Answers
Answer:
C. lenses refract light; mirrors do not
This question involves the concepts of reflection and refraction.
The comparison of lenses and mirrors in their interaction with light is "C. Lenses refract light; mirrors do not.".
LENSES AND MIRRORSWhen it comes to the interaction with light, the key difference between lenses and mirrors is the difference of refraction and reflection. Reflection means the complete rebound of the light rays after striking on a surface without any absorption or transmission. On the other hand, refraction is the bending of light rays, while passing through a medium, without any rebound or absorption.
Lenses are tansparent from both sides, so they refract the light rays. While, mirrors are coated opaque from one side, so they reflect back the light rays.
Learn more about reflection and refraction here:
https://brainly.com/question/3764651
Related Questions
Question 8 of 10
On which parts of the heating curve for water does adding thermal energy
mainly cause the particles to move faster?
200
150 -
B
To
100
Temperature ('C)
A
50
С
0
-50
10
40
50
60
70
Time (min)
O A. C and D
B. A and B
O O O O
O C. Band C
OD. B and D

Answers
Answer:
The correct answer is A
Explanation:
In this exercise we are given a graph of temperature versus time.
In calorimeter processes there are two types
* one that when giving thermal energy to the system its temperature increases, this fundamentally due to the greater kinetic energy of the molecular ones, this process observes in the graphs as a straight line of constant slope
* A process donates all the thermal energy that is introduced is cracked in breaking the molecular bonds, taking matter from one thermodynamic state to another, for example: liquid to gas.
This process in curves as a horizontal line, that is, there is no temperature change,
When analyzing the graph shown, parts C and D are the one that show a change in temperature with thermal energy. The correct answer is A
Answer:
C and D
Explanation:
Just took the quiz
Compare the level of energy of radio and microwaves when compared to other waves on the spectrum.
Answers
Radio waves have photons
with the lowest energies.
Microwaves have a little
more energy than radio
waves. Infrared has still
more, followed by visible,
ultraviolet, X-rays and
Gamma rays.
Six seconds after starting from rest, a car is moving at 15 m/s. What is the car's
average acceleration?
6 m/s2
0-5 m/s?
5 m/s2
2.5 m/s?
-2.5 m/s?
Answers
Answer:
2.5 m/s²
Explanation:
a = ∆v/∆t = (15 m/s)/(6 s) = (15/6) m/s² = 2.5 m/s²
A bicycle camper rides from her starting point to her first campsite one day, then continues to a second campsite the next day. If her average speed for the two days equals the average of her speeds each day, what must be true about her journey?
Answers
Answer:
is there any more to this question
Explanation:
A small sphere of reference-grade iron with a specific heat of 447 J/kg K and a mass of 0.515 kg is suddenly immersed in a water-ice mixture. Fine thermocouple wires suspend the sphere, and the temperature is observed to change from 15 to 14C in 6.35 s. The experiment is repeated with a metallic sphere of the same diameter, but of unknown composition with a mass of 1.263 kg. If the same observed temperature change occurs in 4.59 s, what is the specific heat of the unknown material
Answers
Answer:
The specific heat of the unknown material is 131.750 joules per kilogram-degree Celsius.
Explanation:
Let suppose that sphere is cooled down at steady state, then we can estimate the rate of heat transfer (\(\dot Q\)), measured in watts, that is, joules per second, by the following formula:
\(\dot Q = m\cdot c\cdot \frac{T_{f}-T_{o}}{\Delta t}\) (1)
Where:
\(m\) - Mass of the sphere, measured in kilograms.
\(c\) - Specific heat of the material, measured in joules per kilogram-degree Celsius.
\(T_{o}\), \(T_{f}\) - Initial and final temperatures of the sphere, measured in degrees Celsius.
\(\Delta t\) - Time, measured in seconds.
In addition, we assume that both spheres experiment the same heat transfer rate, then we have the following identity:
\(\frac{m_{I}\cdot c_{I}}{\Delta t_{I}} = \frac{m_{X}\cdot c_{X}}{\Delta t_{X}}\) (2)
Where:
\(m_{I}\), \(m_{X}\) - Masses of the iron and unknown spheres, measured in kilograms.
\(\Delta t_{I}\), \(\Delta t_{X}\) - Times of the iron and unknown spheres, measured in seconds.
\(c_{I}\), \(c_{X}\) - Specific heats of the iron and unknown materials, measured in joules per kilogram-degree Celsius.
\(c_{X} = \left(\frac{\Delta t_{X}}{\Delta t_{I}}\right)\cdot \left(\frac{m_{I}}{m_{X}} \right) \cdot c_{I}\)
If we know that \(\Delta t_{I} = 6.35\,s\), \(\Delta t_{X} = 4.59\,s\), \(m_{I} = 0.515\,kg\), \(m_{X} = 1.263\,kg\) and \(c_{I} = 447\,\frac{J}{kg\cdot ^{\circ}C}\), then the specific heat of the unknown material is:
\(c_{X} = \left(\frac{4.59\,s}{6.35\,s} \right)\cdot \left(\frac{0.515\,kg}{1.263\,kg} \right)\cdot \left(447\,\frac{J}{kg\cdot ^{\circ}C} \right)\)
\(c_{X} = 131.750\,\frac{J}{kg\cdot ^{\circ}C}\)
Then, the specific heat of the unknown material is 131.750 joules per kilogram-degree Celsius.
You do 13 J of work as you lift a 35-N pail of water. Through what height did you lift the pail?
Answers
Height to which the lift of the pail is taken is 0.37m.
Height is the vertical distance of an object from the surface of the Earth.
Work done = 13 J
Weight of the pail of the water = 35-N
Gravity is defined as the force that attracts a body to the Earth or any other physical body that has mass.
The acceleration due to gravity is denoted by 'g' which has the value of 9.81 \(m/s^{2}\).Work done by gravity = mghW = mgh
mg = 13 J
W = 35 N
h = \(\frac{W}{mg}\)
h = \(\frac{13}{35}\)
h = 0.37 m
The height to which the lift of pail will be raised will be 0.37m.
To know more about Height,
https://brainly.com/question/2272699
#SPJ1
Each of the following figures shows a person (not to scale) located on Earth at either 40°N or 40°S latitude. Rank the figures based on how much time the person spends in daylight during each 24-hour period, from most to least. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them.
Answers
The ranking is based on the tilt of the Earth's axis and its orbit around the Sun. The figure at 40°N in June receives the most daylight because it is located at a high latitude during the summer solstice in the Northern Hemisphere. The Earth's axis tilts towards the Sun, resulting in longer days and shorter nights. The figure at 40°S in December receives a moderate amount of daylight as it is located at a lower latitude during the summer solstice in the Southern Hemisphere.
The figure at 40°N in December experiences less daylight because it is located at a high latitude during the winter solstice in the Northern Hemisphere, with shorter days and longer nights. Lastly, the figure at 40°S in June receives the least amount of daylight as it is located at a lower latitude during the winter solstice in the Southern Hemisphere, where the days are shortest and the nights are longest. Based on the information given, the ranking of figures based on the amount of daylight they experience in a 24-hour period, from most to least.
for such more questions on latitude
https://brainly.com/question/23751521
#SPJ8
Question 16 of 17
Figure (a) shows a wire that forms a rectangle (W = 23.0cm, H = 31.0cm) and has a resistance of 4.00 mOhm. Its interior is split into three equal areas, with magnetic fields B₁, B₂, and B. The fields are uniform within each region and directly out of or into the page as indicated. Figure (b) gives the change in the z components B, of the three fields with time t; the vertical axis scale is set by B, = 3.00 μT
and B-2.50B, What are the
(a) the magnitude and
(b) direction of the current induced in the wire?
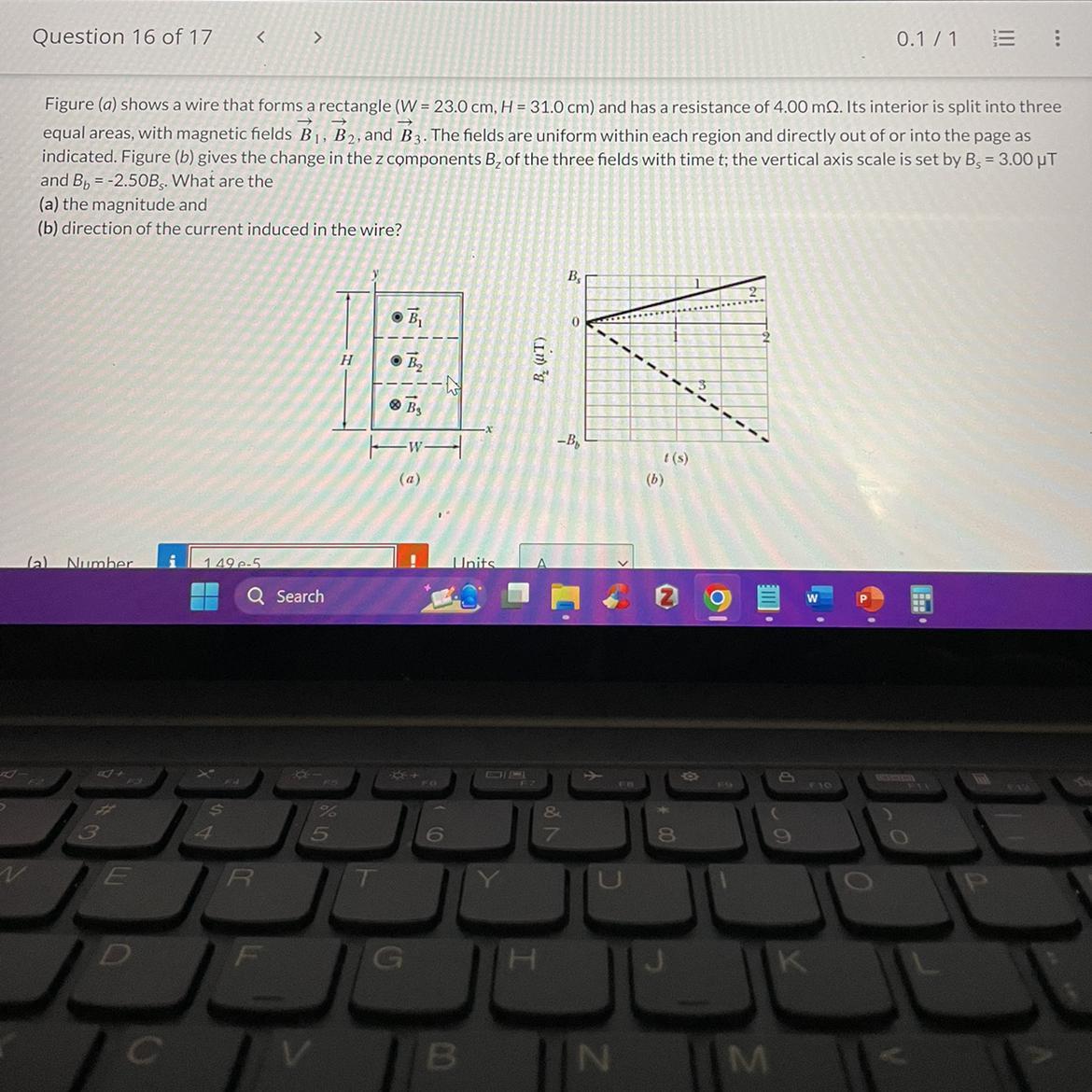
Answers
For the magnetic fields:
(a) 53.8 A(b) The induced current will flow counterclockwise.How to determine magnitude and direction?From Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction, the emf induced in the wire is given by:
emf = -dΦ/dt
where Φ is the magnetic flux through the wire. The negative sign indicates that the induced emf opposes the change in magnetic flux.
The magnetic flux through each of the three regions can be calculated as follows:
Φ₁ = B₁WH/3
Φ₂ = B₂WH/3
Φ₃ = BWH/3
The total magnetic flux through the wire is:
Φ = Φ₁ + Φ₂ + Φ₃ = (B₁ + B₂ + B)WH/3
Taking the time derivative of the magnetic flux:
dΦ/dt = (B₁ + B₂ + B)(WH/3)(dB/dt)
Substituting the given values:
dΦ/dt = (3.00 μT + 2.50(3.00 μT))(0.23 m)(0.31 m)(1.00 m)/(3)(0.010 s) = 0.215 V
The induced emf is equal to the product of the current and the resistance of the wire:
emf = IR
Solving for I:
I = emf/R = 0.215 V / 4.00 mΩ = 53.8 A
The direction of the induced current can be determined using Lenz's law, which states that the direction of the induced current is such that it opposes the change in magnetic flux that produced it. In this case, the induced current will produce a magnetic field that opposes the change in the magnetic field through the wire.
As the magnetic field increases in the downward direction, the induced current will produce a magnetic field in the upward direction to oppose the increase. As the magnetic field decreases in the downward direction, the induced current will produce a magnetic field in the downward direction to oppose the decrease.
Therefore, the direction of the induced current will be counterclockwise.
Find out more on magnetic fields here: v
#SPJ1
A metalrod of length 40.0cm at 20°C is heated to a temperature of 45°C. If the new length is 40.05cm, Calculate its Linear expansivity.
Answers
Answer:
The answer is 5×10‐⁵
Step-by-step Explanation:
\( \alpha = \frac{l2 - l1}{l1( \beta 2 - \beta 1)} \)
let ß be ø
\( \alpha = \frac{40.05 - 40}{40(45 - 20)} \)
\( \alpha = \frac{0.05}{40 \times 25} \)
\( \alpha = \frac{0.05}{1000}\)
\( \alpha = \frac{0.05}{1000}\)\( \alpha = 5.0 \times {10}^{ - 5} \)
Particles q₁ = -29.6 μC, q2 = +37.7 μC, and 93 = -10.8 μC are in a line. Particles q₁ and q2 are separated by 0.630 m and particles q₂ and q3 are separated by 0.315 m. What is the net force on particle q₁ ?
ANSWERED: 22.06 N

Answers
The net force on particle q₁ is approximately +25.6 N.
The electrostatic forces between particle q1 and the other two particles, q2 and q3, must be taken into account in order to determine the net force on particle q1. Coulomb's Law describes the electrostatic force between two charged particles:
F = k * |q₁ * q₂| / r²
F is the force, k is the electrostatic constant (9 x 109 N m2/C2), q1 and q2 are the charges' magnitudes, and r is the distance separating them.
Let's first determine the force between q1 and q2:
F₁₂ = k * |q₁ * q₂| / r₁₂²
F₁₂ = (9 x 10^9 N m²/C²) * |(-29.6 μC) * (+37.7 μC)| / (0.630 m)²
F₁₂ = (9 x 10^9 N m²/C²) * (29.6 x 10^-6 C) * (37.7 x 10^-6 C) / (0.630 m)²
F₁₂ ≈ -7.45 N
The absence of a positive sign suggests an attractive force between q1 and q2.
Let's next determine the force between q2 and q3:
F₂₃ = k * |q₂ * q₃| / r₂₃²
F₂₃ = (9 x 10^9 N m²/C²) * |(+37.7 μC) * (-10.8 μC)| / (0.315 m)²
F₂₃ = (9 x 10^9 N m²/C²) * (37.7 x 10^-6 C) * (10.8 x 10^-6 C) / (0.315 m)²
F₂₃ ≈ +33.05 N
The presence of a positive sign suggests a repulsive force between q2 and q3.
We must now add all the forces in order to determine the net force on q1:
Net force = F₁₂ + F₂₃
Net force ≈ -7.45 N + 33.05 N
Net force ≈ +25.6 N
The presence of a positive sign implies that the net force is pointing to the right, in the same direction as particle q2.
for more such questions on force
https://brainly.com/question/12785175
#SPJ8
PLEASE HELP ME 20 POINTS Some metals have a molecular structure that makes them good conductors. Explain how understanding this relationship can help engineers make more powerful batteries.
PLEASE I KNOW THE STRUCTURE I JUST NEED HOW BY UNDERSTANDING THE RELATIONSHIP THEY CAN MAKE MORE POWERFUL BATTERIES.
PLEASE IM DYEING HERE I JUST NEED THIS ANSWER I WILL GIVE BRAINLIST AND 5 STARS A HEART WHATEVER JUST PLEASEEEEE.
Answers
Answer:
negative plus positive with energy = battery
Explanation:
Calculate the momentum of a Lion of mass 130-kg and moving at a speed of 22.3 m/s [W]
Answers
Answer:
289.9 kg.m/sExplanation:
The momentum of an object can be found by using the formula
momentum = mass × velocity
From the question we have
momentum = 130 × 22.3
We have the final answer as
289.9 kg.m/sHope this helps you
The velocity time graph of an object mass 50 g is shown in figure study graph and answer
1)calculate force acting on object in time interval 0-3 seconds
2)calculate the force acting on the object in the time interval 6-10 seconds
3)Is there any time interval in which no force acts on object.Justify

Answers
1) The force acting on the object during the time interval 0-3 seconds is 1/3 N.
2) The force acting on the object during the time interval 6-10 seconds is -0.5 N.
3) There is no time interval in which no force acts on the object.
(i) Force acting on the object in time interval 0-3 seconds. Force acting on the object is equal to the product of its mass and acceleration, i.e.,F = ma.
In the given velocity-time graph, the acceleration of the object can be determined by determining the slope of the velocity-time graph from 0 to 3 seconds.
Slope = (change in velocity) / (change in time)= (20-0) / (3-0) = 20/3 m/s^2
Acceleration, a = slope= 20/3 m/s^2
Mass of the object, m = 50 g = 0.05 kg
∴ Force acting on the object, F = ma= 0.05 × 20/3= 1/3 N.
Therefore, the force acting on the object during the time interval 0-3 seconds is 1/3 N.
(ii) Force acting on the object in time interval 6-10 seconds. Similar to the first question, the force acting on the object in time interval 6-10 seconds can be determined by determining the acceleration of the object during this time interval.
The slope of the velocity-time graph from 6 seconds to 10 seconds can be determined as follows:
Slope = (change in velocity) / (change in time)= (-20-20) / (10-6) = -40/4= -10 m/s^2 (negative sign indicates that the object is decelerating)
Mass of the object, m = 50 g = 0.05 kg
∴ Force acting on the object, F = ma= 0.05 × (-10)= -0.5 N.
Therefore, the force acting on the object during the time interval 6-10 seconds is -0.5 N.
(iii) Time interval in which no force acts on the object. There is no time interval in which no force acts on the object. This is because, as per Newton's first law of motion, an object will continue to remain in a state of rest or uniform motion along a straight line unless acted upon by an external unbalanced force.In other words, if the object is moving with a constant velocity, there must be a force acting on the object to maintain its motion.
Therefore, there is no time interval in which no force acts on the object.
For more such questions on force, click on:
https://brainly.com/question/12785175
#SPJ8
A 0.5 kg basketball moving 5 m/s to the right collides with a 0.05 kg tennis
ball moving 30 m/s to the left. After the collision, the tennis ball is moving 34
m/s to the right. What is the velocity of the basketball after the collision?
Assume an elastic collision occurred.
O A. 11.4 m/s to the left
O B. 11.4 m/s to the right
O C. 1.4 m/s to the right
O D. 1.4 m/s to the left
Answers
Answer:
1.4 m/s to the left
Explanation:
just took it c:
If you, a physics student, weigh about 70 kg, are standing on the surface of 1
the Moon, who's mass is 7.34 x 10^22 kg what is the force of gravity acting
on the Moon and yourself? The radius of the Moon is 1.71 x 10^6 m.
25 units
400 units
117 N
200 N
Answers
Answer:
it's answer is 117 N
F = Gm1m2/r^2
F = 6.67 * 10 ^-11 * 70 * 7.34 * 10 ^22/(1.71 * 10 ^6)^2
F = 117 N
hope it helps you
Grace is attempting to lift an object off the ground a distance of 3m. She applies 50N of force and generates 75J/s. How long does the lift take?
Answers
To lift an object off the ground a distance of 3m, Grace applies 50N of force and generates 75J/s. The time taken by Grace for the lift is 2 seconds.
What is force?A force is an effect that changes, or accelerates, the velocity of a mass-moving object (such as one that is travelling from a state of rest). It is a vector quantity since it can be a push or a pull and always has magnitude and direction. It is denoted by the letter F and is measured in newtons (N), the SI unit of force.
According to Newton's second law, an object's net force is equal to the speed at which its momentum is changing over time. This rule suggests that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force exerted on the object, is in the direction of the net force, and is inversely proportional to the mass of the object if its mass is constant.
According to the equation,
P = \(\frac{W}{t}\)
where,
P is the power,
W is the work done and,
t is the time taken.
W = F×S
where,
F is the applied force and
S is the distance.
Substituting the values and solving for t,
time taken = 2 seconds
To know more about momentum, visit:
https://brainly.com/question/30487676
#SPJ1
What is sound waves
Answers
Sound waves are a type of mechanical wave that propagate through a medium, typically air but also other materials such as water or solids.
Characteristics of sound wavesFrequency: the frequency of a sound wave refers to the number of cycles or vibrations it completes per second and is measured in Hertz (Hz).
Amplitude: the amplitude of a sound wave refers to the maximum displacement or intensity of the wave from its equilibrium position. It represents the loudness or volume of the sound, with larger amplitudes corresponding to louder sounds and smaller amplitudes corresponding to softer sounds.
Wavelength: the wavelength of a sound wave is the distance between two consecutive points in the wave that are in phase, such as from one peak to the next or one trough to the next. It is inversely related to the frequency of the wave.
Learn more about sound waves at
https://brainly.com/question/1199084
#SPJ1
3. A car with a mass of 1600 kg has a kinetic energy of 125 000 J. How fast is it moving?
Answers
The car is moving at approximately 12.5 meters per second.
The kinetic energy (KE) of an object can be calculated using the formula:
KE = 1/2 * m * \(v^2\)
where
KE = kinetic energy,
m =Mass of the object, and
v = velocity.
In this case, we are given the mass (m) of the car as 1600 kg and the kinetic energy (KE) as 125,000 J. To find the velocity .
Substituting the values , we have:
125,000 J = 1/2 * 1600 kg *\(v^2\)
Now, we can solve for v by rearranging the equation:
\(v^2\) = (2 * 125,000 J) / 1600 kg
\(v^2\) = 156.25 \(m^2/s^2\)
Taking the square root, we find:
v = √156.25\(m^2/s^2\)
v ≈ 12.5 m/s
Therefore, the car is moving at approximately 12.5 meters per second.
Know more about kinetic energy here:
https://brainly.com/question/8101588
#SPJ8
a stone dropps 7,11m how long will it take it to fall
Answers
The time it takes the stone to fall from a height of 7.11 m is 1.2 seconds.
What is time?Time can be defined as an ongoing and continuous sequence of events that occur in succession, from past through the present, and to the future.
To calculate the time it takes the stone to drop from an height of 7.11 m, we use the formula below.
Formula:
H = ut+gt²/2............ Equation 1Where:
H = Heightu = Initial velocityt = Timeg = Acceleration due to gravityFrom the question,
Given:
u = 0 m/sH = 7.11 mg = 9.8 m/s²Substitute these values into equation 1 and solve for t.
7.11 = (0×t)+9.8×t²/27.11 = 4.9t²t² = 7.11/4.9t² = 1.451t = √1.451t = 1.2 secondsHence, the time it takes the stone to fall is 1.2 seconds.
Learn more about time here: https://brainly.com/question/26046491
#SPJ1
Why hurricane is dangerous?
Answers
Answer:
Hurricanes are dangerous because they often carry high winds, in which destroy our homes and other recreational buildings. They also cause flooding, which is a threat to crops, animals, and shelters.
Explanation:
If you enjoyed my answer I would very much appreciate a brainliest. Thank you, and have a great day.
~Kai~
HONI A ball is rolling steady on the floor. (a) Draw and label all the forces acting on the ball. (b) Describe the relationships between all the forces acting on the ball
Answers
a) The image is attached to this answer
b) The kinetic friction force affects the forward force of the ball.
What is the relationship between the forces that act on a rolling ball?
The force that opposes a rolling ball's motion is called rolling friction. It slows the ball down by acting in the opposite direction to that of the ball's motion. The weight of the ball and the type of the surface are two variables that affect rolling friction.
The force that a surface uses to maintain the weight of an object that is resting on it is known as the normal force. When a ball is rolling, the normal force exerts itself perpendicular to the surface the ball is moving on. It maintains the ball's weight balance and offers the required reaction force for rolling motion.
Learn more about rolling ball:https://brainly.com/question/29409976
#SPJ1
31. Which of the following is a way that microwaves and x-rays are similar? (2 points)
O They both have technological uses.
O They are both high energy waves.
O They are both safe to be exposed to at high doses.
O They are both used to transmit information. jjhh
Answers
Option A. They both have technological uses. is the way that microwaves and x-rays are similar.
An X-ray, or, a good deal less usually, X-radiation, is a penetrating shape of excessive-power electromagnetic radiation. Maximum X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, similar to frequencies inside the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz and energies in the range a hundred 45 eV to 124 keV.
X-rays use invisible electromagnetic strength beams to provide pictures of inner tissues, bones, and organs on movie or virtual media. Widespread X-rays are completed for lots motives, inclusive of diagnosing tumors or bone injuries.
Learn more about X-ray here:-https://brainly.com/question/24505239
#SPJ9
A high-wire artist missteps and falls 9.2 m to the ground. What is her velocity upon landing (just before she strikes the ground)?
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
We can use the kinematic equation to find the velocity of the high-wire artist just before she strikes the ground:
vf^2 = vi^2 + 2ad
where vf is the final velocity (the velocity just before she strikes the ground), vi is the initial velocity (which we can assume is 0), a is the acceleration due to gravity (which is approximately 9.81 m/s^2), and d is the distance fallen (which is 9.2 m).
Plugging in the values, we get:
vf^2 = 0 + 2(9.81 m/s^2)(9.2 m)
Simplifying:
vf^2 = 180.24 m^2/s^2
Taking the square root of both sides:
vf = 13.43 m/s
Therefore, the velocity of the high-wire artist just before she strikes the ground is 13.43 m/s.
Answer:
Below
Explanation:
Explanation:
Her POTENTIAL energy (mgh)
will be converted to KINETIC energy (1/2 mv^2)
so
mgh = 1/2 mv^2 divide both sides of the equation by m
gh = 1/2 v^2 solve for 'v'
v = sqrt ( 2 g h) = sqrt ( 2 * 9.81 * 9.2 ) = 13.4 m/s
Select the appropriate shape for the given volume formula.
V = trh
va
V = jwh
V=

Answers
Answer: hope this helps
Explanation:

⦁ A certain resistor is required to dissipate 0.25 W, what standard rating should be used?
Answers
Answer:A
Explanation:
A screwdriver is used to loosen a screw nail. The radius of the handler is 4.0 cm. The nail puts the force at 0.2 cm from the axis. The picture is shown. You apply 10 N force to loosen the nail. How much force does the nail apply to the screwdriver?
Answers
Answer:
200 N
Explanation:
Torque at handle = torque at nail
τ = τ
Fr = Fr
(10 N) (4.0 cm) = F (0.2 cm)
F = 200 N
A plane, diving with constant speed at an angle of 44.1° with the vertical, releases a projectile at an altitude of 611 m. The projectile hits the ground 5.40 s after release. (a) What is the speed of the plane? (b) How far does the projectile travel horizontally during its flight? What were the magnitudes of the (c) horizontal and (d) vertical components of its velocity just before striking the ground? (State your answers to (c) and (d) as positive numbers.)
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
Let the velocity of projection be V .
component of velocity in vertically downward direction = v cos 44.1
component of velocity in horizontal direction = v sin 44.1
s = ut + 1/2 gt²
611 = v cos 44.1 x 5.4 + 1/2 x 9.8 x 5.4²
= 611 = 3.88 v + 142.88
v = 120.65 m /s
b )
horizontal component of velocity of projectile = v sin 44 .1 = 120.65 sin44.1
= 83.96 m /s
horizontal displacement = 83.96 x 5.4 = 453.38 m
c ) horizontal component will remain unchanged so horizontal component
= v sin 44 .1 = 120.65 sin44.1
= 83.96 m /s
d ) velocity of projectile just before striking the ground
v = u + gt
= v cos 44.1 + 9.8 x 5.4
= 120.65 xcos 44.1 + 9.8 x 5.4
= 86.79 + 52.92
= 139.71 m /s
You travel 250 km at 45 degrees South of East in 6.5 hours, then turn and travel 155 km at 45 degrees North of East in 3.5 hours
A) What is the elapsed time?
B) What is the total distanced traveled?
C) What is the total displacement?
D) What is the average speed for the trip?
E) What is the average velocity for the trip?
Answers
B.405km
C. 95km
D.40.5km/h
E. 40.5km/h south east
Calculate the net force (N) acting
on an object with the following: 5 N
to the right and 10 N to the left.
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
its unbalanced
Q 1-1 Marks If a car moved one full circular track of 15 Km, which sentence describes its motion?
Answers
The sentence that best describes the motion is "the motion is a circular motion and has completed one revolution".
Question: "If a car moved one full circular track of 15 Km, which sentence describes its motion?"
What is a circular motion?An object moves in a circle at a constant speed in a motion known as uniform circular motion. Any point on a propeller, for instance, that is spinning continuously, is moving uniformly in circles.
There are two types of circular motion: uniform and non-uniform.
Circular motion can be seen in the orbit of a satellite, ice skaters moving at a constant speed in a circle, and vehicles traveling in a circle.
Learn more about circular motion here:
https://brainly.com/question/29199671
#SPJ1