Find the length and width of a rectangle that has the given perimeter and a maximum area. Perimeter: 352 meters length = ... m
width = ... m
Answers
The length of the rectangle is 88 meters and the width of the rectangle is 88 meters.
To find the length and width of a rectangle that has the given perimeter and a maximum area, we need to use the formula for the perimeter of a rectangle which is P = 2l + 2w, where P is the perimeter, l is the length, and w is the width.
So, we have P = 2l + 2w = 352 meters.
To find the maximum area, we need to use the formula for the area of a rectangle which is A = lw.
We can solve for one variable in terms of the other in the perimeter equation to get:
l = (352 - 2w)/2
l = 176 - w
Now we can substitute this expression for l into the area formula:
A = l(176 - w) = 176l - lw
A = (176 - w)w = 176w - w^2
To find the maximum area, we need to take the derivative of A with respect to w and set it equal to zero:
dA/dw = 176 - 2w = 0
w = 88
Substituting this value of w back into the expression for l, we get:
l = 176 - w = 88
Know more about rectangles here:
https://brainly.com/question/29123947
#SPJ11
Related Questions
The finite geometric sequence has 10 terms. The sum of all terms with even index is 682 and the sum of all terms with odd index is 1364. Determine the first term. Please also state what does "index" refer to in the question?
Answers
Answer:
First term=1024
Common ratio = ½
Step-by-step explanation:
Index means its position
Even index means the 2nd, 4th, 6th ....terms
a storekeeper increased the price of hats by 5%. A hat was originally priced at $15.00
Answers
1.05 x = 33.60
x = 33.60/ 1.05 = original price = $
which table of values represent a linear relationship?
Answers
Table A represents a linear relationship because the values in the y column change at a constant rate as x increases.
Which table of values represents a linear relationship between two variables?To see if a table of numbers exhibits a linear connection, see if the values in the y column move at a constant rate as x grows.
Table A depicts a linear relationship because as x grows by one, y increases by three. This indicates that the slope of the line linking the points in the table is constant, and the relationship is linear.
Table B does not depict a linear relationship since the rate of change in y is not constant as x grows. For example, y increases by 4 between x=1 and x=3, but only by 4 between x=3 and x=5. This indicates that the slope of the line linking the points in the table is not constant, and the relationship is not linear.
Table C does not depict a linear relationship since the rate of change in y is not constant as x grows. For example, between x=1 and x=4, y rises by 6, but from x=4 and x=9, y also increases by 6. This signifies that the slope of the line linking the points in the table is not constant.
Therefore, the table of values that represents a linear relationship is Table A.
To know more about linear relationship, visit
brainly.com/question/11663530
#SPJ1
The complete question is: Which of the following tables of values represents a linear relationship between two variables?
Table A:
x | y
1 | 3
2 | 6
3 | 9
4 | 12
Table B:
x | y
1 | 4
3 | 8
5 | 12
7 | 16
Table C:
x | y
1 | 2
4 | 8
9 | 14
16 | 20
ABCD is a trapezium.
EBC is a straight line.
F is the point on AB so that DFE is a straight line.
Angle BEF = 45°
Angle FBC = 100°
Work out the value of angle ADF.
Give a reason on the same line of each
stage of your working.
+
F
Answer: angle ADF =
E
45°
100°
B
Diagram not drawn to scale
C
Total marks: 4

Answers
Answer:
35 Degrees
Step-by-step explanation:
Given in figure.
Happy to help :)

The solution is, the value of the angle ADF = 35° .
Here, we have,
from the given diagram, we get,
ABCD is a trapezium.
EBC is a straight line.
F is the point on AB so that DFE is a straight line.
Angle BEF = 45°
Angle FBC = 100°
now, we have,
angle FBE = 180 - 100
= 80 degrees
now, from triangle BEF , we get,
Angle EFB = 55 degrees
again, as AFB is vertically opposite angle,
so, angle AFB = Angle EFB = 55 degrees
finally from triangle ADF , we get,
Angle ADF = 180 - 90 - 55
= 90 - 55
= 35 degrees
so, the value of the angle ADF = 35° .
To learn more on angle click:
brainly.com/question/28451077
#SPJ2
Find the solutions to 8x^2-56x=0 check all that apply
Answers
Answer:
\(\boxed{ x = 0 \ \ OR \ \ x = 7}\)
Step-by-step explanation:
\(8x^2 -56 = 0\)
Greatest common factor = 8x
=> \(8x(x-7) = 0\)
Setting results equal to 0
Either:
8x = 0 OR x-7 = 0
x = 0 OR x = 7
Answer:
x= 0 or 7
Step-by-step explanation:
if you factor out the equation by 8, you get 8x(x-7)=0, which if you simplify that, gets you 0 or 7.
can someone help me please

Answers
Answer:
11. Jason needs to sell 35 bird feeders to make a profit of $135.12. 80 guests must attend the picnic to pay for the permit.The accounts receivable department at Rick Wing Manufacturing has been having difficulty getting customers to pay the full amount of their bills. Many customers complain that the bills are not correct and do not reflect the materials that arrived at their receiving docks. The department has decided to implement SPC in its billing process. To set up control charts, 10 samples of 100 bills each were taken over a month's time and the items on the bills checked against the bill of lading sent by the company's shipping department to determine the number of bills that were not correct. The results were:Sample No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10No. of Incorrect Bills 4 3 17 2 0 5 5 2 7 2a) The value of mean fraction defective (p) = _____ (enter your response as a fraction between 0 and 1, rounded to four decimal places).The control limits to include 99.73% of the random variation in the billing process are:UCL Subscript UCLp = ______ (enter your response as a fraction between 0 and 1, rounded to four decimal places).LCLp = ____ (enter your response as a fraction between 0 and 1, rounded to four decimal places).Based on the developed control limits, the number of incorrect bills processed has been OUT OF CONTROL or IN-CONTROLb) To reduce the error rate, which of the following techniques can be utilized:A. Fish-Bone ChartB. Pareto ChartC. BrainstormingD. All of the above
Answers
The value of mean fraction defective (p) is 0.047.
To find the mean fraction defective (p), we need to calculate the average number of incorrect bills across the 10 samples and divide it by the sample size.
Total number of incorrect bills = 4 + 3 + 17 + 2 + 0 + 5 + 5 + 2 + 7 + 2 = 47
Sample size = 10
Mean fraction defective (p) = Total number of incorrect bills / (Sample size * Number of bills in each sample)
p = 47 / (10 * 100) = 0.047
b) The control limits for a fraction defective chart (p-chart) can be calculated using statistical formulas. The Upper Control Limit (UCLp) and Lower Control Limit (LCLp) are determined by adding or subtracting a certain number of standard deviations from the mean fraction defective (p).
Since the sample size and number of incorrect bills vary across samples, the control limits need to be calculated based on the specific p-chart formulas. Unfortunately, the sample data for the number of incorrect bills in each sample was not provided in the question, making it impossible to calculate the control limits.
c) Without the control limits, we cannot determine if the number of incorrect bills processed is out of control or in control. Control limits help identify whether the process is exhibiting random variation or if there are special causes of variation present.
d) To reduce the error rate in the billing process, all of the mentioned techniques can be utilized:
A. Fish-Bone Chart: Also known as a cause-and-effect or Ishikawa diagram, it helps identify and analyze potential causes of errors in the billing process.
B. Pareto Chart: It prioritizes the most significant causes of errors by displaying them in descending order of frequency or impact.
C. Brainstorming: Involves generating creative ideas and solutions to address and prevent errors in the billing process.
Using these techniques together can help identify root causes, prioritize improvement efforts, and implement corrective actions to reduce errors in the billing process.
Know more about mean fraction defective here:
https://brainly.com/question/29386640
#SPJ11
Hi how do I solve this? Step by step please

Answers
Answer:
break it down by using pmedas
. Verify the identities: a) csc a tan a = cos a sec² 8 1+cot ²8 = tan²0 b) = cos ß + cos ß tan² ß cos B cot² 1-sin 8 = csc 8+1 sin 9 d)
Answers
a. the identity is verified. b. the LHS is equal to the RHS, and the identity is verified. c. LHS is equal to the RHS, and the identity is verified.
a) To verify the identity csc(a) tan(a) = cos(a) sec²(a), we start with the left-hand side (LHS):
csc(a) tan(a) = (1/sin(a)) * (sin(a)/cos(a)) = 1/cos(a) = cos²(a)/cos(a) = cos(a) sec²(a)
The last step follows from the fact that sec(a) = 1/cos(a). Thus, we have shown that the LHS is equal to the RHS, and the identity is verified.
To verify the identity 1+cot²(θ) = tan²(θ), we start with the left-hand side (LHS):
1 + cot²(θ) = 1 + cos²(θ)/sin²(θ) = (sin²(θ) + cos²(θ))/sin²(θ) = 1/sin²(θ)
Next, we simplify the right-hand side (RHS):
tan²(θ) = sin²(θ)/cos²(θ) = (sin²(θ) + cos²(θ))/cos²(θ) = 1/cos²(θ)
Since sin²(θ) + cos²(θ) = 1, we can see that the LHS and RHS are equal. Thus, the identity is verified.
b) To verify the identity (cos(β) + cos(β)tan²(β)) / (cos(β)cot²(θ) - sin(θ)) = csc(θ) + 1/sin(θ), we start with the left-hand side (LHS):
(cos(β) + cos(β)tan²(β)) / (cos(β)cot²(θ) - sin(θ))
= cos(β)(1 + tan²(β)) / (cos(β)/sin(θ) - sin(θ))
= cos(β)(sec²(β)) / ((cos(β)-sin²(θ))/sin(θ))
= cos(β)/sin(β) * sin²(θ)/(cos(β)-sin²(θ))
= csc(θ) + 1/sin(θ)
In the second step, we used the identity for cot(θ), which is cot(θ) = cos(θ)/sin(θ). Thus, we have shown that the LHS is equal to the RHS, and the identity is verified.
c) To verify the identity sin(θ)/1+cos(θ) + 1+cos(θ)/sin(θ) = 2csc(θ), we start with the left-hand side (LHS):
sin(θ)/(1+cos(θ)) + (1+cos(θ))/sin(θ)
= sin²(θ)/(sin(θ)(1+cos(θ))) + (1+cos(θ))²/(sin(θ)(1+cos(θ)))
= [sin²(θ) + (1+cos(θ))²] / [sin(θ)(1+cos(θ))]
= [sin²(θ) + 1 + 2cos(θ) + cos²(θ)] / [sin(θ)(1+cos(θ))]
= (2 + 2cos(θ)) / [sin(θ)(1+cos(θ))]
= 2(1+cos(θ)) / [sin(θ)(1+cos(θ))] = 2csc(θ)
In the fourth step, we used the identity sin²(θ) + cos²(θ) = 1. Thus, we have shown that the LHS is equal to the RHS, and the identity is verified.
Learn more about identity here
https://brainly.com/question/24496175
#SPJ11
Bob is taxed at a 21% tax rate for his federal taxes. Last year, he reduced his taxable income by contributing $550 per biweekly paycheck to his tax deferred retirement account and $90 per biweekly paycheck to his FSA. How much did he reduce his annual federal taxes by if his gross biweekly pay is $2,460?
Answers
Answer:
$133.80
Step-by-step explanation:
First, if Bob did not make those contributions, his tax would be 21% of the full $2,460. That is (.21)(2460) = $516.60.
But those contributions reduce his taxable income to
$2,460 - $640 (the $640 is $550 + $90)
His reduced taxable income is $1820. Now his tax is 21% of $1820, which is (.21)(1820) = $382.20
The amount of tax Bob saved is the difference between the two tax amounts.
$516.00 - $382.20 = $133.80
Bob saved $133.80 in taxes. Be like Bob. :-)
10 points please help me and i will mark brainlyist

Answers
Answer:
Min: 32
Lower Quartile: 36
Median: 42
Upper Quartile: 47
Max: 53
Interquartile: 11
Step-by-step explanation:
The min. is just the lowest number. The lower quartile is the number in the middle of the numbers below 42, the median is the number in the very middle, the upper quartile is the middle number above 41 and the interquartile is the upper quartile minus the lower quartile.
Calculate the perimeter of a semi-circle
whose diameter is 14cm
Answers
perimeter of a semicircle is \(\frac{2\pi r}{2}+2r=\frac{d\pi}2 +d\)
$d=14$
so, perimeter= $14\cdot\frac{22}7\cdot \frac{1}2+14=22+14=36$ cm
Answer:
Perimeter of semi-circle = 36 cm
Step-by-step explanation:
diameter = d = 14 cm
Perimeter of semicircle = Circumference of semi-circle + diameter
= \(\frac{1}{2}\pi d + d\)
= \(\frac{1}{2}*\frac{22}{7}*14 +14\\\)
= 22 + 14
= 36 cm
PLS HELP ME ILL MARK BRAINLIEST JUST PLEASE

Answers
Answer:
area of figure (a) = 152cm²
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
same method will be used to solve ( b) and (c)

what is the x and y intercept of y= -2x - 21 ?
Answers
Answer:
To find the x-intercept of a linear equation in the form y = mx + b, we set y = 0 and solve for x. Similarly, to find the y-intercept, we set x = 0 and solve for y.
For the equation y = -2x - 21, to find the x-intercept, we set y = 0 and solve for x:
0 = -2x - 21
2x = -21
x = -21/2
So the x-intercept is (-10.5, 0).
To find the y-intercept, we set x = 0 and solve for y:
y = -2(0) - 21
y = -21
So the y-intercept is (0, -21).
Step-by-step explanation:
the x-intercept of the equation y = -2x - 21 is (-21/2, 0) and the y-intercept is (0, -21). These two points are important in graphing the line defined by this equation.
How to solve the question ?
To find the x-intercept and y-intercept of the linear equation y = -2x - 21, we need to understand what these intercepts represent.
The x-intercept is the point where the graph of the equation crosses the x-axis, meaning that y is equal to zero. In other words, it is the value of x where the line intersects with the x-axis. Conversely, the y-intercept is the point where the graph of the equation crosses the y-axis, meaning that x is equal to zero. It is the value of y where the line intersects with the y-axis.
To find the x-intercept, we set y equal to zero and solve for x:
0 = -2x - 21
2x = -21
x = -21/2
Therefore, the x-intercept is (-21/2, 0).
To find the y-intercept, we set x equal to zero and solve for y:
y = -2(0) - 21
y = -21
Therefore, the y-intercept is (0, -21).
To summarize, the x-intercept of the equation y = -2x - 21 is (-21/2, 0) and the y-intercept is (0, -21). These two points are important in graphing the line defined by this equation. The x-intercept tells us where the line crosses the x-axis, while the y-intercept tells us where the line crosses the y-axis. Knowing these intercepts allows us to draw the line more accurately and understand its behavior in different regions of the coordinate plane.
To know more about intercept visit :-
https://brainly.com/question/24212383
#SPJ1
A number, h, rounded to 1 d.p. is 47.2
Another number, k, rounded to 1 d.p. is 4.8
What are the lower and upper bounds of
h - k?
Answers
The lower and upper bounds of h - k are 42.31 and 42.49 respectively.
Upper and lower bounds are the maximum and minimum values that a number could have been before it was rounded. They can also be called limits of accuracy.
The upper and lower bounds can be written using error intervals
The lowest value of h is 47.15
The greatest value of h is 47.24
The greatest value of k is 4.84
The lowest value of k is 4.75
Thus upper bound of h -k = 47.24 - 4.75 = 42.49
Thus lower bound of h -k = 47.15 - 4.84 = 42.31
Thus the lower and upper bounds of h - k are 42.31 and 42.49 respectively.
Learn more about Upper and lower bounds here :
https://brainly.com/question/28135761
#SPJ1
FILL IN THE BLANK The simple linear regression model y = β0 + β1x + ? implies that if x ________, we expect y to change by β1, irrespective of the value of x.
Answers
The simple linear regression model y = β0 + β1x + ε implies that if x increases by one unit, we expect y to change by β1, irrespective of the value of x. This model is used to understand the relationship between two variables, where x is the independent variable, and y is the dependent variable.
In this equation, β0 represents the intercept, β1 is the slope or coefficient of x, and ε is the random error term, which accounts for any variation in the data not explained by the model.
The coefficient β1 quantifies the average change in y for every one-unit increase in x. The intercept, β0, represents the predicted value of y when x equals zero. The error term, ε, captures unexplained fluctuations in the data, and is assumed to have a mean of zero and a constant variance.
By analyzing the linear relationship between x and y, we can make predictions and draw conclusions about their association. The simple linear regression model assumes a constant rate of change, meaning that the relationship between x and y is consistently linear, irrespective of the value of x.
You can learn more about the regression model at: brainly.com/question/14983410
#SPJ11
The simplest factorial design contains:
A. 1 independent variable with 2 conditions
B. 2 independent variables with 2 conditions
C. 2 independent variables with 3 conditions
D. 3 independent variables with 2 conditions
Answers
The simplest factorial design contains 2 independent variables with 2 conditions. The answer is option B.
A factorial design is a study in which two or more independent variables are manipulated to see their impact on the dependent variable. The simplest factorial design contains two independent variables, each with two conditions, for a total of four conditions. This is referred to as a 2x2 factorial design. The factors analyzed in such a design are the primary factor: Factor A, which has two levels, is known as the primary factor or the rows, and the secondary factor: Factor B, which has two levels, is referred to as the secondary factor or the columns.
Learn more about factorial design:
brainly.com/question/28146573
#SPJ11
When tossing a two-sided, fair coin with one side colored yellow and the other side colored green, determine P(yellow).
yellow over green
green over yellow
2
one half
Answers
The calculated value of the probability P(yellow) is 0.5 i.e. one half
How to determine P(yellow).From the question, we have the following parameters that can be used in our computation:
Sections = 2
Color = yellow, and green
Using the above as a guide, we have the following:
Yellow = 1
When the yellow section is selected, we have
P(yellow) = yellow/section
The required probability is
P(yellow) = 1/2
Evaluate
P(yellow) = 0.5
Hence, the value is 0.5
Read more probability at
https://brainly.com/question/24756209
#SPJ1
Can someone tell me what I did wrong?

Answers
Answer:
40 cm²
Step-by-step explanation:
Surface Area = 4 x Area of Triangle + Area of Square
= 4 x 1/2 x 4 x 3 + 4 x 4
= 24 + 16
= 40 cm²
I cannot tell what you did wrong unless provided with your calculations as well.
answer choices are
a. 90
b. 40
c. 10
d. 50
please help

Answers
Steps:
1. Find value of x.
5x + 4x = 90
9x = 90
x = 10
2. Use x value to find ∠EDH.
∠EDH = 5x
∠EDH = 5(10)
∠EDH = 50°
Write the equation of a line that has a y-intercept of -4 and is perpendicular to the line y=-5x+7
Answers
Answer:
y=1/5 x -4
Step-by-step explanation:
Basically, we first start with perpendicular. Note that 2 lines' that are perpendicular have product = -1. Thus, the slope of the line (in question) is 1/5.
Now, we know y = mx + b by slope intercept. Note that y intercept means (0,-4). Thus, plugging in give the answer.
Hope this helps! (Please mark brainliest :))
Which table shows a bank account balance that increases by a constant amount each month?
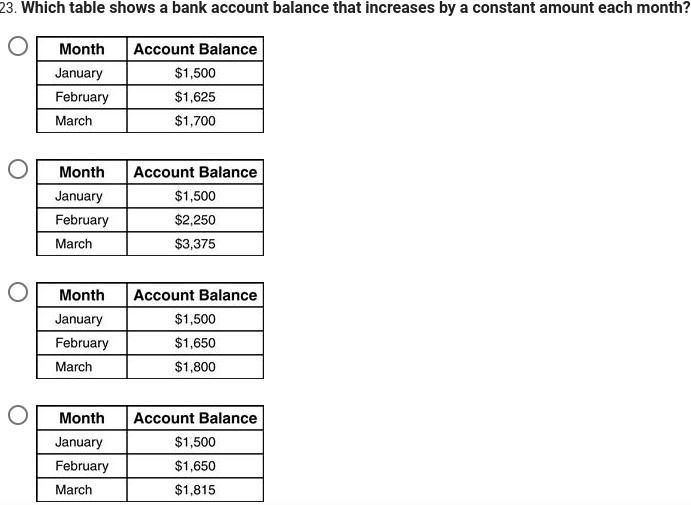
Answers
January $1500
February $1650
March $1800
The constant increase between each month is 150
1650-1500 = 150
1800-1650 = 150
What is the least common denominator (lcd) of 1/2 2/3
Answers
Answer:
6
Step-by-step explanation:
Find the least common multiple (LCM) of the denominators in order to find the least common denominator (LCD).
tallest living man at one time had the height of 237 cm is shortest living man at that time had the height of 139.5 cm height of men at that time had a mean of 177.71 cm and a standard deviation of 6.03 cm which of these two men had the height that was more extreme
Answers
Based on the mean and standard deviation of men's heights at that time, the tallest living man had a more extreme height compared to the shortest living man.
The question asks which of the two men, the tallest living man or the shortest living man at that time, had a height that was more extreme.
To determine this, we need to compare their heights to the mean and standard deviation of men's heights at that time.
The mean height of men at that time was 177.71 cm, and the standard deviation was 6.03 cm.
The tallest living man had a height of 237 cm, which is 59.29 cm above the mean (237 - 177.71 = 59.29).
The shortest living man had a height of 139.5 cm, which is 38.21 cm below the mean (177.71 - 139.5 = 38.21).
To determine which height is more extreme, we can compare the distance from each height to the mean.
The distance from the tallest man's height to the mean is 59.29 cm, while the distance from the shortest man's height to the mean is 38.21 cm.
Since the distance from the tallest man's height to the mean is greater than the distance from the shortest man's height to the mean, we can conclude that the tallest living man had the height that was more extreme.
In summary, based on the mean and standard deviation of men's heights at that time, the tallest living man had a more extreme height compared to the shortest living man.
To know more about standard deviations refer here:
https://brainly.com/question/13336998
#SPJ11
Solve for x.
5x + 3 – 2x = 24
X = [?]
Answers
\(\\ \sf \longmapsto 5x+3-2x=24\)
\(\\ \sf \longmapsto 5x-2x+3=24\)
\(\\ \sf \longmapsto 3x+3=24\)
\(\\ \sf \longmapsto 3x=24-3\)
\(\\ \sf \longmapsto 3x=21\)
\(\\ \sf \longmapsto x=\dfrac{21}{3}\)
\(\\ \sf \longmapsto x=7\)
x = [7]
Step-by-step explanation:
5x + 3 - 2x = 24
Combine like terms
5x - 2x + 3 = 24
Subtract 5x - 2x
3x + 3 = 24
Subtract 3 from both sides
3x = 21
Isolate the variable
x = 21/3
x = 7
What would the equation be

Answers
Answer:
B= x + 5
C= 3x + 7
D= 5 * 7 =35 or 7 + 5= 12
A?= 3x^2 or 3x + x =4x
Step-by-step explanation:
ALGEBRA 2
9) Solve using elimination.
3a = -5b-2
10b=1-6a
Answers
Answer:
No solution.
Step-by-step explanation:
Solving using elimination method:
3a = - 5b - 2
3a + 5b = -2 ------------------(I)
10b = 1 - 6a
6a + 10b = 1 --------------------(II)
\(\sf \dfrac{a_1}{a_2}= \dfrac{3}{6}=\dfrac{1}{2}\\\\\dfrac{b_1}{b_2}=\dfrac{5}{10}=\dfrac{1}{2}\\\\\dfrac{c_1}{c_2} = \dfrac{-2}{1}\)
\(\sf \dfrac{a_1}{a_2}=\dfrac{b_1}{b_2}\neq \dfrac{c_1}{c_2}\)
So, this system of linear equations are two parallel lines and has no solution.
for a standard normal distribution, find: p(-1.62 < z < 2.01)
Answers
The probability of the interval -1.62 < z < 2.01 in a standard normal distribution is approximately 0.9262 or 92.62%.
In a standard normal distribution, the mean is 0 and the standard deviation is 1. The z-score represents the number of standard deviations a data point is from the mean. To find the probability of a specific interval, we calculate the area under the curve between the corresponding z-values.
Given the interval -1.62 < z < 2.01, we need to find the area under the standard normal curve between these two z-values. This can be done using a standard normal distribution table or by using a statistical software or calculator.
By looking up the z-values in the table or using software, we find the corresponding probabilities: P(z < -1.62) = 0.0526 and P(z < 2.01) = 0.9788.
To find the probability of the interval -1.62 < z < 2.01, we subtract the probability of the lower bound from the probability of the upper bound: P(-1.62 < z < 2.01) = P(z < 2.01) - P(z < -1.62 = 0.9788 - 0.0526 = 0.9262.
Learn more about normal distribution here:
https://brainly.com/question/15103234
#SPJ11
HELP ASAP!
Imagine two lines intersect how can the properties of linear pairs and vertical angles help determine the angle measures created by the intersecting lines explain
Answers
Because vertical angles always equal each other. linear pairs always equals 180 degrees always. hope this helps :)
A trapezoid has bases of lengths 14 and 21. Find the trapezoid's height if it's area is 245
Answers
Answer: 8575/2
Step-by-step explanation: