Isabella filled a glass with warm water. She measured the temperature, and it was 30�c. She left the glass on a table in a room that was 20�c. A few hours later, she measured the water temperature again, and it was 24�c. Which best explains why the water temperature changed?.
Answers
The water temperature changed because the heat moved from the warm water to the cooler air in the room.
The process of moving heat from one object to another is called heat transfer. In the given situation, the water temperature changed because the heat moved from the warm water to the cooler air in the room. When the glass of warm water was placed on the table, the heat energy of the water started to transfer to the surrounding cooler air molecules. As a result, the water lost its heat energy to the air in the room and its temperature gradually decreased. This is known as convection.
Convection is the movement of heat energy from one location to another through fluids. In this case, the fluid is air. The warm water heats the air above it. The heated air expands, becoming less dense and rises. The cooler air from the surroundings replaces it, and the cycle continues. This flow of air is called a convection current.
Therefore, the reason for the change in the temperature of the warm water was due to the heat transfer from the warm water to the surrounding cooler air in the room, which is convection.
Learn more about convection here:
https://brainly.com/question/4138428
#SPJ11
Related Questions
Juan makes a measurement in a chemistry laboratory and records the result in his lab report. Suppose that if Juan makes this measurement repeatedly, the standard deviation of his measurements will be o-9 milligrams. Juan repeats the measurement four times and records the mean x of his four measurements.
What is the standard deviation of Juan's mean result? (That is, if Juan kept on making four measurements and averaging them, what would be the standard deviation of all his x's?)
Round your answer to one decimal place.
standard deviation:
mg
How many times, n, must Juan repeat the measurement to reduce the standard deviation of x to 3? Give your answer as a whole number.
Answers
The standard deviation of Juan's mean result:We know that Juan repeats the measurement four times, and the standard deviation of his measurements is 0.9 mg.
Let's assume that the four measurements that Juan takes are a, b, c, and d.The sample mean, x = (a + b + c + d)/4The variance of the sample is calculated as shown below:σ² (x) = [σ²(a) + σ²(b) + σ²(c) + σ²(d)] / nσ² (x)
= [0.9² + 0.9² + 0.9² + 0.9²]/4σ² (x)
= 0.81/4σ² (x)
= 0.2025σ(x)
= √0.2025σ(x)
= 0.45 mgHence, the standard deviation of Juan's mean result is 0.5 mg (rounded to one decimal place).To find out how many times Juan should repeat the measurement to reduce the standard deviation of x to 3, we use the following formula:σ (x) = σ / √nWhere σ (x) is the standard deviation of the sample mean, σ is the standard deviation of the population, and n is the sample size.
To find n, we use the following formula:n = (σ / σ (x))²n = (0.9 / 3)²n
= (1/3)²n
= 1/9n
= 0.1111The number of times Juan must repeat the measurement to reduce the standard deviation of x to 3 is 10 (rounded to a whole number).Answer:Standard deviation of Juan's mean result: 0.5 mg (rounded to one decimal place).Juan must repeat the measurement 10 times to reduce the standard deviation of x to 3.
To know more about measurements visit:
https://brainly.com/question/28913275
#SPJ11
575/2000 in ratio please send me photos of this answer
Answers
Answer:
23 : 80
Not sure
No time for pictures
Answer:
\({\huge{\pink{\underline{\underline{SoLuTiOn}}}}}\)
Refer to above attachment...

List three reasons why the actual yield would be less than theoretical yield.
Answers
Possible reasons for the actual yield being less than the theoretical yield include incomplete reactions, side reactions, and product loss during separation or purification processes.
The actual yield of a chemical reaction refers to the amount of product obtained in a practical scenario, while the theoretical yield is the maximum amount predicted by stoichiometry calculations. Several factors can contribute to the actual yield being less than the theoretical yield.
First, incomplete reactions occur when not all reactants are converted into products due to factors such as limited reaction time, insufficient reactant concentrations, or unfavorable reaction conditions. Second, side reactions may occur alongside the desired reaction, resulting in the formation of unintended products and reducing the overall yield. Lastly, during separation or purification processes, some of the product may be lost due to factors like incomplete recovery from the reaction mixture, losses during filtration or transfer, or adherence to reaction vessels or equipment surfaces.These factors contribute to the discrepancy between the actual yield and the theoretical yield.
You can learn more about actual yield at
https://brainly.com/question/20884766
#SPJ11
What is the molecular formula of the compound with a molecular weight of 112 g/mol and percent composition: 85.6% C and 14.4% H?C8H16CH2C4H8C2H4
Answers
To find the molecular formula of this compound, what we're going to do is to follow up the steps:
Step 1: Pass all the percentages to grams. This is, just to change the unit:
Step 2: Divide each mass by respective molar mass to obtain the moles of each element:
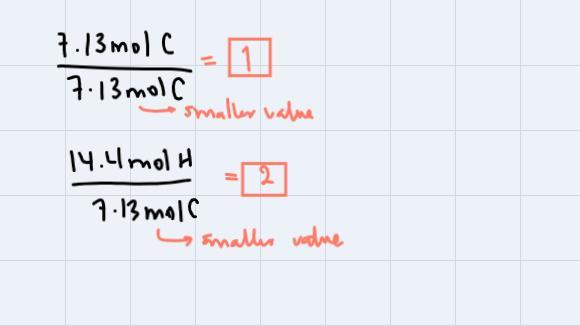
Step 3: Divide all the amounts in moles through by smaller value obtained:
These are the subscripts for C and H respectively. Thus our empirical formula is CH2. We're asked to find the molecular formula so, we could use the fact that the compound has a molecular weight of 112 g/mol. If we analyze, CH2 has a molecular weight of 14g/mol, so:
Step 4: We're going to divide the molecular weight of the compound with molecular formula through by the molecular weight of the compound with empirical formula:
This means that our molecular formula will be eight times the subscripts of the empirical formula. Therefore, the answer is:




5.27x10^45 molecules of h20 is how many moles
Answers
Answer:
6.02 × 10^23 molecules = 1 mole
5.27 × 10^45 molecules = x
x = 5.27 × 10^45/ 6.02 × 10^23 × 1
= 8.754 × 10^21 mol
I don't know if it's correct but based on the question that was the only way I saw how to work it out
you have a coin with a volume of 10cm3 and a mass of 23g. What is the density of the coin
Answers
Answer:
2.3 grams per cubic cm
Explanation:
Density is equal to mass over volume, so
23/10=2.3
Which of the following combinations of gases were most likely the major components of the earth's early atmosphere? a. nitrogen, hydrogen, and methane b. hydrogen, helium, methane, and ammonia c. oxygen, hydrogen, and helium d. oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen, and helium
Answers
The major components of the earth's early atmosphere were most likely nitrogen, hydrogen, and methane (Option A).
What were the major components of the early Earth's atmosphere?Scientists hypothesize that Earth's early atmosphere was primarily composed of hydrogen gas, nitrogen gas, methane gas, and water vapor. They suggest that small amounts of carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, and ammonia were also present.
What is the present Earth's atmosphere composition?At present, Earth's atmosphere is composed of nitrogen gas (78%), oxygen gas (21%), and trace amounts of other gases, including argon, carbon dioxide, neon, helium, and methane.
Hence, the correct answer is Option A.
Learn more about atmosphere here: https://brainly.com/question/28124272
#SPJ11
HELP ILL MATK YOU AS BRAINLEST
Answers
Answer:
Tissues And Organ Systems
Explanation:
The reaction between solid sodium and iron
(III) oxide is one of a series of reactions that
inflate an automobile airbag.
6 Na(s) + Fe2O3(s) --> 3 Na 20 (s) + 2
Fe (s)
If 25. 0 grams of each reactant is used, what is
the limiting reactant?
Answers
From our calculation, we can see that the limiting reactant is iron III oxide.
What is the limiting reactant?The limiting reactant, also known as the limiting reagent, is the reactant that is completely consumed or "used up" in a chemical reaction. It determines the maximum amount of product that can be formed in the reaction.
We know that;
Number of moles of the sodium = 25 g/ 23 g/mol
= 1.1 moles
Number of moles of the iron III oxide = 25 g/ 160 g/mol
= 0.16 moles
If 6 moles of Na reacts with 1 mole of iron III oxide
1.1 moles of Na would react with 1.1 * 1/6
= 0.18 moles
The iron III oxide is the limiting reactants
Learn more about limiting reactant:https://brainly.com/question/10255265
#SPJ4
which statement explains the energy term in this reaction
Answers
Answer:
Mass is lost due to the conversion of mass to energy
Explanation:
The question is not complete, the complete question is given as:
\(^{235}_{72}U +^{1}_{0}n\) ⇒ \(^{140}_{56}Ba+^{93}_{36}Kr+3^{1}_{0}n+energy\)
total mass equals 236.053 u total mass equals 235.868 u
Which statement explains the energy term in this reaction? (1) Mass is gained due to the conversion of mass to energy. (2) Mass is gained due to the conversion of energy to mass. (3) Mass is lost due to the conversion of mass to energy. (4) Mass is lost due to the conversion of energy to mass.
Answer: From Einstein’s equation E = mc², when a radioisotope element undergoes fission or fusion in a nuclear reaction, it loses a tiny amount of mass.This mass lost is converted to energy.
The law of conservation of energy holds for this type of reaction (i.e the sum of mass and energy is remains the same in a nuclear reaction). Mass changes to energy, but the total amount of mass and energy combined remains the same before and after a nuclear reaction.
From the reaction above, the total decrease in mass = 236.053 - 235.868 = 0.185 u
why are many devices that we use powerd by electricity?
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
Because they have electrical cords :P But really, b/c electron movement is a convenient attribute of many elements. The electrons are "loose" on most metals, so they can conduct electricity.
Answer:
The benefits of power electronics are: High power density power supplies. Improved efficiency of up to 99% in power conversion. Noise-sensitive applications such as in medical devices are also transitioning to switching power supplies because of the efficiency and reliability.
write the reaction equation that is associated with the lattice energy of the following compounds: a. li2o(s): b. cas(s): c. fecl3(s):
Answers
The equation associated with the lattice energy of the compound is: -
Li2O (s)---->2 Li+ (g) + O2- (g)
Lattice energy is defined as the energy required for the conversion of one mole of ionic solid constituents to ionic gaseous constituents. Lattice energy is a measure of the strength of the ionic bonds in an ionic compound.
It provides insight into several properties of ionic solids including their volatility, their solubility, and their hardness.
The lattice energy of an ionic solid cannot be measured directly. However, it can be estimated with the help of the Born-Haber cycle. Generally, this quantity is expressed in terms of kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol)
Lattice energy gives us the idea for the entire reaction and its compounds.
Learn more about lattice energy at,
https://brainly.com/question/2240714
#SPJ4
Rank the following in order of increasing bond angles: OF2, SnF2, XeF2(1) OF2 < XeF2 < SnF2(2) OF2 < SnF2 < XeF2(3) SnF2 < OF2 < XeF2(4) XeF2 < OF2 < SnF2(5) XeF2 < SnF2 < OF2
Answers
This is because the bond angle is determined by the number of lone pairs and bonded atoms around the central atom. The correct answer is (2) OF2 < SnF2 < XeF2.
Oxygen in OF2 has 2 lone pairs and 2 bonded atoms, resulting in a smaller bond angle than the other two molecules. Tin in SnF2 has 2 lone pairs and 2 bonded atoms as well, but its larger size allows for a larger bond angle than OF2. Finally, xenon in XeF2 has 3 lone pairs and 2 bonded atoms, resulting in the largest bond angle among the three molecules.
The molecules in order of increasing bond angles. Based on the given options, the correct order is:
(3) SnF2 < OF2 < XeF2
1. SnF2 has a bent molecular geometry with a bond angle of less than 109.5° due to the influence of the lone pair on the Sn atom.
2. OF2 has a bent molecular geometry as well, but with a bond angle of approximately 109.5° because of the two lone pairs on the O atom and the strong electronegativity of the O atom.
3. XeF2 has a linear molecular geometry with a bond angle of 180° due to the presence of three lone pairs on the Xe atom.
So, the order of increasing bond angles is SnF2 < OF2 < XeF2.
Visit here to learn more about bond angle:
brainly.com/question/31501310
#SPJ11
Which factor decide the reactivity of alkyl halide?
Answers
Answer:
The reactivity order reflects both the strength of the C-X bond and the stability of X(-) as a leaving group and leads to the general conclusion that alkyl iodides are the most reactive members of this functional class
PART OF WRITTEN EXAMINATION:
In a corrosion cell, electrons flow in the direction of:
A) anode to the cathode through the electroylte
B) anode to the cathode through the metallic path
C) cathode to the anode through the electrolyte
D) cathode to the anode through the metallic path
Answers
Corrosion cells are a condition on a metal surface in which a flow of electric current occurs between the metal surface and an electrolyte with which it is in contact sufficient to cause the metal to degrade.
In a corrosion cell, electrons flow from the anode to the cathode through the metallic path. Therefore, the correct answer to the question is
B) anode to the cathode through the metallic path.
In the corrosion cell, metal ions formed from metal oxidation (cations) migrate from the anode to the cathode through the electrolyte. The electrons given off by this oxidation reaction move from the anode to the cathode through the electrical connection.
to know more about Corrosion cells click this link-
brainly.com/question/30800443
#SPJ11
if 2.5 moles of each of these compounds are burned completely in o2, which will produce the largest amount of co2?
Answers
Answer:
C3H8
Explanation:
To determine which compound will produce the largest amount of CO2 when 2.5 moles of each is burned completely in O2, we need to compare the mole ratios of the compounds and the CO2 produced in their balanced chemical equations.
The balanced chemical equations for the combustion of the compounds are:
C3H8 + 5O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O
C4H10 + 13/2 O2 → 4CO2 + 5H2O
C8H18 + 25/2 O2 → 8CO2 + 9H2O
From these equations, we can see that 1 mole of C3H8 produces 3 moles of CO2, 1 mole of C4H10 produces 4 moles of CO2, and 1 mole of C8H18 produces 8 moles of CO2.
Therefore, when 2.5 moles of each compound are burned completely in O2, the largest amount of CO2 will be produced by C8H18, which produces 8 moles of CO2 per mole of the compound. The amount of CO2 produced by 2.5 moles of C8H18 would be 8 x 2.5 = 20 moles.
In comparison, 2.5 moles of C3H8 would produce 3 x 2.5 = 7.5 moles of CO2, and 2.5 moles of C4H10 would produce 4 x 2.5 = 10 moles of CO2.
the global warming potential (gwp) of gases in the atmosphere is a function of their heat retention capacity and a. isotope ratio b. natural source c. atmospheric half-life d. color and odor
Answers
The global warming potential (GWP) is a measure of how much a gas contributes to global warming over a given period of time, compared to carbon dioxide (CO2). This means that different gases have different levels of impact on the Earth's climate system, depending on their heat retention capacity, isotope ratio, natural source, atmospheric half-life, color, and odor.
The heat retention capacity of a gas refers to its ability to absorb and trap heat in the atmosphere. This is important because gases like carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide have different heat-trapping capabilities, with methane being about 28 times more potent than CO2. The isotope ratio of a gas can also affect its GWP, as some isotopes can trap more heat than others. The natural source of a gas can also affect its GWP. For example, some gases like methane are naturally emitted by wetlands, while others like fluorinated gases are created through industrial processes. The atmospheric half-life of a gas is another factor that affects its GWP, as some gases can remain in the atmosphere for decades or even centuries, contributing to long-term warming. Finally, the color and odor of a gas do not directly affect its GWP, but they can be useful in identifying different gases and their sources. Overall, understanding the different factors that contribute to the GWP of gases in the atmosphere is important for mitigating the impacts of climate change and reducing our carbon footprint.
For more information on carbon dioxide see:
https://brainly.com/question/13229518
#SPJ11
84 pt =_____ qt
5.0 gal =_____ L
Answers
Answer:
84 pt =__50.4399___ qt
5.0 gal =___18.9271__ L
Explanation:
Have A Wonderful Day!!
Answer: 84 pints = 42 quarts
5.9 gallons = 1.89271
Explanation:
True or False: Positive ions have more electrons than protons
O True
O False
Answers
Answer:
If the atom has more electrons than protons, it is a negative ion, or ANION. If it has more protons than electrons,it is a positive ion.
Explanation:
so yes true
For the reaction 2A + 4B ----> 2C + 2D, at a particular instant in time, the rate of the reaction is 0.0352 M/s. What is the rate of change of B? Show Work!
A. 0.0088 M/s
B. -0.0088 M/s
C. -0.141 M/s
D. -0.0352 M/s
E. 0.141 M/s
Answers
Explanation:
The given chemical equation is:
\(2A + 4B -> 2C + 2D\)
The rate of the reaction is 0.0352 M/s.
During the course of the reaction, the rate of reactants decreases, and the rate of products increases.
The rate of disappearance of B is shown below:
\(rate=-\frac{1}{4} \frac{d[B]}{dt}\)
So, rate of change of B is :
\(rate of change of B =- rate * 4\\=-0.0352 M/s * 4\\=-0.1408M/s\\\\=-0.141M/s\)
Option C.
In the given reaction, rate of change of reactant B is equal to -0.141 M/s.
What is the rate of reaction?Rate of any chemical reaction defines the speed of the completion of that reaction.
In the question given reaction is:
2A + 4B ----> 2C + 2D
Rate of reaction = 0.0352 M/s.
Rate of the reaction with respect to the reactant B is written as:
Rate = \(${\rm{ - }}\frac{{\rm{1}}}{{\rm{4}}}\frac{{\left[ {{\rm{dB}}} \right]}}{{{\rm{dT}}}}$\), where negative sign shows the disappearance of reactant B.
Rate of change of B i.e. \($\frac{{{\rm{dB}}}}{{{\rm{dT}}}}$\) = 4 × (-rate)
\($\frac{{{\rm{dB}}}}{{{\rm{dT}}}}$\) = 4 × (-0.0352) = -0.1408 = -0.141 M/s
Hence, -0.141 M/s is the rate of change of B.
To learn more about Rate of reaction, visit below link:
https://brainly.com/question/7578129
How many protons for the si silicon atom
Answers
Answer:
Silicon has 14 protons in its atoms.
Select the equality for the following and 14 karat gold ring contains 58% gold by mass

Answers
Answer:
100g gold ring - 58g gold.
Explanation:
Assuming that the 100% represents the 100g of the gold ring, with a mathematical rule of three we can calculate the 58% of gold:
\(\begin{gathered} 100\%-100g \\ 58\%-x=\frac{58\%*100g}{100\%} \\ x=58g \end{gathered}\)So, in 100g of the gold ring, there are 58g of gold.
Calculate [NO3-] if 125 mL of 0.35 M NaNO3 is mixed with 450 mL of 1.1 M Mg(NO3)2. Please include some of your work as best as you can in the answer for full marks.
Answers
Answer: 1.76 M
Explanation:
To calculate the number of moles for given molarity, we use the equation:
\(\text{Molarity of the solution}=\frac{\text{Moles of solute}\times 1000}{\text{Volume of solution (in L)}}\) .....(1)
Molarity of \(NaNO_3\) solution = 0.35 M
Volume of solution = 125 mL
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
a) \(0.35M=\frac{\text{Moles of}NaNO_3\times 1000}{125ml}\\\\\text{Moles of }NaNO_3=\frac{0.35mol/L\times 125}{1000}=0.044mol\)
1 mole of \(NaNO_3\) contains = 1 mol of \(NO_3^-\)
Thus \(0.044mol\) of \(NaNO_3\) contain= \(\frac{1}{1}\times 0.044=0.044\) mol of \(NO_3^-\)
b) \(1.1M=\frac{\text{Moles of}Mg(NO_3)_2\times 1000}{450ml}\\\\\text{Moles of }Mg(NO_3)_2=\frac{1.1mol/L\times 450}{1000}=0.495mol\)
1 mole of \(Mg(NO_3)_2\) contains = 2 mol of \(NO_3^-\)
Thus \(0.495mol\) of \(Mg(NO_3)_2\) contain= \(\frac{2}{1}\times 0.495=0.99\) mol of \(NO_3^-\)
Total \([NO_3^-]=\frac {\text {total moles}}{\text {total volume}}=\frac{0.044+0.99}{0.575L}=1.76M\)
Thus \([NO_3^-\) after mixing is 1.76 M
How much energy does it take to boil 100 mL of water? (Refer to table of constants for water. )
A. 100 mL × 1g divided by 1mL × 1mol divided by 18. 02g × 6. 03 kJ/mol = 33. 5 kJ
B. 100 mL × 1g divided by 1mL × 1mol divided by 18. 02g × (–285. 83 kJ)/mol = –1586 kJ
C. 100 mL × 1g divided by 1mL × 1mol divided by 18. 02g × 40. 65 kJ/mol = 226 kJ
D. 100 mL × 1g divided by 1mL × 1mol divided by 18. 02g × 4. 186 kJ/mol = 23. 2 kJ
Answers
Therefore, it takes approximately 23.2 kJ of energy to boil 100 mL of water.
The correct answer is D. 100 mL × 1g divided by 1mL × 1mol divided by 18.02g × 4.186 kJ/mol = 23.2 kJ
To calculate the energy required to boil 100 mL of water, we need to use the specific heat capacity of water, which is approximately 4.186 J/g·°C. The molar mass of water is 18.02 g/mol.
First, we convert the volume of water from milliliters to grams:
100 mL × 1 g/1 mL = 100 g
Then, we calculate the number of moles of water:
100 g × 1 mol/18.02 g = 5.548 mol
Finally, we multiply the number of moles by the molar heat of vaporization of water, which is approximately 40.65 kJ/mol:
5.548 mol × 4.186 kJ/mol = 23.2 kJ
Therefore, it takes approximately 23.2 kJ of energy to boil 100 mL of water.
Learn more about energy
https://brainly.com/question/8630757
#SPJ11
why do we say the partials in a rock lying on the ground have kinetic energy and potential energy
Answers
Answer:
All particles of matter are always in constant motion. In this case, the particles of the rock possess kinetic energy as they vibrate in place. However, the particles also contain potential energy due to their position and arrangement. This form of stored energy is responsible for keeping the particles bonded together.
Explanation:
in molecular orbital theory the stability of a covalent body is related to its __________.
Answers
Molecular orbital theory (MO theory) is a model used to describe the bonding in molecules. According to this theory, a molecule is formed by the combination of atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals. The electrons in these molecular orbitals are delocalized over the entire molecule, rather than being confined to individual atoms.
Bond order is a measure of the strength of the bond between two atoms in a molecule. It is calculated as the difference between the number of bonding electrons and the number of antibonding electrons, divided by 2. Bonding electrons are the electrons in molecular orbitals that contribute to the formation of the bond, while antibonding electrons are the electrons in molecular orbitals that oppose the formation of the bond.
A higher bond order indicates stronger bonding and greater stability, because it means that there are more bonding electrons than antibonding electrons. This results in a net stabilization of the molecule, since the electrons are held more tightly between the two atoms. Conversely, a lower bond order indicates weaker bonding and lower stability, because it means that there are more antibonding electrons than bonding electrons. This results in a net destabilization of the molecule, since the electrons are less strongly held between the two atoms.
Therefore, in molecular orbital theory, the stability of a covalent molecule is related to its bond order, with a higher bond order indicating greater stability and a lower bond order indicating lower stability.
For more questions like orbital visit the link below:
https://brainly.com/question/7297651
#SPJ11
A sample of sodium hydroxide (naoh) has a mass of 160.0 g. the molar mass of naoh is 40.00 g/mol. how many moles of naoh does this sample contain? 4.000 moles 40.00 moles 160.0 moles 6,400 moles
Answers
The number of moles the sample of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) will contain is 4 moles.
How we calculate moles?Moles of any substance will be calculated by using the below formula:
n = W/M, where
W = given mass
M = molar mass
Given mass of NaOH = 160 g
Given molar mass of NaOH = 40 g/mole
On putting these values on the above equation, we get
n = 160 / 40 = 4 moles
Hence, required moles is 4 moles.
To know more about moles, visit the below link:
https://brainly.com/question/15303663
Answer:
A). 4.000
Explanation:
Poopy fart fart

(2r 3s)-2 3-dibromo-3-phenylpropanoic acid melting point
Answers
The melting point of (2R,3S)-2,3-dibromo-3-phenylpropanoic acid is dependent on several factors, including the purity of the compound and the presence of any impurities.
Therefore, an exact melting point cannot be provided without specific experimental data. However, it is generally observed that organic compounds have a range of melting points rather than a single specific value.
If you are conducting an experiment and need to determine the melting point of (2R,3S)-2,3-dibromo-3-phenylpropanoic acid, it is recommended to perform the melting point determination experimentally using appropriate laboratory techniques and equipment. This involves heating a small amount of the compound and observing the temperature range at which it melts. The observed melting point can then be compared to known literature values to assess the purity of the compound.
Know more about phenylpropanoic acid here:
https://brainly.com/question/14407566
#SPJ11
What is a similarity between the respiratory and excretory systems?
A They both break down food.
B They both remove waste from the body.
C They both exchange gases within the body.
D They both transport nutrients throughout the body.
Answers
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The respiratory removes carbon, and the excretory removes other waste products
Which of these is NOT required to ensure that stock solutions are free of contamination?
a. store all solutions in brown bottles
b. do not place dropping pipettes in stock solution bottles
c. never return excess chemicals to stock bottles
d. Replace tops on reagent bottles after use
Answers
Option A "store all solutions in brown bottles" is NOT required to ensure that stock solutions are free of contamination.
A stock solution is a high concentration solution that is created to be diluted for a variety of laboratory activities. For example, if an experimenter wants to prepare 1 L of 0.1 mol/L hydrochloric acid (HCl), they will prepare 83.33 mL of concentrated HCl (12 mol/L) and then add it to 916.67 mL of water to make up the final volume.Steps to ensure stock solutions are free of contamination:One should always use the following steps to ensure that stock solutions are free of contamination:Never return excess chemicals to stock bottles.Do not place dropping pipettes in stock solution bottles.Only replace tops on reagent bottles after use.Store solutions in a cool, dry place. Avoid sunlight. Store all solutions in brown bottles.Keep all solutions labelled to avoid mixing them up.Examine your glassware for cleanliness before using it.Pipette liquids with care.
Avoid spilling on the ground. Avoid placing pipette tips on the table.Never use pipette tips or glassware that have been used to mix or carry other substances.Never attempt to taste or smell any chemicals or solutions.Wear protective gloves and lab coats when dealing with dangerous substances.
Stock solutions should always be checked for contamination before they are used. If contamination is suspected, the solution should be discarded.
Learn more about stock solutions
https://brainly.com/question/21433251
#SPJ11