identify the conditions under which a given system of forces can be reduced to a single force. (check all that apply.)
Answers
The condition under which a system of forces is reduced to a single force is - One can replace the force - couple system at O by a single force R acting along a new line of action if R and vector M₀ are mutually perpendicular.
What is a force?
A force is a push or a pull on an object and it is a vector quantity.Therefore, it has both direction and magnitude.Force can cause a change in the velocity of an object.Friction is created because of the force.The formula of force is a product of mass and acceleration.Hence, the only condition is if R and vector M₀ are mutually perpendicular, then the system of forces can be reduced to a single force.
To learn more about force, visit: https://brainly.com/question/17646386
#SPJ4
Related Questions
HI can anybody tell me what newtons first law is pls don't make it sound too professional pls tyy
Answers
The rate at which the temperature increases with depth is called the geothermal gradient. What is the geothermal gradient in a tectonically stable region where the temperature is 119° C at a depth of 5.0 km?
(Assume a surface rock temperature of 14° C.)
Answers
The geothermal gradient in the tectonically stable region is approximately 21°C/km, indicating that the temperature increases by an average of 21 degrees Celsius per kilometer of depth.
To calculate the geothermal gradient, we need to find the rate at which the temperature increases with depth.
Temperature at the surface (T₁) = 14°C
Temperature at a depth of 5.0 km (T₂) = 119°C
Temperature difference = T₂ - T₁ = 119°C - 14°C = 105°C
Depth difference = 5.0 km - 0 km = 5.0 km
Geothermal gradient = Temperature difference / Depth difference
Geothermal gradient = 105°C / 5.0 km
Calculating this expression, we find:
Geothermal gradient ≈ 21°C/km
learn more about geothermal gradient here:
https://brainly.com/question/27975108
#SPJ11
a positively charged particle passes through a laboratory traveling in an easterly direction. there are both electric and magnetic field in the room and their effects on the charged particle cancel. if the electric field points upward, what must be the direction of the magnetic field? 1. upward 2. north 3. south 4. west 5. downward 6. east
Answers
If there are both electric and magnetic fields in the room and their effects on the charged particle cancel, and the electric field points upward, then the direction of the magnetic field is downwards.
The electric force on a charged particle is provided by an electric field, whereas the magnetic force is provided by a magnetic field. The effect of the electric and magnetic fields on the motion of the particle is a function of the relative directions and magnitudes of the two fields.
If the magnetic field is perpendicular to the electric field and the particle's velocity, the magnetic force is at right angles to both the electric force and the velocity, and it does not adjust the particle's speed. If the electric and magnetic forces on a charged particle are equal and opposite, they cancel each other out, resulting in no acceleration of the charged particle. Since the electric field is pointing upward, the magnetic field should be pointing downward.
In conclusion, the direction of the magnetic field is downward if the electric field is pointing upward, according to the given condition.
To know more about magnetic fields, refer
https://brainly.com/question/14411049
#SPJ11
To compare the hearing capacities of 5 of his friends, Ravi designs a simple experiment. He places a CD player at the end of a long hall containing a CD with 5 well-known songs.
One by one each person hears the same 5 songs he plays softly but at a pre-determined volume.
Each person starts at a distance of 1 metre from the player and moves away from it. The distance at which a person says that he cannot hear the song any more, is noted. Others are not in the room when 1 person is hearing the songs.
Which of these steps may increase the reliability of the results obtained?
A)having each person listen to just 1 song instead of 5
B)allowing all people to stay in the room for the entire experiment
C)having each person start from far and walk towards the C
D )player Dvarying the volume for the different songs being played
Answers
Answer:
A) having each person listen to just 1 song instead of 5.
Explanation:
Ravi could accurately use the outcome to compare the hearing capacities of his friends by this experiment if appropriate precautions are observed.
Playing 5 well known songs simultaneously could result to the interference of sounds when each participant moves away from the player. Which could naturally cause the variation in volume of the songs played with respect to the increasing distance.
Therefore, the reliability of the result from this experiment can be increased if each person listen to just 1 song instead of 5 at a predetermined volume. Each participant would be able to focus on hearing a song during the experiment.
A helium balloon at room temperature ( 25 degree ) occupies a volume of 2.0 L. When the balloon is expanded to 5.0 L, the balloon will finally pop . If the pressure is not changed, at what temperature will this occure
Answers
Answer:
745.4K ~ 472.3 C
Explanation:
This is an Ideal Gas Law problem where we have to manipulate the equation a bit. Let's start with the basic:
PV = nRT will be used for both the initial and final, so we will rearrange this problem to state:
(V(initial))/(T(Initial)) = nR/P
Since we know that the pressure, number of moles of He, and ideal gas constant (R) remain the same from start to finish so we can write the problem as such:
(V(initial))/(T(Initial)) = nR/P = (V(final))/(T(final))
or
(V(initial))/(T(Initial)) = (V(final))/(T(final))
Now lets define some of these values:
T(initial) = 25degree (assuming degrees Celsius) ~ 298.15K
V(initial) = 2.0L
V(final) = 5.0L
T(final) = ?
Since we are solving for T(final) let's rearrange the problem once more to be solving for T(final):
T(final) = (V(final)T(Initial))/V(initial)
Now plug in your values:
T(final) = (5.0L*298.15K)/(2.0L) ~ 745.4K ~ 472.3degrees Celsius
Which device converts chemical energy directly into electrical energy?
A.
A battery
B.
A generator
C.
A light bulb
D.
A motor
Answers
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Name me brainliest plzzzzz
witch is the property of matter in witch a substance can transfer heat or electricity
Answers
Answer:
B. Conductivity.
Explanation:
Conductivity is the quantity of heat passing per second through a slab of unit cross-sectional area when the temperature gradient between the two faces is unity when put in heat.
it is possible for an excited hydrogen atom to return to the ground state by the emission of a single photon. regardless of the initial excited state, this electron transition produces a spectral line in which region of the electromagnetic spectrum?
1. ultraviolet
2. infrared
3. visible light
4. radio waves
Answers
Answer:
1. Ultraviolet
Explanation:
This is called the Balmer series. Transitions ending in the ground state (n = 1) are called the Lyman series, but the energies released are so large that the spectral lines are all in the ultraviolet region of the spectrum.
It is possible for an excited hydrogen atom to return to the ground state by the emission of a single photon. Regardless of the initial excited state, this electron transition produces a spectral line in ultraviolet region of the electromagnetic spectrum. The correct option is 1.
What is electromagnetic spectrum?An electromagnetic spectrum is the spectrum consisting of the colors of radiation of a white light with different wavelengths.
It is possible for an excited hydrogen atom to return to the ground state by the emission of a single photon.
The transitions which ends in the ground state (n = 1) are termed as Lyman series. Energy released is large in amount so that the spectral lines fall in the ultraviolet region of the spectrum.
Thus, regardless of the initial excited state, this electron transition produces a spectral line in ultraviolet region of the electromagnetic spectrum. The correct option is 1.
Learn more about electromagnetic spectrum.
https://brainly.com/question/23727978
#SPJ2
Tariah is riding on her bike at 4m/s (North). If she accelerates at a rate of 1.5 m/s^2 for 2 s, what is her final velocity?
Answers
ANSWER:
7 m/s
STEP-BY-STEP EXPLANATION:
Given:
Initial velocity (u) = 4 m/s
Acceleration (a) = 1.5 m/s^2
Time (t) = 2 s
We can calculate the final velocity using the following formula:
\(v=u+a\cdot t\)We replace and calculate the value of the final velocity:
\(\begin{gathered} v=4+2\cdot1.5 \\ v=4+3 \\ v=7\text{ m/s} \end{gathered}\)The final velocity is equal to 7 m/s.
How long will it take a runner to complete a marathon race of 42. 2 km if that runner can maintain an average speed of 4. 1 m/s?
Answers
It would take the runner approximately 10,268.29 seconds (or about 2 hours, 51 minutes, and 8 seconds) to complete a marathon race of 42.2 km, maintaining an average speed of 4.1 m/s.
We can use the formula:
time = distance ÷ speed
to calculate the time it would take the runner to complete a marathon race of 42.2 km, given an average speed of 4.1 m/s.
First, we need to convert the distance to meters, as the speed is given in meters per second:
42.2 km = 42,200 m
Now, we can substitute the values into the formula:
time = distance ÷ speed
time = 42,200 m ÷ 4.1 m/s
time ≈ 10,268.29 s
Thus the time that the runner would take is 10,268.29 seconds to complete a marathon race.
For such more questions on average speed :
brainly.com/question/6504879
#SPJ11
The distance your vehicle travels from the time the eyes see a hazard to the time the brain knows it's a hazard is called:
Answers
The distance your vehicle travels from the time the eyes see a hazard to the time the brain knows it's a hazard is called perception distance.
Distance perception refers to a process in which a viewer perceives an interval between two points in space. Perception distance is the distance a vehicle travels from the moment you see a hazard until your brain recognizes it. For an alert driver, this is about 3/4 of a second. The velocity of your car affects the distance needed to stop it. The stopping distance is persistent by three factors: perception distance, reaction distance, and braking distance. Perception time is how long it endures to recognize a condition and comprehend that you require to stop.
To learn more about perception distance visit here:
https://brainly.com/question/13034462
#SPJ4
Drop a book and a piece of paper side by side. Now, put the piece of paper flat on top of the
book and drop them together. Explain what happens and why it happens.
Answers
The electrical resistivity of a pure tantalum wire is 35 μΩ. Cm at 100K and 65 μΩ. Cm at 160K.
Calculate the electrical resistivity at room temperature (20°C)?
Answers
The electrical resistivity of a material is a measure of how strongly it resists the flow of electric current. The electrical resistivity of pure tantalum wire at room temperature (20°C) is approximately 78.68 μΩ·cm.
To calculate the electrical resistivity at room temperature (20°C), we can use the given resistivity values at 100K and 160K.
Step 1: Convert the given temperatures from Kelvin to Celsius.
100K = -173°C
160K = -113°C
Step 2: Find the change in resistivity per degree Celsius.
Change in resistivity = resistivity at 160K - resistivity at 100K
Change in resistivity = 65 μΩ·cm - 35 μΩ·cm = 30 μΩ·cm
Step 3: Find the change in temperature.
Change in temperature = 20°C - (-113°C) = 133°C
Step 4: Calculate the change in resistivity per degree Celsius.
Change in resistivity per degree Celsius = Change in resistivity / Change in temperature
Change in resistivity per degree Celsius = 30 μΩ·cm / 133°C
Step 5: Find the change in resistivity for 1°C.
Change in resistivity for 1°C = Change in resistivity per degree Celsius * 1°C
Change in resistivity for 1°C = (30 μΩ·cm / 133°C) x 1°C
Step 6: Calculate the resistivity at 20°C.
Resistivity at 20°C = resistivity at 100K + (Change in resistivity for 1°C x (20°C - (-173°C)))
Now, let's calculate the resistivity at 20°C using the given values.
Resistivity at 20°C = 35 μΩ·cm + [(30 μΩ·cm / 133°C) x (20°C - (-173°C))]
Calculating the above expression, we get:
Resistivity at 20°C = 35 μΩ·cm + [(30 μΩ·cm / 133°C) x 193°C]
Resistivity at 20°C = 35 μΩ·cm + [(30 μΩ·cm / 133°C) x 193°C]
Resistivity at 20°C = 35 μΩ·cm + 43.68 μΩ·cm
Resistivity at 20°C = 78.68 μΩ·cm
Conclusion , The electrical resistivity of pure tantalum wire at room temperature (20°C) is approximately 78.68 μΩ·cm.
To know more about temperature visit:
https://brainly.com/question/7510619
#SPJ11
An object is moving with uniform speed in a circle of radius r. Calculate the distance and displacement
(a) When it completes half the circle,
(b) When it completes full circle,
(c) What type of motion does the object possess ?
Answers
Answer and Explanation:
distance will be 2×3.14 (pie)×r
displacement will be 2r (diameter)
the motion is uniform circular motion as the object is moving in a circular path with uniform motion
Answer:
distance= pi*r=π×r²
displacement=2r
Mark as brainlest answer!
a motorcycle has a constant speed of 25.0 m/s as it passes over the top of a hill whose radius of curvature is 126 m. the mass of the motorcycle and driver is 342 kg. find the magnitudes of (a) the centripetal force and (b) the normal force that acts on the cycle.
Answers
The centripetal force on the motorcycle at the top of the hill is 1696.42 N and the normal force is 1723.57 N.
The speed of the motorcycle is 25 m/s and the mass of the motorcycle is 342 kg and the radius of curvature of the hill is 126m.
(a) The centripetal force on any curvature is given by,
F =MV²/R
Where,
F is the centripetal force,
M is the mass of the motorcycle,
R is the radius of curvature of the hill,
V is the speed at which it is travelling.
Putting all the values,
F = 342 x 25 x 25/126
F = 1696.42 N.
The centripetal force is 1696.42 N.
(b) At the top of the hill, the centripetal force and the normal force will be away from the ground and in opposite direction of the weight of the motorcycle,
N = W- F
W is the weight,
F is centripetal force and N is the normal force.
Putting values,
N = 3420 - 1696.42
N = 1723.57N.
The normal force is 1723.57 N.
To know more about Centripetal force, visit,
https://brainly.com/question/20905151
#SPJ4
If the circumference of a space shuttle's orbit around Earth is 42,522 km and the space shuttle orbits around it 1.4 times
every hour, what is the speed of the space shuttle in km/hour? In meters/second?
Answers
Answer:
105,000km or about 65,244mi
Explanation:
If the space shuttle orbits around it 1.4 times every hour then the speed of the space shuttle in km/hour would be 595330.8 Km/hour, and its speed in meters would be 165369.67 m/s.
What is speed?The total distance covered by any object per unit of time is known as speed. It depends only on the magnitude of the moving object.
Average speed = total distance /Total time
As given in the problem If the circumference of a space shuttle's orbit around Earth is 42,522 km and the space shuttle orbits around it 1.4 times every hour, then we have to find the speed of the space shuttle in km/hour
The total distance covered by the space shuttle in an hour = 42,522×1.4
= 595330.8 Km
The speed of the space shuttle in meters/second = 595330.8 × 1000/3600
= 165369.67 m/s
Thus, the speed of the space shuttle would be 595330.8 Km/hour, and its speed in meters would be 165369.67 m/s.
To learn more about speed here, refer to the link;
brainly.com/question/7359669
#SPJ5
Find the correct statement
The disturbance created by a source of sound in the medium do not travels through the medium but the particles of the medium does.
The disturbance created by a source of sound in the medium travels through the medium and not the particles of the medium
The particles and the disturbance created by a source of sound in the medium do not travels through the medium
The disturbance created by a source of sound in the medium travels through the medium along with the particles of the medium
Answers
Answer:The disturbance created by a source of sound in the medium travels through the medium and not the particles of the medium
Explanation:i hope this is right
The magnitude of a force is:
A) How fast an object moves when it is pushed
B) How far an object moves when it is pushed
C) how hard an object is pushed or pulled
D) how long it takes to push or pull an object
Answers
Answer:
c
Explanation:
force is how hard it is pulled or pushed
In this graph, the slope of the curve is
increasing. Explain this in terms of velocity
and acceleration.

Answers
Answer:
The slope of an x vs. t graph represents instantaneous velocity. As we can see, the slope of this graph is not constant- it is changing. This means that the instantaneous velocity is also changing. Therefore, the object is accelerating.
Explanation:
The Moon illusion can best be explained in terms of the relationship between
A. relative motion and relative height.
B. perceived distance and perceived size.
C. proximity and closure.
D. atmospheric air pressure and diffusion of light waves.
Answers
The Moon illusion is a phenomenon where the Moon appears larger when it's near the horizon compared to when it's high in the sky. This illusion can best be explained in terms of the relationship between perceived distance and perceived size.
When the Moon is near the horizon, it appears to be farther away than when it's high in the sky, which leads our brain to assume that it's larger. This is known as the size-distance illusion. Our brain is used to perceiving objects as smaller when they're farther away, but the Moon is an exception because it's always far away. Therefore, when it's near the horizon, our brain overcompensates and perceives it as larger than when it's high in the sky. This illusion has been studied by scientists for centuries and continues to be a topic of interest in psychology and neuroscience. Overall, the Moon illusion is an example of how our brain interprets visual information and creates illusions based on our past experiences and knowledge.
To Learn more about Moon illusion. Click this!
brainly.com/question/29971722
#SPJ11
Explain what is wrong with the following statement: A man walked at an average
velocity of 5.2m/s.
Answers
Answer:
check explanation
Explanation:
Whenever we talk about velocity ,it means that we r telling them the speed of the object+the direction of the motion of object but here direction isn't mentioned. That's the fault in the statement
PLEASE HELP 50 AND BEST ANSWER
Begin by printing out a copy of the periodic table. Use the file attached to the assignment page or download the file from the Course Resources folder.
1. Label the rows as the electron energy levels.
2. Label the number of valence electrons in Columns 1,2, and 13-18.
3. Label the metals, semi-metals, and non-metals using different colors. Make sure you don't obscure any of the information about different elements by coloring.
4. Label the ion charges for elements in the first 3 rows. Remember all the elements in Columns 1,2,16,17,18 will always have the same charge. Elements in Columns 13,14, or 15 can have different charges within the same row it's especially useful to write these charges on your periodic table. --
5. Label the trends for atomic size, ionization energy, and electron affinity.
Answers
Label the rows as the electron energy levels:
The rows of the periodic table are also known as periods. There are seven periods, and each period corresponds to a particular energy level. You can label them from 1 to 7, starting from the top row.
What are the responses to other questions?Label the number of valence electrons in Columns 1, 2, and 13-18:
Columns 1 and 2 are the s-block elements, and they have 1 and 2 valence electrons, respectively. Columns 13-18 are the p-block elements, and they have 3 to 8 valence electrons, respectively. You can label the number of valence electrons in each column.
Label the metals, semi-metals, and non-metals using different colors:
Metals are on the left side of the periodic table, semi-metals are in the middle, and non-metals are on the right side. You can use different colors to label them without obscuring any of the information about different elements.
Label the ion charges for elements in the first 3 rows:
Elements in the first 3 rows of the periodic table have predictable ion charges. The alkali metals (Group 1) have a charge of +1, the alkaline earth metals (Group 2) have a charge of +2, and the elements in Group 13 have a charge of +3. For Groups 15, 16, and 17, the charges are -3, -2, and -1, respectively. The noble gases (Group 18) are unreactive and do not form ions. You can write these charges for each element in their respective positions.
Label the trends for atomic size, ionization energy, and electron affinity:
Atomic size generally decreases from left to right across a period and increases from top to bottom within a group. Ionization energy generally increases from left to right across a period and increases from bottom to top within a group. Electron affinity generally increases from left to right across a period and becomes less negative from top to bottom within a group. You can label these trends on your periodic table as well.
learn more about electron energy levels: https://brainly.com/question/28101665
#SPJ1

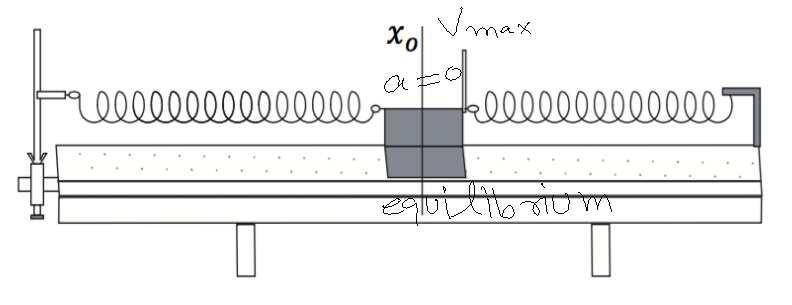
If the glider oscillates back and forth on the air-track, at what point in the motion is the acceleration zero? Where is the velocity maximum? Show with a drawing. 1.
Answers
The acceleration is zero when the glider is at the middle of the air-track, as it changes direction at this point. The velocity is maximum when the glider is at either end of the air-track.
What is velocity?The rate at which an object's location changes in a particular direction is measured by its velocity. Given that it has both its magnitude (or rather, size) and a direction, it is a vector quantity. Metres per second (m/s) is the standard unit of measurement for speed. In addition, it can be stated in different quantities as miles per hour (mph) or kilometres per hour (km/h). Speed, which is a measure of the velocity vector or its length, is connected to velocity. Speed does not have a direction and is typically expressed in the same units as velocity.
To learn more about velocity
https://brainly.com/question/80295
#SPJ4
)how far beyond its natural length (in cm) will a force of 50 n keep the spring stretched? (round your answer one decimal place.)
Answers
The spring will stretch beyond its natural length by 1.5 cm when a force of 50 N is applied.
The amount of stretching a spring experiences when a force of 50 N is applied to it is determined by Hooke's Law. According to Hooke's Law, the force applied to the spring and the extension of the spring are proportional. This means that the greater the force applied to the spring, the greater the extension.
Using Hooke's Law, the amount of extension of the spring when a force of 50 N is applied can be calculated using the following formula:
Extension = Force/Spring Constant
Where the spring constant is a measure of how stiff the spring is.
To calculate how far beyond its natural length (in cm) the spring will be stretched when a force of 50 N is applied, we first need to determine the spring constant of the spring in question. This can be done by measuring the natural length of the spring and then measuring how far it stretches with a known force. Once we have determined the spring constant, we can enter it into the formula above and solve for the extension.
For example, if the natural length of the spring is 15 cm and it extends to 18 cm with a force of 50 N, the spring constant would be 33.33 N/cm.
Using this spring constant, the extension of the spring when a force of 50 N is applied would be 1.50 cm
50/33.33 = 1.50.
Therefore, the spring will stretch beyond its natural length by 1.50 or 1.5 cm when a force of 50 N is applied.
Learn more about spring constant at :https://brainly.com/question/14670501
#SPJ4
What pressure will 14. 0 g of co exert in a 3. 5 l container at 75°c?
a) 4. 1 atm
b) 5. 0 atm
c) 6. 4 atm
d) 1. 1 atm
Answers
The pressure will 14. 0 g of co exert in a 3. 5 l container at 75°c is 4.1atm.
Therefore, option A is correct option.
Given,
Mass m = 14g
Volume= 3.5L
Temperature T= 75+273 = 348 K
Molar mass of CO = 28g/mol
Universal gas constant R= 0.082057L
Number of moles in 14 g of CO is
n= mass/ molar mass
= 14/28
= 0.5 mol
As we know that
PV= nRT
P × 3.5 = 0.5 × 0.082057 × 348
P × 3.5 = 14.277
P = 14.277/3.5
P = 4.0794 atm
P = 4.1 atm.
Thus we concluded that the pressure will 14. 0 g of co exert in a 3. 5 l container at 75°c is 4.1atm.
learn more about pressure:
https://brainly.com/question/22613963
#SPJ4
In an A.C circuit current leads voltage by phase π/2 then circuit is
Answers
Answer:
capacitive
Explanation:
In a capacitive circuit, current is proportional to the derivative of the voltage. For a sinusoidal excitation, this means current is at the highest level when voltage is increasing through zero. That is, current leads the voltage.
when a boxer hits a punching bag, the strength of his punch depends on how much force the bag can
Answers
When a boxer hits a punching bag, the strength of his punch depends on how much force the bag can withstand. The force of the punch is determined by the boxer's muscle strength and technique.
The more force the boxer can generate, the more powerful the punch will be. However, if the bag is not strong enough to withstand the force of the punch, it may break or tear. Therefore, it is important for boxers to use bags that are specifically designed to handle the force of their punches in order to avoid injury and ensure effective training.
The materials used in its manufacture and its shape are only two examples of the many variables that affect a punching bag's resistance. A bag made of a denser material, such heavy canvas or synthetic leather, will absorb more force than one made of a softer material, like vinyl or leather.
The resilience of the bag might also be impacted by its shape. A cylindrical bag will typically rebound more quickly than a bag with a flatter shape, like a banana or teardrop.
The method a boxer uses and their physical qualities, including as speed, power, and accuracy, have an impact on how strong their punches are as well.
Learn more about force here:
https://brainly.com/question/29983155
#SPJ11
PHYSICS.
……………………………………………….

Answers
Answer:
Work, W = F * d, and
Work = change in kinetic energy, so W=deltaKE.
Hence,
deltaKE=F * d
(1/2)*m*v^2 =F * d
d=[(1/2)*m*v^2]/F
d=[(1/2)*0.6*20^2]/5
d=24 m.
Explanation:
Work = change in kinetic energy, so W=deltaKE.
3) Скорость автомобиля увеличилась от 10 м/с до 20 м/с. Во сколько раз увеличилась его
кинетическая энергия?
Answers
sometimes when a chemical change ----------- occurs of a substance will change
shape
color
size
mass
Answers
Answer:
Chemical changes occur when a substance combines with another to form
Explanation:
Chemical changes occur when a substance combines with another to form a new substance, called chemical synthesis or, alternatively, chemical decomposition into two or more different substances. These processes are called chemical reactions and, in general, are not reversible except by further chemical reactions.