Answers
Related Questions
Please help me with the attached image.

Answers
a. The two cars are moving at the same speed at t = 3.88 seconds.
b. The two autos are moving at a speed of 4.18 cm/s at that moment.
c. The cars pass each other at time t = 1.05 s and t = 2.54 s, respectively.
d. At t = 1.05 seconds, the first car is located at 12.15 cm, and the second car is located at 16.55 cm. At t = 2.54 seconds, the first car is located at 10.69 cm, and the second car is located at 17.39 cm.
What is the speed of the two cars?
The speed of the cars is derived using the formula for linear velocity.
The velocity of the first car is calculated as follows:
v = v₀ + at
where;
v₀ is the initial velocity,a is the acceleration, andt is the time elapsed.The velocity of the second car can be calculated as:
v = v₀
where;
v₀ is the initial velocity since there is no acceleration.
We equate the two velocities of the two cars and solve for time:
-4.40 + 2.70t = 6.10
2.70t = 10.50
t = 3.88 seconds
b. To find the speeds of the cars at time t, we can substitute t = 3.88 seconds in the velocity equation for the first car:
For the first car:
v = -4.40 + 2.70 * 3.88
v = 4.18 cm/s
c. Solving for the time when the positions of the cars are equal allows us to determine when they pass one another.
The position of the first car will be:
x = x₀ + v₀t + 1/2 at²
where x₀ is the initial position.
The position of the second car will be:
x = x₀ + v₀t
equating the two positions equal and solving for time:
13.5 - 4.40t + 1/2 * 2.70t² = 10.5 + 6.10t
1.35t² + 1.70t + 3.00 = 0
Solving the quadratic equation, we get two times:
t = 1.05 s and t = 2.54 s
d. We can re-insert the time values into the position equation for each car to determine where the automobiles were at the times indicated in (c).
For t = 1.05 seconds:
First car:
x = 13.5 - 4.40 * 1.05 + 1/2 * 2.70 * 1.05²
x = 12.15 cm
Second car:
x = 10.5 + 6.10 * 1.05
x = 16.55 cm
For t = 2.54 seconds:
First car:
x = 13.5 - 4.40 * 2.54 + 1/2 * 2.70 * 2.54²
x = 10.69 cm
Second car:
x = 10.5 + 6.10 * 2.54
x = 17.39 cm
Learn more about speed and location at: https://brainly.com/question/29223620
#SPJ1
help pls!!
Fig above shows a wave traveling through a medium. Use the fig to answer the questions below.
A) What is the amplitude of the wave ? Include correct units.
B) Use the graph to determine the time of one wave. Use it to find the frequency.
C) If the speed of the wave is 25 cm/s, what is the wavelength of the wave ? Show data listing, equation , substitution leading to the answer for full credit.

Answers
(a) The amplitude of the wave is determined as 8 cm.
(b) The period of the wave motion is 20 s and the frequency of the wave is 0.05 Hz
(c) The wavelength of the wave is 500 cm.
What is the amplitude of the wave ?(a) The amplitude of the wave is the maximum displacement of the wave.
from the graph, amplitude of the wave = 8 cm
(b) The period of the wave motion is calculated as;
T = 20 s
The frequency of the wave = 1/T = 1/20 s = 0.05 Hz
(c) The wavelength of the wave is calculated by applying the following wave formula.
λ = v / f
λ = 25 cm/s / 0.05 Hz
λ = 500 cm
Learn more about wavelengths here: https://brainly.com/question/10728818
#SPJ1
When a skater pulls her arms in, it
reduces her moment of inertia from
2.12 kg m² to 0.699 kg-m². If she was
initially spinning 3.25 rad/s, what is
her final angular velocity?
Answers
The skater's final angular velocity is approximately 9.86 rad/s.
The skater's final angular velocity can be calculated using the principle of conservation of angular momentum. The equation for angular momentum is given by:
L = Iω
where L is the angular momentum, I is the moment of inertia, and ω is the angular velocity.
Initially, the skater has an angular momentum of:
L_initial = I_initial * ω_initial
Substituting the given values:
L_initial = 2.12 kg m² * 3.25 rad/s
The skater's final angular momentum remains the same, as angular momentum is conserved:
L_final = L_initial
The final moment of inertia is given as 0.699 kg m². Therefore, the final angular velocity can be calculated as:
L_final = I_final * ω_final
0.699 kg m² * ω_final = 2.12 kg m² * 3.25 rad/s
Solving for ω_final:
ω_final = (2.12 kg m² * 3.25 rad/s) / 0.699 kg m²
Hence, the skater's final angular velocity is approximately 9.86 rad/s.
For more such questions on angular velocity, click on:
https://brainly.com/question/29566139
#SPJ8
Is Saturn less dense than water which has a
density of 997 kg/m³? Find out by calculating the density of Saturn in kg/m³. The mass of Saturn is 5.68 x 1026 kg, and its radius is 5.6 x 107 m.
Density of Saturn:
Answers
The density of water at STP, which is \(997 kg/m^3\), we can see that Saturn is less dense than water.
To determine whether Saturn is less dense than water, we must compute its density and compare it to the density of water at standard temperature and pressure (STP), which is \(997 kg/m^3\).
Saturn's density can be computed using the following formula:
density equals mass divided by volume
Saturn's mass and volume may be computed given its mass and radius.
The volume of Saturn can be determined using the sphere volume formula:
volume =\((4/3) \pi (r^3)\)
where r is Saturn's radius.
Filling in the blanks:
volume = \((4/3) \pi (5.6 \times 107) m^3\)
8.27 x 1023 \(m^3\)volume
Saturn's mass is given as \(5.68 \times 10^{26} kg.\)
We can now compute Saturn's density:
density equals mass divided by volume
density= \((5.68 x 10^{26 }kg\)) /\((8.27 \times 10^{23 }\)m³) a density of\(687 kg/m^3\)
This is due to the fact that Saturn is mostly made up of hydrogen and helium, which are far less dense than water. In reality, Saturn is the least dense planet in the Solar System, and it would float in a large enough body of water.
For more question on density visit:
https://brainly.com/question/28734050
#SPJ11
The pressure at the bottom of a jug filled with water does NOT depend on the
__________.
A) depth of the liquid
B) acceleration due to gravity
C) density of water
D) surface area of the water
E) none of the above
Answers
5. A spring of k-500 N/m that is initially compressed 2m is used to launch a 100N load of bricks up a 2 m tall
hill. Find the speed of the bricks at the top of the hill.
a. Qualitatively complete the energy flow diagram and the energy bar graphs.
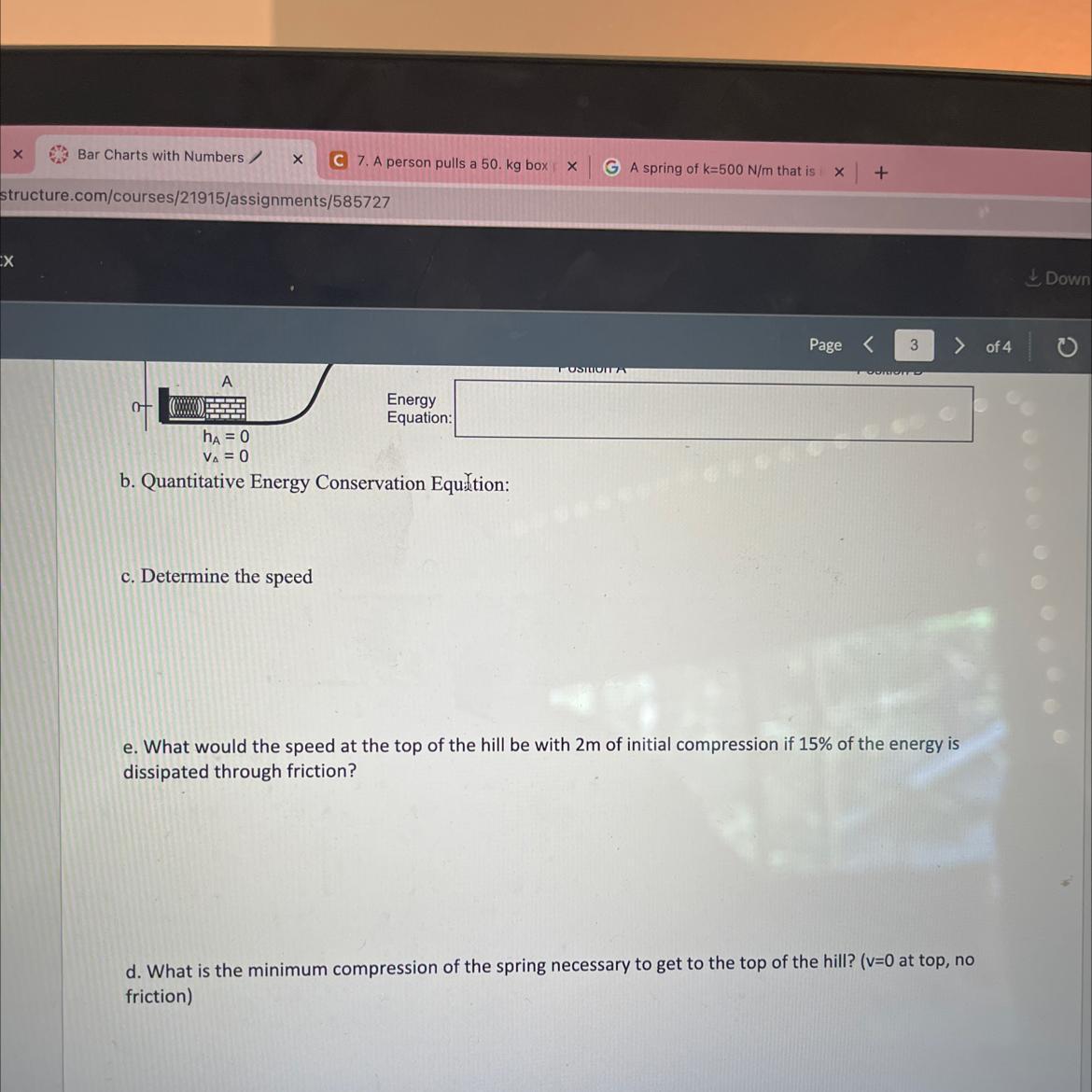
Answers
The kinetic energy of the brick equal the elastic potential energy at the top of the hill. Using this, the speed of the brick is 14 m/s.
What is elastic potential ?The elastic potential of a spring is directly proportional to the squire of the displacement.
Then,
p = 1/2 k x²
Given that, spring constant k = 500 N/m
height of the hill x = 2 m
weight of the load = 100 N
then mass = 100N/9.8 m/s² =10.20 Kg.
At the top of the hill, kinetic energy of the hill is equal to the elastic potential.
then, 1/2 mv² = 1/2 k x²
speed v of the brick = √kx²/m
v = √(500 N/m × 2 m²/10.20 kg)
= 14 m/s.
Therefore, the speed of the brick at the top of the hill is 14 m/s.
Find more on elastic potential :
https://brainly.com/question/12807194
#SPJ1
1. Which court is the ordinary trial courts of the Illinois Judicial Branch?
a. Illinois Supreme Court
c. Circuit Courts
b.Appellate Courts
d.District Courts
Answers
The circuit courts in Illinois have original jurisdiction as trial courts. There are 24 judicial circuits in the state, and each one includes one or more of the 102 counties that make up Illinois.
In Illinois, which court serves as the primary or general trial court?All cases filed in the State of Illinois other than those for which the Supreme Court has original jurisdiction are first heard by the Circuit Court, which is the trial court with wide jurisdiction.
Which courts in Illinois have legal authority?A Supreme Court, an Appellate Court, and Circuit Courts are in charge of the legal system. (Source: Constitution of Illinois.) JUDICIAL DISTRICTS SECTION 2 For the purpose of choosing judges for the Supreme and Appellate Courts, the State is divided into five judicial districts.
To know more about Illinois Judicial Branch visit:-
https://brainly.com/question/17479440
#SPJ1
One mole of iron (6 x 10^23 atoms) has a mass of 56 grams, and its density is 7.87 grams per cubic centimeter, so the center-to-center distance between atoms is 2.28 x 10^-10 m. You have a long thin bar of iron, 2.3 m long, with a square cross section, 0.12 cm on a side. You hang the rod vertically and attach a 149 kg mass to the bottom, and you observe that the bar becomes 1.17 cm longer. From these measurements, it is possible to determine the stiffness of one interatomic bond in iron.
ks = 20014.1 N/m
Number of side-by-side long chains of atoms = 4.81e^12
Number of bonds in total length = 1.096e^10
What is the stiffness of a single interatomic "spring"?
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
Given that:
length l = 2.3 m
a = 0.12 cm = \(0.12 \times 10^{-2} \ m\)
\(x = 1.17 \ cm = 1.17 \times 10^{-2}\ m\)
m = 149 kg
\(\delta = 7.87 \ g/cm^3\)
\(da = 2.28 \times 10^{-10}\ m\)
\(F_{net} = F-mg\\ \\0 = F - mg \\ \\ F = mg \\ \\ k_sx = mg \\ \\\)
∴
\(k_s = \dfrac{149(9.8)}{1.17 \times 10^{-2}} \\ \\ k_s = 124803.42 \ N /m\)
\(N_{chain} = \dfrac{A_{wire}}{A_{atom}} = \dfrac{A_w}{da^2}\)
\(N_{chain} = \dfrac{(a)^2}{(da)^2} = (\dfrac{a}{da})^2\)
\(N_{chain} = (\dfrac{0.12 \times 10^{-2} }{2.28 \times 10^{-10}})^2\)
\(N_{chain} = 2.77 \times 10^{13}\)
\(N_{bond} = \dfrac{L}{da} \\ \\ = \dfrac{2.3}{2.28 \times 10^{-10}} \\ \\ N_{bond} = 1.009 \times 10^{10}\)
\(\text{Finally; the stiffness of a single interatomic spring is:}\)
\(k_{si} =\dfrac{N_{bond}}{N_{chain}}\times k_s\)
\(k_{si} =\dfrac{(1.009 \times 10^{10})}{2.77*10^{13}}}\times (124803.42)\)
\(\mathbf{k_{si} =45.46 \ N/m}\)
To measure the acceleration due to gravity on a distant planet, an astronaut hangs a 0.055 kg ball from the end of a wire. The wire has a length of 0.95 m and a linear density of 1.2×10^-4 kg/m . Using electronic equipment, the astronaut measures the time for a transverse pulse to travel the length of the wire and obtains a value of 0.016 seconds. The mass of the wire is negligible compared to the mass of the ball. Determine the acceleration due to gravity.
Answers
The acceleration due to gravity with a mass of the ball of 0.055 kg and a length of wire is 0.95m with a linear density of 1.2×10⁻⁴kg/m is 7.69m/s².
Acceleration due to gravity is defined as the object getting accelerated due to gravitational force acting on the freely falling body. The unit of acceleration is m/s².
From the given,
mass of ball (m) = 0.055kg
length of the wire (l) = 0.95 m
linear density = 1.2×10⁻⁴kg/m
time (t) = 0.016 s
acceleration due to gravity (g) =?
The tension of the wire, v = √(F)/m/L
The force F= v²×L/m
To find speed (v) the ratio between Lenght and time gives speed.
v = L/t
= 0.95 / 0.016
= 59.37 m/s.
The speed v is 59.37 m/s.
F = v²×m×L
= 59.37×59.37×1.2×10⁻⁴
= 0.423 N
The force is F = 0.423 N.
Force , F = W
= m×g
F/m = g
0.423 / 0.055 = g
g = 7.69 m/s².
Thus, the acceleration due to gravity is g = 7.69 m/s².
To learn more about acceleration due to gravity:
https://brainly.com/question/29135987
#SPJ1
5. With gears, force is multiplied when the _______________ gear is smaller and has fewer teeth than the _______________ gear.
a) output, input b) input, output
Answers
Answer:
b
Explanation:
IF- force you use
OF- force the machine give you
1.How much work does it take to get a 2Kg ball moving 15m/s if it starts from rest?
2. If a force of 235N was added to the ball, through what distance would this force have to act to give the ball a velocity of 15m/s
Answers
water pressurized to 450000 pa is flowing at 5.0m/s in a horizontal pipe which contracts to 1/3 its former area. what are the pressure and velocity of the water after the contraction?
Answers
the pressure of the water after the contraction is -50000 Pa (or 50 kPa below atmospheric pressure), and the velocity of the water after the contraction is 15.0 m/s.
The continuity equation states that the product of the cross-sectional area and the velocity of an incompressible fluid is constant along a pipe, so we can use it to relate the pressure and velocity before and after the contraction:
A₁v₁ = A₂v₂
where A₁ and v₁ are the area and velocity of the pipe before the contraction, and A₂ and v₂ are the area and velocity of the pipe after the contraction.
We can also use the Bernoulli equation, which relates the pressure and velocity of a fluid along a streamline:
P₁ + 1/2 ρv₁² = P₂ + 1/2 ρv₂²
where P₁ and v₁ are the pressure and velocity of the fluid before the contraction, and P₂ and v₂ are the pressure and velocity of the fluid after the contraction, and ρ is the density of the fluid, which we assume to be constant.
Solving for the pressure and velocity after the contraction, we can use the continuity equation to express v₁ in terms of v₂ and substitute it into the Bernoulli equation:
A₁v₁ = A₂v₂
v₁ = (A₂/A₁) v₂
P₁ + 1/2 ρ((A₂/A₁) v₂)² = P₂ + 1/2 ρv₂²
Simplifying and solving for P₂, we get:
P₂ = P₁ + 1/2 ρ(v₁² - v₂²)
Substituting the given values, we get:
A₂ = (1/3) A₁
v₁ = 5.0 m/s
P₁ = 450000 Pa
ρ = 1000 kg/m³
Using the continuity equation, we can find the value of v₂:
A₁v₁ = A₂v₂
v₂ = (A₁/A₂) v₁
v₂ = 3 × 5.0 m/s
v₂ = 15.0 m/s
Substituting this value into the Bernoulli equation, we can find the pressure P₂:
P₂ = P₁ + 1/2 ρ(v₁² - v₂²)
P₂ = 450000 Pa + 1/2 × 1000 kg/m³ × (5.0 m/s)² - (15.0 m/s)²
P₂ = 450000 Pa - 500000 Pa
P₂ = -50000 Pa
Learn more about velocity here:
https://brainly.com/question/17127206
#SPJ1
how will you use the information you've learned from dan ariely's talk to inform your future decisions?
Answers
One important takeaway from Dan Ariely's talk is that our decision-making processes are frequently irrational and influenced by variables outside of our conscious consciousness.
Social norms, emotional states, and cognitive biases, for example, can all influence our choices. As a result, one method to put this knowledge to use is to become more aware of these influences and actively consider them when making decisions.
This may entail devoting more time to decision-making, seeking out diverse views, and being aware of our own biases and tendencies.
Another key takeaway from the talk is the significance of considering the long-term consequences of our choices rather than focusing solely on short-term gains or losses.
This may entail weighing the risks and benefits of various options, as well as considering the effect of decisions on others as well as ourselves.
Overall, the information presented by Dan Ariely can be used to make more thoughtful and informed decisions by becoming more aware of our own biases and tendencies, considering diverse viewpoints, and thinking critically about the potential repercussions of our decisions.
learn more about decisions here
https://brainly.com/question/1249089
#SPJ1
The graph below shows the variation with distance r from the nucleus of the square of the wave function, Ψ^2, of a hydrogen atom according to Schrödinger theory.
A. is most likely to be near a.
B. is always a.
C. is always less than a.
D. is always greater than a.

Answers
The region a represents the distance of the electron from the nucleus.
According to the wave mechanical model of the atom, the probability of finding an electron within a given volume element (representing the atom) is the square of the wave function psi.
Since a is the region in space where there is the greatest probability of finding the electron in the atom, it follows that distance of the electron form the atom is always a.
Learn more about the wave mechanical model: https://brainly.com/question/1382157
Calculate the quantity of heat energy which must be transferred to 2.25 kg of brass to raise its temperature from 20°C to 240°C if the specific heat of brass is 394 J/kgK.
Answers
The quantity of heat energy that must be transferred to 2.25 kg of brass to raise its temperature from 20 °C to 240 °C is 195030 J
How do i determine the quantity of heat energy?First, we shall list out the given parameters from the question. This is shown below:
Mass of brass (M) = 2.25 Kg Initial temperature of brass (T₁) = 20 °CFinal temperature of brass (T₂) = 240 °CChange in temperature of brass (ΔT) = 240 - 20 = 220 °CSpecific heat capacity of brass (C) = 394 J/kgKQuantity of heat energy (Q) =?The quantity of heat energy that must be transferred can be obtained as follow:
Q = MCΔT
= 2.25 × 394 × 220
= 195030 J
Thus, we can conclude quantity of heat energy that must be transferred is 195030 J
Learn more about heat:
https://brainly.com/question/16398667
#SPJ1
When seismic waves encounter a new layer of earth materials they will either
telling us about the composition of that layer.
Answers
According to seismic waves, the Earth's interior is made up of a number of concentric shells, including a solid inner core, a liquid outer core, a mantle, and a thin outer crust.
What seismic waves, a new layer of earth materials?The wave's course will be bent or refracted as it enters the new layer if it moves at a different speed there. The wave will be somewhat curved in the direction of the contact between the two layers if it can move through it more quickly in the new layer.
Therefore, We can learn about just the layers that make up the Earth by understanding how waves behave as they pass through various materials.
Learn more about seismic waves here:
https://brainly.com/question/13056218
#SPJ1
PLS PLS HELP TIMED TEST!!!!!!
A baseball rises through the air after being hit. What energy conversion is occurring?
a. potential to thermal
b. kinetic to potential
c. kinetic to thermal
d. potential to kinetic
Answers
Answer:
hi
Explanation:
hey
Answer:
(A) potential energy
I think it helps you
Polio is a disease that can cause paralysis. Doctors treated patients with casts and braces, but the work of Elizabeth Kenny led to the use of hot baths and exercise to treat polio victims. These patients had less incidence of paralysis. Kenny’s ideas and their acceptance were due to
Answers
Kenny’s ideas and their acceptance were due to open-mindedness because she led to the use of hot baths and exercise to treat polio victims.
Who was Elizabeth Kenny?Elizabeth Kenny was a world-renowned nurse from Australia who develop a treatment for poliomyelitis, a very serious viral disease caused by poliovirus.
Elizabeth Kenny's ideas were controversial because they may be considered to be against conventional medical treatments.
In conclusion, Kenny’s ideas and their acceptance were due to open-mindedness because she led to the use of hot baths and exercise to treat polio victims.
Learn more about Elizabeth Kenny here:
https://brainly.com/question/10653494
#SPJ1
A fireman standing on a 3.3 m high ladder operates a water hose with a round nozzle of
diameter 2.03 inch. The lower end of the hose
(3.3 m below the nozzle) is connected to the
pump outlet of diameter 3.82 inch. The gauge
pressure of the water at the pump is
P
(gauge)
pump = P
(abs)
pump − Patm
= 65.3 PSI = 450.228 kPa .
Calculate the speed of the water jet emerging from the nozzle. Assume that water is an
incompressible liquid of density 1000 kg/m3
and negligible viscosity. The acceleration of
gravity is 9.8 m/s
2
.
Answer in units of m/s.
Answers
The speed of the water jet emerging from the nozzle with a water density of 1000 kg/m³ is 30.107 m/s.
What is Speed?Speed can be defined as the rate of change in the distance of an object. It is a scalar quantity due to only magnitude and no direction.
Height = 3.3 m
Diameter = 2.03 inch
Gauge pressure = 450.228 kPa
We need to calculate the speed of the water jet emerging from the nozzle
Using Bernoulli's equation,
1/2ρ(Vn² - Vp²) = P gauge - ρgh
(Vn² - Vp²) = (2/P) Pgauge - 2gh
Vn² - (An/ Ap)²Vn² = (2/P) Pgauge - 2gh
Vn² - (rn/ rp)⁴Vn² = (2/P) Pgauge - 2gh
Vn² = \(\sqrt{(2/P) Pgauge - 2gh/ (1- (rn/ rp)^4)}\)
Vn = \(\sqrt{[((2/1000)(450.228 X 10^3)) - 2 X 9.8 X 3.3]/ 1 - (1.01/ 1.91)^4}\)
Vn = \(\sqrt{(2 X 450.228 - 64.68)/ 1- (1.04/ 13.30)}\)
Vn = \(\sqrt{(900.45 - 64.68)/ (13.30- 1.04)/13.30}\)
Vn = \(\sqrt{(835.776)/ (12.26/ 13.30)}\)
Vn = \(\sqrt{(835.776)/ 0.922}\)
Vn = \(\sqrt{906.48}\)
Vn = 30.107 m/s
Learn more about Speed here:
https://brainly.com/question/28224010
#SPJ1
Consider the system of two blocks shown in Fig. P6.81, but with a different friction force on the 8.00 kg block. The blocks are released from rest. While the two blocks are moving, the tension in the light rope that connects them is 37.0 N. (a) During a 0.800 m downward displacement of the 6.00 kg block, how much work has been done on it by gravity? By the tension T in the rope? Use the work–energy theorem to find the speed of the 6.00 kg block after it has descended 0.800 m. (b) During the 0.800 m displacement of the 6.00 kg block, what is the total work done on the 8.00 kg block? During this motion how much work was done on the 8.00 kg block by the tension T in the cord? By the friction force exerted on the 8.00 kg block? (c) If the work–energy theorem is applied to the two blocks con- sidered together as a composite system, use the theorem to find the net work done on the system during the 0.800 m downward displacement of the 6.00 kg block. How much work was done on the system of two blocks by gravity? By friction? By the tension in the rope?
Answers
a) The speed of the 6.00 kg block after descending 0.800 m is 2.07 m/s.
b) We cannot calculate the work done by the friction force.
c) The net work done on the system of two blocks during the 0.800 m downward displacement of the 6.00 kg block is 29.13 J. The work done by gravity is 47.04 J, the work done by friction is unknown, and the work done by the tension in the rope is zero.
(a) The work done on the 6.00 kg block by gravity can be calculated using the formula:
Work_gravity = force_gravity * displacement * cos(theta),
where force_gravity is the weight of the block, displacement is the downward displacement of the block, and theta is the angle between the force and displacement vectors (which is 0 degrees in this case).
The weight of the block is given by:
force_gravity = mass * acceleration_due_to_gravity = 6.00 kg * 9.8 m/s^2 = 58.8 N.
Plugging in the values, we get:
Work_gravity = 58.8 N * 0.800 m * cos(0) = 47.04 J.
The work done on the 6.00 kg block by the tension in the rope is given by:
Work_tension = tension * displacement * cos(theta).
Plugging in the values, we get:
Work_tension = 37.0 N * 0.800 m * cos(180) = -29.6 J.
The negative sign indicates that the tension is in the opposite direction of the displacement.
Using the work-energy theorem, we can find the speed of the 6.00 kg block after descending 0.800 m:
Work_net = change_in_kinetic_energy.
Since the block starts from rest, its initial kinetic energy is zero. Therefore:
Work_net = Final_kinetic_energy - Initial_kinetic_energy = 1/2 * mass * velocity^2.
Solving for velocity, we get:
velocity = sqrt(2 * Work_net / mass).
The net work done on the block is the sum of the work done by gravity and the tension:
Work_net = Work_gravity + Work_tension = 47.04 J - 29.6 J = 17.44 J.
Plugging in the values, we get:
velocity = sqrt(2 * 17.44 J / 6.00 kg) = 2.07 m/s.
Therefore, the speed of the 6.00 kg block after descending 0.800 m is 2.07 m/s.
(b) The total work done on the 8.00 kg block during the 0.800 m displacement can be calculated using the work-energy theorem:
Work_net = change_in_kinetic_energy.
Since the 8.00 kg block is not moving vertically, its initial and final kinetic energies are zero. Therefore:
Work_net = Final_kinetic_energy - Initial_kinetic_energy = 0.
The work done on the 8.00 kg block by the tension in the rope is given by:
Work_tension = tension * displacement * cos(theta).
Plugging in the values, we get:
Work_tension = 37.0 N * 0.800 m * cos(0) = 29.6 J.
The work done on the 8.00 kg block by the friction force can be calculated using the formula:
Work_friction = force_friction * displacement * cos(theta),
where force_friction is the frictional force on the block. However, the problem statement does not provide the value of the friction force. Therefore, we cannot calculate the work done by the friction force.
(c) The net work done on the system of two blocks during the 0.800 m displacement of the 6.00 kg block can be found using the work-energy theorem:
Work_net = change_in_kinetic_energy.
Since the system starts from rest, the initial kinetic energy of the system is zero. Therefore:
Work_net = Final_kinetic_energy - Initial_kinetic_energy = 1/2 * (6.00 kg + 8.00 kg) * velocity^2.
Simplifying, we get:
Work_net = 1/2 * 14.00 kg * velocity^2.
Using the value of velocity calculated in part (a), we get:
Work_net = 1/2 * 14.00 kg * (2.07 m/s)^2 = 29.13 J.
The work done on the system of two blocks by gravity is the sum of the work done on the individual blocks by gravity:
Work_gravity_system = Work_gravity_6kg + Work_gravity_8kg = 47.04 J + 0 J = 47.04 J.
The work done on the system of two blocks by the tension in the rope is the sum of the work done on the individual blocks by the tension:
Work_tension_system = Work_tension_6kg + Work_tension_8kg = -29.6 J + 29.6 J = 0 J.
Therefore, the net work done on the system of two blocks during the 0.800 m downward displacement of the 6.00 kg block is 29.13 J. The work done by gravity is 47.04 J, the work done by friction is unknown, and the work done by the tension in the rope is zero.
Note: The calculations for part (b) and (c) were based on the given information, but the value of the friction force was not provided in the problem statement.
For more such questions on work done, click on:
https://brainly.com/question/8119756
#SPJ8
Caleb opens a soda can by pulling on the tab. The picture shows Caleb opening the soda can. The
tab is a simple machine. What is the mechanical advantage of the tab?
Answers
Answer:
leverage to open it
Explanation:
The mechanical advantage of the tab of a soda can is that, it acts as a second class lever.
What is meant by a lever ?Lever is defined as a simple machine that increases the force. Lever is used to lift loads or weight by reducing the work.
Here,
Caleb opened a soda can by puling the tab of the can. The tab of the soda can here acts as a simple machine to open it.
The tab of the soda can is used to open the can such that it makes the task super easy. The tab of the can is an application of a second class lever.
Second class lever is the type of lever in which the fulcrum is located at one end and the load is in the middle such that the effort is applied in the other end. In the tab, the force is applied at one end upwards and the other end of the tab opens downwards to the can and thus it is opened. This is the working of the tab of a soda can.
Hence,
The mechanical advantage of the tab of a soda can is that, it acts as a second class lever.
To learn more about lever, click:
https://brainly.com/question/4532561
#SPJ2
A body of mass 12kg travelling at 4.2m/s² collides with a second body of mass 18kg at rest. Calculate their common velocity of the two bodies coalesce after collision
Answers
When a body of mass 12kg travelling at 4.2m/s² collides with a second body of mass 18kg at rest, their common velocity after the collision is 1.68 m/s.
When two objects of different masses collide, they can exchange momentum. An object's mass and velocity together make up its momentum. When two objects collide, their momentum is conserved, meaning that the total momentum of the two objects before the collision equals the total momentum of the two objects after the collision. This principle can be used to calculate the velocity of the two objects after a collision.A body of mass 12 kg is travelling at a velocity of 4.2 m/s and collides with a second body of mass 18 kg at rest. The total mass of the system is 12 kg + 18 kg = 30 kg. To determine the velocity of the two objects after the collision, we need to use the conservation of momentum principle. Before the impact, the system's entire momentum is:momentum before = \((mass_1 x velocity_1) + (mass_2 x velocity_2)\)where mass1 is the mass of the first object, velocity1 is the velocity of the first object, \(mass_2\) is the mass of the second object, and \(velocity_2\) is the velocity of the second object. In this case,\(mass_1 = 12 kg, velocity_1 = 4.2 m/s, mass_2 = 18 kg\), and \(velocity_2 = 0\) (because the second object is at rest). Substituting these values into the equation above, we get: momentum before = (12 kg x 4.2 m/s) + (18 kg x 0)momentum before = 50.4 kg m/sFollowing the collision, the system's overall momentum is:momentum after =\((mass_1 + mass_2) * velocity\)where mass1 + mass2 is the total mass of the system, and velocity is the velocity of the two objects after the collision. Let's call this velocity "v". Substituting the values we know into the equation above, we get: momentum after = (12 kg + 18 kg) x vmomentum after = 30 kg x vUsing the conservation of momentum principle, we know that momentum before = momentum after. Therefore, we can set these two equations equal to each other and solve for v.50.4 kg m/s = 30 kg x vv = 50.4 kg m/s ÷ 30 kgv = 1.68 m/sFollowing the impact, the two bodies' common velocity is 1.68 m/s. Hence, the answer to this problem is that when a body of mass 12kg travelling at 4.2m/s² collides with a second body of mass 18kg at rest, their common velocity after the collision is 1.68 m/s.For more questions on collision
https://brainly.com/question/30044264
#SPJ8
An object is thrown down from a tall building with an initial velocity of 2 m/s. How fast is it going after 5 seconds of free fall?
Answers
Answer: Vf = Vi + A(t)
Vf= -2+ (-9.8)(5)
Vf = -51 m/s
Explanation:
The final velocity is equal to the initial velocity plus the acceleration multiplied by the time
(-9.8) is used for the acceleration for this question because that is the speed at which things in free fall accelerate when they are on earth
-2 is used as the initial velocity because the ball was thrown in the negative direction which is down.
The time of 5 was given in the question so you can plug it in for time
Answer:
Explanation:
Given:
V₀ = 2 m/s
g = 9.8 m/s²
t = 5 s
____________
V - ?
Axis OX direct vertically down. Then:
V = Vₓ = V₀ₓ + g·t
V = 2 + 9.8*5 = 51 m
A flat circular ring is made from a very thin sheet of metal. Charge Q is uniformly distributed over the ring. Assuming w≪R, what is the surface charge density n? What exactly does w≪R mean?
Answers
The surface charge density of the ring is given by, n = Q / πR^2. and also it is given by n = 2λ / R.
In this context, "w << R" means that the width (w) of the circular ring is much smaller than the radius (R) of the ring. Mathematically, this can be expressed as w/R << 1.
To find the surface charge density (n) of the ring, we can use the formula:
n = Q / A
where Q is the total charge on the ring and A is the area of the ring. For a circular ring, the area is given by:
A = π(R^2 - r^2)
where R is the outer radius of the ring and r is the inner radius of the ring. Since the ring is very thin, we can assume that the inner radius is negligible compared to the outer radius (i.e., r ≈ 0). Thus, we can simplify the formula for the area as:
A ≈ πR^2
Substituting this expression for A into the formula for surface charge density gives:
n = Q / πR^2
Therefore, the surface charge density of the ring is n = Q / πR^2.
Note that since the charge is uniformly distributed over the ring, we can also express the total charge Q in terms of the linear charge density λ (charge per unit length) and the circumference of the ring C:
Q = λC
Substituting this expression for Q into the formula for surface charge density gives:
n = λC / πR^2
However, since the ring is a complete circle, we know that the circumference is equal to 2πR, so we can simplify this expression further:
n = λ(2πR) / πR^2
n = 2λ / R
For more question on density click on
https://brainly.com/question/30694157
#SPJ11
It has been proposed that we could explore Mars using inflated balloons to hover just above the surface. The buoyancy of the atmosphere would keep the balloon aloft. The density of the Martian atmosphere is 0.0154 (although this varies with temperature). Suppose we construct these balloons of a thin but tough plastic having a density such that each square meter has a mass of 4.60 . We inflate them with a very light gas whose mass we can neglect. So far I found the following: What should be the radius of these balloons so they just hover above the surface of Mars? Radius of the balloon = /896 m What should be the mass of these balloons so they just hover above the surface of Mars? Mass of balloon = 4.64*10^-2 kg If we released one of the balloons from part A on earth, where the atmospheric density is 1.20 , what would be its initial acceleration assuming it was the same size as on Mars? If on Mars these balloons have five times the radius found in part A, how heavy an instrument package could they carry?
Answers
Answer:
the radius of the balloon r = 0.896 m and mass m = 4.64 × 10⁻² kg
the initial acceleration is a = 753.47 m/s²
the an instrument package could they carry a required mass of 4.64 kg
Explanation:
a) What should be the radius of these balloons so they just hover above the surface of Mars?
Given that :
The density of the Martian atmosphere, ρ = 0.0154 kg/m³
The volume of the sphere, V = (4/3)πr³
The area of the sphere, A = 4πr²
The mass of the balloon is m = (4.60 g/m²)A
m = (4.60×10⁻³ kg/m²)(4πr²)
The formula for the buoyant force is expressed as :
F = ρVg
m×g = ρ×V×g
m = ρ×V
Now;
(4.60×10⁻³ kg/m²)(4πr²)= ρ(4/3)πr³
r = 3(4.60×10⁻³ kg/m²)/ ρ
r = 3(4.60×10⁻³ kg/m²)/ 0.0154 kg/m³
r = 0.896 m
Thus; the radius of the balloon r = 0.896 m
The mass of the balloon is (4.60×10⁻³ kg/m²)(4πr²)
m = (4.60×10⁻³ kg/m²)(4π×0.896²)
m = 4.64 × 10⁻² kg
b) what would be its initial acceleration assuming it was the same size as on Mars?
The density of the air on earth, ρ = 1.20 kg/m³
The volume of the balloon is V = (4/3)(π)(0.896 m)³
V = 3.01156 m³
Considering the net force acting on the balloon ; we have
ΣF = ρVg - mg = ma
However; making the initial acceleration a of the balloon the subject ; we have:
a = (ρVg - mg)/m
a = (1.20 kg/m³)(3.01156 m³)(9.8 m/s²) - (4.64×10⁻² kg)(9.8 m/s²)]/(4.64×10⁻² kg)
a = 753.47 m/s²
c) If on Mars these balloons have five times the radius found in part A, how heavy an instrument package could they carry?
The volume of the total system is V' = (4/3)π(5r)³
V' = (4/3)π(5)³(0.896 m)³
V' =376.446 m³
The mass of the total system is m = (4.60×10⁻³ kg/m²) (4π(5r)²)
m = [4.60×10⁻³ kg/m²][4π][25](0.896 m)²
m = 1.159587 kg
We can then say that the buoyant force is equals to the weight of the total mass (balloon+load) and is expressed as:
F = (m + m')g
ρV'g = (m + m')g
ρV' = (m + m')
Thus; the required mass m' is = ρV' - m
m' = ρV' - m
m' = (0.0154 kg/m³)(376.446 m³) - (1.159587 kg)
m' = 4.64 kg
Thus; the an instrument package could they carry a required mass of 4.64 kg
100 g of water at 25 °C is poured into an insulating cup. 50 g of ice at 0 °C is added to the water. The water is stirred until the temperature of the water has fallen to 0 °C. 18 g of ice remains unmelted. The specific heat capacity of water is 4.2 J / g °C. Which value does this experiment give for the specific latent heat of fusion of ice?
Answers
The specific latent heat of fusion of ice obtained from this experiment is approximately 583.33 J/g.
To determine the specific latent heat of fusion of ice using the given experiment, we need to consider the energy transferred during the process.First, we need to calculate the energy lost by the water to cool down from 25 °C to 0 °C. The energy lost is given by:
Q1 = m1 * c * ΔT1
Where:
m1 = mass of water = 100 g
c = specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 J/g °C
ΔT1 = change in temperature = (0 °C - 25 °C) = -25 °C
Q1 = 100 g * 4.2 J/g °C * (-25 °C) = -10,500 J
Next, we calculate the energy released by the water to freeze and cool the remaining ice. The energy released is given by:
Q2 = m2 * Lf
Where:
m2 = mass of ice = 18 g
Lf = specific latent heat of fusion of ice (to be determined)
Q2 = 18 g * Lf
Since energy is conserved in the system, the energy lost by the water (Q1) is equal to the energy released by the water (Q2):
-10,500 J = 18 g * Lf
Solving for Lf:
Lf = -10,500 J / 18 g = -583.33 J/g
The negative sign indicates that energy is being released during the process of freezing.
For more such questions on heat
https://brainly.com/question/934320
#SPJ8
define electric field intensity
Answers
Answer:
Electric field intensity is a Vector Field. Electric field intensity (E, N/C or V/m) is a vector field that quantifies the force experienced by a charged particle due to the influence of charge not associated with that particle
Explanation:
Three forces act on a moving object. One force has a magnitude of 84.4 N and is directed due north. Another has a magnitude of 42.7 N
and is directed due west. What must be (a) the magnitude and (b) the direction of the third force, such that the object continues to
move with a constant velocity? Express your answer as a positive angle south of east.
Answers
The direction of the third force, such that the object continues to
move with a constant velocity is 94.5N at 0.19° south of east.
What is applied force?The force that one thing exerts on another. A barrel being pushed by a human is an illustration of applied force. When the individual pushes the barrel, the barrel experiences an applied force. Newton's second law of motion defines the force formula as follows: A force is equal to an object's mass times its acceleration, or F = m a. You must use SI units when applying this formula: kilograms for mass, meters per second squared for acceleration, and newtons for force. a push or pull that an object has experienced. Here, an object is given a force by a person or any other thing. A chair being pushed to the opposite side of the room, for instance.
For the object to move with constant velocity the total acceleration must be zero.
So,
Total F = \(F_{1} +F_{2} +F_{3}\)
ma = 0
\(F_{1}\) = 84.4N
\(F_{2}\) = 42.7 N
\(F_{3} = -F_{1} - F_{2}\)
= 94.58 N
TanФ = 0.19°
Hence \(F_{3}\) = 94.5N at 0.19° south of east.
To know more about force ,visit:
https://brainly.com/question/2855467
#SPJ9
Masses m and 2m are joined by a light inextensible string which runs without slipping over a uniform circular pulley of mass 2m and radius a. Using the angular position of the pulley as generalized coordinate, write down the Lagrangian function and Lagrange's equation. Find the acceleration of the masses.

Answers
Answer: the acceleration of the masses is given by = 0, which means the angular acceleration of the pulley is zero. This implies that the masses m and 2m move with constant velocity, they are in equilibrium.
Vector A has a magnitude of 5 meters and points west vector B has a magnitude of 5 meters pointing east what is the direction and magnitude
Answers
The direction and magnitude of the net vector is:
Direction: None Magnitude: 0 meters.How to find the resultant and magnitude of the resultant vectorWhen vector A with magnitude of 5 meters pointing west and
vector B with magnitude of 5 meters pointing east are added,
they will result in a net vector with a magnitude of the difference between the magnitudes of the vectors and a direction equal to the direction of the vector with the largest magnitude.
Since both vectors have the same magnitude (5 meters), the net vector will have a magnitude of 0 meters.
This means that the vectors completely cancel each other out and there is no net vector remaining.
Learn more about vectors at:
https://brainly.com/question/110151
#SPJ1