A student wants to draw a model of an atom. which statement describes how to find the number of neutrons to include in the model?
A: add the number of electrons to the number of protons
B: Subtract the number of electrons from the number of protons
C: Add the atomic number and the mass number of protons
D:Subtract the atomic number from the mass number
Answers
D:Subtract the atomic number from the mass number
The correct option for the statement, which describes how to find the number of neutrons is "D: Subtract the atomic number from the mass number."
The atomic number of an element is defined as the number of electrons orbiting the nucleus of the atom of that element. It also represents the number of protons inside the nucleus of the atom.
The mass number is defined as the sum of the number of protons and the number of neutrons inside the nucleus of the atom of an element.
Hence, when we subtract the atomic number from the mass number, we get the number of neutrons, as follows:
=> Mass Number - Atomic Number
=> (No. of Neutrons + No. of Protons) - No. of Protons
=> No. of Neutrons
Therefore,
Mass Number - Atomic Number = No. of Neutrons
Learn more about the atomic number and mass number here:
https://brainly.com/question/1891125?referrer=searchResults
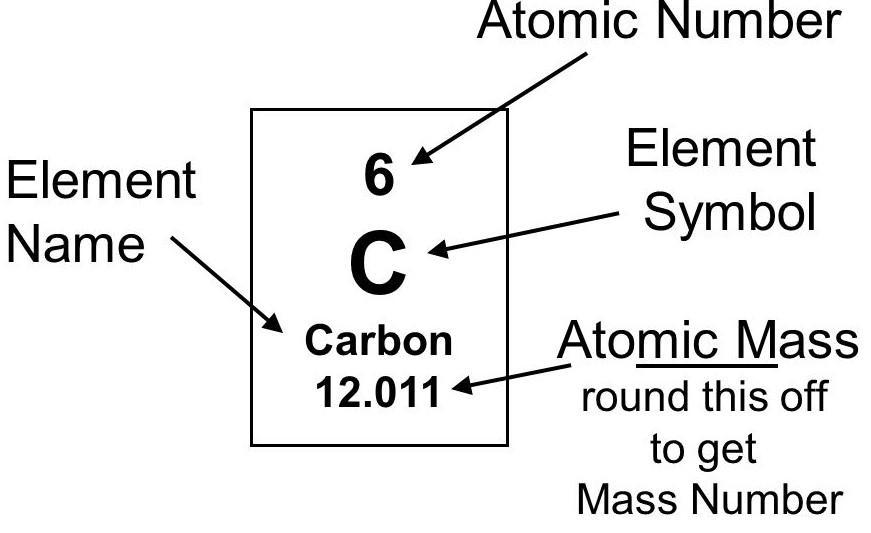
The attached picture shows the atomic number and mass number with the help of an example from the periodic table.
Related Questions
When light travels from one medium to another with a different index of refraction, how is the light's frequency and wavelength affected
Answers
Answer:
The frequency does not change, but the wavelength does
Explanation:
Here are the options
A. When a light wave travels from a medium with a lower index of refraction to a medium with a higher index of refraction, the frequency changes and the wavelength does not.
B. The frequency does change, but the wavelength remains unchanged.
C. Both the frequency and wavelength change.
D. When a light wave travels from a medium with a lower index of refraction to a medium with a higher index of refraction, neither the wavelength nor the frequency changes.
E. The frequency does not change, but its wavelength does.
When light goes through one medium to the next, the frequency doesn't really change seeing as frequency is dependent on wavelength and light wave velocity. And when the wavelength shifts from one medium to the next.
\(n= \frac{C}{V} \ and\ \frac{\lambda_o}{\lambda_m}\)
where \(\lambda_o\) indicates wavelength in vacuum
\(\lambda_m\) indicates wavelength in medium
n indicates refractive index
v indicates velocity of light wave
c indicates velocity of light
And wavelength is medium-dependent. Frequency Here = v\(\lambda\) and shift in wavelength and velocity, not shifts in overall frequency.
Therefore the correct option is E
During a car accident on the NJ Turnpike, the airbags deploy. A 79 kg passenger traveling at 32 m/s makes impact with the airbag over a time of 0.25 seconds. What
was the impact force experienced by the passenger?
Answers
Hi there!
Recall that:
Impulse = Δ in momentum = mΔv
Impulse = Force · time
Begin by calculating the change in momentum, or impulse.
I = mΔv = m(vf - vi)
I = (79)(0 - 32) = -2528 Ns
Now, we can use the equation relating force and time to impulse.
I = Ft
Rearrange for time:
I/F = t
-2528/0.25 = -10112 N
**OR, if magnitude ⇒ |-10112| = 10112 N
The magnitude of the electric field due to a point charge object at a distance 4.0 m is 9 N/C. From the same
charged object the electric field of magnitude, 16 N/C will be at a distance of
Answers
The electric field of magnitude 16 N/C will be at a distance of 6.0 meters from the charged object.
The magnitude of the electric field due to a point charge object follows the inverse square law, which states that the magnitude of the electric field is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the charged object. Mathematically, this is expressed as:
\(E = k*q/r^2\)
where E is the electric field, k is Coulomb's constant (\(k = 9 x 10^9 N*m^2/C^2\)), q is the charge of the object, and r is the distance from the object.
We can use this formula to find the distance at which the electric field has a magnitude of 16 N/C. Let's call this distance x:
16 = \(k*q/x^2\)
We can rearrange this equation to solve for x:
x = \(\sqrt(k*q/16)\)
To find q, we need another piece of information. We know that the electric field has a magnitude of 9 N/C at a distance of 4.0 m. Using the same formula as before, we can solve for q:
9 = \(k*q/4^2\)
q = \(9*4^2/k\)
Now we can substitute this value for q into the equation for x:
x =\(\sqrt(k*(9*4^2/k)/16)\)
x =\(\sqrt(9*4^2/16)\)
x = \(\sqrt(36)\)
x = 6.0 meters
Therefore, the electric field of magnitude 16 N/C will be at a distance of 6.0 meters from the charged object.
Know more about electric field here:
https://brainly.com/question/14372859
#SPJ11
A uniform electric field ai + bj intersects a surface of area A. What is the flux through this area if the surface lies (a) in the yz plane? (b) in the xz plane? (c) in the xy plane?
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
The electric flux through a surface is given by the dot product of the electric field and the area vector of the surface:
Φ = E · A
where Φ is the electric flux, E is the electric field, and A is the area vector of the surface.
(a) If the surface lies in the yz plane, its area vector is in the x direction. Therefore, the area vector can be written as A = Ax i, where Ax is the magnitude of the area. The electric field is given as E = ai + bj. Therefore, the flux through the surface is:
Φ = E · A = (ai + bj) · (Ax i) = aAx
(b) If the surface lies in the xz plane, its area vector is in the y direction. Therefore, the area vector can be written as A = Ay j, where Ay is the magnitude of the area. The electric field is given as E = ai + bj. Therefore, the flux through the surface is:
Φ = E · A = (ai + bj) · (Ay j) = bAy
(c) If the surface lies in the xy plane, its area vector is in the z direction. Therefore, the area vector can be written as A = Az k, where Az is the magnitude of the area. The electric field is given as E = ai + bj. Therefore, the flux through the surface is:
Φ = E · A = (ai + bj) · (Az k) = 0
since the dot product of perpendicular vectors is zero.
Suppose that 2 J of work is needed to stretch a spring from its natural length of 24 cm to a length of 42 cm. (a) How much work is needed to stretch the spring from 32 cm to 34 cm
Answers
Answer:
Workdone = 0.025 Joules
Explanation:
Given the following data;
Workdone = 2J
Extension = 42 - 24 = 18 cm to meters = 18/100 = 0.18m
The workdone to stretch a string is given by the formula;
Workdone = ½ke²
Where;
k is the constant of elasticity.
e is the extension of the string.
We would solve for string constant, k;
2 = ½*k*0.18²
2 = ½*k*0.0324
Cross-multiplying, we have;
4 = 0.0324k
k = 4/0.0324
k = 123.46 N/m
a. To find the workdone when e = 32, 34.
Extension = 34 - 32 = 2 to meters = 2/100 = 0.02m
Workdone = ½*123.46*0.02²
Workdone = 61.73 * 0.0004
Workdone = 0.025 Joules
Therefore, the amount of work (in J) needed to stretch the spring from 32 cm to 34 cm is 0.67.
Based on Kepler's work, which best describes the orbit If a planet around the Sun?
a circle with the Sun at the very center
an ellipse with the Sun at the very center
a circle with the Sun at one edge
an ellipse with the Sun at one focus
Answers
Answer:
D. an ellipse with the Sun at one focus
Explanation:
Based on Kepler's work, the orbit of a planet around the Sun is an ellipse with the Sun at one focus.
What is Kepler's law of planetary motion?The sun is at one of the foci of the planets' elliptical orbits around the sun, according to Kepler's first law. Perihelion, the name for the point at which a planet is closest to the sun, and aphelion, the name for the point at which a planet is farthest from the sunThe radius vector extended from the sun to the planet sweeps out equal areas in equal amounts of time, according to Kepler's second law.The square of a planet's period of revolution around the sun in an elliptical orbit is directly proportional to the cube of its semi-major axis, states Kepler's law of periods.Hence according to Kepler's first law of planetary motion, the orbit of a planet around the Sun is an ellipse with the Sun at one focus.
Find more about planetary motion refer the link:
https://brainly.com/question/3488967
#SPJ5
What is the density of a 700 kg object with a volume of 649 m3
Answers
mass = 700
volume = 649
density = 700/649
density = 1.07
Hope this helps! I apologize if I’m incorrect
Which change to an object would reduce its kinetic energy by half?
A. Reducing its mass to one-quarter of its original value
B. Reducing its mass to one-half of its original value
C. Increasing its velocity to twice its original value
D. Increasing its velocity to four times its original value
SUBMI
Answers
A. Reducing its mass to one-quarter of its original value; will reduce the kinetic energy of the object by half.
Kinetic energy is a type of power that a moving object or particle possesses. An item accumulates kinetic energy when work, which involves the transfer of energy, is done on it by exerting a net force. A moving object or particle has kinetic energy, which depends on both its mass and its rate of motion. The type of motion can be vibration, rotation on an axis, translation (or travel along a path from one place to another), or any combination of these.
A body's translational kinetic energy is equal to half of the product of its mass, m, and its velocity, sq,v,
The formula of kinetic energy = 1/2 x mv^2
Since it is based on the mass of the object, the kinetic energy also gets reduced by half along with the mass.
To learn more about kinetic energy please visit-
https://brainly.com/question/12669551
#SPJ9
The length of the river span of a bridge is 2799.0 ft. The total length of the bridge is 6998ft. Convert the length of the river span of the bridge to meters.
Answers
According to the question the length of the river span of the bridge in meters is 853.3232 m.
What is Length?Length is a physical quantity that measures the distance between two points. It is one of the fundamental units in the International System of Units (SI). It is usually measured in meters, although it can also be measured in other units such as centimeters, kilometers, feet, yards, miles, and so on.
The length of the river span of the bridge is 2799.0 ft. To convert this length to meters, we need to use a conversion factor. There are 0.3048 meters in one foot, so the conversion factor we will use is 1 ft
= 0.3048 m.
To convert 2799.0 ft to meters, we multiply by the conversion factor:
2799.0 ft * 0.3048 m/ft
= 853.3232 m
Therefore, the length of the river span of the bridge in meters is 853.3232 m.
To learn more about Length
https://brainly.com/question/20599103
#SPJ1
Two lenses with focal lengths 10cm and 20cm and made of same material are placed coaxially
separated by distance d. The value of d such that the system is achromatic is
A) 20 om
) 30cm
C) 10 cm
D) 15 cm
Answers
examples of ohmic conductors
Answers
The examples of ohmic conductors are :
Silver(Ag), copper(Cu), aluminium(Al) etc.
How can we conclude that these are ohmic conductors?Ohmic conductors means which conductors strictly obey the Ohm's law, are known as Ohmic conductors.
Resistance= \(\frac{Voltage}{Current}\)
In other words there is a linear relationship between voltage and current for all values. That means all the ohmic conductor materials shows a linear character in the V-I characteristic graph.
So, the examples of ohmic conductors are:
Silver(Ag), copper(Cu), aluminium(Al) etc.
All the conductors we mentions here, they all show a linear line in the V-I characteristic graph.
From the above discussion we can conclude that, Silver(Ag), copper(Cu), aluminium(Al) etc. these are the ohmic conductors.
Learn more about Ohmic conductors:
https://brainly.in/question/522731
#SPJ9
The mixing entropy formula derived in the previous problem actually applies to any ideal gas, and to some dense gases, liquids, and solids as well. For the denser systems, we have to assume that the two types of molecules are the same size and that molecules of different types interact with each other in the same way as molecules of the same type (same forces, etc.). Such a system is called an ideal mixture. Explain why, for an ideal mixture.
Answers
For an ideal mixture of two or more substances, the mixing entropy can be derived based on the same principles as for ideal gases. The reason is that ideal mixtures also have particles that are in constant random motion, and the entropy of mixing is still related to the number of possible ways the particles can be arranged.
Ideal mixture explained.
In an ideal mixture, the assumption is that the molecules of different substances are the same size and shape, and have the same intermolecular forces with each other as they do with their own kind. This means that there are no attractive or repulsive forces between particles of different types, which simplifies the calculation of the entropy of mixing.
The mixing entropy of an ideal mixture is determined by the number of possible ways the molecules of the two substances can be distributed among the available volume. Just as in the case of ideal gases, this leads to an increase in entropy when the two substances are mixed, as there are more ways to distribute the molecules than when they are separated.
Therefore, the concept of an ideal mixture allows us to apply the same principles of thermodynamics to denser systems as we do for ideal gases, which makes it a useful tool for studying a wide range of physical and chemical processes involving mixtures.
Learn more about ideal mixture below.
https://brainly.com/question/30611851
#SPJ1
The mixing entropy formula applies to ideal mixtures because there are no intermolecular forces between different species, there are no volume changes upon mixing, and the mixing is completely random.
What is Ideal Mixing Entropy Formula?An ideal mixture is a hypothetical mixture of gases, liquids or solids where the components are assumed to behave as an ideal gas, and where the two types of molecules are the same size and interact with each other in the same way as molecules of the same type (same forces, etc.). In an ideal mixture, the mixing entropy formula applies due to the following reasons:
No intermolecular forces between different species: In an ideal mixture, the molecules of the different components do not attract or repel each other. This means that the interactions between the different species are negligible and the enthalpy of mixing is zero.No volume changes upon mixing: In an ideal mixture, the components have the same size and shape, and the volume of the mixture is equal to the sum of the volumes of the individual components. Therefore, there are no volume changes upon mixing, and the entropy of mixing is solely dependent on the number of ways of arranging the molecules.Random mixing: The assumption of ideal mixing also implies that the mixing is completely random, with no preferential interactions between the different species. This means that the entropy of mixing is solely dependent on the number of ways the molecules can be arranged, and this is given by the mixing entropy formula.Therefore, the mixing entropy formula applies to ideal mixtures because there are no intermolecular forces between different species, there are no volume changes upon mixing, and the mixing is completely random.
Learn more on entropy here https://brainly.com/question/419265
#SPJ1
doing the same amount of work in less time requires more power true or false
Answers
2(a)Find the density of air filled in polythene container with mass of 0.419kg when it is empty. When filled with extra air its mass increased to 0.428kg also the top of polythene container mass connected to the perplex box of volume 1000cm³ and the number of times of air inside was 7.2 times
Answers
When filled with extra air its mass increased to 0.428kg also the top of polythene container mass connected to the perplex box of volume 1000cm³ and the number of times of air inside was 7.2 times. The density of the air filled in the polythene container is approximately 1.25 kg/m³.
The density of air filled in the polythene container can be determined by considering the change in mass and volume of the container before and after filling it with air. Given that the mass of the empty container is 0.419 kg and the mass of the container when filled with extra air is 0.428 kg, and the volume of the perplex box is 1000 cm³.
Calculate the mass of the air inside the container by subtracting the mass of the empty container from the mass of the container when filled with air:
Mass of air = Mass of filled container - Mass of empty container
= 0.428 kg - 0.419 kg
= 0.009 kg
Calculate the volume of the air inside the container using the given number of times the air inside is 7.2:
Volume of air = Volume of perplex box * Number of times air inside
= 1000 cm³ * 7.2
= 7200 cm³
Convert the volume of air to cubic meters (m³) by dividing by 1000000:
Volume of air = 7200 cm³ / 1000000
= 0.0072 m³
Calculate the density of air using the formula:
Density = Mass / Volume
Density = 0.009 kg / 0.0072 m³
≈ 1.25 kg/m³
Therefore, the density of the air filled in the polythene container is approximately 1.25 kg/m³.
For more such questions on density, click on:
https://brainly.com/question/6838128
#SPJ8
Before a collision, a 25 kg object is moving at 12 m/s to the right. After a collision with stationary box, the 25 kg object moves at 8 m/s to the right. What is the resulting momentum of the box?
Answers
The initial momentum of the 25 kg object is 25 kg * 12 m/s = 300 kgm/s. After the collision, the momentum of the 25 kg object is 25 kg * 8 m/s = 200 kgm/s. According to the conservation of momentum, the momentum lost by the 25 kg object is equal to the momentum gained by the box. Therefore, the resulting momentum of the box is 300 kgm/s - 200 kgm/s = 100 kg*m/s.
A 2.50 kg ball moving at 7.50 m/s is caught by a 70.0 kg man while the man is standing on ice. How
fast will the man / ball combination be moving after the ball is caught by the man?
Answers
Explanation:(2.5kg) (7.5) m/s +70 kg(0) =(2.5kg +70 kg (v3) 18. 75 =72.5 =v3
v3=.26m/s 2.5+70
8. Miss D. Water, a stunt diver in the circus, had 15,000.0 J of kinetic energy immediately before diving
into a bucket of water at a speed of 24.0 m/s. What is her mass?
Answers
The mass of the bucket of water is 52.08kg whose kinetic energy is 15,000J with the speed of 24 m/s.
What is Kinetic energy?Kinetic energy is defined as the energy which is due to the motion of an object. When we want to accelerate an object, we must apply a force, thus by applying a force we need to do work. After the work is done, energy has been transferred to the object which will continue to move with a new constant speed.
The kinetic energy is given by
\(K.E.= \frac{1}{2} mass* velocity^2\)
For above given example,
K.E.= 15,000 J
velocity= 24m/s
\(15000= 1/2 mass *\) \((24)^2\)
\(\frac{15000* 2}{24*24} = Mass\)
\(Mass= \frac{30000}{576}\)
Mass= 52.08 kg
Thus, the mass of the bucket of water is 52.08kg whose kinetic energy is 15,000J with the speed of 24 m/s.
Learn more about Kinetic energy, here:
https://brainly.com/question/26472013
#SPJ9
I'd like you to think back on 2 events in
your life, one that made you feel great happiness and
one that caused sadness. Describe the situations and
how you felt in those moments. Fast forward to noW,
how did those events impact who you are today?
What did you learn and are you grateful that you had
those moments? Explain.
Answers
Answer:
Holi
biwali
these are best events and love to celebrate withmy family and friends it contains lot of happiness and joy
12.
A hiker walks for 5km on a bearing of 053" true (North 53° East). She then turns and
walks for another 3km on a bearing of 107° true (East 17° South).
(a)
Find the distance that the hiker travels North/South and the distance that she travels
East/West on the first part of her hike.
Answers
The hiker travelled 4.02 km North/South and 4.74 km East/West during her hike.
This question involves vector addition, the resolution of vectors, the use of bearings, and trigonometry in the calculation of the hiker's movement.
This may appear to be a difficult problem, but with some visual aid and the proper use of mathematical formulas, the issue can be addressed correctly.
Resolution of VectorThe resolution of a vector is the process of dividing it into two or more components.
The angle between the resultant and the given vector is equal to the inverse tangent of the two rectangular components.
Angles will always be expressed in degrees in the solution.
The sine, cosine, and tangent functions in trigonometry are denoted by sin, cos, and tan.
The tangent function can be calculated using the sine and cosine functions as tan x = sin x/cos x. Also, in right-angled triangles, Pythagoras’ theorem is used to find the hypotenuse or one of the legs.
Distance Travelled North/SouthThe hiker traveled North for the first part of the hike and South for the second.
The angles that the hiker traveled in the first part and second parts are 53 degrees and 17 degrees, respectively.
The angle between the two is (180 - 53 - 17) = 110 degrees.
The angle between the resultant and the Northern direction is 110 - 53 = 57 degrees.
Using sine and cosine, we can calculate the north/south distance traveled to be 5 sin 57 = 4.02 km, and the east/west distance to be 5 cos 57 = 2.93 km.
Distance Travelled East/WestThe hiker walked East for the second part of the hike.
To calculate the distance travelled East/West, we must first calculate the component of the first part that was East/West.
The angle between the vector and the Eastern direction is 90 - 53 = 37 degrees.
Using sine and cosine, we can calculate that the distance travelled East/West for the first part of the hike is 5 cos 37 = 3.88 km.
To determine the net distance travelled East/West, we must combine this component with the distance travelled East/West in the second part of the hike.
The angle between the second vector and the Eastern direction is 17 degrees.
Using sine and cosine, we can calculate the distance traveled East/West to be 3 sin 17 = 0.86 km.
The net distance traveled East/West is 3.88 + 0.86 = 4.74 km.
Therefore, the hiker travelled 4.02 km North/South and 4.74 km East/West during her hike.
For more questions on travelled
https://brainly.com/question/750474
#SPJ8
6.
least 2 m. If the same car is moving with the speed 80K/h,what is the minimum stopping distance?
A car moving with a speed of 40 km/h can be stopped by applying the brakes after at-
Answers
The minimum stopping distance of the car is determined as 8 m.
What is the minimum stopping distance?The minimum stopping distance of the car is calculated as follows;
d = (u²)/(2a)
where;
d is the minimum stopping distanceu is the initial velocitya is the acceleration of the carwhen the minimum stopping distance = 2 m, initial velocity = 40 km/hr = 11.11 m/s
2 = (11.11²)/(2a)
a = (11.11²)/(2 x 2)
a = 30.86 m/s²
when the speed becomes 80 km/h, the minimum stopping distance is calculated as;
u = 80 km/h = 22.22 m/s
d = (22.22² )/ (2 x 30.86)
d = 8 m
Learn more about minimum stopping distance here: https://brainly.com/question/13030196
#SPJ1
What characteristics determine how easily two substances change temperature? Check all that apply.
volume of the two substances in contact
amount of time the two substances are in contact
Oarea in contact between the two substances
specific heat of the material that makes up the substances
density of the two substances in contact
Answers
Answer:
The characteristics that determine how easily two substances change temperature are:
specific heat of the material that makes up the substancesarea in contact between the two substancesThe volume and density of the substances and the amount of time they are in contact do not directly affect how easily they change temperature.
Explanation:
formula for inertia speed
Answers
Answer:
The equation of momentum for a linear system is simply P = mv where P = momentum (kg·m/sec or lb·ft/sec); m = mass (kg or lb); and v = velocity (m/s or ft/sec). ... By reducing her inertia (I = mr2 where r has been decreased) her angular velocity, ω, must increase in order for the angular momentum to remain constant.
https://www.gstatic.com/education/formulas2/355397047/en/moment_of_inertia.svg
hope this helps?
Explanation:
A Student 330 m 990m from another tall flip between the the Student stands Sound Interval beteeen cliff is cliff from of 1 st and 630 tall Hip which speed of 330 if the 330 m/s 2nd eh what is echo?
Answers
The interval between the first and second echo is 7 seconds. This means that after the initial sound wave reaches the first cliff, it takes a total of 7 seconds for the sound to travel to the second cliff and then return to the student as the second echo.
To determine the interval between the first and second echo, we need to consider the time it takes for sound to travel from the student to the first cliff, and then from the first cliff to the second cliff, and finally back to the student.
Let's break down the distances and calculate the time for each part of the journey:
Distance from the student to the first cliff: 330 meters
Time taken: t₁ = distance / speed = 330 m / 330 m/s = 1 second
Distance from the first cliff to the second cliff: 990 meters
Time taken: t₂ = distance / speed = 990 m / 330 m/s = 3 seconds
Distance from the second cliff back to the student: 990 meters
Time taken: t₃ = distance / speed = 990 m / 330 m/s = 3 seconds
Now, we can calculate the total interval between the first and second echo by adding up the individual times:
Interval between first and second echo = t₁ + t₂ + t₃ = 1 s + 3 s + 3 s = 7 seconds
Therefore, the interval between the first and second echo is 7 seconds. This means that after the initial sound wave reaches the first cliff, it takes a total of 7 seconds for the sound to travel to the second cliff and then return to the student as the second echo.
It's important to note that this calculation assumes a straight path for the sound waves and neglects factors such as air temperature and wind that can affect the speed of sound. Additionally, it assumes perfect reflection of sound waves off the cliffs, which may not be the case in real-world scenarios.
For more such questions on echo visit;
https://brainly.com/question/30750512
#SPJ8
Note the complete questions is:
A student stands 330m from a tall cliff which is 990m from another tall cliff. If the speed of sound between the cliffs is 330m/s.What is the interval between the first and second echo?
The foundation of psychology is?
Case Studies
O Experiments
O Research
O Analysis
Answers
Answer:
Case Studies
Explanation:
A case study in psychology is a descriptive research approach used to obtain in-depth information about a person, group, or phenomenon.Case studies use techniques such as personal interviews, direct observation, psychometric tests, and archival records to gather information.
You push a 15N cat in a box horizontally across the floor for 5m. What is the work done on the cat? W=Fx
Answers
Answer:
w=fx
w=(15)(5)
w=75
the angle between the deplacement and N is 0
A rock falls from a vertical cliff that is 4.0 m tall and experiences no significant air resistance as it falls. At what speed will it's gravitational potential energy (relative to the base of the cliff) be equal to its kinetic energy in m/s?
Answers
Answer:
v = 6.3 m/s
Explanation:
Since no significant air resistance exists, total mechanical energy must be kept constant at any time.At the top of the cliff, all the energy is gravitational potential energy, as follows:\(E_{i} = K_{i} + U_{i} = 0 + U_{i} (1)\)
If we choose the ground level as our zero reference level for the gravitational potential energy, Ui is simply:Ui = m*g*h (1)At any height, the sum of the kinetic and the gravitational potential energy must be equal to (1).We know from the question, that at the point of interest, both types of energies must be equal each other, so we can write the following expression from (1):\(m*g* h = 2*\frac{1}{2}*m*v^{2} (2)\)
Dividing both sides by m, simplifying, and solving for v, we get:\(v = \sqrt{g*h} =\sqrt{9.8m/s2*4.0m} = 6.26 m/s (3)\)
v = 6.3 m/s (with two significative figures)a basketball weighing 0.5 kg is flying through the air at 10 m/s. what is its kinetic energy
Answers
Answer:
KE=(mv^2)/2. So (.5)(10^2)/2 = 25 J
Explanation:
What is the Density of a 150g irregularly shaped rock that displaces 25 ml of water, when it is dropped into a
graduated cylinder?
Answers
Answer:
6 g/mL
Explanation:
given:
mass = 150g
volume = displaced volume of water = 25 mL
recall that density = mass / volume
density = 150g / 25 mL = 6 g/mL
Part B
Enter into the table your calculated value for the spring constant, then play with different values of mk
until you get a close match to the motion. (Note: It will never be perfect. Remember that there are two
kinds of spring damping. Both are at work here, but we are not going to model both.) Once you're
satisfied with your model, record your model values in the table below.
Answers
The spring stiffness is quantified by the spring constant, or k. For various springs and materials, it varies.
What is Spring constant?The stiffer the spring is and the harder it is to stretch, the larger the spring constant.
Springs are pliable mechanical devices that regain their previous shape after deforming, i.e. after being stretched or compressed. They are an essential part of many different mechanical devices.
The well-known metal coil has evolved into an essential element in the modern world, appearing in everything from engines to appliances to tools to automobiles to medical equipment and even basic ball-point pens. The spring's ability to store mechanical energy accounts for its widespread use and applications.
Therefore, The spring stiffness is quantified by the spring constant, or k. For various springs and materials, it varies.
To learn more about Spring constant, refer to the link:
https://brainly.com/question/29975736
#SPJ1
what is the similaries between parallel and series circuits
Answers
Answer:
same power source
can have more than 1 light bulb in a circuit
requires a source of energy
Explanation: