Clark's rule is a formula used to determine pediatric doses of over the counter medicine.
The formula says
The weight of a child divided by 150 multiplied by the adult dose is the same as the child dose
if an adult dose of acetaminophen is 1,000 mg and a child weighs less than 90 pounds, what is
the recommended range of doses?
A. x≤ 600
B. x ≥ 600
C. 500
D. 500 ≤x≤ 600
Answers
500 ≤x≤ 600 is the recommended range of doses. Typically, a phase I or early phase II clinical trial involves dose range.
How to calculate doses ?To solve this problem using Clark's rule, we need to determine the range of pediatric doses for a child who weighs less than 90 pounds and for whom the adult dose is 1,000 mg.
A mathematical formula known as Clark's rule is used in medicine to determine the right dosage of medication for patients aged 2 to 17 depending on their weight and the recommended adult dose.
First, we can use the formula provided to calculate the child dose:
Child dose = (Weight of child / 150) * Adult dose
Since the weight of the child is less than 90 pounds, we can set the weight of the child to the minimum value in the range, which is 50 pounds. This gives us:
Child dose = (50 / 150) * 1000 mg
= 333.33 mg
Next, we can set the weight of the child to the maximum value in the range, which is 89 pounds. This gives us:
Child dose = (89 / 150) * 1000 mg
= 593.33 mg
Therefore, the recommended range of doses for a child who weighs less than 90 pounds and for whom the adult dose is 1,000 mg is 500 mg ≤ x ≤ 600 mg.
So, the correct answer is D. 500 ≤x≤ 600.
To learn more about dosage refer :
https://brainly.com/question/7152738
#SPJ1
Related Questions
Look at the picture and tell me

Answers
Poppy's sister used approximately 3.14 inches more wire per wall hanging than Poppy.
How to find the amount of wire used ?To find the amount of wire used by both Poppy and her sister, we'll calculate the circumference of their respective wall hangings using the formula:
C = 2πr
Since the diameter is twice the radius, we can find her sister's radius as follows:
Poppy's radius = 6.25 inches
Poppy's diameter = 2 * 6.25 = 12.5 inches
Sister's diameter = Poppy's diameter + 1 = 12.5 + 1 = 13.5 inches
Sister's radius = 13.5 / 2 = 6.75 inches
Now, we'll calculate the circumferences using the given value for π:
Poppy's circumference = 2 x 3.14 x 6.25 ≈ 39.25 inches
Sister's circumference = 2 x 3.14 x 6.75 ≈ 42.39 inches
Difference = Sister's circumference - Poppy's circumference
Difference = 42.39 - 39.25 = 3.14 inches
Find out more on wire at https://brainly.com/question/29205033
#SPJ1
In a group of students, 30% like Computer only, 25% like both Computer and Optional Maths and 5% don't like any of the subjects. If 390 students like Optional Maths, find the total number of students by drawing a Venn-diagram. (Ans: 600)
Answers
Answer:
Let's use a Venn diagram to solve this problem.
First, let's label the three regions of the Venn diagram: Computer only (C), Optional Maths only (M), and both Computer and Optional Maths (C ∩ M). We can also label the region outside the circles as neither Computer nor Optional Maths (N).
We know that 30% of the students like Computer only, which means that the percentage of students in region C is 30%. Similarly, 25% of the students like both Computer and Optional Maths, so the percentage of students in region C ∩ M is 25%.
We are also given that 5% of the students don't like either subject, so the percentage of students in region N is 5%.
Finally, we are told that 390 students like Optional Maths, which includes the students in regions M and C ∩ M. We don't know the percentage of students in region M, but we do know that the percentage of students in region C ∩ M is 25%.
Using this information, we can set up an equation to solve for the total number of students:
C + M + C ∩ M + N = 100%
Substituting the percentages we know, we get:
30% + M + 25% + 5% = 100%
Simplifying the equation, we get:
M = 40%
This means that 40% of the students like Optional Maths only, which is the percentage of students in region M.
Now we can use the fact that 390 students like Optional Maths to solve for the total number of students:
M + C ∩ M = 390
0.4T + 0.25T = 390
0.65T = 390
T = 600
Therefore, the total number of students is 600.
what fraction is eqivilant to 500%
Answers
Answer:
5/1
Step-by-step explanation:
Answer:
5/1
Step-by-step explanation:

PLEASE PLEASE HELPPP

Answers
4/7 of a number is 84 . Find the number.
Answers
Answer: 28
Step-by-step explanation:
To find the number, we need to use the fact that 4/7 of a number is 84 to set up an equation that we can solve. Since 4/7 of a number is 84, we can write the following equation:
(4/7) * x = 84
To solve this equation, we need to first get rid of the fraction by multiplying both sides of the equation by 7/4:
(4/7) * x * (7/4) = 84 * (7/4)
This gives us the equation:
(4/7) * (7/4) * x = 84 * (7/4)
Since (4/7) * (7/4) = 1, we can simplify the equation as follows:
1 * x = 84 * (7/4)
We can then simplify the right side of the equation by multiplying the numerator and denominator of the fraction by 4:
1 * x = 84 * (7/4) = 84 * (28/28) = 28
Finally, we can solve for x by dividing both sides of the equation by 1:
1 * x / 1 = 28 / 1
This gives us the final equation:
x = 28
Therefore, the number is 28.
6. [4 Points] Let \( \mathrm{X} \) and \( \mathrm{Y} \) be independent random variables that are uniformly distributed on the interval \( [0,1] \). What is the PDF of the random variable \( Z=\frac{Y}
Answers
The PDF of the random variable \(\(Z = \frac{Y}{X}\) is \(f_Z(z) = z\) for \(0 \leq z \leq 1\) and \(f_Z(z) = 0\)\) otherwise.
To find the probability density function (PDF) of the random variable \(\(Z = \frac{Y}{X}\)\), where \(X\) and \(Y\) are independent random variables uniformly distributed on the interval \([0,1]\), we can use the method of transformations.
Let's denote the PDF of \\(\(X\) as \(f_X(x)\) and the PDF of \(Y\) as \(f_Y(y)\).\)
Since X and Y are independent and uniformly distributed on [0,1], their PDFs are constant within that interval and zero outside of it. Therefore, we have:
\(\(f_X(x) = \begin{cases} 1, & 0 \leq x \leq 1 \\ 0, & \text{otherwise} \end{cases}\)\)
\(\(f_Y(y) = \begin{cases} 1, & 0 \leq y \leq 1 \\ 0, & \text{otherwise} \end{cases}\)\)
To find the PDF of Z, we need to determine the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of Z and then differentiate it to obtain the PDF.
The cumulative distribution function (CDF) of Z is given by:
\(\(F_Z(z) = P(Z \leq z)\)\)
To find \(\(P(Z \leq z)\)\), we can consider the range of values that Z can take. Sinc\(\(0 \leq X \leq 1\) and \(0 \leq Y \leq 1\), the range of \(Z\) is \(0 \leq Z \leq \frac{1}{0} = \infty\) (assuming \(X \neq 0\)).\)
For a given z, Z can take values less than or equal to z if and only if\(\(Y \leq zX\).\)
Therefore, we can express \(\(P(Z \leq z)\)\) as an integral:
\(\(P(Z \leq z) = \int_{0}^{1} \int_{0}^{zx} f_Y(y) f_X(x) \, dy \, dx\)\)
Substituting the PDFs of \(X\) and \(Y\) into the integral, we have:
\(\(P(Z \leq z) = \int_{0}^{1} \int_{0}^{zx} 1 \cdot 1 \, dy \, dx\)\)
\(\(P(Z \leq z) = \int_{0}^{1} zx \, dx\)\(P(Z \leq z) = \left[\frac{1}{2}z^2x^2\right]_{0}^{1}\)\(P(Z \leq z) = \frac{1}{2}z^2\)\)
Now, to obtain the PDF of (Z), we differentiate the CDF with respect to (z):
\(\(f_Z(z) = \frac{d}{dz} \left(\frac{1}{2}z^2\right)\)\(f_Z(z) = z\)\)
Therefore, the PDF of Z is given by:
\(\(f_Z(z) = \begin{cases} z, & 0 \leq z \leq 1 \\ 0, & \text{otherwise} \end{cases}\)\)
This is the PDF of the random variable\(\(Z = \frac{Y}{X}\)\), where X and Y are independent random variables uniformly distributed on the interval [0,1].
learn more about random variable from this link.
https://brainly.com/question/33983110
#SPJ11
Help me help me help me

Answers
Answer:
the answer is ____
Step-by-step explanation:
first study more
then clean that computer
and then dont ask on here okau
Sketch the region enclosed by the curves and find its
area.
y=x,y=3x,y=−x+4
Answers
The region enclosed by the curves y = x, y = 3x, and y = -x + 4 needs to be sketched, and its area should be found.
To sketch the region enclosed by the curves, we need to plot the three given curves on a coordinate plane. The first curve is y = x, which represents a straight line passing through the origin (0,0) with a slope of 1. The second curve is y = 3x, which is also a straight line passing through the origin but with a steeper slope of 3. The third curve is y = -x + 4, which represents a line with a y-intercept of 4 and a negative slope of -1. By plotting these three lines on the same coordinate plane, we can see that they intersect at three points: (0,0), (1,3), and (3,1). The region enclosed by these curves is a triangular region with vertices at these three points. To find the area of this triangular region, we can use the formula for the area of a triangle: A = (1/2) * base * height. Let's draw the graph:
|
4 | . (2, 2)
| .
| .
| .
0 |_____________________
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
In this graph, the first equation (y = x) is depicted by a diagonal line passing through the origin (0,0). The second equation (y = 3x) is a steeper line, while the third equation (y = -x + 4) is a downward-sloping line with a y-intercept of 4. In this case, the base of the triangle is the distance between the points (0,0) and (3,1), which is 3 units. The height of the triangle is the distance between the point (1,3) and the line y = -x + 4, which is also 3 units. Substituting these values into the area formula, we get A = (1/2) * 3 * 3 = 4.5 square units.
Learn more about triangle here:
https://brainly.com/question/31240589
#SPJ11
suppose that X is a continious random variable with a strictly increasing cdf F(x). Find the density of Y
Answers
To find the density of Y, we need to apply the transformation method. Let's denote the random variable Y as Y = F(X).
Start by finding the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of Y, denoted as G(y):
G(y) = P(Y ≤ y) = P(F(X) ≤ y)
To find G(y), we substitute F(X) with y and solve for X:
F(X) ≤ y
X ≤ F^(-1)(y)
Now, we calculate the density of Y, denoted as g(y), by differentiating G(y) with respect to y:
g(y) = dG(y)/dy
Substitute the expression for X we found earlier into g(y):
g(y) = d/dy [P(X ≤ F^(-1)(y))]
= d/dy [F(F^(-1)(y))]
= d/dy [y]
= 1
The density of Y is 1, which means Y is a uniform random variable on the interval [0, 1].
The density of Y is 1, indicating that Y is a uniform random variable on the interval [0, 1]. The given problem asks us to find the density of Y, where Y is a continuous random variable defined as Y = F(X), and X is another continuous random variable with a strictly increasing cumulative distribution function (CDF), denoted as F(x). To solve this problem, we can use the transformation method. We start by finding the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of Y, denoted as G(y). We have G(y) = P(Y ≤ y) = P(F(X) ≤ y). To find G(y), we substitute F(X) with y and solve for X. This leads us to X ≤ F^(-1)(y). Next, we calculate the density of Y, denoted as g(y), by differentiating G(y) with respect to y. This gives us g(y) = 1. Therefore, the density of Y is 1, indicating that Y is a uniform random variable on the interval [0, 1].
The density of Y, defined as Y = F(X), is 1, which implies that Y is a uniform random variable on the interval [0, 1].
To learn more about transformation method visit:
brainly.com/question/33730025
#SPJ11
write the equations of all the circles

Answers
The equation of a circle with center (a, b) and radius r is:
(x - a)^2 + (y - b)^2 = r^2
(x, y) represents any point on the circle
What is a circle?A circle is described as a shape consisting of all points in a plane that are at a given distance from a given point, the center.
The properties of the circle are as follows:
The circles are said to be congruent if they have equal radii.The diameter of a circle is the longest chord of a circle.Equal chords of a circle subtend equal angles at the centre.The radius drawn perpendicular to the chord bisects the chord.Learn more about properties of the circle at: https://brainly.com/question/4244936
#SPJ1
if l is parallel to m find the values of x and y (10x-17) (6y+29) (8x+1)

Answers
X = 22
Y = 15
youre welcome! Brainliest would be appreciated :)
p and q are both prime numbers with p < q.
They are each less than 18
Give an example where p + q is odd but not prime.
Answers
The value of p is 2 and q is either 7 or 13 and their sum is either 9 or 15.
It is given that the value of p and q is a prime number, and p<q.
But it is also given that the value of both should be less than 18 as well as a prime number.
Therefore the value of both should be 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and 17.
And it is also given that p<q.
Now we have to find the value of p + q which is odd but not a prime number.
To have a sum as an odd number one number should be even and as it is given that p<q, therefore p=2, and q = 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17.
So
p + q = 2 + 5 = 7, which is odd but it is prime
Now again, q = 7
p + q = 2 + 7 = 9 , which is odd as well as not prime.
Again take q = 11
p + q = 2 + 11 = 13, which is odd but prime
Now take q = 13
p + q = 2 + 13 = 15, which is odd as well as not prime.
Now take q = 17
p + q = 2 + 17 = 19, which is odd and prime.
Therefore we have p =2 and q = 7 or 13 and sum p + q =9 or 15 which is odd but not prime.
To know more about the prime number refer to the link given below:
https://brainly.com/question/792663
#SPJ1
What is the value of the expression z2+3z-3 when z=6?
Answers
Answer:
51
Step-by-step explanation:
Order of Operations: BPEMDAS
Step 1: Define
z² + 3z - 3
z = 6
Step 2: Substitute and Evaluate
6² + 3(6) - 3
36 + 18 - 3
36 + 15
51
A survey of 125 freshmen business students at a local university produced the results listed below. How many students took history and math, but not music? 30 took history; 32 took math; 33 took music; 14 took history but not math; 9 took math and music; 13 took history and music; 2 took all three
Answers
Answer:
Total Number of students taking Math and History and not music are 68.
Number of students who took both math and history at the same time is 6.
Step-by-step explanation:
History = 30
Math = 32
Music= 33
Math and Music= 9
History and Music= 13
History and Music and Math = 2
History but not math = 14
We have to find students taking history and math but not music.
Total number of students = 125
From the figure number of students taking Math and History and not music are
=30+6+32= 68
Number of students who took both math and history at the same time is 6.

−7 + 3(8n − 8) = 8(7 + 3n) please show work
Answers
Answer:
Step 1: Simplify both sides of the equation.
−7+3(8n−8)=8(7+3n)
−7+(3)(8n)+(3)(−8)=(8)(7)+(8)(3n)(Distribute)
−7+24n+−24=56+24n
(24n)+(−7+−24)=24n+56(Combine Like Terms)
24n+−31=24n+56
24n−31=24n+56
Step 2: Subtract 24n from both sides.
24n−31−24n=24n+56−24n
−31=56
Step 3: Add 31 to both sides.
−31+31=56+31
0=87
Answer:
There are no solutions.
Step-by-step explanation:
Name the marked angle in 2 different ways.

Answers
Answer:
angle TVU
Step-by-step explanation:
angle UVT
please mark as brainliest
Does anybody know this? I really need help.

Answers
Answer:
22 is th area
Step-by-step explanation:
A t distribution Multiple choice question. is either positively skewed or negatively skewed. has a nonzero mean. has slightly broader tails than the Z distribution. does not have asymptotic tails.
Answers
The answer to the multiple choice question is that a t distribution has slightly broader tails than the Z distribution. This is because the t distribution is based on smaller sample sizes and therefore has more variability, leading to wider tails.
Additionally, the explanation for the other options is as follows:
- A t distribution can be positively or negatively skewed depending on the sample size and distribution of the data.
- A t distribution does have a nonzero mean, just like any other distribution.
- As mentioned earlier, a t distribution has slightly broader tails than the Z distribution.
- A t distribution does have asymptotic tails, meaning they approach but never reach zero as the degrees of freedom increase.
To know more about distribution visit:
brainly.com/question/31364473
#SPJ11
\( \frac{1}{2} + \frac{1}{4} \)
can you please tell me how to do easy way can you please show me in numbers how to multiply
Answers
Explanation: Find a common denominator (bottom number) for both fractions. 4. Multiply the 1 and 2 in 1/2 to get 2/4. Then just add the numerators (top number). This gives you 3/4.
I noticed you also said show me how to multiply. For fractions, you just mutiply the numeration and denominator apart.
1 x 1 1
- - = -
2x 4 8
we first look at the denominators, hmmm we have 2 and 4, and then do a quick prime factoring.
2 = 2 * 1
4 = 2 * 2 * 1
well, let's notice that 4 contains 2 already, plus another 2 and 1 so, we can just use that our LCD.
\(\cfrac{1}{2}+\cfrac{1}{4}\implies \cfrac{(2)1~~ + ~~(1)1}{\underset{\textit{using this LCD}}{4}}\implies \cfrac{2+1}{4}\implies \cfrac{3}{4}\)
what's the difference between the arithmetic and geometric average return (conceptually, not mathematically), and when is it best to use each?
Answers
Conceptually, the arithmetic and geometric average returns are different measures used to describe the performance of an investment or an asset over a specific period.
The arithmetic average return, also known as the mean return, is calculated by adding up all the individual returns and dividing by the number of periods. It represents the average return for each period independently.
On the other hand, the geometric average return, also called the compound annual growth rate (CAGR), considers the compounding effect of returns over time. It is calculated by taking the nth root of the total cumulative return, where n is the number of periods.
When to use each measure depends on the context and purpose of the analysis:
1. Arithmetic Average Return: This measure is typically used when you want to evaluate the average return for each individual period in isolation. It is useful for analyzing short-term returns, such as monthly or quarterly returns. The arithmetic average return provides a simple and straightforward way to assess the periodic performance of an investment.
2. Geometric Average Return: This measure is more suitable when you want to understand the compounded growth of an investment over an extended period. It is commonly used for long-term investment horizons, such as annual returns over multiple years.
The geometric average return provides a more accurate representation of the overall growth rate, accounting for the compounding effect and reinvestment of returns.
In summary, the arithmetic average return is suitable for analyzing short-term performance, while the geometric average return is preferred evaluating long-term growth and the compounding effect of returns.
learn more about Average Return here:
https://brainly.com/question/29662426
#SPJ11
2 4/5 3.5 4 1/4 5.3 in order greatest to least
Answers
Answer:
5.3, \(4\frac{1}{4}\), 3.5, \(2\frac{4}{5}\)
Step-by-step explanation:
please help me out here :’(

Answers
Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
We are going to use the areas given to find the lengths of the sides of each of their respective squares. For the purple square, the area is 35 units squared. Because the formula for the area is A = s * s, then we can fill in the value for the area and solve for s, the side length, of the purple square.
\(35=s^2\) and
\(s=\sqrt{35}\). That side length also serves as the height of the right triangle. Now on to the blue square on the bottom. It has an area of 50 units squared, so
\(50=s^2\) and
\(s=\sqrt{50}\). We could feasibly simplify that, but it's not necessary, really. That side serves as the base of the right triangle. Now we can use Pythagorean's Theorem to find the length of the hypotenuse of the right triangle, which also serves as the side of the big blue square. We will call the side of the big blue square x.
\(x^2=(\sqrt{35})^2+(\sqrt{50})^2\) and
\(x^2=35+50\) and
\(x^2=85\) and
\(x=\sqrt{85}\). That is the side length of the large blue square. The area for the square is s * s, and since we know the side length to be √85:
\(A=(\sqrt{85})(\sqrt{85})\) so
A = 85 units squared
In normal distribution Z ~ N (1,0)
If X ~ B (100, 0.36), then P (22 ≤ 33) ≈
Answers
The probability P(22 ≤ X ≤ 33) for the given binomial distribution is approximately 0.0667, using the normal approximation to the binomial distribution.
To find the probability P(22 ≤ X ≤ 33) for a binomial distribution with parameters n = 100 and p = 0.36, we need to approximate it using the normal distribution.
In this case, we can use the normal approximation to the binomial distribution, which states that for large values of n and moderate values of p, the binomial distribution can be approximated by a normal distribution with mean μ = np and standard deviation σ = √(np(1-p)).
For X ~ B(100, 0.36), the mean μ = 100 * 0.36 = 36 and the standard deviation σ = √(100 * 0.36 * (1 - 0.36)) ≈ 5.829.
To find P(22 ≤ X ≤ 33), we convert these values to standard units using the formula z = (x - μ) / σ. Substituting the values, we have z1 = (22 - 36) / 5.829 ≈ -2.395 and z2 = (33 - 36) / 5.829 ≈ -0.515.
Using the standard normal distribution table or a calculator, we can find the corresponding probabilities for these z-values. P(-2.395 ≤ Z ≤ -0.515) is approximately 0.0667.
Therefore, the probability P(22 ≤ X ≤ 33) for the given binomial distribution is approximately 0.0667.
Note that the normal approximation to the binomial distribution is valid when np ≥ 5 and n(1-p) ≥ 5. In this case, 100 * 0.36 = 36 and 100 * (1-0.36) = 64, both of which are greater than or equal to 5, satisfying the approximation conditions.
To learn more about binomial distribution click here: brainly.com/question/29163389
#SPJ11
590 ÷ 5 with the remainder of what
Answers
Answer:
118 r0
Step-by-step explanation:
590/5=118
there is no remainder
hope this helps :3
if it did pls mark brainliest
An object moves in the xy-plane so that its position at any time tis given by the parametric equations x(t) = t° - 3t + 2 and y (t) = /t² + 16. What is the rate of change of y with respect to x when t = 3 ? A 1/90 B 1/15 3/5 D 5/2
Answers
The rate of change of y with respect to x when t = 3 is = 3/25 and the answer is not one of the options given.
How to determine of rate of change y with respect to x?An object moves in the xy-plane so that its position at any time tis given by the parametric equations x(t) = t° - 3t + 2 and y (t) = /t² + 16.
To find the rate of change of y with respect to x, we need to find dy/dx, which can be computed using the chain rule of differentiation:
(dy/dt) / (dx/dt) = dy/dx
We first compute dx/dt and dy/dt:
dx/dt = 1 - 3 = -2
dy/dt = 2t / (t² + 16)
When t = 3, we have:
dx/dt = -2
dy/dt = 2(3) / (3² + 16) = 6/25
Therefore, the rate of change of y with respect to x when t = 3 is:
(dy/dt) / (dx/dt) = (6/25) / (-2) = -3/25
So, the answer is not one of the options given.
Learn more about parametric equations.
brainly.com/question/28537985
#SPJ11
PLEASE HELP FAST
EMERGENCY

Answers
According to the information in the graph, the money that was collected was $79.5.
How to make a graph of this problem?To make a graph of this problem, we must relate the number of units sold of special dinners and lunches and the total price obtained for these sales.
How does this graph help us find the total price of the food sold?This graph helps us because it allows us to visualize how much money we got from the sale of these.
According to the graph the total price of lunches and dinners would be $79.5.
Learn more about prices in: https://brainly.com/question/19091385
#SPJ1

The side length of a cube is 8 cm, and the side length of a smaller cube is 2 cm.
The volume of the larger cube is how many times the volume of the smaller cube?
Answers
Answer:
64 times larger
Step-by-step explanation:
8^3=512
2^3=8
512/8=64
Continuing Case 5. Time Value of Money A. Jamie Lee needs to save a total of $9,000 in order to get started in her cupcake café venture. She is presently depositing $1,800 a year in a regular savings account. Calculate the future value of these deposits. B. Assuming that she leaves her emergency fund of $3,100 untouched, how much will her emergency fund be worth? C. What if Jamie Lee had a relative that could give her money now that she could invest? What is the minimum amount she would need now to ensure that she had $9,000 when she wanted to open the cupcake café? D. As Jamie Lee is planning ahead for operating the cupcake café, she calculates that she will need $24,000 per year in salary. What is the value of five years of salary when the cupcake café opens? (Assume that she will take the salary as a one-time payment each year.) Use the table below and Exhibit 1-A, Exhibit 1-B, Exhibit 1-C, and Exhibit 1-D to calculate the balances of the information provided above. Assume that the time period for each scenario is 5 years, and the interest rate is 2%. Use the table below and Exhibit 1-A, Exhibit 1-B, Exhibit 1-C, and Exhibit 1-D to calculate the balances of the information provided above. Assume that the time period for each scenario is 5 years, and the interest rate is 2%. A. Future Value of a Series of Deposits Regular deposit amount times Future value of annuity factor equals Future value amount $ 0.00 B. Future Value of a Single Amount Current amount times Future value factor equals Future value amount $ 0.00 C. Present Value of a Single Amount Future amount desired times Present value factor equals Present value amount $ 0.00 D. Present Value of a Series of Deposits Regular amount to be withdrawn times Present value of annuity factor equals Present value amount $ 0.00
Answers
Answer:
A. Future Value of Jamie Lee's deposits: $49,075.20
B. Future Value of Jamie Lee's emergency fund: $3,484.40
C. Minimum amount Jamie Lee would need now: $8,001
D. Value of five years of salary: $522,576
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the future value of Jamie Lee's deposits, we need to use the future value of an annuity formula. The formula is:
Future Value = Regular deposit amount x Future value of annuity factor
Given that Jamie Lee is depositing $1,800 per year and the time period is 5 years with an interest rate of 2%, we can find the future value of these deposits using the table below:
Period 2% Future Value of Annuity
1 5.102
2 10.305
3 15.717
4 21.362
5 27.264
A. Future Value of a Series of Deposits:
Future Value = $1,800 x 27.264 = $49,075.20
Therefore, the future value of Jamie Lee's deposits will be $49,075.20.
B. To calculate the future value of her emergency fund, we need to use the future value of a single amount formula:
Future Value = Current amount x Future value factor
Given that her emergency fund is $3,100 and the time period is 5 years with an interest rate of 2%, we can find the future value using the table below:
Period 2% Future Value Factor
1 1.104
2 1.109
3 1.114
4 1.119
5 1.124
B. Future Value of a Single Amount:
Future Value = $3,100 x 1.124 = $3,484.40
Therefore, her emergency fund will be worth $3,484.40.
C. To calculate the minimum amount Jamie Lee would need now to ensure she has $9,000 in the future, we need to use the present value of a single amount formula:
Present Value = Future amount desired x Present value factor
Given that she wants $9,000 in the future and the time period is 5 years with an interest rate of 2%, we can find the present value using the table below:
Period 2% Present Value Factor
1 0.898
2 0.896
3 0.893
4 0.891
5 0.889
C. Present Value of a Single Amount:
Present Value = $9,000 x 0.889 = $8,001
Therefore, the minimum amount Jamie Lee would need now is $8,001 to ensure she has $9,000 in the future.
D. To calculate the value of five years of salary, we need to use the present value of a series of deposits formula:
Present Value = Regular amount to be withdrawn x Present value of annuity factor
Given that she needs $24,000 per year for 5 years and the interest rate is 2%, we can find the present value using the table below:
Period 2% Present Value of Annuity
1 4.451
2 8.818
3 13.165
4 17.486
5 21.774
D. Present Value of a Series of Deposits:
Present Value = $24,000 x 21.774 = $522,576
Therefore, the value of five years of salary when the cupcake café opens is $522,576.
know more about Future Value Factor: brainly.com/question/32270000
#SPJ11
12. Determine the missing angle measures.
M<1
M<3
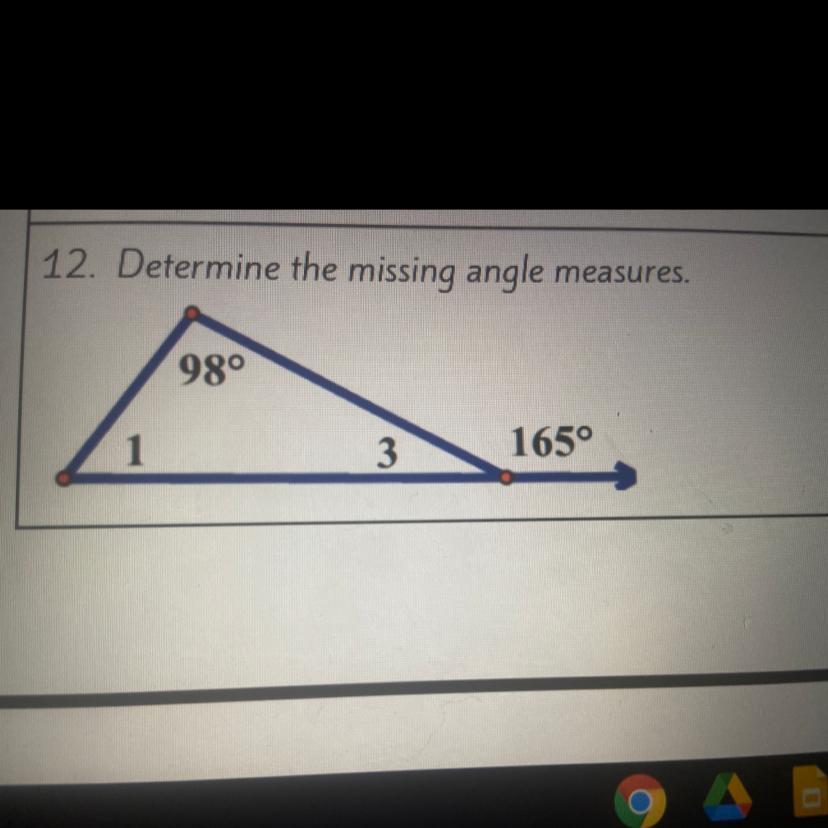
Answers
Answer:
3 is 15 degrees and 1 is 67 degrees
Given m||n, find the value of x

Answers
Answer:
17 is the value of x...
Step-by-step explanation:
9x + 7 = 10x-10 reason ( being alternate angle
or, x = 17