Not a good idea to contribute to the protection of the environment? a. recycle waste products b. buy magazines and newspapers online c. turn off appliances that aren't in use d. water ur garden between 11 and 15
Answers
Buy magazines and newspapers online and water ur garden between 11 and 15 Not a good idea to contribute to the protection of the environment. Thus, option "B and D" is the answer.
How can we reduce pollution?When we carpool to work, that reduces the number of cars on the road which reduces air pollution. Landscaping with native plants means that there is less resource usage because the plants have adapted to the area.
Reducing the waste you have by recycling goods and also maintaining cars will ensure that pollution is reduced.
Find out more on reducing pollution at
brainly.com/question/940272.
#SPJ1
Related Questions
What is distillation?
Answers
Answer:
Distillation is the action of purifying a liquid by a process of heating and cooling.
Describe the process of succession using the 6 steps from the video.
Answers
In biology, succession refers to the process of change in the species structure of an ecological community over time.
How does succession happen ?There are two forms of succession: primary and secondary. Primary succession commences in regions where there is barren soil, for instance, on bare rock or sand. This form starts with the colonization of pioneer species like mosses and lichens which help erode the surface, gradually creating favorable soil conditions. As a result, other animals and plants can move into the area to establish themselves.
Secondary succession, however, takes place in areas already habited by organisms - disturbed or ruined due to external factors such as wildfire, floods, and human interaction; thereby imposing substantial ecological modifications.
Find out more on succession at https://brainly.com/question/13731138
#SPJ1
Explain the processes involved in the transportation of absorbed
nutrients throughout the body.
Answers
Answer:
Absorption: The process of absorbing nutrients occurs primarily in the small intestine. Once the food is broken down into smaller molecules through digestion, these molecules are absorbed into the bloodstream. For example, carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars, proteins into amino acids, and fats into fatty acids and glycerol.
Circulatory System: The circulatory system, composed of the heart, blood vessels, and blood, plays a crucial role in transporting absorbed nutrients. The blood vessels form an extensive network that reaches all tissues and organs in the body.
Hepatic Portal System: After absorption, most of the nutrients are transported to the liver through a specialized system called the hepatic portal system. This system ensures that the liver, which performs various metabolic functions, receives a concentrated supply of nutrients before they are distributed throughout the body.
Bloodstream Transport: Once in the bloodstream, nutrients are carried by the plasma, the liquid component of blood. Different nutrients use specific mechanisms for transport:
Glucose: It is transported by facilitated diffusion or active transport, depending on the concentration gradient, with the help of insulin.
Amino Acids: They are transported through the bloodstream by specific carrier proteins.
Fats: Dietary fats are initially packaged into structures called chylomicrons and transported through the lymphatic system before entering the bloodstream. Once in the bloodstream, fats are carried by lipoproteins such as low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL).
Distribution to Tissues: As the blood circulates, nutrients are distributed to various tissues and organs according to their specific needs. Nutrients are delivered to cells through the capillaries, the smallest blood vessels in the body, which have thin walls that allow for the efficient exchange of nutrients and waste products.
Cellular Uptake: Nutrients are taken up by cells through various mechanisms. For instance, glucose enters cells with the help of insulin, while amino acids are transported into cells through specific carrier proteins. Fats are taken up by cells through receptor-mediated endocytosis or by diffusion.
Metabolism: Once inside the cells, nutrients undergo metabolic processes to produce energy or build new molecules. Glucose, for example, can be metabolized through glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation to generate ATP, the cell's energy currency.
Waste Removal: Metabolic byproducts, such as carbon dioxide and urea, are generated during nutrient metabolism. These waste products are transported back into the bloodstream and eventually eliminated from the body through the lungs (carbon dioxide) or the kidneys (urea).
It's important to note that different nutrients may have different transport mechanisms and pathways. The body's ability to efficiently transport and utilize absorbed nutrients is vital for maintaining proper functioning and overall health.
What is mercury bioaccumulation? What are the main issues with that type of bioaccumulation?what organisms does it affect? What are the causes? What could humans do to prevent it?
Answers
Bioaccumulation is the total accumulation of certain chemicals/contaminants in an organism, coming from diverse sources such as water, air, and diet. Therefore the case of mercury occurs when mercury is accumulated in an organism, for example, fish. The most common pathway for this to happen is through the food chain, nonetheless can occur through abiotic means, an example is in fish, where methylmercury is acquired through the gills.
When methylmercury is absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract & enters the bloodstream and goes rapidly to other parts of the body.
Mercury is a persistent substance, which can bioaccumulate, in living organisms, inflicting increasing levels of harm on higher-order species such as predatory fish and fish-eating birds and mammals through a process known as "biomagnification"
The release of processed mercury can lead to a progressive increase in the amount of atmospheric mercury, which enters the atmospheric-soil-water distribution cycles where it can remain in circulation for years. Mercury poisoning is the result of exposure to mercury or mercury compounds resulting in various toxic effects depending on its chemical form and route of exposure.
The major route of human exposure to methylmercury (MeHg) is largely through eating contaminated fish, seafood, and wildlife that have been exposed to mercury through the ingestion of contaminated lower organisms.
King mackerel, marlin, orange roughy, shark, swordfish, tilefish, ahi tuna, and all contain high levels of mercury.
Human activity is the main cause of mercury release, especially coal-fired power stations, residential coal burning for heating and cooking, industrial processes, waste incinerators, and as a result of mining for mercury, gold, and other metals.
Reducing consumption of raw materials and products generating mercury releases
Substitution by non-mercury alternativesEnd-of-pipe techniquesWaste managementWhat is the best overall approach to reducing emissions?What further research and information are needed?National initiativesRegional and international initiativesTo learn more about mercury bioaccumulation visit,
https://brainly.com/question/12536211
5. The mechanism for evolution is natural selection. Traits become more or less
common in a population depending on whether they are beneficial or harmful.
An example of evolution by natural selection can be found in the deer mouse,
species Peromyscus maniculatus. In Nebraska this mouse is typically brown, but
after glaciers carried lighter sand over the darker soil in the Sand Hills, predators
could more easily spot the dark mice. Natural selection favored the light mice,
and over time, the population became light colored. What was the environmental
change that resulted in a change in the deer mouse?
O A. The Ice Age
O B. Environment changed color
O C. Became colder
O D. No change
Answers
Answer: A
Explanation: the ice age posed a new chalenge to deer mice and on the ice the preadators could spot the darker deer mice better than the light deer mice.
When storm clouds produce lightning and thunder,
electric potential
energy changes to
energy and
energy.
Answers
Which of the following statements is/are false for all E. coli DNA polymerases?
a. They do not require a primer to initiate synthesis
b. They use dNTPs to synthesize new DNA
c. They possess 3'-5' exonuclease activity
d. all of the above
e. a and b
Answers
The false statement among the options provided is option a: "They do not require a primer to initiate synthesis." E coli DNA polymerases, like most DNA polymerases, require a primer to initiate DNA synthesis.
Here correct answer is E)
DNA polymerases cannot start synthesis from scratch; they require an existing strand of DNA or RNA as a primer to begin synthesizing new DNA. The primer provides the initial nucleotide sequence for the DNA polymerase to extend from.
Once a primer is present, E. coli DNA polymerases can utilize dNTPs (deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates) to synthesize new DNA strands in the 5'-to-3' direction, matching the template strand. Additionally, E. coli DNA polymerases do possess 3'-5' exonuclease activity, allowing them to proofread and correct errors during DNA replication. Therefore, the correct answer is option e: "a and b."
Know more about DNA polymerases here
https://brainly.com/question/29585040#
#SPJ11
why do you think estuaries and kelp forests exhibit high productivity?
Answers
Estuaries and kelp forests exhibit high productivity because they are nutrient-rich environments that support a diverse array of plant and animal life.
Estuaries, which are areas where freshwater and saltwater meet, are highly productive ecosystems due to the influx of nutrients from both sources. These nutrients support the growth of phytoplankton, which form the base of the food chain and support a diverse array of animal life.
Similarly, kelp forests are highly productive ecosystems due to their nutrient-rich waters and the presence of kelp, which provides food and shelter for a variety of marine animals. Kelp also helps to filter pollutants from the water, further supporting the health and productivity of the ecosystem.
In conclusion, estuaries and kelp forests are highly productive ecosystems due to their nutrient-rich environments and the presence of diverse plant and animal life.
Learn more about Ecosystems at https://brainly.com/question/1061425
#SPJ11
Humans, cats, whales, and bats belong to the phylum chordate. Based on the structure of their forelimbs, what can you infer about chordates?
Answers
Answer:
They have a common ancestor (forelimbs are homolog structures in these species)
Explanation:
Homologous organs/structures refer to structures/organs which are similar in different species due they have been inherited from a common ancestor. The forelimbs of vertebrates (e.g., birds, humans, crocodiles, whales, bats, etc) are homologous structures derived from the same ancestral structure. In consequence, small variations related to the structure of the forelimbs in mammals such as humans, cats, whales, and bats represent adaptive functional modifications to their common early ancestors. On the other hand, analogous structures/organs are those that are similar and have the same function but evolved independently in two living organisms (e.g., the wings of birds and of bees).
Explain How a multicellular organism is a collection of differentiated cells.
Answers
Answer:
the picture is just your answer
Explanation:
read what's on the picture to get your answer

Why is having a cell that is too large detrimental?
Answers
Explanation:
If a cell became too large, an "information crisis" would occur. The cell has more trouble moving enough nutrients and wastes across the cell membrane. The rate at which food, oxygen, and water enter the cell, as well as wast products leave the cell, depends on the surface area of the cell and the cell's volume.
Frigidia is a colony in Antarctica. The colony is 1,000 square kilometers in size. Currently, 30,000 people live there. Last year, 10,000 children were born and 2,000 people immigrated. 20,000 people died and 5,000 emigrated. It is believed that the island could support up to 50 people per square kilometer.
The current growth rate is ___.
43%
-43%
4.3 %
-4.3%
Answers
If the femoral nerve was severed would that person be able to stand? why or why not?.
Answers
Answer:
Yes, but it would be hard to do so.
Explanation:
I tried to put up some information, but it said it was inappropriate.
Anyways, hope this helps! :)
5. EASY WILL GIVE BRAINLIEST
Ryan puts a beaker of ice and water on a hot plate, and the ice slowly
begins to melt as shown in the figure below. After a few minutes, only liquid
water is in the beaker. Eventually, the water becomes hot and boils. The
liquid water changes to water vapor. In what way is the liquid water
different from the water vapor? *
OO
The liquid particles move slower.
The liquid has a higher boiling point.
The vapor has a lower temperature.
The vapor particles have less energy.
lo

Answers
Which is the most common method of tree harvesting for an even-aged forest stand?
Shelterwood cutting
Selective cutting of groups of trees
Selective cutting of single trees
Clear-cutting
Answers
Answer:
Selective cutting of single trees
Candace is wanting to be sure that she is doing what she can to prevent the spread of disease. Which of the following should she sure to do?
Answers
Answer: She should Avoid Contact with other people's bodily fluids.
Explanation: Hope that helps! (:
Answer:
She should avoid contact with other peoples bodily fluids
Explanation:
I just did the lesson and this is the correct answer.
Because all of the cells in a multi-cellular organism come from a single cell, all of its cells will have the same number of
Answers
Answer:
Chromosomes
Explanation:
Multicellular organism are organisms that have more than one cells in their body. However, from the very beginning of every living organism including multicellular organisms, only ONE cell is required. In the case of multicellular organisms, this one cell undergoes division by mitosis to form other cells.
Since the cells divide by mitosis i.e 1 forms 2, 2 forms 4 etc.,. each of the cells are genetically identical to one another. Hence, this means that all the cells will contain the same number of chromosomes in their genome. For example, a dog as a multicellular organism has cells that emanate from one cell. If that one cell contain 39 chromosomes, all cells in the dog will also contain 39 chromosomes.
Identify the similarities between regular neurons and neuroendocrine cells. (Select all that apply.)
Both release a neurotransmitter into a synapse when they fire.
Both generate action potentials if they are excited past threshold.
Both receive synaptic input from other neurons.
Both facilitate the reuptake of excess neurotransmitter
Answers
The similarities between regular neurons and neuroendocrine cells: Both generate action potentials if they are excited past threshold , Both receive synaptic input from other neurons , Both release a neurotransmitter into a synapse when they fire . Therefore, the correct options are A, B, and C
Both regular neurons and neuroendocrine cells share the following similarities:
A. Both release a neurotransmitter into a synapse when they fire. Neurotransmitters are chemicals that help transmit signals across a synapse. Both regular neurons and neuroendocrine cells release neurotransmitters to communicate with other cells.
B. Both generate action potentials if they are excited past threshold. This means that when the cell is stimulated enough to surpass a certain level, it will produce an electrical signal known as an action potential.
C. Both generate action potentials if they are excited past threshold. This means that they can both receive signals from other neurons through synapses, which are the junctions between two nerve cells where they can transmit or receive information.
Therefore , the correct options are A, B, and C. Both release a neurotransmitter , Both generate action potentials if they are excited past threshold into a synapse when they fire, Both generate action potentials if they are excited past threshold .
To know more about neurons
https://brainly.com/question/6260412
#SPJ11
now mate your gamete with a gamete from another group. draw the chromosomes of the new zygote after fertilization. is this organism genetically unique when compared to the chromosomes of each parent? why is this important for sexually reproducing organisms?
Answers
Meiosis creates gametes, which are genetically distinct reproductive cells with half as many chromosomes as their parent cells. A diploid cell divides to produce haploid cells during meiosis.
Two haploid cells (gametes) combine during fertilisation to create a diploid zygote. A gamete (a reproductive cell with one set of chromosomes, like an egg or sperm) combines with another gamete to form a zygote, which eventually develops into an organism made up of cells with two sets of chromosomes. Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves this complex life cycle.
To know more about gametes, click here:
https://brainly.com/question/29882202
#SPJ4
what is 20 degrees Celsius in Fahrenheit
Answers
Answer:
68 degrees Fahrenheit
Explanation:
divide by 5 (20/5=4)
multiply by 9 (4 x 9= 36)
add 32 (36+32=68)
Answer:
68 degrees F
Explanation:
20 x 1.8 + 32
20= C
(multiply C by 1.8 then add 32!!)
Ribosomal RNA is also known as rRNA
and is located on the ribosome.
Which of these is TRUE about rRNA?
A. It helps mRNA move along the ribosome.
B. It creates extra cytoplasm.
C. It unzips DNA strands.
D. It takes DNA outside the nucleus.
Answers
The ribosome is where ribosomal RNA, commonly known as rRNA, is found. Strands of DNA are unzipped.
Where can one locate ribosomal RNA?80% of the total RNA in a cell is made up of rRNAs, which are located in ribosomes. The 50S subunit, which is a substantial component of ribosomes, and the 30S subunit, which is a smaller component, are each made up of unique rRNA molecules.
What does ribosomal RNA gene mean?an RNA ribosome All living things need ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA), which is the RNA component of the ribosome and crucial for protein synthesis. About 60% of the ribosome's mass is made up of rRNA, and the remaining 40% is made up of protein.
To know more about Ribosomal RNA visit:-
https://brainly.com/question/12878512
#SPJ1
Answer: It helps mRNA move along the ribosome
Explanation:
An area is described as having mild temperatures in the summer and being cool and rainy in the winter. on a day in may, the area experienced snow. which best describes this day in terms of weather and climate?
select one:
a. the weather was different from the normal climate for the area.
b. the climate was different from the normal weather for the area.
c. weather and climate were different from the normal properties for the area.
d. climate and weather were changing into a new set of normal properties for the area.
Answers
Answer:
the answer is a .IAM sure
Wells
A. Lane B
B. Lane D
C. Lane C
D. Lane A
80 70 60 40
。 |||
|
c| | || |
I
80%
Electrodes
Agarose Gel
A
25 10 5
||
||
Lane (D) of Known
fragment sizes.
Kilobase pairs
Chamber filled with
Unknown DNA size samples buffer solution
Answers
By comparing the migration distances of the unknown DNA samples in Lane D with the known fragment sizes in Lane D, it is possible to estimate the size of the unknown DNA fragments.
In the given information, a DNA agarose gel electrophoresis setup is described. The gel contains wells labeled A, B, C, D, and E, and lanes are represented by letters A, B, C, and D. The numbers 80, 70, 60, and 40 indicate the known fragment sizes (in kilobase pairs) in Lane D.
The gel is filled with a buffer solution, and the Lane D contains the unknown DNA samples.To analyze the unknown DNA samples, the gel electrophoresis process is conducted. DNA samples are loaded into the wells of the gel, and an electric current is applied.
The negatively charged DNA fragments move through the gel towards the positively charged electrode. The smaller fragments migrate faster, while the larger fragments move more slowly.
If the unknown DNA fragments migrate to positions that align with the known fragment sizes, it suggests a similarity in size between the unknown fragments and the known fragments. This information can be useful for determining the approximate size of the unknown DNA samples.
For more such questions on DNA
https://brainly.com/question/28282298
#SPJ8
An igneous rock is light in color and has extremely coarse grains. What is the most likely origin of the rock? O a magma chamber O the bottom of the ocean an outer slope of a volcano O the shore of a volcanic island
Answers
Answer:
its a
Explanation:
Answer:
a
Explanation:
Explain the similarities and differences between substitutions, insertions, and deletions
Answers
Answer:
Substitutions, insertions, and deletions are types of genetic mutations that can occur in DNA or RNA sequences.
A substitution, also known as a point mutation, is a change in a single nucleotide base pair in the DNA or RNA sequence. There are three types of substitutions: silent, missense, and nonsense mutations. A silent mutation is a substitution that does not result in a change in the amino acid sequence of the protein that is produced. A missense mutation is a substitution that does result in a change in the amino acid sequence, potentially affecting the function of the protein. A nonsense mutation is a substitution that creates a premature stop codon, resulting in a truncated protein.
An insertion mutation occurs when one or more nucleotide base pairs are added to the DNA or RNA sequence, causing a shift in the reading frame. This can result in a frameshift mutation, which changes the way the entire sequence is read and can affect the protein produced.
A deletion mutation occurs when one or more nucleotide base pairs are removed from the DNA or RNA sequence, also causing a frameshift mutation. Like an insertion, a deletion can affect the protein produced, depending on where in the sequence it occurs.
In summary, substitutions, insertions, and deletions are all types of genetic mutations that can occur in DNA or RNA sequences. Substitutions involve a change in a single nucleotide base pair, while insertions and deletions involve the addition or removal of one or more base pairs, respectively. Insertions and deletions can result in a frameshift mutation, which changes the reading frame of the sequence and can have significant effects on the protein produced.
Explanation:
what is the answer I really need it quick plz
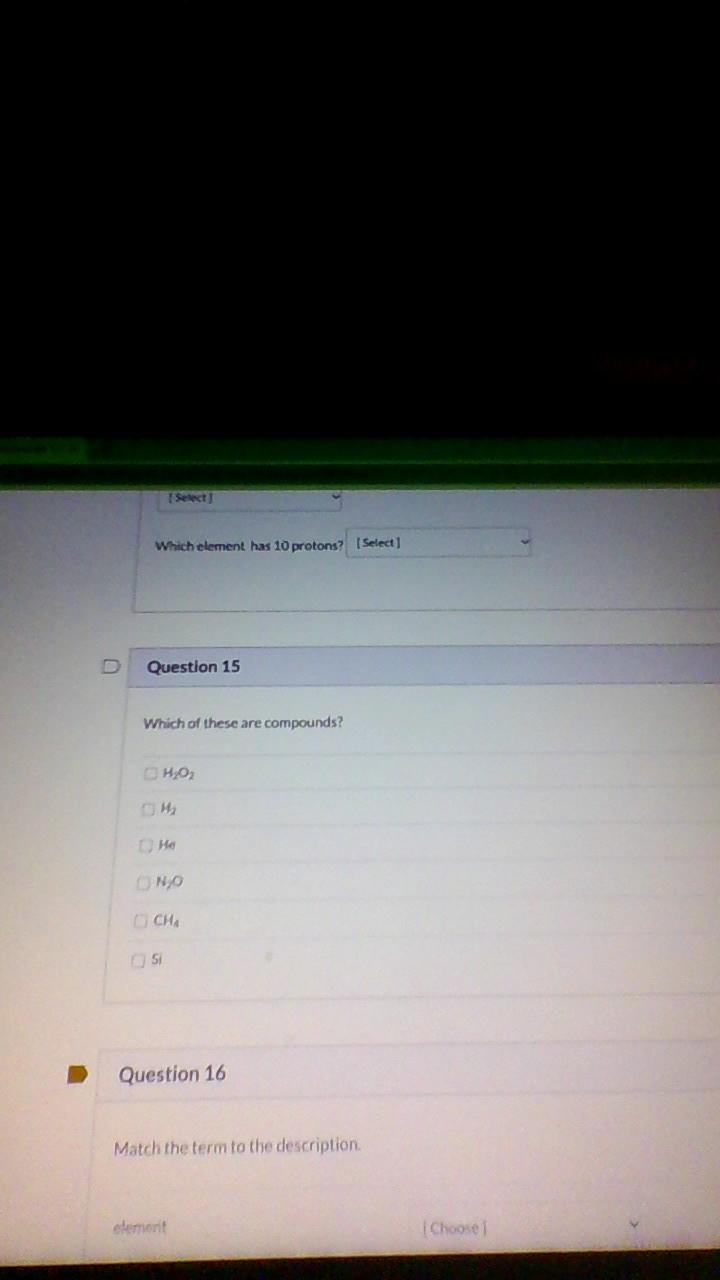
Answers
HELP ME PLEASE IM BEING TIMED

Answers
What is it called when a drug is no longer effective but organism is susceptible in vitro?
Answers
When a drug is no longer effective but an organism is susceptible in vitro, it is called intermediate.
What is it known as when a drug loses its effectiveness but an organism is still susceptible in vitro?When a bacterial strain is susceptible in vitro to a concentration of an antibiotic drug that is linked to a questionable therapeutic effect, it is said that the bacterium's sensitivity to that antibiotic is intermediate. Thus, When a drug is no longer effective but an organism is susceptible in vitro, it is called intermediate.The designation "intermediate" suggests that while the same antibiotic may not be sufficiently effective against the same organism if it is located in other places, such as the meninges, it may readily be eliminated in bodily compartments that are easily accessible by the medicine, such as the urinary tract.To learn more about susceptibility refer:
https://brainly.com/question/28169324
#SPJ4
Which of these pairs does not correctly match a carbohydrate with its function?

Answers
Of the available options, the first one states that cellulose is a structural part of the hair, this is not correct for several reasons, first cellulose is a biopolymer characteristic of cellular walls in plants, and it's not present in animal cells, secondly human hair is formed mainly of keratin a protein, therefore their basic units are amino acids, not carbohydrates. Therefore taking this into consideration, the correct answer is option 1.
How many atoms are present in 3H^2O
Answers
Answer:
3486784401
Explanation:
3^20 is 3486784401
I'm not 100 percent sure though, I'm sorry
Answer:
there are 6 hydrogen atom and 3 oxygen atoms
present