A student is interested in studying the amount spent on rent for apartments in the gainesville area. She takes a random sample of 100 local apartment complexes. She is interested in studying the center, shape and spread of the data. What type of graph does she make?.
Answers
A histogram is an effective way to present and analyze the center, shape, and spread of continuous data, allowing the student to gain a better understanding of the distribution of rent amounts in the Gainesville area.
To study the center, shape, and spread of the data for the amount spent on rent for apartments in the Gainesville area, the student would typically create a histogram.
A histogram is a type of graph that represents the distribution of continuous data by dividing it into intervals, or bins, and displaying the frequency or count of data points falling within each interval. It provides insights into the center (central tendency), shape, and spread (dispersion) of the data.
In the student's case, the amount spent on rent for apartments would be the continuous variable, and the student would group the data into intervals (e.g., rent ranges) and count the number of apartment complexes falling within each interval.
By creating a histogram, the student can visually analyze the distribution of rent amounts, identify the most common rent ranges (mode), and observe the shape of the distribution (symmetric, skewed, etc.). The histogram can also provide insights into the spread of the data, such as the range of rent amounts and the presence of outliers.
Overall, a histogram is an effective way to present and analyze the center, shape, and spread of continuous data, allowing the student to gain a better understanding of the distribution of rent amounts in the Gainesville area.
Learn more about histogram here
https://brainly.com/question/30545730
#SPJ11
Related Questions
Tan θ =
\( \sqrt{13} \div \sqrt{2} \)
Answers
Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
Tan θ = \(\sqrt{13} \div \sqrt{2}\) = 2.5495
Therefore θ = \(Tan^{-1}\) (2.5495) =68.5832°
Answer:
Tan θ = 2.5495097...
[Image: Vertical number line ranging from negative 5 to 5.]
On this number line, zero represents sea level. Plot the following points based on the description provided.
• -3 1/2
[Image: Vertical number line ranging from negative 5 to 5.]
On this number line, zero represents sea level. Plot the following points based on the description provided.
• opposite of –5
Answers
Answer:
Positive 5.
Step-by-step explanation:
Opposite of negative 5 is positive 5.
The point will be on the positive side, which is above sea level. So it will be on 5 above the zero.
Answer:positive 5
Step-by-step explanation:
X+y=150/2
x+y=75 find the solution using cramers rule
Answers
Answer:
I didn’t know if I was solving for x or for y but I believe that the answer is x=75-y
Step-by-step explanation:
Solve by simplifying both sides of the equation, then isolating the variable.
In a region where there is a uniform electric field, the potential, v1, is 1. 3 v at position y1=26 cm. At position y2=28 cm , the potential, v2, is 3. 9 v. What is the change in electric potential energy of an alpha particle (charge = +2e) if it is moved from y1 to y3?.
Answers
The change in electric potential energy of an alpha particle is:
1.3V/cm
"Information available from the question"
In a region where there is a uniform electric field, the potential, v1, is 1. 3 v at position y1=26 cm.
At position y2=28 cm , the potential, v2, is 3. 9 v.
Now, According to the question:
Calculation of magnitude:
Since V1 is 1.3 V at position y1=26 cm. At position y2=28 cm, the potential, V2, is 3.9 V
So, We know that
\(E =\frac{V_2-V_1}{Y_2-Y_1}\)
\(E=\frac{3.9-1.3}{28-26}\)
\(E=\frac{2.6}{2}\)
E = 1.3V/cm
Learn more about Magnitude at:
https://brainly.com/question/14452091
#SPJ4
Simplify the expression 7‐²(-3)²
Answers
Answer:
The answer to that question is 58
A circle has a circumference of 1{,}133.541,133.541, comma, 133, point, 54 units.
What is the diameter of the circle?
Answers
Answer: Radius is 21.2537 units, to 6 sig figs
Step-by-step explanation:
I'll assume the circumference is simply 133.541 units^2. Circumference (C) is C = 2*pi*R, where R is the radius. Thus, R = C/(2*pi),
R = (133.541/2*(3.14159) to 6 sig figs
R = 21.2537 units
Cual es el intercepto de (1,5) (0,4)
Answers
The points where the graphics touch the coordinate axes are known as the function intercepts.
How can I determine what the intercept is?The points where the graphics touch the coordinate axes are known as the function intercepts. These points, which have the forms (1,5) and (0,4), are the points of the function that are the easiest to identify, and as a result, we frequently seek them out because they provide us information that is useful in real-world applications.As a result, if x = 1 5, then y = c. As a result, the point of intersection of the parabola with the Y axis will always be (0, 4).Keep in mind that the pendent is negative. Additionally, the intercept (0, 4) shows that the straight line passes through the coordinated system's origin.
To learn more about intercepto de refer to:
https://brainly.com/question/7674871
#SPJ1
Writ an equation of a parabola that has a vertex (1,3) and passes through the point (2,5)
Answers

Answer:
y=2x+1
Step-by-step explanation:
Jacob is going on a road trip across the country. He covers 10 miles in
15 minutes. He then spends 10 minutes buying gas and some snacks at the
gas station. He then continues on his road trip.
Describe the distance traveled between 10 minutes and 15 minutes.

Answers
The distance covered between 10 minutes and 15 minutes is increasing
What is an equation?An equation is an expression that shows the relationship between two or more numbers and variables.
Speed is the ratio of total distance travelled to total time taken. It is given by:
Speed = distance / time
From the graph:
The distance covered between 10 minutes and 15 minutes is increasing
Find out more on equation at: https://brainly.com/question/29797709
#SPJ1
Please help asap!!!!!!!!

Answers
The y-coordinate for the solution to the system of equations is -3.
What is a system of equations?
A finite set of equations for which common solutions are sought is referred to in mathematics as a set of simultaneous equations, often known as a system of equations. The intersection of two lines represents the system of equations' solution.
Given system of equations are,
6x + 11y = -3
4x + y = 17
To solve these equations, we must first remove x or y terms.
To do this we must make the removing term's coefficients the same.
In this case, let's remove y.
We are multiplying the second equation by 11. Then,
6x + 11y = -3
44x + 11y = 187
Now we will subtract the second equation from the first.
- 38x = -190
x = 5
Now to find y, substitute x in any one of the equations.
6 * 5 + 11y = -3
11y = -33
y = -3
Hence the y-coordinate for the solution to the system of equations is -3.
To learn more about the system of equations, follow the link.
https://brainly.com/question/25976025
#SPJ1
Do the data in the table support the authors’
proposed pairing of bases in DNA?
A) Yes, because for each given organism, the
percentage of adenine is closest to the percentage
of thymine, and the percentage of guanine is
closest to the percentage of cytosine.
B) Yes, because for each given organism, the
percentage of adenine is closest to the percentage
of guanine, and the percentage of cytosine is
closest to the percentage of thymine.
C) No, because for each given organism, the
percentage of adenine is closest to the percentage
of thymine, and the percentage of guanine is
closest to the percentage of cytosine.
D) No, because for each given organism, the
percentage of adenine is closest to the percentage
of guanine, and the percentage of cytosine is
closest to the percentage of thymine.
Answers
Choice A is the answer. Yes, because for each given organism, the percentage of adenine is closest to the percentage of thymine, and the percentage of guanine is closest to the percentage of cytosine.
Since the authors said that, "the bases will be present almost entirely in their most probable forms. If this is true, the conditions for forming hydrogen bonds are more restrictive, and the only pairs of bases possible are: adenine with thymine, and guanine with cytosine” (lines 31-35).
The table demonstrates that the percentages of the base pairs adenine/thymine and guanine/cytosine in the DNA of all creatures mentioned are strikingly comparable. B is the wrong answer. Although "Yes" is the right answer, the reasoning for that answer misrepresents the information in the table.
The table does support the authors' hypothesized pairing of nitrogenous bases in DNA molecules, hence options C and D are incorrect.
Here's another question with an answer similar to this about DNA:
https://brainly.com/question/12499113
#SPJ4
Answer:
A) Yes, because for each given organism, the percentage of adenine is closest to the percentage of thymine, and the percentage of guanine is closest to the percentage of cytosine.
Step-by-step explanation:
Carmen works at a company where she gets a set 5% raise every year. If her current salary is $66,000, what
will her salary be in 12 years?
Answers
A line passes through the point (-6,2) and has a slope of -4/3
Write an equation in point-slope form for this line.
Answers
Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:

The volume of a cuboid is 360cm3. The length is 3cm and the width is 80mm. Work out the height of the cuboid in cm.
Answers
Answer:
\(15\:cm\)
Step-by-step explanation:
Use the formula for the volume of a cuboid.
\(V=lwh\)
\(80\:mm=8\:cm\)
\(360=3 \times 8 \times h\)
\(360=24 \times h\)
\(360 \div 24 = h\)
\(15=h\)
The height of the cuboid 15 cm.
What is volume?In mathematics, volume is the space taken by an object. Volume is a measure of three-dimensional space. It is often quantified numerically using SI derived units or by various imperial or US customary units. The definition of length is interrelated with volume.
Here, we have,
The volume of a cuboid is 360cm3.
The length is 3cm and the width is 80mm.
now,
80mm=8cm
volume= l*w* h
i.e. 360 = 3* 8*h
so, h= 15
Hence, The height of the cuboid 15 cm.
To learn more on volume click :
brainly.com/question/1578538
#SPJ2
The base of a solid is the region in the first quadrant bounded by the y-axis, the graph of y = ????????????-1x, the horizontal line y = 3 and the vertical line x = 1. For this solid, each cross section perpendicular to the x-axis is a square. What is the volume of the solid?
Answers
The volume of the solid is 9 cubic units, which is determined by the base in the first quadrant bounded by the y-axis, the graph of y = x-1, the horizontal line y = 3, and the vertical line x = 1. As the cross sections perpendicular to the x-axis are squares, the volume can be calculated.
The volume of the solid can be calculated by finding the area of the base and then multiplying it by the height of the solid. The base of the solid is in the first quadrant and is bounded by the y-axis, the graph of y = x-1, the horizontal line y = 3, and the vertical line x = 1. This region forms a trapezoid, with an area of 6. As the cross sections perpendicular to the x-axis are squares, the height of the solid is 3 units. Thus, the volume of the solid is 6 multiplied by 3, which gives us a total volume of 9 cubic units. To calculate the volume, it is important to identify the base of the solid and the shape of the cross sections perpendicular to the x-axis. This will allow us to calculate the area of the base, and multiply it by the height of the solid to determine the total volume.
Learn more about volume here
https://brainly.com/question/16134180
#SPJ4
HELP WITH MATH PLEASE

Answers
Answer: 5 and the power is 2
the power used is 2
Step-by-step explanation:
Consider a particle of mass m moving in the square well, i.e., in the interval [0,a], where V(x)=0 in this interval, and V(x)=[infinity] for x>a and x<0. The energy levels are given by: E=En= n^2 π^2 h^2/2ma^2 ,n=1,2,…,
and the corresponding eigenfunctions: ψ n (x)= √2/a sin( nπx/a) from which it follows that: ψ n (x,t)= √2/a sin( nπx/a) e (n^2 π^2 h^2)/2ma^2
(a) (5 marks) Compute E e n(X), where E p n
(X) denotes the expectation value of X in the state ψ n
(b) (5 marks) Compute E v n(X 2). (c) (5 marks) Compute E ψ n(P). (d) (5 marks) Compute E φ˙n(P 2). (e) (5 marks) State the uncertainty relation and determine the state ψ n for which the uncertainty is a minimum.
Answers
(a) To compute\(E_e_n\)(X), we need to find the expectation value of the operator X in the state ψ_n.
The operator X corresponds to the position of the particle. The expectation value of X in the state ψ_n is given by:
\(E_e_n\)(X) = ∫ ψ_n* X ψ_n dx,
where ψ_n* represents the complex conjugate of ψ_n. Since ψ_n = √(2/a) sin(nπx/a), we can substitute these values into the integral:
\(E_e_n\)(X) = ∫ (2/a) sin(nπx/a) * X * (2/a) sin(nπx/a) dx.
The integral is taken over the interval [0, a]. The specific form of the operator X is not provided, so we cannot calculate \(E_e_n\)(X) without knowing the operator.
(b) To compute \(E_v_n\)(X^2), we need to find the expectation value of the operator X^2 in the state ψ_n. Similar to part (a), we can calculate it using the integral:
\(E_v_n\)(X^2) = ∫ (2/a) sin(nπx/a) * X^2 * (2/a) sin(nπx/a) dx.
Again, the specific form of the operator X^2 is not given, so we cannot determine \(E_v_n\)(X^2) without knowing the operator.
(c) To compute E_ψ_n(P), we need to find the expectation value of the momentum operator P in the state ψ_n. The momentum operator is given by P = -iħ(d/dx). We can substitute these values into the integral:
E_ψ_n(P) = ∫ ψ_n* P ψ_n dx
= ∫ (2/a) sin(nπx/a) * (-iħ(d/dx)) * (2/a) sin(nπx/a) dx.
(d) To compute E_φ˙n(P^2), we need to find the expectation value of the squared momentum operator P^2 in the state ψ_n. The squared momentum operator is given by P^2 = -ħ^2(d^2/dx^2). We can substitute these values into the integral:
E_φ˙n(P^2) = ∫ ψ_n* P^2 ψ_n dx
= ∫ (2/a) sin(nπx/a) * (-ħ^2(d^2/dx^2)) * (2/a) sin(nπx/a) dx.
(e) The uncertainty relation in quantum mechanics is given by the Heisenberg uncertainty principle:
ΔX ΔP ≥ ħ/2,
where ΔX represents the uncertainty in the position measurement and ΔP represents the uncertainty in the momentum measurement. To determine the state ψ_n for which the uncertainty is a minimum, we need to find the values of ΔX and ΔP and apply the uncertainty relation. However, the formulas for ΔX and ΔP are not provided, so we cannot determine the state ψ_n for which the uncertainty is a minimum without further information.
To know more about minimum visit;
brainly.com/question/29088643
#SPJ11
If MZAEB = 38°
what is x?
HELP ASAP

Answers
Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
2x+38=180
2x=142
x=71
"write an equation of the perpendicular bisector or the segment with endpoints Q(-2,0) and R(6,12). what does y equal?

Answers
Answer:
The equation of perpendicular bisector of QR is:
y = -\frac{2}{3}x+\frac{22}{3}y=−32x+322
Step-by-step explanation:
Given points are:
Q(-2,0)\ and\ R(6,12)Q(−2,0) and R(6,12)
First of all, we have to find the slope of the given line
So,
m = \frac{y_2-y_1}{x_2-x_1}m=x2−x1y2−y1
Here
(x1,y1) = (-2,0)
(x2,y2) = (6,12)
Let m1 be the slope of QR:
Then
\begin{gathered}m_1 = \frac{12-0}{6+2}\\= \frac{12}{8}\\= \frac{3}{2}\end{gathered}m1=6+212−0=812=23
Let m2 be the slope of perpendicular bisector
We know that the product of slopes of two perpendicular lines is -1
\begin{gathered}m_1.m_2 = -1\\\frac{3}{2}.m_2 = -1\\m_2 = -1 * \frac{2}{3}\\m_2 = -\frac{2}{3}\end{gathered}m1.m2=−123.m2=−1m2=−1∗32m2=−32
The bisector will pass through the mid-point of QR
\begin{gathered}M = (\frac{x_1+x_2}{2} , \frac{y_1+y_2}{2})\\M = (\frac{-2+6}{2}, \frac{0+12}{2})\\M = (\frac{4}{2}, \frac{12}{2})\\M = (2,6)\end{gathered}M=(2x1+x2,2y1+y2)M=(2−2+6,20+12)M=(24,212)M=(2,6)
Slope-intercept form of equation is:
y = m_2x+by=m2x+b
Putting the value of slope
y = -\frac{2}{3}x+by=−32x+b
Putting (2,6) in the equation
\begin{gathered}6 = -\frac{2}{3}(2)+b\\6 = -\frac{4}{3}+b\\b = 6+\frac{4}{3}\\b = \frac{18+4}{3}\\b = \frac{22}{3}\end{gathered}6=−32(2)+b6=−34+bb=6+34b=318+4b=322
So,
y = -\frac{2}{3}x+\frac{22}{3}y=−32x+322
Hence,
The equation of perpendicular bisector of QR is:
y = -\frac{2}{3}x+\frac{22}{3}y=−32x+322
18 m
6 m
6 m
16 m
16 m
14 m

Answers
Solve the differential equations 2xy(dy/dx)=1 y^2. y(2)=3
Answers
The solution to the given differential equation 2xy(dy/dx) = y², with the initial condition y(2) = 3, is y = (27 * e⁽ˣ⁻²⁾\()^{1/4}\).
To solve the given differential equation
2xy(dy/dx) = y²
We will use separation of variables and integrate to find the solution.
Start with the given equation
2xy(dy/dx) = y²
Divide both sides by y²:
(2x/y) dy = dx
Integrate both sides:
∫(2x/y) dy = ∫dx
Integrating the left side requires a substitution. Let u = y², then du = 2y dy:
∫(2x/u) du = ∫dx
2∫(x/u) du = ∫dx
2 ln|u| = x + C
Replacing u with y²:
2 ln|y²| = x + C
Using the properties of logarithms:
ln|y⁴| = x + C
Exponentiating both sides:
|y⁴| = \(e^{x + C}\)
Since the absolute value is taken, we can remove it and incorporate the constant of integration
y⁴ = \(e^{x + C}\)
Simplifying, let A = \(e^C:\)
y^4 = A * eˣ
Taking the fourth root of both sides:
y = (A * eˣ\()^{1/4}\)
Now we can incorporate the initial condition y(2) = 3
3 = (A * e²\()^{1/4}\)
Cubing both sides:
27 = A * e²
Solving for A:
A = 27 / e²
Finally, substituting A back into the solution
y = ((27 / e²) * eˣ\()^{1/4}\)
Simplifying further
y = (27 * e⁽ˣ⁻²⁾\()^{1/4}\)
Therefore, the solution to the given differential equation with the initial condition y(2) = 3 is
y = (27 * e⁽ˣ⁻²⁾\()^{1/4}\)
To know more about differential equation:
https://brainly.com/question/2273154
#SPJ4
please help ASAP
please
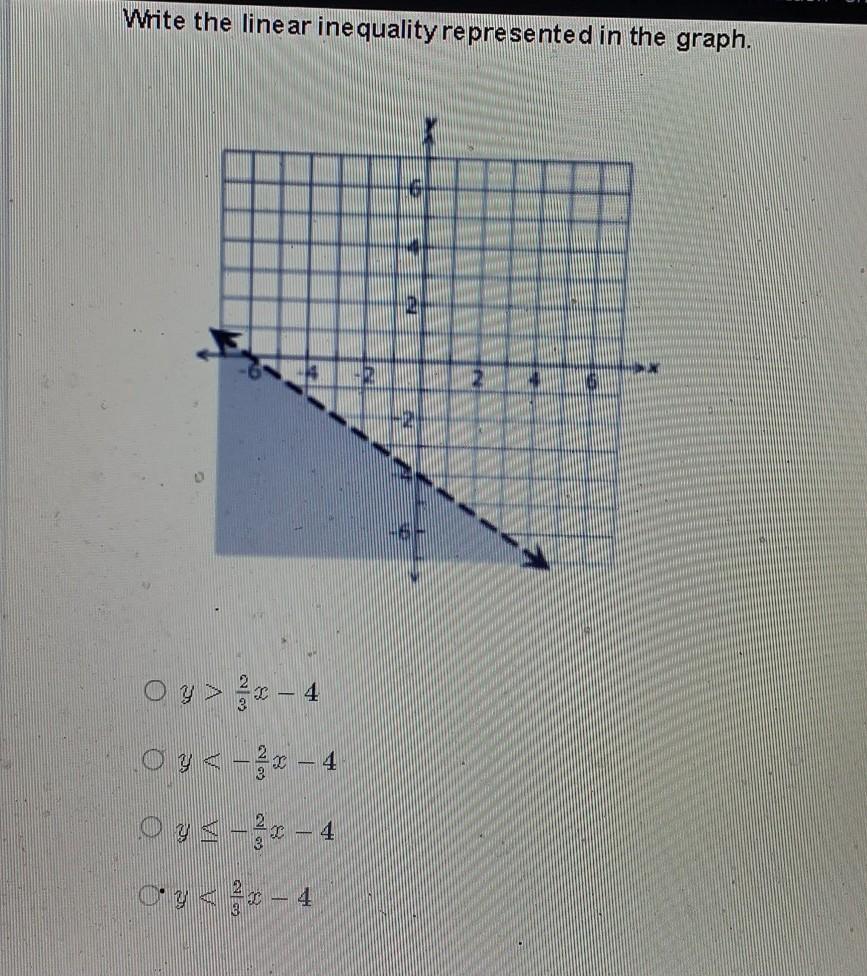
Answers
Answer:
I think its b
Step-by-step explanation:
good luck!!!!
Consider the function where xy U = for (x, y) = (0,0), x² + y² and v= = 0 for all x and y. X 2.1 Show that all partial derivatives of u and v exist at (x, y) = (0, 0), and thus satisfy the Cauchy- Riemann equations. (5) 2.2 Show that is not continuous at (0,0), and hence f is not differentiable at (0, 0). U (5) 2.3 Investigate whether f is analytic or not. (5) 2.4 Investigate whether f has a harmonic complex conjugate or not. (5) 2.5 Show that the function f (x, y) = x² - y² —y is harmonic and determine its harmonic conjugate. - f = u + iv,
Answers
2.1 To show that all partial derivatives of u and v exist at (x, y) = (0, 0) and satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann equations, we need to calculate the partial derivatives of u and v and check their existence and the Cauchy-Riemann conditions.
The function is given as u(x, y) = xy and v(x, y) = x² + y².
Partial derivatives of u:
∂u/∂x = y
∂u/∂y = x
Partial derivatives of v:
∂v/∂x = 2x
∂v/∂y = 2y
All partial derivatives exist at (x, y) = (0, 0) since they are simple functions and do not have any singularities.
Now, let's check if the Cauchy-Riemann equations are satisfied:
∂u/∂x = ∂v/∂y
y = 2y
This equation holds true for all values of y, including y = 0.
∂u/∂y = -∂v/∂x
x = -2x
This equation also holds true for all values of x, including x = 0.
Therefore, all partial derivatives of u and v exist at (x, y) = (0, 0), and they satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann equations.
2.2 To show that f is not continuous at (0, 0) and hence not differentiable at (0, 0), we can examine the behavior of f as (x, y) approaches (0, 0).
The function f(x, y) = u(x, y) + iv(x, y) = xy + i(x² + y²)
As (x, y) approaches (0, 0), both u(x, y) = xy and v(x, y) = x² + y² approach 0. However, f(x, y) = xy + i(x² + y²) approaches 0 + i(0) = i(0) = 0i = 0, which is a different value.
Therefore, f is not continuous at (0, 0), and hence it is not differentiable at (0, 0).
2.3 To investigate whether f is analytic or not, we need to check if it is differentiable in a neighborhood around every point.
Since we have already shown that f is not differentiable at (0, 0), it implies that f is not analytic because differentiability is a necessary condition for analyticity.
2.4 To investigate whether f has a harmonic complex conjugate or not, we need to check if u and v satisfy the Laplace's equation (∇²u = 0 and ∇²v = 0) and if they satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann equations.
The Laplace's equation is not satisfied by u(x, y) = xy because ∇²u = ∂²u/∂x² + ∂²u/∂y² = 0 + 0 ≠ 0.
Therefore, f does not have a harmonic complex conjugate.
2.5 To show that the function f(x, y) = x² - y² - iy is harmonic, we need to demonstrate that it satisfies the Laplace's equation (∇²u = 0 and ∇²v = 0).
For u(x, y) = x² - y², we have ∇²u = ∂²u/∂x² + ∂²u/∂y² = 2 - 2 = 0.
For v(x, y) = -y, we have ∇²v = ∂²v/∂x² + ∂²v/∂y² = 0 + 0 = 0.
Both u and v satisfy the Laplace's equation, indicating that f(x, y) = x² - y² - iy is a harmonic function.
To determine the harmonic conjugate of f, we can integrate the partial derivative of v with respect to x and y, and obtain the imaginary part of the function:
h(x, y) = ∫ (∂v/∂y) dy = ∫ 0 dy = C(y)
Where C(y) is an arbitrary function of y.
The harmonic conjugate of f is given by:
g(x, y) = u(x, y) + ih(x, y) = x² - y² + iC(y)
Therefore, the harmonic conjugate of f(x, y) = x² - y² - iy is g(x, y) = x² - y² + iC(y), where C(y) is an arbitrary function of y.
Learn more about Cauchy-Riemann here -: brainly.com/question/30385079
#SPJ11
To show that all partial derivatives of u and v exist at (x, y) = (0, 0) and satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann equations, we need to calculate the partial derivatives of u and v and check their existence and the Cauchy-Riemann conditions.
The function is given as u(x, y) = xy and v(x, y) = x² + y².
Partial derivatives of u:
∂u/∂x = y
∂u/∂y = x
Partial derivatives of v:
∂v/∂x = 2x
∂v/∂y = 2y
All partial derivatives exist at (x, y) = (0, 0) since they are simple functions and do not have any singularities.
Now, let's check if the Cauchy-Riemann equations are satisfied:
∂u/∂x = ∂v/∂y
y = 2y
This equation holds true for all values of y, including y = 0.
∂u/∂y = -∂v/∂x
x = -2x
This equation also holds true for all values of x, including x = 0.
Therefore, all partial derivatives of u and v exist at (x, y) = (0, 0), and they satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann equations.
2.2 To show that f is not continuous at (0, 0) and hence not differentiable at (0, 0), we can examine the behavior of f as (x, y) approaches (0, 0).
The function f(x, y) = u(x, y) + iv(x, y) = xy + i(x² + y²)
As (x, y) approaches (0, 0), both u(x, y) = xy and v(x, y) = x² + y² approach 0. However, f(x, y) = xy + i(x² + y²) approaches 0 + i(0) = i(0) = 0i = 0, which is a different value.
Therefore, f is not continuous at (0, 0), and hence it is not differentiable at (0, 0).
2.3 To investigate whether f is analytic or not, we need to check if it is differentiable in a neighborhood around every point.
Since we have already shown that f is not differentiable at (0, 0), it implies that f is not analytic because differentiability is a necessary condition for analyticity.
2.4 To investigate whether f has a harmonic complex conjugate or not, we need to check if u and v satisfy the Laplace's equation (∇²u = 0 and ∇²v = 0) and if they satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann equations.
The Laplace's equation is not satisfied by u(x, y) = xy because ∇²u = ∂²u/∂x² + ∂²u/∂y² = 0 + 0 ≠ 0.
Therefore, f does not have a harmonic complex conjugate.
2.5 To show that the function f(x, y) = x² - y² - iy is harmonic, we need to demonstrate that it satisfies the Laplace's equation (∇²u = 0 and ∇²v = 0).
For u(x, y) = x² - y², we have ∇²u = ∂²u/∂x² + ∂²u/∂y² = 2 - 2 = 0.
For v(x, y) = -y, we have ∇²v = ∂²v/∂x² + ∂²v/∂y² = 0 + 0 = 0.
Both u and v satisfy the Laplace's equation, indicating that f(x, y) = x² - y² - iy is a harmonic function.
To determine the harmonic conjugate of f, we can integrate the partial derivative of v with respect to x and y, and obtain the imaginary part of the function:
h(x, y) = ∫ (∂v/∂y) dy = ∫ 0 dy = C(y)
Where C(y) is an arbitrary function of y.
The harmonic conjugate of f is given by:
g(x, y) = u(x, y) + ih(x, y) = x² - y² + iC(y)
Therefore, the harmonic conjugate of f(x, y) = x² - y² - iy is g(x, y) = x² - y² + iC(y), where C(y) is an arbitrary function of y.
Learn more about Cauchy-Riemann here -: brainly.com/question/30385079
#SPJ11
How many separate samples would be needed for a two-factor, independent-measures research study with 2 levels of factor a and 3 levels of factor b?
Answers
The separate samples would be needed for a two-factor, independent-measures is 6.
According to the statement
we have to find that the number of separate samples be required with the help of the given information.
So, For this purpose, we know that the
Sample is a representative part or a single item from a larger whole or group especially when presented for inspection or shown as evidence of quality.
So,
From given information from the statement is :
2 levels of factor a and 3 levels of factor b
And Now, The
Number of samples required = 2*3
Number of sample required = 6.
hence there are the 6 separate samples needed.
So, The separate samples would be needed for a two-factor, independent-measures is 6.
Learn more about Samples here
https://brainly.com/question/13628349
#SPJ4
What is the measure of the unknown angle?
50°
Answers
someone help pls!
4x+3=5x+21

Answers
Answer:
x=-18
Step-by-step explanation:
given that x is an odd integer and 2y is an even integer which of the following must be true
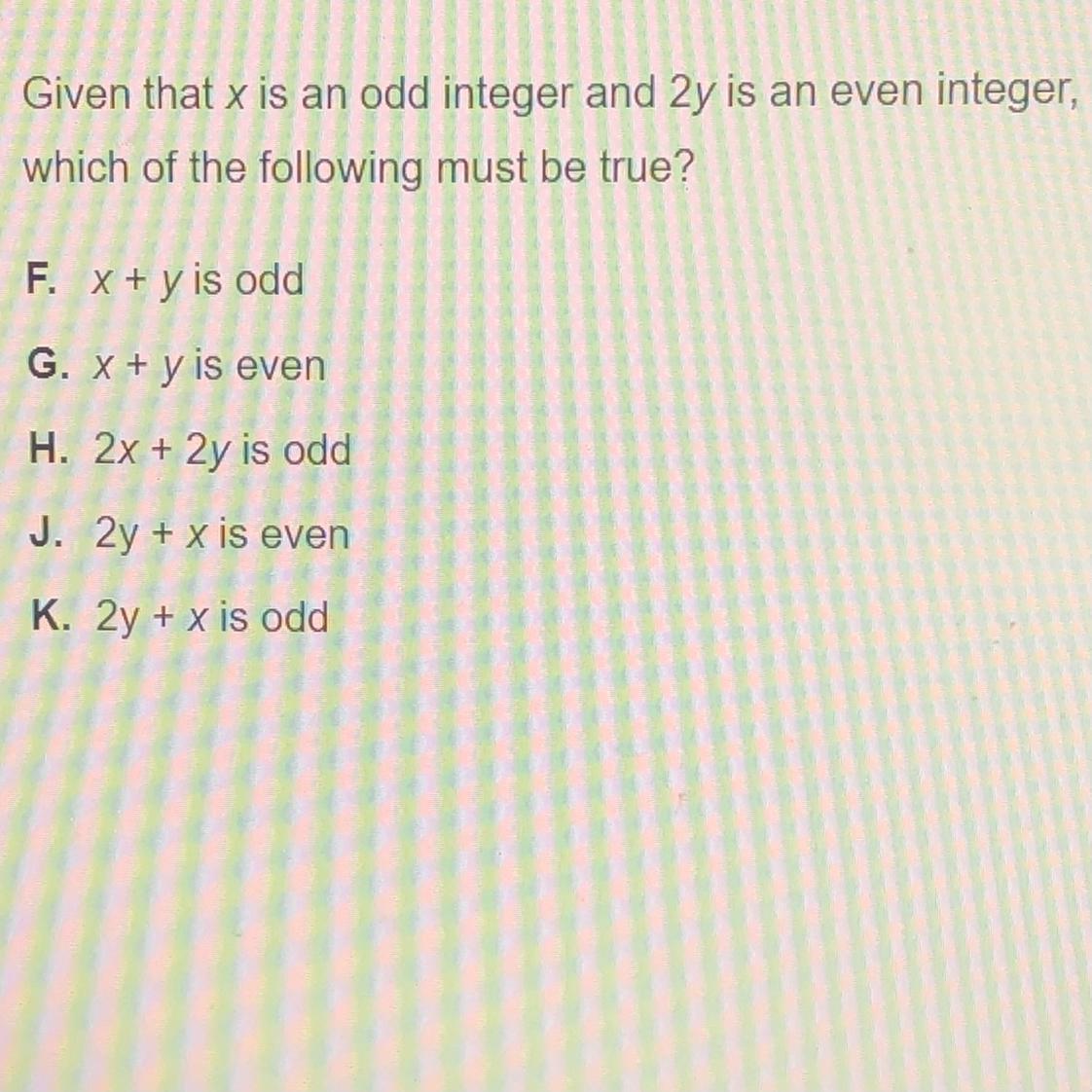
Answers
Answer:
K
Step-by-step explanation:
K
Hope that helps!
If x is an odd integer and 2y is an even integer then K. 2y x is odd.
What are some concepts related to arithmetic operations of odd and even numbers?Odd + Odd = Even.
Odd + Even = Even + Odd = )dd.
Even + Even = Even.
Odd × Odd = Even.
Even × Even = Even.
Odd × Even = Even × Odd = Odd.
Odd ÷ Odd = Even.
Even ÷ Odd = Even Or Odd.
Odd ÷ Even = Fraction/Decimal.
Given, x is an odd integer and 2y is an even integer.
So, y can be even or odd we are not sure.
Therefore, the only option that must be true is 2y + x is odd.
learn more about odd and even numbers here :
https://brainly.com/question/28721864
#SPJ2
on which of the following roads are you least likely to lose traction
Answers
Roads that are well-maintained, dry, and free from hazards are generally less likely to result in traction loss.
The likelihood of losing traction depends on various factors such as road conditions, weather, vehicle type, and driver behavior. However, in general, roads that are well-maintained, dry, and free from debris or hazards are less likely to result in traction loss. Additionally, roads with good grip surfaces, such as asphalt or concrete, tend to provide better traction compared to unpaved or slippery surfaces. It's important to drive cautiously and adapt to the specific conditions of the road to minimize the risk of losing traction.
To know more about traction,
https://brainly.com/question/5039394
#SPJ11
find k so that x-1 is a factor of x^3 -3x^2 + kx - 1
Answers
By the remainder theorem, if p(x) = x³ - 3x² + kx - 1 and x - 1 is a factor p(x), then the remainder upon dividing p(x) by x - 1 is p (1) = 0.
So we have
p (1) = 1³ - 3 • 1² + k - 1 = 0
Solve for k :
1 - 3 + k - 1 = 0
k = 3
A nurse provides a back massage as a palliative care measure to a client who is unconscious, grimacing, and restless. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as indicating a therapeutic response? (Select all that apply.)
A. the shoulders droop
B. the facial muscles relax
C. the RR increases
D. the pulse is within the expected range
E. the client draws his legs into a fetal position
Answers
A nurse provides a back massage as a palliative care measure to a client who is unconscious, grimacing, and restless.
The therapeutic response that the nurse should identify in the client after a back massage includes relaxing of facial muscles and the pulse remaining within the expected range.
Massage is a fundamental nursing measure that is often utilized as part of palliative care for patients. The purpose of back massage is to promote relaxation, improve blood circulation, reduce muscle tension, and alleviate pain, stress, and anxiety. The nursing assessment of the patient before and after the massage is essential to determine its effectiveness as a therapeutic intervention for the patient.
When providing back massage as a palliative care measure to an unconscious, grimacing, and restless client, the nurse should identify several therapeutic responses as follows;
The shoulders droop: The nurse should expect the shoulders of the client to relax during massage therapy. If this occurs, it is a sign that the patient is experiencing relaxation and tension relief.
The facial muscles relax: Relaxation of the facial muscles is a common therapeutic response during back massage. The nurse should observe the patient's face for any signs of relaxation, which may include softening of facial lines, eyelids drooping, or a general expression of peacefulness.
The respiratory rate (RR) decreases: The nurse should expect the client's respiratory rate to decrease during a back massage. This is because relaxation stimulates the parasympathetic nervous system, resulting in decreased respiratory rate, heart rate, and blood pressure.
The pulse is within the expected range: The nurse should expect the client's pulse to remain within the expected range during a back massage. A normal pulse rate is between 60-100 beats per minute for adults. If the pulse remains within this range, it is a sign that the patient is responding positively to the massage therapy.
In conclusion, providing back massage as a palliative care measure to an unconscious, grimacing, and restless client can help to promote relaxation, improve blood circulation, reduce muscle tension, and alleviate pain, stress, and anxiety. The nurse should identify therapeutic responses in the patient during the massage therapy, which may include relaxation of the shoulders, facial muscles, decreased respiratory rate, and pulse remaining within the expected range.
To know more about blood circulation visit:
brainly.com/question/28915450
#SPJ11