Answers
Answer:
\(3.01\times 10^{10}\ J\)
Explanation:
It is given that,
The average New Jersey home uses 8386 kWh of electricity in one year.
We need to find the electricity that make in one year.
We know that,
\(1\ kWh=3.6\times 10^6\ J\)
or
\(8386\ kWh=8386 \times 3.6\times 10^6\ J\\\\=3.01\times 10^{10}\ J\)
So, it will make \(3.01\times 10^{10}\ J\) or energy in one year.
Related Questions
why the ocean near Christchurch is a different temperature than we’d expect for its latitude
Answers
Why the ocean near Christchurch is a different temperature than we'd expect for its latitude (distance from the equator)? Water moving from the equator is warmer than would be expected based on latitude, and so is warmer than the air it passes.
Changes to prevailing winds affect ocean currents. Changes to ocean currents affect how much energy is brought to (or taken away from) a location. In El Niño years, the prevailing winds that normally drive a warm current from the Equator past New Zealand are disrupted and may stop or even reverse.
In Einstein’s theory of gravitation, gravity is due to:
A)the acceleration of the universe
B)the presence of mass
C)the rotation of the universe
D)the curvature of spacetime
E)the speed of light
Answers
Answer:
B, caused by the presence of mass
Explanation:
what is attribute conformity? what is the resulting decision from attribute measurement results?
Answers
Attribute conformity is one that classifies each item in the sample as either having some attribute or not having it.
Variation present in your measurement system will affect the quality of the product and can damage your company's brand.
Purpose of Attribute measurement system analysis:
Accuracy check:
To access the customer standard, need to fulfill the customer's requirement, which means MSA performs to identify how good is our measurement system with our masters.
Precision check:
To determine that, the inspector can measure correctly. Is he checking with the same criteria across all shifts, machines, etc… to measure and evaluate parts and also called Repeatability
To know more about attribute conformity:
https://brainly.com/question/17290596
#SPJ4
identify the n values for which the equation is to be verified in order to prove the given statement. (you must provide an answer before moving to the next part.)
Answers
The statement n^2 + 1 > 2n where n is an integer in [1, 4]. n values for which the equation is to be verified in order to prove the given statement are 1,2,3 and 4.
About mathematical statementBasically, a logical mathematical statement is a sentence that is either true or false, but not both.
Meanwhile, a sentence is said to be not a statement if we cannot determine whether the sentence is true or false or contains a relative meaning.
There are two types of statements, namely closed statements and open statements. A closed statement is a statement whose truth value can be ascertained, while an open statement is a statement whose truth value cannot be ascertained.
Learn more about mathematical statement at
https://brainly.com/question/17029275
#SPJ4
If Bugs bunny can accelerate at a rate of 10m/s?, how long (in seconds) will it take him to
reach a speed of 300m/s, if starting from rest?
HELPPPP ME PLS NEED WORK SHOWN
Answers
I believe that it would take 30 seconds, as he accelerates at 10 m/s and 10 x 30 = 300
hope this helps! good luck :)
This leaves the answer being time=30sec

A rigid body is rotating with constant angular speed 3 radians per second about a fixed axis through the points A. (4, 1, 1), B. (2, -1; 0), distances being measured in centimeters. The rotation is in the left-handed sense relative to the direction AB
1, Determine the unit vector pointing in the direction BA.
2, What is the angular velocity () of the of the body?
3, Write the position vector of point P: P .
Find the instantaneous velocity of particle P [hint v = w×r)
4, What is meant by left-handed rotation (left-handed coordinate system)?
5, Write the position vectors of points A and B The rotation axis AB has direction BA. Write the direction BA in terms of the components given above.
Answers
1.Unit vector in the direction BA: BA/|BA| = (2/3, 2/3, 1/3)
2.The angular velocity (ω) of the body is given as 3 radians per second.
3.Without the position of point P given, it is not possible to write the position vector of P.
4.Left-handed rotation refers to the direction of rotation where the rotation follows the left-hand rule.
5.Position vector of point A: (4, 1, 1)
Position vector of point B: (2, -1, 0)
The direction vector BA = (-2, -2, -1)
1.To determine the unit vector pointing in the direction BA, we subtract the coordinates of point B from the coordinates of point A and normalize the resulting vector.
The direction vector BA is given by:
BA = (4 - 2, 1 - (-1), 1 - 0) = (2, 2, 1)
To obtain the unit vector in the direction of BA, we divide the direction vector by its magnitude:
|BA| = √(2^2 + 2^2 + 1^2) = √(4 + 4 + 1) = √9 = 3
Unit vector in the direction BA: BA/|BA| = (2/3, 2/3, 1/3)
2.The angular velocity (ω) of the body is given as 3 radians per second.
3.Without the position of point P given, it is not possible to write the position vector of P. Please provide the position of point P to proceed with the calculation.
4.Left-handed rotation refers to the direction of rotation where the rotation follows the left-hand rule. In a left-handed coordinate system, if you curl the fingers of your left hand in the direction of rotation, your thumb will point in the direction of the rotation axis. It is the opposite direction to a right-handed rotation.
5.The position vectors of points A and B are:
Position vector of point A: (4, 1, 1)
Position vector of point B: (2, -1, 0)
The direction vector BA can be obtained by subtracting the coordinates of point A from the coordinates of point B:
BA = (2 - 4, -1 - 1, 0 - 1) = (-2, -2, -1)
For more such questions on vector
https://brainly.com/question/30895553
#SPJ8
Read the following scenarioKelley chooses to move a bookshelf in his room so that he can better access it. He wants to start by moving it into the centerof the room Standing behind it, he begins to pushBased on this information, which of the following statements is correct?(1 point)It will move forward Owe to an unbalanced forceIt will move to the left because of its magnitudeIt will stay st because of the bodies grzetyIt will move to the right to a balanced force

Answers
Answer:
It will move forward due to an unbalanced force
Explanation:
Kelly is standing behind the bookshelf and begins to push, so he is applying a force that goes forward. Therefore, there will be an unbalanced force in the bookshelf and it will move in the direction of the force, forward.
So, the answer is
It will move forward due to an unbalanced force
In the district soccer championship finals, Elizabeth kicks a 0.78 kg soccer ball with a
force of 33.0 N. How much does she accelerate the soccer ball from rest in the
process?
Answers
Answer:
42.36 m/ s^2
Explanation:
First implement the formula f=m*a. f=33Nmass=0.78kg.where acceleration comes 42.36 m/ s^ 2
Elizabeth accelerates the soccer ball with an acceleration of 42.3 m/s² from rest in the process.
What is acceleration?Acceleration of an object can be defined as the rate of change of velocity of an object with respect to time. The acceleration of an object is a vector quantity with both magnitude and direction. Acceleration is also defined as the second derivative of position w.r.t. time and the first derivative of velocity of an object w.r.t. time.
According to Newton's second law of motion, the force is equal to the product of the mass and acceleration of an object.
F = ma
And, a = F/m
Therefore, the acceleration of a body is inversely proportional to the mass of the body.
Given, the force with which, Elizabeth kicks a soccer ball
F = 33.0 N
The mass of the soccer ball = 0.78 Kg
The acceleration of the soccer ball = 33/0.78 = 42.3 m/s²
Therefore, the acceleration of the soccer ball when it gets kicked is 42.3m/s².
Learn more about acceleration, here:
brainly.com/question/3046924
#SPJ5
Obtain the formula for the focal length of a lens in terms of object distance (u)
and magnification (m)
Answers
Answer:
m=image distance÷object distance
The graph below shows the variation with distance r from the nucleus of the square of the wave function, Ψ^2, of a hydrogen atom according to Schrödinger theory.
A. is most likely to be near a.
B. is always a.
C. is always less than a.
D. is always greater than a.

Answers
The region a represents the distance of the electron from the nucleus.
According to the wave mechanical model of the atom, the probability of finding an electron within a given volume element (representing the atom) is the square of the wave function psi.
Since a is the region in space where there is the greatest probability of finding the electron in the atom, it follows that distance of the electron form the atom is always a.
Learn more about the wave mechanical model: https://brainly.com/question/1382157
A 42.4 N block is sliding down an inclined plane with a constant speed. The kinetic friction acting on the block is N.
Answers
When a mass m particle is released onto a smooth inclined plane (where the frictional force F=0), it will glide down the slope.
We resolve in the direction of motion in order to get the particle's sliding acceleration.
F=ma,
mg cos(90∘−θ)=ma,
g cos(90∘−θ)=a,
g sin(θ)=a.
How many Newtons is the net force while the block is travelling at a constant speed?
Zero. Newton's first law of motion states that any object travelling at a constant speed experiences no net external forces, hence the total amount of forces acting on the object must be zero. The mathematical expression for an item being under no net external force is Fnet=0 or F=0.
To know more about Newton's laws, visit:
https://brainly.com/question/9405021
#SPJ1
(11) The speed of radio waves is 300 000 000 m/s.
A radio wave has a frequency of 31 MHZ.
what is wavelength of this radio wave.
Answers
Answer:
Wavelength = 9.68 meters
Explanation:
Given the following data;
Speed = 300,000,000m/s
Frequency = 31 Megahertz to Hertz = 31 * 10⁶ Hz
To find the wavelength;
Wavelength = speed/frequency
Wavelength = 300,000,000/31,000,000
Wavelength = 9.68 meters
Please help me!!
1 a) Compare the speed that light waves travel in air to the speed that sound waves travel in the air. (Show results in meters/second)
1 b) How many times faster do light waves travel in the air in comparison to sound waves in air? (show working out)
2) Compare the speed of light in water to the speed of sound in water. (Show results in meters/second)

Answers
Answer:A sound wave is a pressure disturbance that travels through a medium by means of particle-to-particle interaction.As one particle becomes disturbed,it exerts a force on the next adjacent particle, disturbing that particle from rest and transporting the energy through the medium.Like any wave,the speed of a sound wave refers to how fast the disturbance is passed from particle to particle.While frequency refers to the number of vibrations that an individual particle makes per unit of time, speed refers to the distance that the disturbance travels per unit of time.
Since the speed of a wave is defined as the distance that a point on a wave (such as a compression or a rarefaction)travels per unit of time,it is often expressed in units of meters/second (abbreviated m/s). In equation form, this is speed = distance/time
The faster a sound wave travels,the more distance it will cover in the same period of time.If a sound wave were observed to travel a distance of 700 meters in 2 seconds,then the speed of the wave would be 350 m/s. A slower wave would cover less distance - perhaps 660 meters - in the same time period of 2 seconds and thus have a speed of 330 m/s.Faster waves cover more distance in the same period of time.
The speed of any wave depends upon the properties of the medium through which the wave is traveling.Typically there are two essential types of properties that affect wave speed - inertial properties and elastic properties.Elastic properties are those properties related to the tendency of a material to maintain its shape and not deform whenever a force or stress is applied to it.A material such as steel will experience a very small deformation of shape and dimension when a stress is applied to it.Steel is a rigid material with a high elasticity.On the other hand,a material such as a rubber band is highly flexible;when a force is applied to stretch the rubber band,it deforms or changes its shape readily.A small stress on the rubber band causes a large deformation.Steel is considered to be a stiff or rigid material,whereas a rubber band is considered a flexible material. At the particle level,a stiff or rigid material is characterized by atoms and/or molecules with strong attractions for each other.The phase of matter has a tremendous impact upon the elastic properties of the medium.For this reason,longitudinal sound waves travel faster in solids than they do in liquids than they do in gases.Even though the inertial factor may favor gases,the elastic factor has a greater influence on the speed (v) of a wave,thus yielding this general pattern:solids > liquids > gases The density of a medium is an example of an inertial property.The greater the inertia (i.e.mass density) of individual particles of the medium,the less responsive they will be to the interactions between neighboring particles and the slower that the wave will be. However,within a single phase of matter,the inertial property of density tends to be the property that has a greatest impact upon the speed of sound.Like any liquid,water has a tendency to evaporate.As it does,particles of gaseous water become mixed in the air.The temperature will affect the strength of the particle interactions an elastic property.At normal atmospheric pressure,the temperature dependence of the speed of a sound wave through dry air is approximated by the following equation:
v = 331 m/s + (0.6 m/s/C)•T
where T is the temperature of the air in degrees Celsius.Using this equation to determine the speed of a sound wave in air at a temperature of 20 degrees Celsius yields the following solution.
v = 343 m/s
(The equation itself does not have any theoretical basis;it is simply the result of inspecting temperature-speed data for this temperature range.Other equations do exist that are based upon theoretical reasoning and provide accurate data for all temperatures.The speed of light as it travels through air and space is much faster than that of sound;it travels at 300 million meters per second or 273,400 miles per hour.Visible light can also travel through other things besides through air and through space.The speed of light in water is approximately 2.26×108 2.26 × 10 8 meters per second.
What is the answer can you explain it to me

Answers
Answer:
C) 300 Ohm.
Explanation:
In a series circuit, total resistance is just adding all the resistance together. So R (total) = 75 +75 +75+ 75 = 300 ohms
Parallel circuit are different because you add the inverses of resistance and you flip the final answer.
You can confirm your answers using the tools below:
https://www.omnicalculator.com/physics/series-resistor
https://www.omnicalculator.com/physics/parallel-resistor
A 2.0 kg bucket is attached to a horizontal ideal spring and rests on frictionless ice. You have a 1.0 kg mass
that you must drop into the bucket. Where should the bucket be when you drop the mass (so it is moving
purely vertically when it lands in the bucket) if your goal is to:
(a) Maximize the amplitude of the oscillation of the resulting 3.0 kg mass and spring system.
(b) Minimize the amplitude of the oscillation of the resulting 3.0 kg mass and spring system.
Answers
Answer:
x = A cos (w \sqrt{2y_{o}/g})
a) maximun Ф= \sqrt{\frac{2}{3} \frac{2 y_{o} }{g} }
b) minimun Ф = \(\frac{\pi }{2}\) - \sqrt{\frac{2}{3} \frac{2 y_{o} }{g} }
Explanation:
For this exercise let's use kinematics to find the time it takes for the mass to reach the floor
y = y₀ + v₀ t - ½ g t²
as the mass is released from rest, its initial velocity is zero (vo = 0) and its height upon reaching the ground is zero (y = 0)
0 = y₀ - ½ g t²
t = \(\sqrt{2y_{o}/g}\)
The bucket-spring system has a simple harmonic motion, which is described by
x = A cos wt
in this expression we assumed that the phase constant (Ф) is zero
let's replace the time
x = A cos (w \sqrt{2y_{o}/g})
this is the distance where the system must be for the mass to fall into it.
a) The new system has a total mass of m ’= 3.0 kg, so its angular velocity changes
w = \(\sqrt{k/m}\)
In the initial state
w = \sqrt{k/2}
When the mass changes
w ’= \sqrt{k/3}
the displacement in each case is
x = A cos (wt)
for the new case
x ’= A cos (w’t + Ф)
the phase constant is included to take into account possible changes due to the collision of the mass.
we see that this maximum expressions when the cosine is maximum
cos (w´t + Ф) = 1
w’t + Ф = 0
Ф = -w ’t
Ф = - \(\sqrt{k/3}\) \(\sqrt{2y_{o}/g}\)
\sqrt{\frac{2}{3} \frac{2 y_{o} }{g} }
b) the function is minimun if
cos (w’t + fi) = 0
w’t + Ф = π / 2
Ф = π / 2 - w ’t
Ф = \(\frac{\pi }{2}\) - \sqrt{\frac{2}{3} \frac{2 y_{o} }{g} }
How are magnetic fields like vectors?
Answers
Answer:Magnetic fields from two sources add up as vectors at each point, so the strength of the field is not necessarily the sum of the strengths1. Magnetic fields are vectors, which means they have direction as well as size. Therefore, the sum of two magnetic fields is not simply the sum of their magnitudes2.
Explanation:
Potential energy is
OA. energy of moving charges
OB. energy of motion
O C. nuclear energy
D.
energy of position or location
Answers
Explanation:
potential energy is the energy held by an object because of its position relative to other objects, stresses within itself, its electric charge, or other factors.
Hopefully this helps! :)
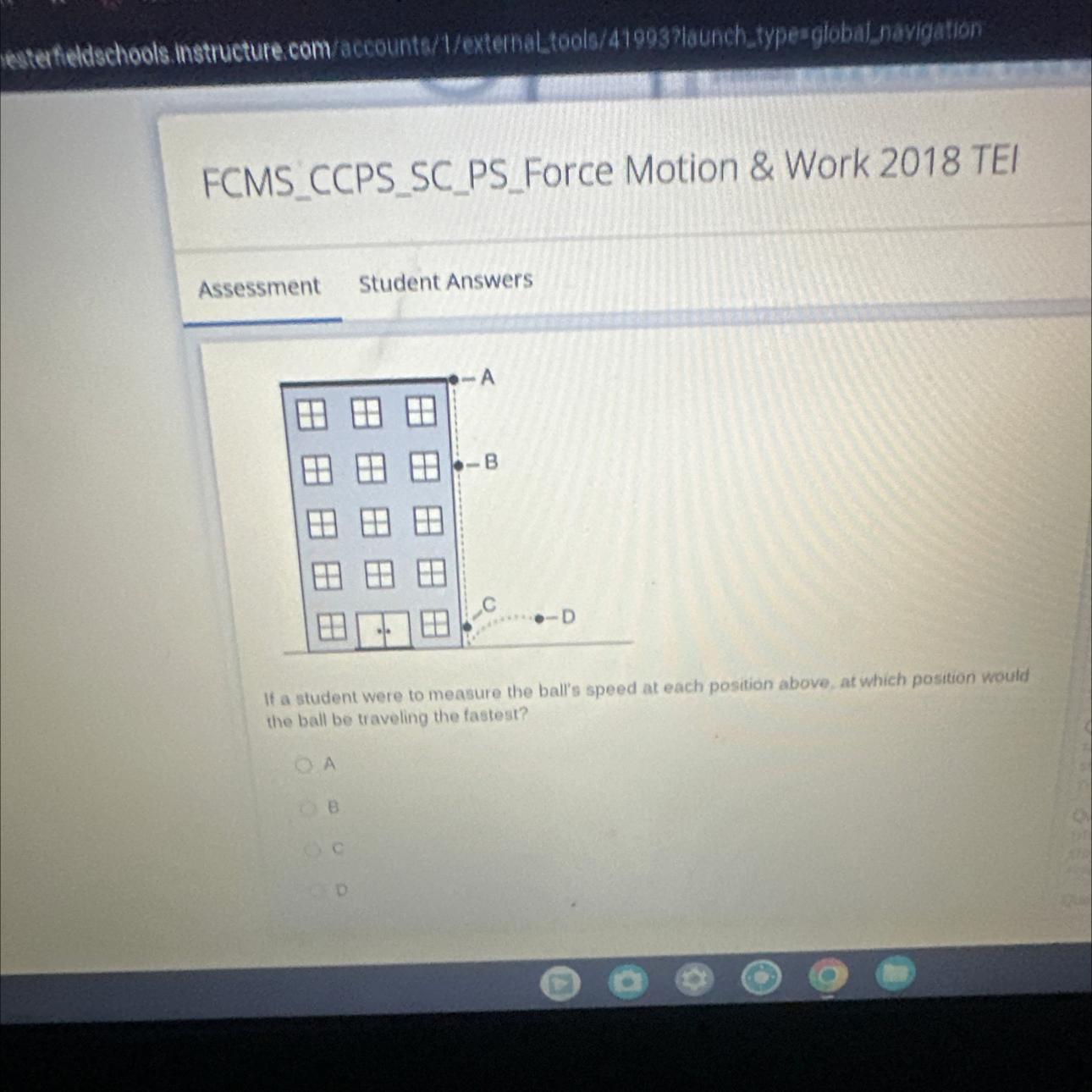
If a student were to measure the ball's speed at each position above, at which position would
the ball be traveling the fastest?
A
B
C
D
Answers
Answer:
The ball would be traveling fastest at point (C).
Point (D) appears to be the same height as point (C) but the ball would probably have lost some speed on rebounding,
The work-energy theorem states that the change in the kinetic energy of an object is equal to what?
Answers
The work-energy theorem states that the change in the kinetic energy of an object will be equal to the net work done on the object.
Mathematically, it can be expressed as;
ΔKE = W
Where; ΔKE represents the change in kinetic energy of the object,
W represents the net work done on the object.
This theorem states that when work is done on an object, it results in a change in its kinetic energy. If work is done on an object, its kinetic energy increases, and if work is done by an object, its kinetic energy decreases.
This theorem is a fundamental principle in physics that relates the concepts of work and energy, and it is often used to analyze the motion and behavior of objects in various physical systems.
To know more about work-energy theorem here
https://brainly.com/question/30236175
#SPJ1
A 0.0780 kg lemming runs off a
5.36 m high cliff at 4.84 m/s. What
is its potential energy (PE) when it
lands?
Answers
The potential energy of the lemming when it lands is 0.9108672 J.
To determine the potential energy (PE) of the lemming when it lands, we need to consider the conservation of energy. The potential energy of an object is given by the formula PE = mgh, where m is the mass of the object, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the height.
Given:
Mass of the lemming (m) = 0.0780 kg
Height of the cliff (h) = 5.36 m
First, let's calculate the potential energy when the lemming is on the cliff. Using the given formula, we have:
PE = mgh
PE = 0.0780 kg * 9.8 m/s² * 5.36 m
PE = 0.413616 J
Next, we need to determine the final kinetic energy of the lemming just before it lands. We can use the equation for kinetic energy (KE) given by KE = (1/2)mv², where v is the velocity of the lemming.
Given:
Velocity of the lemming (v) = 4.84 m/s
Calculating the kinetic energy, we have:
KE = (1/2) * 0.0780 kg * (4.84 m/s)²
KE = 0.9108672 J
According to the conservation of energy, the potential energy at the top of the cliff is equal to the kinetic energy just before landing.
for such more questions on potential
https://brainly.com/question/26978411
#SPJ8
A 2 m long wire carrying 2 A of current pointing to the right is placed in a magnetic field of 4 T directed away from you. Which direction does the force on the wire point?
A. Down
B. Up
C. Left
D. Right
Answers
Explanation:
To determine the direction of the force on the wire, we can use the right-hand rule for the cross product of two vectors. The force on the wire is given by:F = I * L x Bwhere I is the current, L is the length of the wire, and B is the magnetic field.
If we point our right-hand thumb in the direction of the current (to the right), and our fingers in the direction of the magnetic field (away from us), then our palm will point in the direction of the force.
So, using the right-hand rule, we can see that the force on the wire will be directed downward. Therefore, the correct answer is A. Down.What term describes someone whose biological sex is both male and female
Answers
intersex (more specific term: hermaphroditism) might be what you're looking for
An object is attached to a trolley with a 0.80 kg mass, which is then pushed into an identical trolley at a speed of 1.1 m / s. The two trolleys couple together and move at a speed of 0.70 m / s after the collision. Calculate the mass of the object.
Answers
The mass of the object is approximately 0.457 kg.
The mass of the object attached to the trolley can be calculated using the principle of conservation of momentum. Since the two trolleys couple together and move as a single system after the collision, the total momentum before and after the collision should be the same. Given the mass of one trolley is 0.80 kg and the initial speed is 1.1 m/s, the momentum before the collision is 0.80 kg * 1.1 m/s = 0.88 kg·m/s. After the collision, the total mass is the sum of the two trolleys, and the final speed is 0.70 m/s.
Using the momentum equation, the mass of the object can be calculated as follows:
Total momentum before collision = Total momentum after collision
0.88 kg·m/s = (0.80 kg + mass of the object) * 0.70 m/s
Solving for the mass of the object, we get:
0.88 kg·m/s = (0.80 kg + mass of the object) * 0.70 m/s
0.88 kg·m/s = 0.56 kg + 0.70 kg * mass of the object
0.88 kg·m/s - 0.56 kg = 0.70 kg * mass of the object
0.32 kg = 0.70 kg * mass of the object
Dividing both sides by 0.70 kg, we find:
mass of the object = 0.32 kg / 0.70 kg = 0.457 kg
The two trolleys collide and couple together, the total momentum before the collision is equal to the total momentum after the collision according to the principle of conservation of momentum.
The momentum of an object is defined as the product of its mass and velocity. In this case, the mass of one trolley is known (0.80 kg) and the initial speed is given (1.1 m/s), allowing us to calculate the momentum before the collision.
After the collision, the two trolleys move together at a new speed (0.70 m/s). By setting the initial momentum equal to the final momentum and solving for the unknown mass of the object, we can find its value.
In the calculation, we subtract the masses of the two trolleys from the total mass in order to isolate the mass of the object.
Dividing the difference in momentum by the product of the known mass and the new speed, we obtain the mass of the object. In this case, the mass of the object is approximately 0.457 kg.
for such more questions on mass
https://brainly.com/question/86444
#SPJ8
Which factor limits interference between waves? A constant phase relationship between waves Similar wave amplitudes Unequal wavelengths Radiation through the same region
Answers
Answer:
Unequal Wavelengths
Explanation:
Got it right on the exam
Unequal wavelengths limit interference between waves because the waves will have different frequencies and will not be able to form a stable interference pattern. When waves of different wavelengths interact, they will interfere constructively and destructively at different points, creating an unpredictable pattern.
Answer:
Unequal wavelengths
Explanation:
Got it correct on the quiz.
A 104 kg man is skiing across level ground at a speed of 8.7 m/s when he comes to the small slope 1.2 m higher than ground level shown in the following figure. 1.2 m (a) If the skier coasts up the hill, what is his speed (in m/s) when he reaches the top plateau? Assume friction between the snow and skis is negligible. m/s (b) What is his speed (in m/s) when he reaches the upper level if a 75 N frictional force acts on the skis? m/s †
Answers
The speed of skier's when he reaches the top plateau is 5.26 m/s, and the speed of skier's when he reaches the upper level with a frictional force of 75 N is 4.23 m/s.
We can use the conservation of mechanical energy to solve this problem. Initially, the skier has kinetic energy, and at the top of the slope, he will have both potential and kinetic energy.
Since friction is negligible, the only force acting on the skier is the force of gravity. The work done by this force will be equal to the change in the skier's potential energy as he climbs up the slope. Therefore;
mgh = (1/2)mv²
where m = 104 kg is mass of the skier, g = 9.8 m/s² is the acceleration due to gravity, h = 1.2 m is height of the slope, and v is the skier's velocity when he reaches the top.
Solving for v, we get;
v = √(2gh) = √(29.81.2) = 5.26 m/s
Therefore, the skier's speed when he reaches the top plateau is 5.26 m/s.
In this case, there is also a frictional force acting on the skier, which does negative work on the skier as he moves up the slope. The work done by the frictional force is equal to the force of friction multiplied by the distance traveled;
W = Fd = μmgd
where μ = F/N is the coefficient of kinetic friction, N is the normal force acting on the skier (equal to the skier's weight), and d is the distance traveled up the slope (equal to the height of the slope, 1.2 m).
The net work done on the skier will be equal to the change in his mechanical energy;
Wnet = ΔK + ΔU = (1/2)m\(V_{f}\)² - (1/2)m\(V_{i}\)² + mgh
where vi = 8.7 m/s is the skier's initial velocity, \(V_{f}\) is his final velocity at the top of the slope, and ΔK and ΔU are the changes in kinetic and potential energy, respectively.
Since the net work done on the skier is equal to the work done by the gravitational force minus the work done by the frictional force, we have;
Wnet = mgh - μmgd
Substituting the expressions for Wnet and mgh, we get:
(1/2)m\(V_{f}\)² - (1/2)m\(V_{i}\)² = μmgd
Solving for \(V_{f}\), we get:
\(V_{f}\) = √(\(V_{i}\)² + 2μgd) = √(8.7² + 20.729.8×1.2) = 4.23 m/s
Therefore, the skier's speed when he reaches the upper level with a frictional force of 75 N is 4.23 m/s.
To know more about frictional force here
https://brainly.com/question/13707283
#SPJ1
In an open circuit like the picture
A. the light bulb will produce light
B. a resistor controls the flow of current
C. the light bulb will be off
D. current will flow

Answers
This is due to the reason that the wire doesn’t go back to the battery :)
In an open circuit like the picture the light bulb will be off. So, option (C) is correct.
What is electric circuit?Electric circuit is a way for current to flow through electricity. An electric circuit consists of a source of energy for the charged particles that make up the current, like a battery or generator; sources of current-using equipment, like lamps, electric motors, or computers; and the connecting wires or transmission lines.
Ohm's law and Kirchhoff's rules are two of the fundamental mathematical laws that define how electric circuits function.
In the given diagram, the circuit is open. So, no current passes through it and the light bulb will be off. Hence, option (C) is correct.
Learn more about electric circuit here:
https://brainly.com/question/29032441
#SPJ2
First you lift an object from the floor onto a shelf. Then you move the object back to the floor. do you perform the same amount of work each time? Explain.
Answers
A student pushes a 6.0-kg box to the right with a
constant force FSB. The box moves at a constant velocity. The box experiences a
friction force f from the floor.
a. What type of friction does the box experience? Explain your reasoning.
b. Identify the four forces acting on the box.
Answers
b. The four forces acting on the box are:
1. Force of gravity (weight), which acts downwards towards the center of the earth, and has a magnitude of mg, where m is the mass of the box and g is the acceleration due to gravity.
2. Normal force, which is the force exerted by the floor on the box, perpendicular to the surface of contact, and has a magnitude of mg when the box is at rest or moving at a constant velocity.
3. Force applied by the student, denoted as FSB, which is directed to the right and has a magnitude that is equal to or greater than the force of friction.
4. Force of friction, denoted as f, which opposes the motion of the box and is directed to the left, opposite to the direction of the applied force. The magnitude of the frictional force is equal to the magnitude of the force applied by the student, as long as the box is moving at a constant velocity.
A driver of an automobile travelling at a constant speed of 20m/s suddenly applies a brake and the automobile comes to rest in 2 seconds after skidding for a certain distance. What is the length of the skid distance? A. 400m B. 20m C. 40m D. 10m.
Answers
Answer:
20 meters
Explanation:
d = (1/2) * a * t^2
where:
d is the distance (skid distance),
a is the acceleration,
t is the time.
In this case, the automobile comes to rest, so the final velocity is 0 m/s. We know the initial velocity is 20 m/s, and the time is 2 seconds.
To find the acceleration, we can use the formula:
a = (final velocity - initial velocity) / time
a = (0 - 20) / 2 = -20 / 2 = -10 m/s^2
Substituting the values into the equation of motion:
d = (1/2) * (-10) * (2^2)
d = (1/2) * (-10) * 4
d = -20 meters
The length of the skid distance is 20 meters (option B).
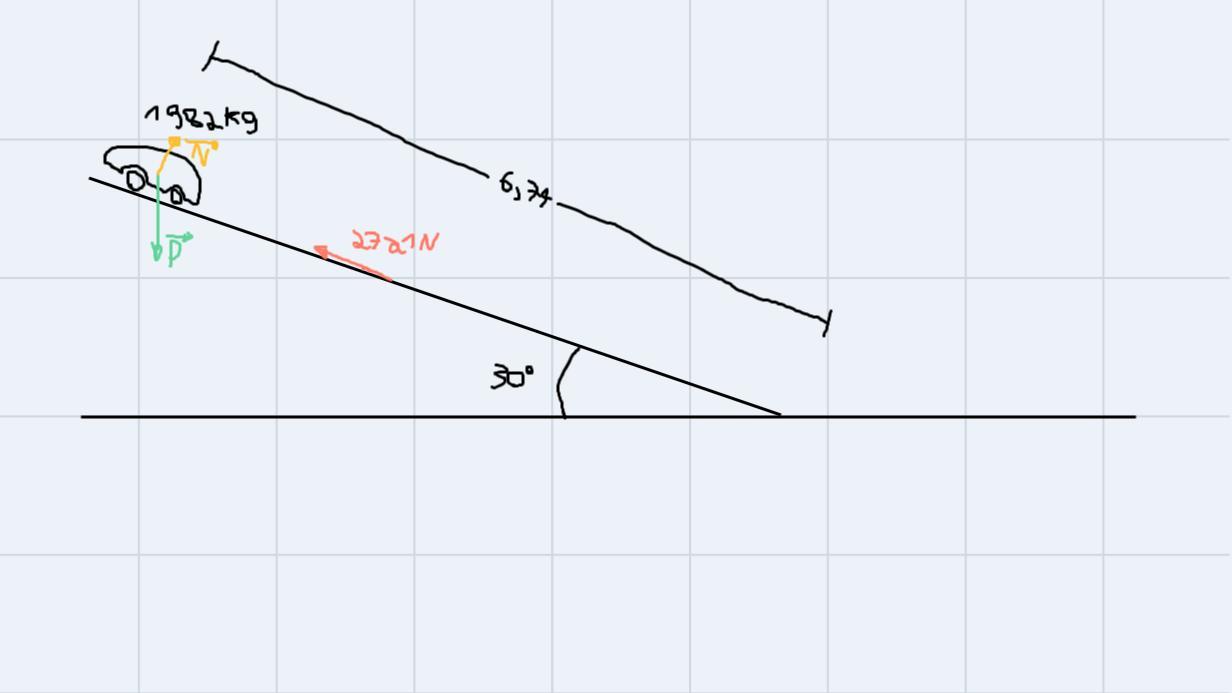
A 1,982-kg car starts from rest at the top of a driveway 6.74 m long that is sloped at an angle of 30 degrees with the horizontal. If an average friction force of 2,721 N impedes the motion of the car, find the speed (in m/s) of the car at the bottom of the driveway.Use the approximation that g ≈ 10 m/s2.
Answers
In this situation, we cannot apply the law of conservation of energy, as there is friction. For us to solve, let us start by writing the balance equations. We'll have:
\(\sum F_x=P*sin(30)-Fat=ma\)\(\sum F_y=N-P*cos(30)=0\)In order to find out the acceleration, we can use the first equation:
\(a=\frac{P*sin(30)-Fat}{m}=\frac{1982*10*sin(30)-2721}{1982}=3.627\frac{m}{s^2}\)The car will then suffer this acceleration on the sloped plane. With this, we can calculate its speed by the end using the equations for a uniformly accelerated movement:
\(S(t)=S_0+v_0t+\frac{at^2}{2}\Rightarrow6.74=\frac{3.627*t^2}{2}\Rightarrow t=1.928s\)This is the time the car will take to reach the bottom. By replacing this on the equation for the velocity we get:
\(v(t)=v_0+at=0+3.627*1.928=7\frac{m}{s}\)Then, our final answer is 7 m/s