calculate the time in seconds it would take for a radio frequency signal to travel round-trip between earth and an meo satellite at 20,000 km.
Answers
The speed of light is 299,792,458 m/s.
What is speed of light?
The speed of light is a fundamental physical constant denoted by the letter c. It is the speed at which light propagates through empty space, a vacuum. In the International System of Units (SI), the speed of light is given as exactly 299,792,458 meters per second. This is the speed of light in a vacuum, and because light does not travel at the same speed through different substances, the speed of light in a material is always less than this value.
This means that it takes 1 second for light to travel 299,792,458 m.
Therefore, it would take (20,000,000,000 m / 299,792,458 m/s) = 66.66 seconds for a radio frequency signal to travel round-trip between earth and a MEO satellite at 20,000 km.
To learn more about speed of light
https://brainly.com/question/100983
#SPJ4
Related Questions
When a 2.75-kg fan, having blades 18.5 cm long, is turned off, its angular speed decreases uniformly from 10.0 rad/s to 6.30 rad/s in 5.00 s. (a) What is the magnitude of the angular acceleration of the fan? (b) Through what angle (in degrees) does it turn while it is slowing down during the 5.00 s? (c) If its angular acceleration does not change, how long after it is turned off does it take the fan to stop.
Answers
The magnitude of the angular acceleration of the fan is approximately 0.74 rad/s². The fan turns approximately 1800 degrees while slowing down during the 5.00 s. Meanwhile, if the angular acceleration does not change, it would take the fan approximately 0 seconds to stop after being turned off.
(a) To find the magnitude of the angular acceleration of the fan, we can use the formula for angular acceleration:
\(angular acceleration (a) =\frac{d (change in angular speed)}{time}\)
Initial angular speed (ω1) = 10.0 rad/s
Final angular speed (ω2) = 6.30 rad/s
Time (t) = 5.00 s
Using the formula:
\(a = \frac{w2 - w1}{t} \\a =\frac{6.30 rad/s - 10.0 rad/s}{5.00 s}\)
Calculating the expression, we find:
α = -0.74 rad/s^2
The magnitude of the angular acceleration of the fan is approximately 0.74 rad/s^2.
(b) To determine the angle through which the fan turns while slowing down, we can use the formula for angular displacement:
\(angular displacement (θ) =\frac{initial angular speed + final angular speed}{2 x time} \\\)
θ = (ω1 + ω2) / 2 x t
θ = (10.0 rad/s + 6.30 rad/s) / 2 x 5.00 s
Calculating the expression, we find:
θ = 31.5 rad
To convert the angle from radians to degrees:
θ_degrees = θ x (180° / π rad)
θ_degrees = 31.5 rad x (180° / π rad)
Calculating the expression, we find:
θ_degrees ≈ 1800°
Therefore, the fan turns approximately 1800 degrees while slowing down during the 5.00 s.
(c) If the angular acceleration does not change, we can use the formula for time to stop:
time to stop = (final angular speed) / (angular acceleration)
Final angular speed (ω2) = 0 rad/s (when the fan stops)
Using the formula:
time to stop = ω2 / α
time to stop = 0 rad/s / -0.74 rad/s^2
Calculating the expression, we find:
time to stop ≈ 0 s
Therefore, if the angular acceleration does not change, it would take the fan approximately 0 seconds to stop after being turned off. 0.74 rad/s² is the magnitude of the angular acceleration of the fan. While slowing down during the 5.00 s, the fan turns approximately 1800 degrees.
Learn more about angular acceleration here:
https://brainly.com/question/13014974
#SPJ11
What's centripetal force..........
Answers
Answer:
a force that acts on a body moving in a circular path and is directed toward the center around which the body is moving.
Explanation:
Answer:
A net force that acts on an object to keep it moving along a circular path
at Newton's first lawExternal force and here centripetal force
A 0.1 kg toy contains a compressed spring. when the spring is released the toy fly
0.45 m upwards from ground level before falling back down to the ground. what is the speed of the toy when it hits the ground.
It’s 5 marks (gsce level)
Answers
Answer:
d
Explanation:
An object's speed is 0.8 m/s, and its momentum is 200 kg-m/s What is the mass of the object?
A. 250kg
B. 200kg
C.160kg
D.128kg
Answers
Answer:
A: The mass would be 250kg
Explanation:
In terms of an equation, the momentum of an object is equal to the mass of the object times the velocity of the object. where m is the mass and v is the velocity. The equation illustrates that momentum is directly proportional to an object's mass and directly proportional to the object's velocity.
p= mv
m= p/ v
The explanation to that is:
momentum = mass× velocity
mass= momentum / velocity
THE ANSWER IS A
Hope this helps!
a charged paint is spread in a very thin uniform layer over the surface of a plastic sphere of diameter 11.0 cm, giving it a charge of -11.0 μc.
Answers
The charged paint has been spread in a very thin uniform layer over the surface of a plastic sphere with a diameter of 11.0 cm, resulting in a charge of -11.0 μC. The charge of the paint indicates that there is an excess of negative charge on the sphere.
When a charge is spread over a conductive object, such as a metal sphere, it distributes itself uniformly on the surface. However, in this case, the sphere is made of plastic, which is an insulator. Due to the insulating nature of plastic, the charge will not be able to move freely across the surface.
The charge on the plastic sphere creates an electric field around it. This electric field affects other charged objects in its vicinity. For example, if a positively charged object is brought close to the negatively charged sphere, it will experience an attractive force due to the electric field.
The magnitude of the charge (-11.0 μC) does not depend on the size or diameter of the sphere. It solely represents the amount of excess negative charge on the surface.
To summarize, spreading the charged paint over the plastic sphere creates a negatively charged surface. This charge distribution creates an electric field around the sphere, influencing the behavior of other charged objects in its vicinity. The magnitude of the charge (-11.0 μC) indicates the amount of excess negative charge on the sphere.
To know more about charge visit:
https://brainly.com/question/1922668
#SPJ11
The phenomena addressed is pertinent to physics, especially the concept of electrostatics. They reiterate how excess negative charge quickly moves to the outer surface of spheres due to electrostatic repulsion, creating an electric field outside similar to that of a central point charge. This is crucial for achieving a uniform electric potential over the sphere surface.
Explanation:The subject of your question pertains to physics, specifically, electrostatics. Here, a plastic sphere is coated with a thin layer of charged paint, with the given charge being -11.0 μC. You are dealing with the phenomena of distribution of charge on the surface of objects. When an object is charged, the excess charge tends to move to the surface of the object due to electrostatic repulsion.
The radius of the given sphere would be half the diameter, which equates to 5.5 cm or 0.055 m. Now, to summarize the behavior of the sphere: the electric field inside a charged sphere is zero, and the electric field outside can be considered the same as the electric field of a point charge located at the center of the sphere. Meanwhile, the charge on the sphere is at the surface.
The fact that the charge is uniformly distributed on the sphere's surface and does not remain inside can be linked to the concept of electric potential, which is the same at every point on the surface of a sphere. This phenomenon occurs because the excess charge quickly moves to the outer surface due to the repelling effect amongst themselves.
Learn more about Distribution of Charge here:https://brainly.com/question/492163
#SPJ12
If 120 g of naoh were used to prepare 500 ml of solution, what would the concentration be?.
Answers
If 120 g of NaOH were used to prepare 500 ml of solution, the concentration would be 6 M
Molarity = ( Weight of solute * 1000 ) / ( GMV * V )
GMV = Gram molecular weight
V = Volume of solution
GMV of NaOH = 26 + 16 + 1
GMV of NaOH = 40
Molarity = ( 120 * 1000 ) / ( 40 * 500 )
Molarity = 120 / 20
Molarity = 6
Molarity or molar concentration is the concentration of chemical species mainly solute in a solution. It is the amount of substance per unit volume of solution.
Therefore, the concentration of NaOH is 6 M
To know more about Molarity
https://brainly.com/question/16727614
#SPJ4
If an aircraft is equipped with a fixed-pitch propeller and a float-type carburetor, the first indication of carburetor ice would most likely be
Answers
The first sign of carburetor ice would probably be a decrease in rpm if an aircraft had a fixed-pitch propeller and a float-type carburetor.
What is carburetor ice?The temperature decrease in the carburetor as a result of gasoline evaporation and the temperature loss related to the pressure drop in the venturi is what lead to carburetor ice.
The temperature decrease in the carburetor is what leads to carburetor icing. The throttle valve will get frozen with water vapor if the temperature falls below freezing.
While initially increasing the Venturi effect, this ultimately inhibits airflow. When the outside air temperature is below 70 degrees F, carb icing most frequently happens (21 degrees C).
Engine sluggishness, loss of RPM, and loss of manifold pressure are signs of carb ice. In general, if you suspect carb ice, immediately administer carb heat or alternative air.
Hence, the first sign of carburetor ice would probably be a decrease in rpm.
To learn more about the carburetor ice refer;
https://brainly.com/question/14305701
#SPJ1
A small statue is recovered in an archaeological dig. Its weight is measured to be 96 lb, and its volume 0.08 ft3.a.What is the statue’s weight density in lbs/ft3? b.What substance is it?
Answers
ANSWER:
a. 1200 lb/ft^3
b. Gold
STEP-BY-STEP EXPLANATION:
Given:
Weight (W) = 96 lb
Volume (V) = 0.08 ft^3
a.
Weight density is equal to the quotient of weight to volume, therefore:
\(\begin{gathered} d=\frac{W}{V} \\ \\ \text{ We replacing} \\ \\ d=\frac{96}{0.08} \\ \\ d=1200\text{ lb/ft}^3 \end{gathered}\)b.
We can say that this weight density is equal to the weight density of Gold
A 1,800kg rollercoaster is going down a hill with a kinetic energy of 25,000J. What
is the velocity of the rollercoaster going down the hill?
Answers
The velocity of the rollercoaster going down the hill is equal to 5.270 m/s.
Given the following data:
Mass of rollercoaster = 1,800 kilograms.Kinetic energy =25,000 Joules.To calculate the velocity of the rollercoaster going down the hill:
Formula for kinetic energy.Mathematically, kinetic energy is calculated by using the formula;
\(K.E = \frac{1}{2} MV^2\)
Where:
K.E is the kinetic energy.M is the mass of an object.V is the velocity of an object.Making V the subject of formula, we have:
\(V =\sqrt{\frac{2K.E}{M} }\)
Substituting the given parameters into the formula, we have;
\(V =\sqrt{\frac{2\times 25000}{1800} }\\\\V=\sqrt{27.7778}\)
Velocity, V = 5.270 m/s
Read more on kinetic energy here: https://brainly.com/question/17081653
What is Heat engine?
Answers
Answer:
An engine made of heat!
Okay actual answer, A heat engine is a mechanical energy converter that transforms heat or thermal energy to mechanical energy.
Which nucleus completes the following equation?

Answers
IGNORW irritating but not even on the golden bath bath and
A person bungee-jumping from a bridge. The person is attached to a long elastic rope . At one point during the fall, she reaches her maximum speed.
State her acceleration at this point.
Answers
The bungee jumper's acceleration is zero when she achieves her top speed. This is due to the fact that acceleration is the rate at which velocity changes, and since velocity is constant at maximum speed, there is neither change nor acceleration.
What is the bungee jumper's greatest rate of acceleration?This is evident because when the bungee cord is completely stretched, the upward force is at its strongest. Within 2.4 seconds, or in the midst of the second free-fall phase, the jumper arrived at the highest position. Around -9.8 m/s2 of downward acceleration is present.
When someone bungee jumps, what force is used?The elastic force from the bungee cord pushing up against the jumper as it expands slows his descent and temporarily stops him.
To know more about acceleration visit:-
https://brainly.com/question/12550364
#SPJ1
Provide the length of daylight for each of the following latitudes on June 21-22 of any year. You may use the same number more than once.
90 degrees N latitude has hour(s) and minutes of daylight.
40 degrees S latitude has hour(s) and minutes of daylight.
40 degrees N latitude has hour(s) and minutes of daylight.
0 degrees latitude has hour(s) and minutes of daylight.
Answers
June 21-22 is the summer solstice in the Northern Hemisphere and the winter solstice in the Southern Hemisphere. On these days, the daylight hours are the longest at the North Pole and the shortest at the South Pole.
Using online tools or astronomical calculations, we can determine the length of daylight for each of the given latitudes:
90 degrees N latitude (North Pole): 24 hours of daylight (the sun does not set)
40 degrees S latitude: 9 hours and 39 minutes of daylight
40 degrees N latitude: 14 hours and 55 minutes of daylight
0 degrees latitude (equator): 12 hours of daylight (the sun rises at 6:00 am and sets at 6:00 pm)
Note that these values are approximate and may vary slightly depending on the exact location and year.
To know more about daylight of the latitudes :
https://brainly.com/question/30709382?
#SPJ11
I’ll give brainliest if it’s correct ;-;z
Someone help!!!
3 different earthquakes that were measured with broadband seismographs, 3 earthquakes long period, and 3 earthquakes measured with short period instruments.
Answers
Explanation:
what is the question? could you pls provide it
What is the type of radioactive decay represented by the equation above? A. Gamma B. Fusion C. Alpha D. Fission 40. Alberta uses clean coal technology. This means that the coal has a lower i content than coal in other parts of Canada, which results in reduced ii The statement above is completed correctly by the information in row olla sdf to ridW Row i A. sulfur greenhouse gas emissions acid deposition sulfur carbon greenhouse gas emissions acid deposition carbon B. C. D. 29. Which of the following graphs depicts the relationship between gravitational field strength and the mass of the International Space Station orbiting Earth? A. Field Strength (N/kg) C. Field Strength (N/kg) Mass (kg) Mass (kg) B. Field Strength (N/kg) D. Field Strength (N/kg) Mass (kg) CADLC 30. Which of the following sequences of colours represents the changing temperatu from the surface to the atmosphere of the sun? a A. Red, orange, yellow, blue B. Yellow, red, orange, blue C. Orange, yellow, blue, red D. Blue, yellow, orange, red 1. When a star undergoes a blue shift, the star is A. moving away from an observer B. moving towards an observer C. moving parallel to an observer D. stationary Mass (kg)
Answers
The sun is Yellow, red, orange, and blue. Therefore option B is correct.
The star is moving toward an observer. Therefore option B is correct.
39. The type of radioactive decay represented by the equation provided Gamma. Therefore option A is correct.
40. The statement is completed correctly by the information which states that the coal in Alberta has a lower carbon content than coal in other parts of Canada, resulting in reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
29. graph B depicts the relationship between gravitational field strength and the mass of the International Space Station orbiting Earth.
30. The correct sequence of colors representing the changing temperature from the surface to the atmosphere of the sun is Yellow, red, orange, and blue. Therefore option B is correct.
1. When a star undergoes a blue shift, it indicates that the star is moving toward an observer. Therefore option B is correct.
Know more about radioactive decay:
https://brainly.com/question/1770619
#SPJ12
When light hits a surface it usually bounces off at a larger angle. True or false? Justify
Answers
Answer:That only applies to highly polished surfaces, eg mirrors.
If you take a high quality laser (ie with low divergence) and aim it at a wall, you can see the spot where the laser beam reaches the wall from anywhere with a direct line-of-sight to the spot where the laser beam reaches the wall. This due to micro imperfections on the surface of the wall. At a microscopic level, the wall surface is very rough and pointing in all directions.
As to why, a beam of light bounces of a highly polished surface, I can only surmise that it is essentially due to kinematics, ie the only force opposing the light beam is normal to the surface, hence there no forces along the reflective surface. Since there are no forces along the reflective surface, the speed component of light along the reflective surface remains unchanged. However, on the plane perpendicular to the reflective surface the, the light photons bounce off at the same speed at which the hit the reflective surface because the mass of the reflective surface is much much much larger than the mass of the photons, which means that the reflective surface won’t move at all. Since conservation of momentum requires that momentum after the collision be the same as the momentum before the collision then the only way for that to happen is if the velocity of the photon perpendicular to the reflective surface is of exactly the same magnitude but in the opposite direction. Vector resolution of the speed component of the reflected beam means that the angle of reflection must be the same as the angle of incidence.
Explanation:
b. Two vectors with dimensions A = 5i + 3j + k and B = 4i + j + 2k are used for the following calculation. Determine: i. ii. iv. The dot product A.B. [2 marks] [3 Marks] The angle between vectors A and B. The cross product A XB. [2 marks] The area of the parallelogram spanned by the vectors A and B. [3 Marks]
Answers
The dot product is 25, the angle is \(\theta = cos^{-1} \frac{25}{\sqrt{35} \times \sqrt{21}}\), the cross product is 1i + (-6)j + (-7)k, and the area of the parallelogram spanned by vectors A and B is \(\sqrt{86}\).
Given,
A = 5i + 3j + k
B = 4i + j + 2k
i. Dot Product (A · B):
The dot product of two vectors A and B is given by the sum of the products of their corresponding components.
\(A.B = (A_x \times B_x) + (A_y \times B_y) + (A_z \times B_z)\\A.B = (5 \times 4) + (3 \times 1) + (1 \times 2) \\= 20 + 3 + 2 \\= 25\)
ii. Angle between vectors A and B:
The angle between two vectors A and B can be calculated using the dot product and the magnitudes of the vectors.
\(cos\theta = (A.B) / (|A| \times |B|)\\\theta = \frac{1}{cos} ((A.B) / (|A| \times |B|))\\A = \sqrt{(5^2 + 3^2 + 1^2)} =\\ \sqrt{35}\\B = \sqrt{(4^2 + 1^2 + 2^2)} \\= \sqrt{21}cos\theta = \frac{(A.B) / (|A| \times |B|)\\\theta = \frac{1}{cos} \frac{25}{\sqrt{35} \times \sqrt{21}}}\)
iv. Cross Product (A × B):
The cross product of two vectors A and B is a vector that is perpendicular to both A and B and its magnitude is equal to the area of the parallelogram spanned by A and B.
\(A\times B = (A_y \timesB_z - A_z \timesB_y)i + (A_z \timesB_x - A_x \timesB_z)j + (A_x \times B_y - A_y \times B_x)k\\A\times B = ((3 \times 2) - (1 \times 1))i + ((1 \times 4) - (5 \times 2))j + ((5 \times 1) - (3 \times 4))k\\= 1i + (-6)j + (-7)k\)
Area of the parallelogram spanned by vectors A and B:
The magnitude of the cross product A × B gives us the area of the parallelogram spanned by A and B.
Area = |A × B|
Area of the parallelogram spanned by vectors A and B:
Area = |A × B| =
\(\sqrt{(1^2 + (-6)^2 + (-7)^2}\\\sqrt{1+36+49\\\\\sqrt{86}\)
Learn more about vectors, here:
https://brainly.com/question/24256726
#SPJ4
A sample of gas is moved from a 5 liter container to a 2 liter container.
a.) What happens to the pressure of the gas with this change in volume (Assume there is no change in temperature)?
b.) Why does this change happen?
Answers
Answer:
Pressure would increase
Explanation:
This is because pressure is calculated by the number of times particles hit the container that they are stored it.
More collisions would lead to an increase in pressure.
So when you move a sample of has from a 5 litre container to a 2 litre container, pressure would increase as there is less space for particles to move around. This would mean that there would be more particles colliding with the container, and so an increase in pressure.
Hope this helps!
The change in pressure occurs because the same number of gas molecules are confined to a smaller volume, leading to more frequent collisions with the container walls and an increase in pressure.
a.) When a sample of gas is moved from a 5-liter container to a 2-liter container while keeping the temperature constant, the pressure of the gas will increase.
The relationship between pressure (P), volume (V), and temperature (T) for a given amount of gas is described by the ideal gas law:
PV=nRT
Where:
P is the pressure of the gas
V is the volume of the gas
n is the amount of gas (usually measured in moles)
R is the ideal gas constant
T is the temperature in Kelvin
Since the amount of gas (n) and the temperature (T) are constant in this scenario, we can simplify the equation to:
PV=constant
This means that as the volume (V) decreases, the pressure (P) must increase to keep the product of pressure and volume constant. In other words, as you reduce the volume of the container, the gas molecules will collide more frequently with the walls of the container, resulting in a higher pressure.
b.) This change in pressure happens due to the nature of gas molecules and their behavior. Gas molecules are in constant motion, moving in all directions. When the volume of the container is reduced, the same number of gas molecules now have less space to move around. As a result, they collide more frequently with the walls of the container.
These collisions exert a force on the walls, and pressure is defined as the force per unit area. With more frequent collisions, the force on the walls increases, and therefore the pressure increases. The gas molecules are essentially exerting more pressure per unit area because they have less space to spread out.
To know more about pressure
https://brainly.com/question/33528297
#SPJ3
How does the sun maintain its high temperature and energy output?
Answers
Answer:
The core of the sun is the region that extends from the center to about 20–25% of the solar radius. It is here, in the core, where energy is produced by hydrogen atoms (H) being converted into nuclei of helium (He). ... The core is the only part of the sun that produces an appreciable amount of heat through fusion.
Explanation:
I got you
By not running out of fuel (Hydrogen).
Rest assured ... When the sun runs low on Hydrogen, it'll go through several complex changes, and it'll end up at much much lower temperature, with much much lower energy output.
Why do tin roofs make creaking sounds on hot days?
Answers
Answer: Yes, on many slate-roofed homes as temperatures change, such as cooling at night or heating during the day, thermal expansion or contraction of the slates may cause movement that in turn causes snapping, popping, or cracking noises, even bangs and clanks or clicks from the roof.
Explanation:
Answer:
because of its mealting
Explanation:
hope it helps you
A blue line with 5 orange tick marks then one red tick mark then 4 orange tick marks. The number zero is above the red tick mark.Assume each tick mark represents 1 cm.Calculate the total displacement from 0 if an object moves 3 cm to the left, then 7 cm to the right, and then 6 cm to the left.The object moves cm to the left.What is the total distance the object travels? cm
Answers
Answer:
16 cm
Explanation:
Given that,
The object begins from 0 and moves 3cm towards left side followed by 7 cm towards the right and then, 6 cm towards the left side.
Let the x-axis to be the +ve and on the right side and -ve on the left
Thus, displacement would be:
= 0 -3 + 7 -6
= -2 cm
This implies that the object displaces 2cm towards the left.
While the total distance covered by the object equal to,
= 0cm + 3cm + 7cm + 6cm
= 16 cm
Thus, 16 cm is the total distance.
Answer:
Its 2 to the right
Explanation:
edge :p
what is the main difference between a substance going through a physical change and one going through a chemical ?
Answers
Answer: Physical changes only change the appearance of a substance, not its chemical composition. Chemical changes cause a substance to change into an entirely substance with a new chemical formula. Chemical changes are also known as chemical reactions.
Answer:
just give the other person brainlyest
Explanation:
What are the x / y-components? I'd also like a step-by-step explanation please.
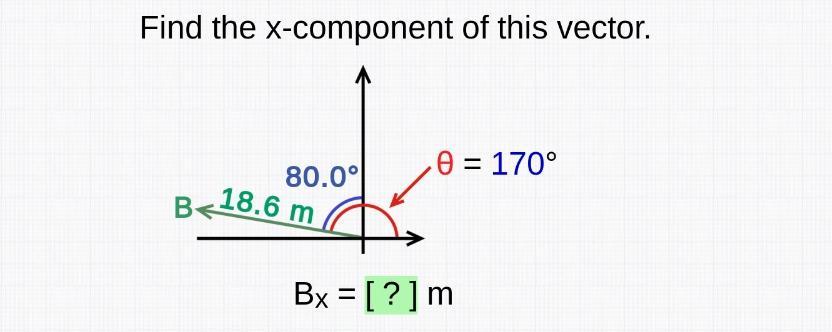
Answers
The x and y component of the vector are -18.32 m and 3.23 m respectively.
What are the x and y components of the vector?The x and y component of the vector is calculated by applying the following formula.
Bx = B cosθ
By = B sinθ
where;
B is the magnitude of the vectorBx is the x componentBy is the y componentθ is the angle of the vector measured above x axisThe vector is located in negative x direction but positive y direction.
The angle of the vector from x axis = 90⁰ - 80⁰ = 10⁰
Bx = B cosθ = -18.6 m x cos ( 10 ) = -18.32 m
By = B sinθ = 18.6 m x sin ( 10 ) = 3.23 m
Learn more about x and y components here: https://brainly.com/question/27996986
#SPJ1
Among the many discoveries made with the Hubble Space Telescope are four new moons of Saturn, the largest being just about 70.0 km in diam-eter. Suppose this moon is covered by a highly reflective coating, thus forming a spherical convex mirror. Another moon happens to pass by at a distance of 1.00 × 10? km. What is the image distance?
Answers
The approximate image distance (di) of the passing moon when reflected off the highly reflective coating on the spherical convex mirror is approximately 0.0286 km, or 28.6 meters.
To determine the image distance of the passing moon when reflected off the highly reflective coating on the spherical convex mirror (the large moon with a diameter of 70.0 km), we can use the mirror equation:
1/f = 1/do + 1/di,
where f is the focal length, do is the object distance, and di is the image distance.
Since we are dealing with a convex mirror, the focal length (f) is positive. For a spherical convex mirror, the focal length is half the radius of curvature (R). However, the radius of curvature is not given in the information provided, so we cannot directly calculate the focal length.
However, we can make use of the fact that a convex mirror always produces a virtual image. In this case, the image distance (di) will be negative, indicating a virtual image formed behind the mirror.
Given:
Diameter of large moon = 70.0 km
Distance of passing moon = 1.00 × 10? km
Since the distance of the passing moon is much greater than the diameter of the large moon, we can approximate the object distance (do) as the distance of the passing moon (1.00 × 10? km).
Substituting these values into the mirror equation:
1/f = 1/do + 1/di,
we can rearrange the equation to solve for the image distance (di):
1/di = 1/f - 1/do.
Since a convex mirror has a positive focal length and we have a virtual image, the term 1/f will be positive and 1/do will be negative.
Substituting the values and performing the calculations:
1/di = 1/f - 1/do
= 1/2f - 1/do
≈ 1/2f (assuming 1/do is negligible compared to 1/2f)
Now, we need to determine the approximate value of 1/2f. Since we don't have the radius of curvature or focal length information, we cannot calculate an exact value. However, we can make an estimation based on the given information.
Assuming the large moon is roughly spherical, we can consider its diameter of 70.0 km as the approximate diameter of its curvature. The radius of curvature (R) would be half the diameter, or 35.0 km.
Since the focal length (f) of a spherical convex mirror is half the radius of curvature, we can estimate the focal length as 17.5 km.
Substituting this estimated value into the equation:
1/di ≈ 1/2f
= 1/(2 * 17.5 km)
≈ 1/35.0 km^-1
= 0.0286 km^-1.
Therefore, the approximate image distance (di) of the passing moon when reflected off the highly reflective coating on the spherical convex mirror is approximately 0.0286 km, or 28.6 meters.
For more such questions on spherical convex mirror visit:
https://brainly.com/question/27725287
#SPJ11
PLZZ HELP ME PLZ I NEED YALL HELP WITH THIS LAST QUESTION

Answers
Answer:
The 5 Forces
Explanation:
The five forces that influence wind speed and direction are: Pressure gradient force (flow from high to low pressure) Coriolis force (apparent deflecting force due to the rotation of the Earth) Turbulent drag (Earth's surface or objects like trees or grass resist air flow and decrease wind speed near the ground)
How is air resistance similar to gravity? give me two ways.
Answers
Answer:
1. they both act on an object in free fall
Explanation:
2. both help determine how fast the object will accelerate
stored energy and the energy of positions are ________________ energy
Answers
Answer:
Gravitational Energy
The histogram shows the number of classes missed by students in a class during the school year. what percent of the class missed three or fewer days?
Answers
Answer:
Let's say there are 60 bars up to and including the bar for three missed days. If the total number of bars in the histogram is 100, then we can calculate the percentage as follows:
Percentage = (Number of bars up to and including three missed days / Total number of bars) x 100.Percentage = (60 / 100) x 100 = 60%.60% of the class missed three or fewer days during the school year.About histogramHistogram is a graphical display of frequency tabulation which is illustrated with bar graphics as a manifestation of data binning. Each bar display shows the proportion of frequencies in each category series that are contiguous at non-overlapping intervals. The vertical ordinate axis is a pixel representation with the tonal value of each bin series on its horizontal axis.
You can learn more about Histogram at https://brainly.com/question/28508589
#SPJ11
Friction is a force in which two objects __________. A. Collide and move in one direction B. Are repelled from each other C. Slide against each other D. Are attracted from a distance Please select the best answer from the choices provided. A B C D.
Answers
Answer: (C) Slide against each other
Explanation:
Think about rubbing our palms together, and they get warm that right there is friction.
Answer:
slide against each other
Explanation:
If you blow up a balloon, tie it off, and release it, it will fall to the ground.
Why does it fall instead of float?
NO LINKS YA FILTHY VERMINS
Answers
Answer:
carbon dioxide (what you are blowing up the balloon with) is a heavy gas. so when you fill the Balloon with it, the balloon will not float. helium is a light gas and floats. gravity takes another. part in this