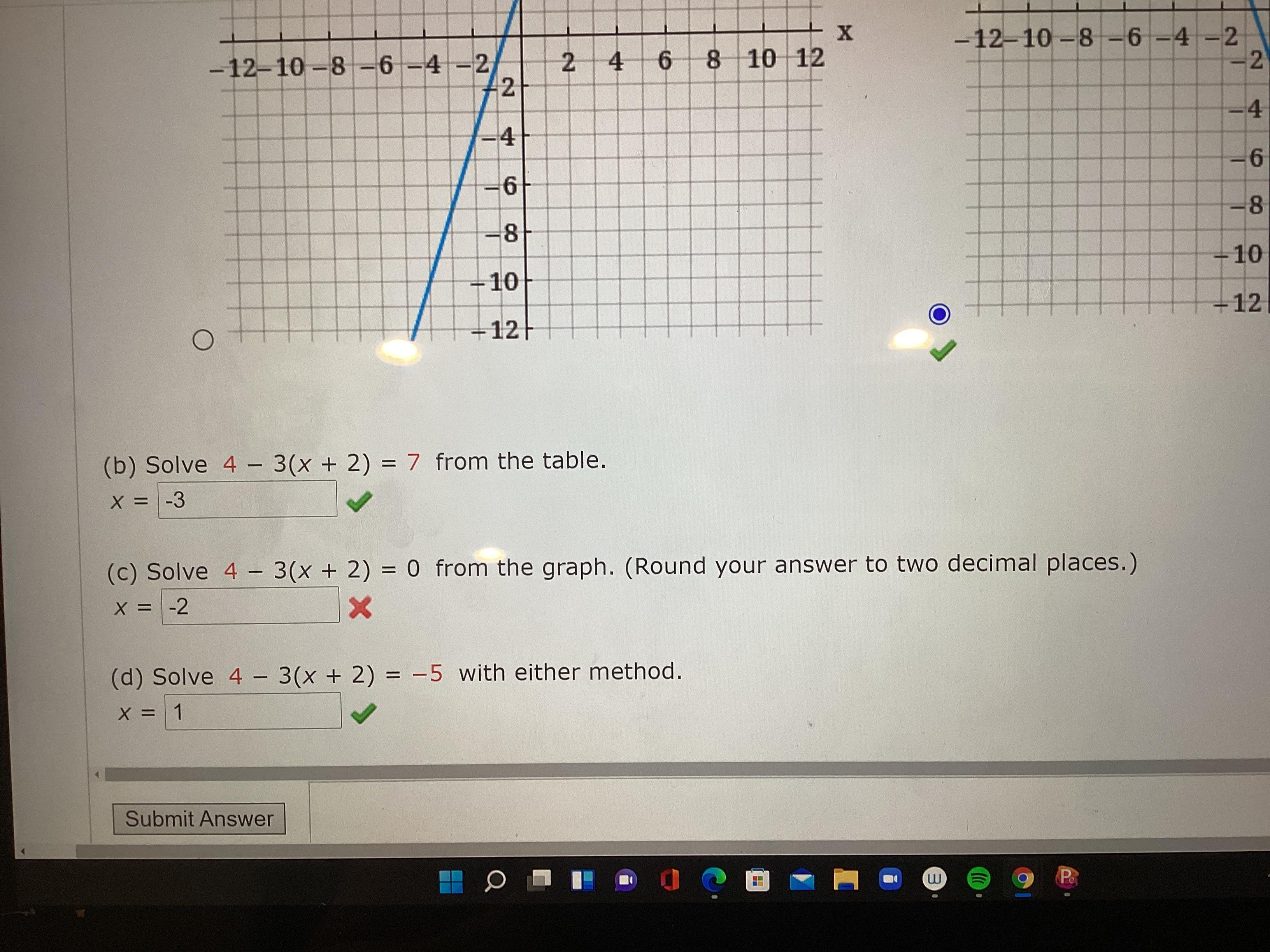
Answers
We are given the following equation:
\(4-3(x+2)=0\)We are asked to solve for "x". To do that we will subtract 4 from both sides:
\(\begin{gathered} 4-4-3(x+2)=-4 \\ -3(x+2)=-4 \end{gathered}\)Now we will divide both sides by -3:
\(\begin{gathered} \frac{-3(x+2)}{-3}=-\frac{4}{-3} \\ \\ x+2=\frac{4}{3} \end{gathered}\)Now we will subtract 2 from both sides:
\(\begin{gathered} x+2-2=\frac{4}{3}-2 \\ x=-\frac{2}{3} \end{gathered}\)Therefore, the value of "x" is -2/3.
A wildebeest calf is cruising at its top speed of v= 10 m/s when it passes over a sleeping cheetah. By the time the cheetah stands up and begins pursuit, the wildebeest is d= 7.0 ma head of the cheetah. If the cheetah is able to maintain a constant acceleration of a= 9.5 m/s^2until it catches the wild-beast, then how much time t must pass before the cheetah catches up to the wildebeast? (Hint: you will need to usethe quadratic formula.) For the limits check, investigate what happens to t as the initial separation distance approaches zero.
Answers
The time when the cheetah catches up with the widebeest is 1.53 s
If the initial separation distance approaches zero, it will take the cheetah 1.05 s to catch the widebeest.
The given parameters;
speed of the wildebeest calf, Vw = 10 m/sdistance traveled by the calf before the cheetah stands up = 7 mconstant acceleration of the cheetah, a = 9.5 m/s²Let the speed of the cheetah = Vc
let the time the cheetah catches up with the wildebeest = t
\(a = \frac{V_c}{t}\)
\(V_c = at\)
Apply relative velocity formula to determine the time when the cheetah catches up with the widebeest;
Assuming the wildebeest and the cheetah are running in the same direction;
\((V_c - V_w) t = 7 \\\\(at - V_w) t = 7\\\\(9.5t - 10)t = 7\\\\9.5t^2 - 10t = 7\\\\9.5t^2 -10t-7 = 0\\\\solve \ the \ quadratic \ equation \ using \ formula \ method;\\\\a = 9.5 \ b= -10 \ , c =-7\\\\t = \frac{-b \ \ +/- \ \ \sqrt{b^2-4ac} }{2a} \\\\t = \frac{-(-10)\ \ +/- \ \ \sqrt{(-10)^2-4(9.5\times -7)} }{2(9.5)}\\\\t = \frac{10 \ \ +/- \ \ 19.13}{19} \\\\t = 1.53 \ s\)
The time when the cheetah catches up with the widebeest is 1.53 s
If the initial separation distance approaches zero;
\((V_c - V_w) t = 0\\\\(at - V_w) t = 0\\\\(9.5t - 10)t = 0\\\\9.5t^2 - 10t = 0\\\\9.5t^2 = 10t\\\\9.5t = 10\\\\t = \frac{10}{9.5} = 1.05 \ s\)
Thus, if the initial separation distance approaches zero, it will take the cheetah 1.05 s to catch the widebeest.
Lear more here: https://brainly.com/question/24430414
1000N and pa = 10 ^8 .then find area
Answers
Pressure in pa = (total force) x (area)
10⁸ pa = (1000 N) x (area)
Divide each side of the equation by 1000N.
10⁸ pa/1000N = area
area = 10⁵ square meters
A 0.125 kg mass is placed on a vertically oriented spring that is stretched 0.32 meters from its equilibrium position. If the spring constant is 250 N/m, how fast will the mass be moving when it reaches the equilibrium position? Hint: you cannot ignore the change in gravitational potential energy in this problem. Please give your answer in units of m/s.
Answers
The mass will be moving at 14.3 m/s when it reaches the equilibrium position.
To determine the speed of the mass when it reaches the equilibrium position, we need to consider the conservation of mechanical energy, which includes both the spring potential energy and the gravitational potential energy.
The total mechanical energy (E) of the system is the sum of the potential energy and the kinetic energy:
E = PE (potential energy) + KE (kinetic energy)
At the equilibrium position, all the potential energy is converted into kinetic energy, so the total mechanical energy is entirely in the form of kinetic energy.
The potential energy stored in the spring (PE_spring) is given by Hooke's Law:
PE_spring = (1/2) * k * \(x^{2}\)
Where k is the spring constant (250 N/m) and x is the displacement from the equilibrium position (0.32 m).
PE_spring = (1/2) * 250 N/m *\((0.32 m)^2\)
PE_spring = 12.8 J
The change in gravitational potential energy (ΔPE_gravity) is given by:
ΔPE_gravity = m * g * h
Where m is the mass (0.125 kg), g is the acceleration due to gravity (9.8 m/\(s^2\)), and h is the change in height (which is zero in this case since the height doesn't change).
ΔPE_gravity = 0 J
Therefore, the total mechanical energy (E) is equal to the potential energy stored in the spring:
E = PE_spring
E = 12.8 J
Since the total mechanical energy is entirely in the form of kinetic energy at the equilibrium position, we can calculate the speed (v) using the equation:
E = (1/2) * m * \(v^2\)
Rearranging the equation, we get:
\(v^2\) = (2 * E) / m
\(v^2\) = (2 * 12.8 J) / 0.125 kg
\(v^2\) = 204.8 \(m^2\)/\(s^2\)
Taking the square root of both sides:
v = √ 204.8 \(m^2\)/\(s^2\)
v ≈ 14.3 m/s
Therefore, the mass will be moving at approximately 14.3 m/s when it reaches the equilibrium position.
know more about kinetic energy here:
https://brainly.com/question/8101588
#SPJ8
The arrows in the figure represent the
gravitational force between marbles that have
equal mass.
How should the force arrows look if a marble
that has greater mass replaces one of these
marbles?
A. Both arrows should be drawn longer.
B. Both arrows should stay the same length.
C. The arrow from the marble with less mass
should be longer than the other arrow.
D. The arrow from the marble with less mass
should be shorter than the other arrow.

Answers
Option D. The arrow from the marble with less mass should be shorter than the other arrow if a marble that has greater mass replaces one of these marbles.
Force arrows are used to show both the magnitude and direction of forces. The length of the arrow corresponds to the magnitude of the force, longer arrows indicate forces of greater magnitude. The direction of the arrow corresponds to the actual direction of the force.
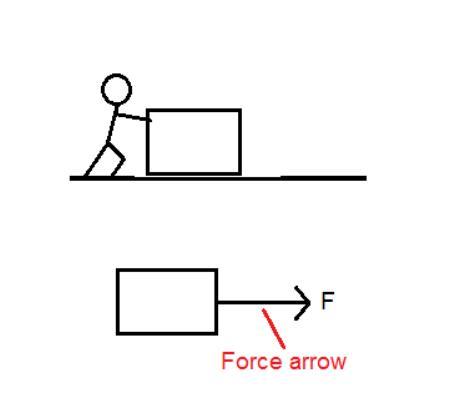
For example if a man pushes a block then the force exerted by that man and the direction of force can be represented as shown in the picture.
Since given figure shows marbles of equal mass therefore the arrows are equal. Further if the marble is replaced by the heavier marble than the arrow size will definitely change.
To know more about Force arrows,
https://brainly.com/question/27943165
#SPJ1
Electric circuits provide energy for light bulbs. Which of these prevents the flow of electrons?
O a circuit that is closed
O a series circuit
O a circuit that is open
O a parallel circuit
Answers
A circuit that is closed prevents the flow of electrons. So, the correct option is A.
What is an Electric circuit?An electrical circuit is defined as an interconnection of electrical components or a model of such interconnection, consisting of electrical elements. An electrical circuit is described as a network consisting of a closed loop, which provides a return path for current.
A closed circuit is required to carry current. When there is a break anywhere in the path, the circuit will open and no current will flow, and the metal atoms in the wire will quickly become cool and electrically neutral.
Thus, a circuit that is closed prevents the flow of electrons. So, the correct option is A.
Learn more about Electric circuit, here:
https://brainly.com/question/29583307
#SPJ6
You are flying a hang glider at 14 mph in the northeast direction (45°). The wind is blowing at 4 mph from due north.
a) What is your airspeed?
b) What angle (direction) are you flying?
c) The wind increases to 14 mph from the north. Now what is your airspeed and what direction are you flying? If your destination is to the northeast, how would you change your speed or direction so you might make it there?
Answers
Answer:
a) 17.05 mph
b) 54.7° northeast direction
c) 10.71 mph
The direction is -22.58° relative to the east.
To head northeast, you must either increase your gliding speed or increase your angle relative to the x-axis greater than 45°.
Explanation:
The question is a little confusing but, I guess the correct question should be;
You are flying a hang glider at 14 mph in the northeast direction (45°). The wind is blowing at 4 mph due north.
a) What is your airspeed?
b) What angle (direction) are you flying?
c) The wind increases to 14 mph from north. Now what is your airspeed and what direction are you flying? If your destination is to the northeast, how would you change your speed or direction so you might make it there?
NB: The difference in the question and my suggestion is highlighted boldly.
Your speed = 14 mph
direction is 45° northeast
Th wind speed = 4 mph
direction is north
We resolve the your speed and the wind speed into the horizontal and vertical components
For vertical the component component
\(V_{y}\) = 14(sin 45) + 4 = 9.89 + 4 = 13.89 mph
For the horizontal speed component
\(V_{x}\) = 14(cos 45) + 0 = 9.89 + 0 = 9.89 mph
Resultant speed = \(\sqrt{V^{2} _{y}+V^{2} _{x} }\)
==> \(\sqrt{13.89^{2} +9.89^{2} }\) = 17.05 mph This is your airspeed
b) To get your direction, we use
tan ∅ = \(V_{y}\) /\(V_{x}\)
tan ∅ = 13.89/9.89 = 1.413
∅ = \(tan^{-1}\)(1.413) = 54.7° northeast direction
c) If the wind increases to 14 mph from the north, then it means the wind blows due south. As before, only the vertical component is affected .
In this case,
\(V_{y}\) = 14(sin 45) - 14 = 9.89 - 14 = -4.11 mph
Resultant speed = \(\sqrt{V^{2} _{y}+V^{2} _{x} }\)
==> \(\sqrt{4.11^{2} +9.89^{2} }\) = 10.71 mph This is your airspeed
Your direction will be,
tan ∅ = \(V_{y}\) /\(V_{x}\)
tan ∅ = -4.11/9.89 = -0.416
∅ = \(tan^{-1}\)(-0.416) = -22.58° this is the angle you'll travel relative to the east.
To head northeast, you must either increase your gliding speed or increase your angle relative to the x-axis greater than 45°.
Mark weighs 375 N and is carrying a full-sized cello as he climbs the stairs to a height of 4 m. It takes him 3 seconds to do this.
How does the amount of work he does change if he were to climb the same flight of stairs again in the same amount of time, but this time without the cello?
A) It depends on the weight of the cello.
B) It remains the same.
C) It increases
D) It decreases.
Answers
Mark's work decreases when he climbs the same flight of stairs again in the same amount of time without the cello.
The correct answer is option D.
The amount of work Mark does depends on the weight of the cello, as well as the distance he climbs and the time it takes. Work is calculated using the formula :
Work = Force × Distance.
In the given scenario, Mark is carrying a full-sized cello while climbing the stairs. The weight of the cello adds to the force he exerts. So, the total force Mark exerts is the weight of the cello plus his own weight (375 N).
When Mark climbs the stairs with the cello, he is doing work against the force of gravity.
The work done is equal to the force exerted multiplied by the distance climbed (375 N + weight of cello) × 4 m.
Now, if Mark were to climb the same flight of stairs again in the same amount of time (3 seconds), but this time without the cello, the amount of work he does would decrease. This is because without the cello, the force exerted would only be Mark's weight (375 N), which is less than the total force exerted with the cello.
Therefore, mark's work decreases.
For more such questions on work visit:
https://brainly.com/question/28356414
#SPJ8
Can someone explain how to do the algebra for this question? I know everything else, I just don’t know how to rearrange the question to solve for v.

Answers
Answer:
Refer to the step-by-step Explanation.
Step-by-step Explanation:
Simplify the equation with given substitutions,
Given Equation:
\(mgh+(1/2)mv^2+(1/2)I \omega^2=(1/2)mv_{_{0}}^2+(1/2)I \omega_{_{0}}^2\)
Given Substitutions:
\(\omega=v/R\\\\ \omega_{_{0}}=v_{_{0}}/R\\\\\ I=(2/5)mR^2\)\(\hrulefill\)
Start by substituting in the appropriate values: \(mgh+(1/2)mv^2+(1/2)I \omega^2=(1/2)mv_{_{0}}^2+(1/2)I \omega_{_{0}}^2 \\\\\\\\\Longrightarrow mgh+(1/2)mv^2+(1/2)\bold{[(2/5)mR^2]} \bold{[v/R]}^2=(1/2)mv_{_{0}}^2+(1/2)\bold{[(2/5)mR^2]}\bold{[v_{_{0}}/R]}^2\)
Adjusting the equation so it easier to work with.\(\Longrightarrow mgh+\dfrac{1}{2} mv^2+\dfrac{1}{2} \Big[\dfrac{2}{5} mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v}{R} \Big]^2=\dfrac12mv_{_{0}}^2+\dfrac12\Big[\dfrac25mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v_{_{0}}}{R}\Big]^2\)
\(\hrulefill\)
Simplifying the left-hand side of the equation:
\(mgh+\dfrac{1}{2} mv^2+\dfrac{1}{2} \Big[\dfrac{2}{5} mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v}{R} \Big]^2\)
Simplifying the third term.
\(\Longrightarrow mgh+\dfrac{1}{2} mv^2+\dfrac{1}{2} \Big[\dfrac{2}{5} mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v}{R} \Big]^2\\\\\\\\\Longrightarrow mgh+\dfrac{1}{2} mv^2+\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot \dfrac{2}{5} \Big[mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v}{R} \Big]^2\\\\\\\\\Longrightarrow mgh+\dfrac{1}{2} mv^2+\dfrac{1}{5} \Big[mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v}{R} \Big]^2\)
\(\\ \boxed{\left\begin{array}{ccc}\text{\Underline{Power of a Fraction Rule:}}\\\\\Big(\dfrac{a}{b}\Big)^2=\dfrac{a^2}{b^2} \end{array}\right }\)
\(\Longrightarrow mgh+\dfrac{1}{2} mv^2+\dfrac{1}{5} \Big[mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v^2}{R^2} \Big]\\\\\\\\\Longrightarrow mgh+\dfrac{1}{2} mv^2+\dfrac{1}{5} \Big[mR^2 \cdot\dfrac{v^2}{R^2} \Big]\)
"R²'s" cancel, we are left with:
\(\Longrightarrow mgh+\dfrac{1}{2} mv^2+\dfrac{1}{5} \Big[mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v^2}{R^2} \Big]\\\\\\\\\Longrightarrow mgh+\dfrac{1}{2} mv^2+\dfrac{1}{5}mv^2\)
We have like terms, combine them.
\(\Longrightarrow mgh+\dfrac{1}{2} mv^2+\dfrac{1}{5} \Big[mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v^2}{R^2} \Big]\\\\\\\\\Longrightarrow mgh+\dfrac{7}{10} mv^2\)
Each term has an "m" in common, factor it out.
\(\Longrightarrow m(gh+\dfrac{7}{10}v^2)\)
Now we have the following equation:
\(\Longrightarrow m(gh+\dfrac{7}{10}v^2)=\dfrac12mv_{_{0}}^2+\dfrac12\Big[\dfrac25mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v_{_{0}}}{R}\Big]^2\)
\(\hrulefill\)
Simplifying the right-hand side of the equation:
\(\Longrightarrow \dfrac12mv_{_{0}}^2+\dfrac12\cdot\dfrac25\Big[mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v_{_{0}}}{R}\Big]^2\\\\\\\\\Longrightarrow \dfrac12mv_{_{0}}^2+\dfrac15\Big[mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v_{_{0}}}{R}\Big]^2\\\\\\\\\Longrightarrow \dfrac12mv_{_{0}}^2+\dfrac15\Big[mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v_{_{0}}^2}{R^2}\Big]\\\\\\\\\Longrightarrow \dfrac12mv_{_{0}}^2+\dfrac15\Big[mR^2\cdot\dfrac{v_{_{0}}^2}{R^2}\Big]\\\\\\\\\Longrightarrow \dfrac12mv_{_{0}}^2+\dfrac15mv_{_{0}}^2\Big\\\\\\\\\)
\(\Longrightarrow \dfrac{7}{10}mv_{_{0}}^2\)
Now we have the equation:
\(\Longrightarrow m(gh+\dfrac{7}{10}v^2)=\dfrac{7}{10}mv_{_{0}}^2\)
\(\hrulefill\)
Now solving the equation for the variable "v":
\(m(gh+\dfrac{7}{10}v^2)=\dfrac{7}{10}mv_{_{0}}^2\)
Dividing each side by "m," this will cancel the "m" variable on each side.
\(\Longrightarrow gh+\dfrac{7}{10}v^2=\dfrac{7}{10}v_{_{0}}^2\)
Subtract the term "gh" from either side of the equation.
\(\Longrightarrow \dfrac{7}{10}v^2=\dfrac{7}{10}v_{_{0}}^2-gh\)
Multiply each side of the equation by "10/7."
\(\Longrightarrow v^2=\dfrac{10}{7}\cdot\dfrac{7}{10}v_{_{0}}^2-\dfrac{10}{7}gh\\\\\\\\\Longrightarrow v^2=v_{_{0}}^2-\dfrac{10}{7}gh\)
Now squaring both sides.
\(\Longrightarrow \boxed{\boxed{v=\sqrt{v_{_{0}}^2-\dfrac{10}{7}gh}}}\)
Thus, the simplified equation above matches the simplified equation that was given.
Can you list the offensive position on a flag football team?
Answers
Answer:
yes u can flag football has everything that pad football has so you can enlist on being offensive position but you have to play like you want that position
Explanation:
20. For each improvement in glider design, engineers follow
O A. the written instructions that are provided in the hang glider build kit.
O B. an iterative process of testing, modifying, retesting, and modifying again.
O C. a complicated process of checks and balances while obtaining financing.
O D. a mathematical process, rejecting designs that don't follow blueprint dimensions.
Turn In

Answers
A 3.00kg mass is attached to an ideal spring with k=200N\m if the velocity of body at 0.25m Is 2.3m\s find the amplitude and maximum velocity
Answers
To solve this we must be knowing each and every concept related to velocity. Therefore, the amplitude and maximum velocity are 0.23 m and 2.75 m/s respectively.
What is velocity?V is the velocity measurement of an object's rate of motion and direction of motion. As a result, in order to calculate velocity using this definition, we must be familiar with both magnitude and direction.
For example, if an item travels west with 5 meters a second (m/s), its velocity to the west will be 5 m/s. The most frequent and simplest approach to determine velocity is using the formula shown below.
v = √(k / m) ×A
v = velocity of the mass
k= spring constant
m =mass of the object
A= amplitude of the oscillation.
substituting all the given values in the above equation, we get
2.3 m/s = √(200 N/m / 3.00 kg)×A
A = 2.3 m/s / √(200 N/m / 3.00 kg)
= 0.23 m
v =√(200 N/m / 3.00 kg) ×0.23 m
= 2.75 m/s
Therefore, the amplitude and maximum velocity are 0.23 m and 2.75 m/s respectively.
To learn more about velocity, here:
https://brainly.com/question/13372043
#SPJ1
if the body is floating in a liquid then can we say that the rise in the level of the liquid is equal to the height of the body
Answers
Yes, if a body is floating in a liquid, the rise in the liquid level is equal to the body height. This phenomenon is known as Archimedes' principle.
Archimedes' principle says when a body is immersed in a fluid (liquid or gas), it experiences an upward buoyant force equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the body. Buoyant forces act in the opposite direction to gravity.
When a body floats in a liquid, it displaces a volume of liquid equal to its volume. As a result, the liquid level rises by an amount equal to the height of the submerged part of the body.
This principle holds for objects that float or are partially immersed in a liquid, such as a buoyant boat or a floating object. However, if the body sinks completely into the liquid, the liquid level rise will no longer be equal to its height. Instead, it depends on the density and volume of the submerged object.
Question 4 of 25
A person drops two objects from the same height. One object weighs 15 N,
and the other weighs 10 N. How does the mass of the objects relate to the
force of gravity on them?
A. The 15 N object has twice the mass of the 10 N object.
B. The 15 N object has more mass than the 10 N object.
C. The 10 N object has more mass than the 15 N object.
D. The 10 N object has the same mass as the 15 N object.
Answers
Which of the following statements is NOT true about sunspots?
А
Sunspots appear and disappear in a cycle that lasts approxi-
mately 15 years.
B
Sunspots occur in pairs.
с
Sunspots are darker because they are cooler than the surround
area.
D
none of the above
Answers
REAL ANSWERS ONLY PLS

Answers
Answer:
The statement of the student is correct.
Since B attained a higher velocity in a short amount of time, that is it accelerated faster(having a larger slope).
Slope = dy/dx
That is, Velocity
Time
which is acceleration.
That's my guess.
Hope it's right.
Background information:
We know that power is the rate that work is done; what that
really means is that power tells up how much work is done every
second. To calculate power we just divide the amount of work that
was done by the time it took to do it (Power=work/time). Work is
measured in Joules and time is measured in seconds, we end up with Joules/sec when we calculate power. A Joule/sec is a Watt; we’ll use Watts to measure and compare power.
We also know that the work done on an object is the amount of energy it has gained. For this activity, you’ll be raising your body up as you do pushups which means you’ll be giving your body gravitational potential energy (GPE). To calculate the amount of GPE we multiply mass time gravity times the height raised (GPE=mgh).
What to do (record everything in the table):
1. You need to have a decent estimate of your mass in kilograms: On earth, every
kilogram weighs 2.2 pounds. Either measure your weight on a scale or just
estimate it (in pounds) then divide by 2.2 to get your mass in kilograms.
2. Measure or estimate the length of your upper arm from your elbow to your
shoulder in centimeters...this is how high you raise yourself for every pushup.
3. Decide if you’ll do regular pushups (on your toes) or simpler pushups (knees). If
you are doing regular pushups, multiply your mass by 0.68 because you’ll only be lifting about 68% of your mass each time; if you’re doing simpler pushups, multiply your mass by 0.52 because you’ll only be lifting about 52% of your mass each time.
4. Measure the time it takes for you to do 10 pushups.

Answers
Answer:
Power is the rate at which work is done. It is the work/time ratio. Mathematically, it is computed using the following equation. The standard metric unit of power is the Watt.
Explanation:
what is light emitting diode
Answers
Answer:
A light emitting diode (a semiconductor diode which glows when voltage is applied.
how in a simple machine direction changer
Answers
In a simple machine the direction changes by using the pulley. By applying the force on the pulley, by pushing down and the object moves up.
The simple machine allows to change the direction is a pulley. The pulley machine acts as a direction changer and is also used to change the direction of the force. When the wheel rotates, the cord can move in either direction.
The pulley has a wheel and hook. By attaching the hook to the cord, the wheel rotates making the object move up or down much easier when the force is applied to the pulley. These machines use pivot points to balance.
Hence, the simple machine called a pulley, is used to change the direction of force and makes the object moves up.
To learn more about Pulley:
https://brainly.com/question/28974480
#SPJ1
ASAP what causes the earth to orbit just like Mars
Answers
Answer:
Like all the planets in our solar system, Earth and Mars orbit the sun. But Earth is closer to the sun, and therefore races along its orbit more quickly. Earth makes two trips around the sun in about the same amount of time that Mars takes to make one trip.
Two long straight wires are parallel and 9.5 cm apart. They are to carry equal currents such that the magnetic field at a point halfway between them has magnitude 280 T.
(a) Should the currents be in the same or opposite directions?
(b) How much current is needed?
Answers
Answer:
(a) the current will flow in opposite direction
(b) the current needed is 33.25 A
Explanation:
(a) At the center of the two parallel wires, the two wires will have the same magnitude of magnetic field. In order to have a non a zero value of magnetic field at the center, the field must be in the same direction and the current will flow in opposite direction according to right hand rule.
(b) How much current is needed
Given;
distance between the two parallel wires, d = 9.5 cm = 0.095 m
magnitude of magnetic field at a point halfway between the wires, \(B_c\) = 280 μT (This unit was corrected to obtain feasible current)
The magnetic field at distance R due to an infinite wire is given by;
\(B = \frac{\mu_o I}{2\pi R}\)
At the center of the wire, \(B_c = 2B\)
\(B_c = 2(\frac{\mu_o I}{2\pi R} )\\\\B_c = \frac{\mu_o I}{\pi R}\)
where;
μ₀ is permeability of free space = 4π x 10⁻⁷ m/A
R is the center point between the wires, R = d/2 = 0.095m / 2 = 0.0475 m
I is the current needed
\(B_c = \frac{\mu_o I}{\pi R} \\\\I = \frac{B_c \pi R}{\mu_o} \\\\I = \frac{280* 10^{-6}*\pi *0.0475}{4\pi *10^{-7}} \\\\I = 33.25 \ A\)
The resultant of three vectors is 90.00 cm 34o N of W. If two of these three vectors are 17.89 cm 27o W of S, and 36.00 cm NW, what is the magnitude and direction of the third vector? (Ans: 57.85 cm, 44.76o N of W)
Answers
Answer:
Magnitude of the third vector: 57.85 cm
The direction of the third vector: 44.76 N of W
Explanation:
Light travels from rarer medium 1 to a denser medium 2. The angle of incident and refraction are respectively 450 and 300. Calculate the (i) refractive index of second medium with respect to the first medium and (ii) refractive index of medium 1 with respect to the medium 2.
Answers
The refractive index of the second medium with respect to the first medium is 0.707. The refractive index of medium 1 with respect to medium 2 is 1.414.
The refractive index of an optical medium is a dimensionless wide variety that offers an indication of the light bending capacity of that medium. The refractive index determines how a good deal of the path of mild is bent or refracted while entering a material.
Angle of incidence = 45°
The angle of refraction = 30°
According to the laws of refraction = the angle of incidence/angle of refraction
Mediun 1 = rearer
Medium 2 = denser
(i) refractive index of the second medium with respect to the first medium
refractive index = sin 30°/sin 45°
= 1/2 / 1/\(\sqrt{2\)
= \(\sqrt{2\)/2
= 0.707
(ii) refractive index of medium 1 with respect to the medium 2
refractive index = sin 45°/sin 30°
= 1/\(\sqrt{2\)/1/2
= 2/√2
= 1.414
Learn more about the refractive index here:-https://brainly.com/question/10729741
#SPJ9
Which one of the following has exactly 3 significant figures?
A. 0.0451
B. 450
C. 32.10
D. 370.0
Answers
Because leading zeros don’t count
Which of the following is NOT true about the mass of an object?
A)
Mass is measured in kilograms.
B)
Mass is a measurement of force.
C)
Mass is a measurement of the amount of matter in an object.
D)
Mass does not change based on your location.
Answers
Answer:
B) Mass is a measurement of force
Explanation:
Mass is not a measurement of force, mass is a measurement of the amount of matter in an object.
_______, ________, and ________ are renewable resources.
biomass energy, hydropower, and coal energy
hydropower, coal energy, and wind energy
biomass energy, hydropower, and wind energy
biomass energy, coal energy, and wind energy
✎help its an exam✎ ☕︎if any links I WILL REPORT☕︎
Answers
Answer:
biomass energy, hydropower and wind energy