Arrange the following H atom electron transitions in order of increasing frequency of the photon absorbed or emitted:
(d) n = 4 to n = 3
Answers
The order of increasing frequency of the photon absorbed or emitted by the H atom is :
d → a → c → b.
The wavelength is calculated using the Rydberg's formula given by,
\(\frac{1}{\lambda} = R_h (\frac{1}{n_1^2}-\frac{1}{n_2^2} )\),
where λ is the wavelength of the photon emitted or absorbed from an H atom electron transition from \(n_1\) to \(n_2\) and \(R_h\) = 109677 is the Rydberg Constant.
Now the frequency, \(f=\frac{c}{\lambda}\) , where c = \(3\times 10^8 ms^{-1}\) is the speed of light.
(a) \(n_1\) =2 to \(n_2\) = 4
\(\frac{1}{\lambda} = 109677\times (\frac{1}{2^2}-\frac{1}{4^2} )\) = 20564.4375 [since 1/infinity = 0] Therefore, f =c/ \(\lambda\) = 61693.3125 x\(10^8\) Hz
(b) \(n_1\)=2 to \(n_2\) = 1
\(\frac{1}{\lambda} = 109677\times (\frac{1}{2^2}-\frac{1}{1^2} )\) = -82257.75
Therefore, f=c/ \(\lambda\) = 246773.25 x \(10^8\) Hz
(c) \(n_1\)=2 to \(n_2\) = 5
\(\frac{1}{\lambda} = 109677\times (\frac{1}{2^2}-\frac{1}{5^2} )\) = 23032.17
Therefore, f=c/\(\lambda\) = 69096.51 x \(10^8\) Hz
(d) \(n_1\)=4 to \(n_2\) = 3
\(\frac{1}{\lambda} = 109677\times (\frac{1}{4^2}-\frac{1}{3^2} )\) = -5331.52
Therefore, f =c/\(\lambda\) = - 15994.56x \(10^8\) Hz
We compare the frequencies considering only the magnitudes of the frequency. Because the sign of the frequency implies whether a photon is emitted or absorbed.
Thus the increasing order of frequencies of the photon absorbed or emitted in H atom electron transitions is d → a → c → b.
Learn more about the Rydberg's formula at https://brainly.com/question/14649374
#SPJ4
Related Questions
Which example best demonstrates stewardship of the atmosphere
Answers
Incomplete question. However, I provided a specific example of stewardship of the atmosphere.
Explanation:
First, note that the term stewardship refers to the belief that humans are obligated to take care and look after our environment (which includes the atmosphere.
An example of this is: deciding to change our mode of transportation: What this entails is that we may decide to switch to riding a bicycle to places rather than going by car. By so doing you will be reducing the number of greenhouse gases emitted into the environment as bicycles do not emit harmful gases when used.
Which of the following are elements? Select all that apply.
a. KBr
b. Li
c. CO
d. Ca
Answers
D Ca
—————————————-
Answer: Choices B and D
Explanation: Elements are what you see on the periodic table and compounds are the product of you adding elements together. A good trick to find this is to look at capitalization. If it has more than one upper-case letter, it is most likely a compound. Elements either have only one upper-case letter or one upper-case letter followed by a lower-case letter. If we keep this in mind, we see that answers A and C can easily be dismissed. KBr is made with two elements, Potassium and Bromine. That leaves us with B and D, which are both elements.
Therefore, the correct answers are B. Li and D. Ca.
I hope this helps! Pls give brainliest!! :)
what are Metals that are less reactive than alkali metals and alkaline-earth metals called
Answers
Answer:
The first ionization energies (I1) of the alkaline earth metals are not as low as the alkali metals. The alkaline earth metals are therefore less reactive than the alkali metals (Be and Mg are the least reactive of the alkaline earth metals). Several physical properties of these elements are compared in Table 7.7.
Wind energy is dependent on which factor?
Answers
Answer:
on it iis renewable energy it is independent
Jesus is coming soon you guys need not repent today not tomorrow every day counts now repent today.....
Answers
Which of the following is an ionic compound?
(A) CO₂
B) NH3
C) KBr
D) C12

Answers
Answer:
co2
Explanation:
it is an ionic compound
I neeeeed heeeeeelppppppp

Answers
Answer:
I think no. 4
Explanation:
It is true that Earth’s orbit is not a perfect circle. It is slightly elongated, so that during part of the year, Earth is closer to the Sun than at other times. However, in the Northern Hemisphere, we are having winter when Earth is closest to the Sun and summer when it is farthest away!
There is a completely different reason for Earth's seasons.
Earth's axis is an imaginary pole going right through the center of Earth from "top" to "bottom." Earth spins around this pole, making one complete turn each day. That is why we have day and night, and why every part of Earth's surface gets some of each.
Earth has seasons because its axis doesn't stand up straight
(to be clear I just copied it from some resources)
How many times faster will nitrogen gas effuse when compared to sulfur trioxide gas?
Answers
Nitrogen gas will effuse approximately 2.52 times faster than sulfur trioxide gas under the same conditions.
The rate of effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its molar mass. This relationship is described by Graham's law of effusion.
The molar mass of nitrogen gas (\(N_2\)) is approximately 28 g/mol, while the molar mass of sulfur trioxide gas (\(SO_3\)) is approximately 80 g/mol. Therefore, the square root of the molar mass of \(SO_3\) is greater than the square root of the molar mass of \(N_2\).
Using Graham's law of effusion, we can calculate the ratio of the rates of effusion of the two gases:
rate of effusion of \(N_2\)/ rate of effusion of \(SO_3\) = √(molar mass of \(SO_3\)) / √(molar mass of \(N_2\))
rate of effusion of \(N_2\)/ rate of effusion of \(SO_3\) = √(80 g/mol) / √(28 g/mol)
rate of effusion of \(N_2\)/ rate of effusion of \(SO_3\) ≈ 2.52
For more question on Nitrogen gas click on
https://brainly.com/question/15842685
#SPJ11
The ability to conduct an electric current, dissolve in water (solubility) , and melt are _______________.
Group of answer choices
chemical bonding
physical properties
physical changes
chemical properties
Answers
Answer:
chemical bonding
Explanation:
i hope this helped :)
When filling a buret for a titration, first adjust the buret in the clamp so that ______________ then, choose... to add the titrant into the buret. the titrant should be filled ___________
Answers
When filling a buret for a titration, first adjust the buret in the clamp so that it is vertical. Then, choose an appropriate funnel to add the titrant into the buret. The titrant should be filled to just above the zero mark on the buret, and the buret tip should be briefly opened to remove any bubbles.
After that, the buret can be adjusted to the desired volume and the titration can proceed. It is important to take note of the initial buret reading before starting the titration to ensure accurate measurement of the titrant volume.
When filling a buret for a titration, it is important to first adjust the buret in the clamp so that it is vertical and its tip is below eye level to ensure accurate volume measurements. Next, choose an appropriate method to add the titrant into the buret, such as using a funnel or a pipette.
It is important to avoid splashing or spilling the titrant to ensure accurate and precise measurements. The titrant should be filled above the zero mark on the buret and then slowly drained until the bottom of the meniscus is aligned with the zero mark.
This process is called "buret priming" and it helps to remove any air bubbles from the buret tip that can affect the accuracy of the measurements. Once the buret is primed and filled with the titrant, it is ready to be used for the titration.
For more question on titration click on
https://brainly.com/question/16839748
#SPJ11
Which of the following is not a fundamental particle
2) Neutron
1) Proton
3) a-particle
4) Electron
Answers
3)a-particle.
In which binding sites can mixed inhibitors bind in relation to the substrate-enzyme complex and the enzyme?
Answers
The binding sites that mixed inhibitors bind in relation to the substrate-enzyme complex and the enzyme are the active site and allosteric site.
Mixed inhibitors can bind to both the free enzyme and the enzyme-substrate complex. They exhibit a combination of competitive and noncompetitive inhibition characteristics. Competitive inhibition occurs when the inhibitor binds to the active site of the enzyme, directly competing with the substrate for binding. In this case, the inhibitor's binding affinity is influenced by the substrate concentration.
Noncompetitive inhibition, on the other hand, involves the inhibitor binding to an allosteric site (a site distinct from the active site) on the enzyme. This binding may cause conformational changes in the enzyme, reducing its catalytic activity. In noncompetitive inhibition, the inhibitor can bind to either the free enzyme or the enzyme-substrate complex, and its binding is not affected by substrate concentration.
In mixed inhibition, the inhibitor can bind to both the free enzyme and the enzyme-substrate complex. However, its binding affinity for each form may differ. The binding of the mixed inhibitor to the enzyme can alter the enzyme's conformation, leading to reduced catalytic activity, and may also affect the enzyme's affinity for the substrate. This type of inhibition displays a mixture of competitive and noncompetitive inhibition properties, with the inhibitor exhibiting variable binding affinities for the enzyme and enzyme-substrate complex.
Know more about Mixed inhibitors here :
https://brainly.com/question/31590577
#SPJ11
Class C fires are with energized electrical equipment or appliances. They are extinguished with non-conducting agents only. Class D fires are fueled by combustible metals, such as magnesium, lithium, and sodium. They require special extinguishing agents and techniques.
Answers
Class C fires are fueled by energized electrical equipment and are extinguished using non-conducting agents whereas Class D fires are fueled by combustible metals and require specialized extinguishing agents and techniques.
Class C fires involve energized electrical equipment or appliances. These fires pose a unique challenge because using water or other conducting agents can result in electric shock or the spread of the fire. Non-conducting agents are used to extinguish Class C fires.
These agents, such as dry chemical powders or carbon dioxide (CO2), do not conduct electricity and can safely be used on electrical fires. They work by smothering the fire and interrupting the chemical reaction that sustains it.
Class D fires, on the other hand, are fueled by combustible metals like magnesium, lithium, and sodium. These fires require specialized extinguishing agents and techniques due to the unique properties of these metals.
Water, foam, or conventional fire extinguishers are ineffective against Class D fires as they can react violently with the metal and even intensify the fire.
To extinguish Class D fires, specific extinguishing agents such as dry powders specifically designed for metal fires are used. These powders work by coating the burning metal and separating it from the oxygen in the air, thereby preventing the fire from spreading.
Additionally, techniques like heat reduction and containment may be employed to control Class D fires safely. It is crucial to remember that fighting fires, especially those involving electricity or combustible metals, should primarily be left to trained professionals.
To know more about Class C fires refer here:
https://brainly.com/question/31239889#
#SPJ11
What are the differences between Class C fires and Class D fires in terms of fuel and extinguishing methods?
what substrate cant undergo e2 mechanism
Answers
The substrate that cannot undergo E2 mechanism is tertiary substrates.
E2 (Elimination bimolecular) is a type of elimination reaction that occurs in one step.
In an E2 mechanism, a base pulls the hydrogen of the substrate (usually a tertiary substrate) and simultaneously knocks out the leaving group; this leads to the formation of an alkene. E2 mechanism will only work with certain substrates, specifically substrates that are secondary or primary. Tertiary substrates cannot undergo E2 mechanism because the steric hindrance around the substrate is too great, which makes the reaction improbable. Tertiary substrates are compounds that have three alkyl or aryl groups attached to the carbon atom that is being deprotonated by the base. This causes a lot of steric hindrance around the carbon atom, which makes it challenging for the base to approach and pull the proton. As a result, the elimination reaction becomes impossible.
To know more about E2 mechanism click here:
https://brainly.com/question/31325618
#SPJ11
3. Differentiate between saturated and unsaturated fats
Answers
Answer:
Fats that are tightly packed with no double bonds between the fatty acids are called saturated fats.
Explanation:
How many additional electrons does this atom of oxygen need in its valence shell to satisfy the octet rule?

Answers
Answer:
2
Explanation:
cause it is what it is :> mark me brainlest
Answer:
A-two
Explanation:
1. The following figure represent a type of flame used in the laboratory. (a) Explain how the brightness of the flame can be increased.
Answers
The ways that the brightness of the flame can be increased are shown below.
How can the brightness of a laboratory flame be increased?By boosting the airflow into the burner, the flame's brilliance can be improved. Increasing the gas flow rate or changing the air intake valve can do this.
Using a gas that generates a brighter flame, like propane or butane, will increase the brightness of the flame. These gases produce a yellow flame because they have a higher carbon to hydrogen ratio than natural gas.
Learn more about laboratory flame:https://brainly.com/question/9018811
#SPJ1

Which new diagnosis would prompt the provider to discontinue a prn order for magnesium hydroxide? group of answer choices renal failure cirrhosis hemorrhoids prostatitis
Answers
Renal failure is the new diagnosis that the provider would prompt to discontinue a PRN order for magnesium hydroxide.
What is Renal failure?Renal failure is a special condition where the person is unable to manage the function of the kidney organ.
The magnesium hydroxide may cause renal failure because this salt must be eliminated by the kidney and therefore it may trigger health complications.
In conclusion, renal failure is the new diagnosis that the provider would prompt to discontinue a PRN order for magnesium hydroxide.
Learn more about Renal failure here:
https://brainly.com/question/20404873
#SPJ1
What is the density of a rock that has a mass of 555 g and a volume of 101.1 cm?
Answers
Answer:
the volume should be in cubic cm so I assumed that you wanted to write the same . then the answer is 5489.07 kg/m^3
Answer:
\(\boxed {\boxed {\sf d\approx5.49 \ g/cm^3}}\)
Explanation:
Density can be found by dividing the mass by the volume.
\(d=\frac{m}{v}\)
The mass of the rock is 555 grams and the volume is 101.1 cubic centimeters.
\(m=555 \ g \\v= 101.1 \ cm^3\)
Substitute the values into the formula.
\(d=\frac{555 \ g}{101.1 \ cm^3}\)
Divide.
\(d=5.48961424 \ g/cm^3\)
Let's round to the nearest hundredth to make the answer more concise.
The 9 in the thousandth place tells us to round up. In the tenth place, the 8 will become a 9.
\(d\approx5.49 \ g/cm^3\)
The density of the rock is about 5.49 grams per cubic centimeter.
What is the net ionic equations of Cu (s) + 2 AgC2H3O2 (aq) --> Cu(C2H3O2)2(aq) + 2 Ag(s) ?
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
Cu(s) + 2Ag+ ======> Cu^(2+) + Ag(s)
Notice what happened. Silver started out as an ion. It took on 2 electrons that were donated by the copper.
The silver then became a solid ppte. This equation wil take on much more meaning when you take up oxidation and reduction. Until then, you need only know who gave up elections and who took them up.
select the best explanation for why methanol, ch3oh, cannot be used as a solvent for the deprotonation of a terminal alkyne by sodium amide, nanh2.
Answers
Answer:
d. Methanol is more acidic than the alkyne and will be deprotonated instead.
Explanation:
because acidity is the ability to lose H+, leaving an anion behind; acidity depends on the stability of the anion.
NEED ANSWERED ASAP
An ideal gas is at volume V at temperature T. If the volume is doubled at constant pressure and the same amount of gas particles, the temperature will be
unchanged
halved
doubled
four times
Answers
Considering the Charles's law, the correct answer is the third option: if the volume is doubled at constant pressure and the same amount of gas particles, the temperature will be doubled.
Charles' lawCharles' law establishes the relationship between the temperature and the volume of a gas when the pressure is constant. Jack Charles observed that when the temperature was increased the volume of the gas also increased and that as it cooled the volume decreased. That is, the volume is directly proportional to the temperature of the gas.
Mathematically, Charles' law states that if the amount of gas and the pressure remain constant, the ratio between the volume and the temperature always has the same value:
V÷T=k
where:
V is the volume.
T is the temperature.
k is a constant.
Considering an initial state 1 and a final state 2, it is fulfilled:
V₁÷T₁= V₂÷T₂
This caseIn this case, the volume is doubled at constant pressure and the same amount of gas particles. This is, V₂= 2×V₁
Replacing in the Charles' law:
V₁÷T₁= 2×V₁÷T₂
(V₁÷T₁)×T₂= 2×V₁
T₂= 2×V₁ ÷(V₁÷T₁)
T₂= 2×T₁
Finally, the temperature will be doubled.
Learn more about Charles' law:
brainly.com/question/4147359
#SPJ1
C3.26 The diagram shows the arrangement of the outer electrons only in a molecule of ethanoic acid.
a, Name the different elements found in this
compound.
b What is the total number of atoms present in
this molecule?
C
Between which two atoms is there a double
covalent bond?
d
How many covalent bonds does each carbon
atom make?
e
Would you expect this compound to be a solid
or a liquid at room temperature? Give a reason
for your answer.
f,
Ethanoic acid will dissolve in methylbenzene.
Would you expect the solution to conduct
electricity? Give a reason for your answer.
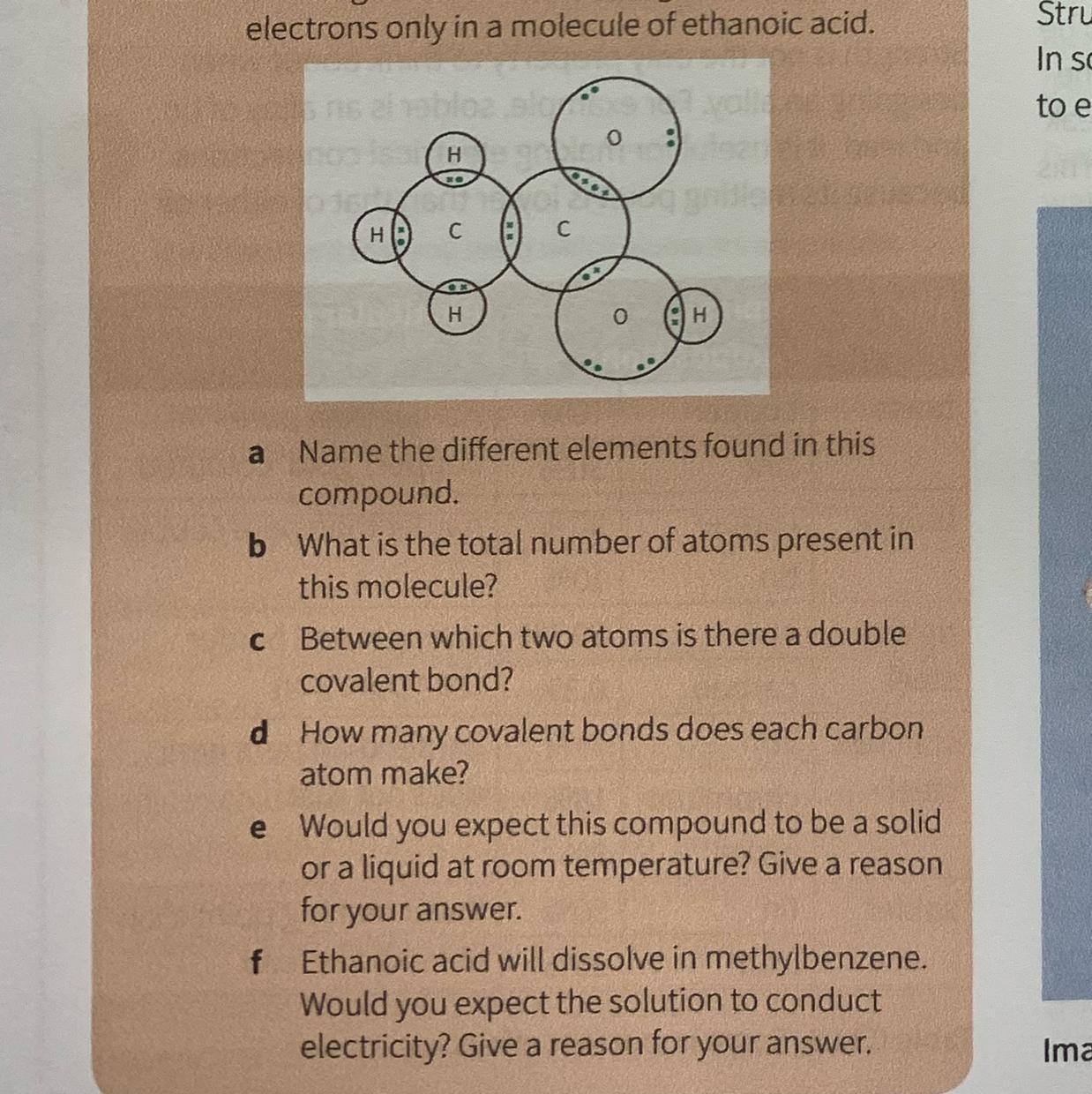
Answers
The diagram shows the arrangement of the outer electrons only in a molecule of ethanoic acid.
elements are = Carbon, Hydrogen and oxygentotal no. of atoms = 8double bond = between one carbon and oxygentotal covalent bond = 7liquid at room temperaturea) The different elements found in this compound is Carbon, Hydrogen and oxygen.
b) The total number of atoms present in this molecule is 8.
c) Between which two atoms is there a double covalent bond is in the between of one carbon atom and oxygen atom.
d) number of the covalent bonds does each carbon atom make is 7.
e) this compound to be a liquid at room temperature
Thus, The diagram shows the arrangement of the outer electrons only in a molecule of ethanoic acid.
elements are = Carbon, Hydrogen and oxygentotal no. of atoms = 8double bond = between one carbon and oxygentotal covalent bond = 7liquid at room temperatureTo learn more about covalent bond here
https://brainly.com/question/10777799
#SPJ1
A nucleus whose mass is 3.499612×10 −25
kg undergoes spontaneous alpha decay. The original nucleus disappears and there appear two new particles: a He−4 nucleus of mass 6.640678×10 −27
kg (an "alpha particle" consisting of two protons and two neutrons) and a new nucleus of mass 3.433132×10 −25
kg (note that the new nucleus has less mass than the original nucleus, and it has two fewer protons and two fewer neutrons). a. When the alpha particle has moved far away from the new nucleus (so the electric interactions are negligible), what is the combined kinetic energy of the alpha particle and new nucleus? b. How many electron volts is this? In contrast to this nuclear reaction, chemical reactions typically involve only a few eV.
Answers
a) Calculating the right side of the equation: K_alpha + K_new_nucleus ≈ 3.149648×10^(-10) J b) the combined kinetic energy of the alpha particle and the new nucleus is approximately 1.96382×10^9 electron volts (eV).
a. To calculate the combined kinetic energy of the alpha particle and the new nucleus, we need to consider the conservation of energy. We assume that the original nucleus was at rest before the alpha decay occurred.
The initial energy of the system is solely the rest mass energy of the original nucleus, given by Einstein's mass-energy equivalence:
E_initial = mc^2
Where m is the mass of the original nucleus and c is the speed of light.
The final energy of the system is the sum of the kinetic energies of the alpha particle and the new nucleus.
E_final = K_alpha + K_new_nucleus
Since energy is conserved, we can equate the initial and final energies:
mc^2 = K_alpha + K_new_nucleus
To find the combined kinetic energy, we rearrange the equation:
K_alpha + K_new_nucleus = mc^2
Plugging in the given values:
K_alpha + K_new_nucleus = (3.499612×10^(-25) kg) * (2.998×10^8 m/s)^2
b. To convert the combined kinetic energy from joules to electron volts (eV), we can use the conversion factor:
1 eV = 1.602×10^(-19) J
Dividing the combined kinetic energy by this conversion factor:
(3.149648×10^(-10) J) / (1.602×10^(-19) J/eV)
Calculating the right side of the equation:
≈ 1.96382×10^9 eV
This value highlights the large difference in energy between nuclear reactions and chemical reactions. Chemical reactions typically involve energy changes on the order of a few electron volts (eV), while in this nuclear reaction, the combined kinetic energy is in the billions of electron volts. This significant difference is due to the much stronger forces and larger energy scales involved in nuclear interactions compared to chemical interactions.
Learn more about electron at: brainly.com/question/12001116
#SPJ11
Choose all the answers that apply.
Plasma is made of _____.
ions
clumped atoms
neutral atoms
free electrons
free protons
Answers
Answer:
neutral atoms
Explanation:
What group will elements in the 7th column bond to?
Answers
An electron cannot have the quantum numbers n = ________, l = ________, ml = ________.
A) 2, 0, 0
B) 2, 1, -1
C) 3, 1, -1
D) 1, 1, 1
E) 3, 2, 1
Answers
An electron cannot have the quantum numbers n = 1, l = 1, and ml = 1. Therefore, option (D) is correct.
What are the quantum numbers?The set of numbers that can describe the position and energy of a particular electron are known as quantum numbers. Four quantum numbers are principal quantum numbers, azimuthal, magnetic, and spin quantum numbers.
Principal quantum numbers (n) can designate the principal electron shell and the most probable distance between electrons and the nucleus. The azimuthal quantum number (l) can designate the shape of an orbital and has a value equal to n -1.
The magnetic quantum number can designate the total number of orbitals in a particular subshell and the orientation of orbitals. It has value -l to l.
Therefore, n = 1 then l = 0, and ml = 0 as well.
Learn more about quantum numbers, here:
brainly.com/question/16977590
#SPJ1
Using the periodic table, identify the name and symbol of the three neutral atoms given their atomic numbers and masses. The neutral atom with an atomic number of 1 and a mass number of 1. bol. name: Hydrogen atomic symbol: H The neutral atom with an atomic number of 11 and a mass number of 23. name: (Sodium name: Sodium atomic symbol: | 22 Na dionie sympat yang The neutral atom with an atomic number of 7 and a mass number of 14. name: Nitrogen Nitrogen atomic symbol: 0 atomic symbol: N | N º
Answers
The neutral atom with an atomic number of 1 and a mass number of 1 is Hydrogen (H).
The neutral atom with an atomic number of 11 and a mass number of 23 is Sodium (Na).
The neutral atom with an atomic number of 7 and a mass number of 14 is Nitrogen (N).
The atomic number of an element corresponds to the number of protons in its nucleus, which determines its identity. The mass number represents the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom.
For the first atom, with an atomic number of 1 and a mass number of 1, there is only one proton and no neutrons, which corresponds to Hydrogen (H).
The second atom, with an atomic number of 11 and a mass number of 23, has 11 protons and 12 neutrons. This corresponds to the element Sodium (Na).
The third atom, with an atomic number of 7 and a mass number of 14, has 7 protons and 7 neutrons, which corresponds to Nitrogen (N).
To learn more about atomic numbers, here
https://brainly.com/question/16858932
#SPJ4
What components must be present in the atmosphere to create photochemical smog in addition to volatile organic compounds VOCs?
Answers
To create photochemical smog, in addition to volatile organic compounds (VOCs), the presence of nitrogen oxides (NOx) is required. The combination of these two groups of pollutants can lead to the formation of ground-level ozone and other harmful secondary pollutants.
In addition to volatile organic compounds (VOCs), the presence of nitrogen oxides (NOx) is required to create photochemical smog. NOx is a term used to describe the family of nitrogen oxides, which include nitrogen monoxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2), both of which are produced mainly from vehicle emissions, industrial processes, and combustion of fossil fuels.
When VOCs and NOx are emitted into the atmosphere and are exposed to sunlight, a series of complex photochemical reactions occur. This can result in the formation of ground-level ozone, a key component of photochemical smog, as well as other harmful secondary pollutants such as peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN) and aldehydes.
Therefore, to create photochemical smog, the presence of both VOCs and NOx is necessary.
Learn more about photochemical smog here: brainly.com/question/15728274
#SPJ4
The enzyme 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase is part of the pentose pathway for glucose oxidation. What enzyme that is involved in glucose oxidation by the citric acid cycle has a very similar reaction mechanism to 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase?
A) isocitrate dehydrogenase
B) alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase (wrong answer)
C) succinate dehydrogenase (wrong answer)
D) malate dehydrogenase
E) pyruvate dehyrogenase
Answers
The enzyme that is involved in glucose oxidation by the citric acid cycle and has a very similar reaction mechanism to 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase is isocitrate dehydrogenase.
Isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) is a key enzyme in the citric acid cycle, which is also known as the Krebs cycle or the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. This enzyme catalyzes the conversion of isocitrate to alpha-ketoglutarate, which is a critical step in the cycle. The reaction mechanism of IDH is very similar to that of 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase, which also catalyzes a dehydrogenation reaction involving the transfer of electrons to NAD+ and the formation of a carboxylic acid group. Therefore, the correct answer is A) isocitrate dehydrogenase.
The enzyme involved in glucose oxidation by the citric acid cycle with a very similar reaction mechanism to 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase is isocitrate dehydrogenase. Both enzymes catalyze oxidative decarboxylation reactions and use NAD+ as a cofactor.
Learn more about isocitrate dehydrogenase
https://brainly.com/question/23454980
#SPJ11