Answers
The centripetal force is given by
\(\frac{mv^2}{r}=N sin 18+fs cos 18\)
So, the car's radial acceleration is= 8.16 m/s2.
The car's speed is
\(v=\sqrt{ar} =\sqrt{8.16 X 90}= 27.1 m/s\\\)
So, the speed of the car is 27.1 m/s.
The car can travel around the curve at a maximum speed of 23.7 m/s without skidding.
Examples of static friction are given below.A force called static friction prevents an object from moving along the path. This friction happens when two materials are slid over one another. Conflict is there all around us. For instance, when we walk, our feet are in contact with the ground.
Why is friction either static or dynamic?When two bodies are in touch with one another and at rest, they experience static friction. Friction is what keeps anything from moving while it is motionless. Dynamic friction, also known as kinetic friction, is friction that prevents a body from moving while it is already moving.
To know more about speed visit:-
brainly.com/question/28224010
#SPJ1
Related Questions
A small, 300 gg cart is moving at 1.80 m/sm/s on a frictionless track when it collides with a larger, 5.00 kgkg cart at rest. After the collision, the small cart recoils at 0.810 m/sm/s . Part A What is the speed of the large cart after the collision
Answers
The velocity of the large cart after the collision is approximately 0.0486 m/s in the opposite direction of its initial motion.
We can use the principle of conservation of momentum to find the speed of the large cart after the collision. According to this principle, the total momentum before the collision is equal to the total momentum after the collision.
The momentum (p) of an object is calculated by multiplying its mass (m) by its velocity (v). Therefore, the momentum of the small cart before the collision is:
p_small_before = (mass_small) * (velocity_small) = (0.300 kg) * (1.80 m/s) = 0.540 kg·m/s.
Since the large cart is at rest before the collision, its initial momentum is zero:
p_large_before = 0 kg·m/s.
After the collision, the small cart bounces back at a speed of 0.810 m/s. According to the law of conservation of momentum, the total momentum after the collision should equal the total momentum before the collision. Therefore, the momentum of the small cart after the collision is:
p_small_after = (mass_small) * (velocity_small_after) = (0.300 kg) * (-0.810 m/s) = -0.243 kg·m/s.
The momentum of the large cart after the collision is labeled p_large_after. Since the initial momentum of the large cart is zero and the momentum after the collision is determined by the momentum of the small cart, we can write:
p_large_after = -0.243 kg·m/s.
To find the speed of the large cart after the collision, we divide the momentum by its mass:
velocity_large_after = p_large_after / (mass_large) = (-0.243 kg·m/s) / (5.00 kg) = -0.0486 m/s.
For more such questions on momentum ,
https://brainly.com/question/1042017
#SPJ11
Select the correct answer.
What is the force that can cause two pieces of iron to attract each other?
A.
gravitational force
B.
magnetic force
C.
elastic force
D.
electrostatic force
Answers
Answer:
A. gravitational force always true.
B, C and D could be true under the correct conditions
What is utilization of energy
Answers
Explanation:
Energy utilization focuses on technologies that can lead to new and potentially more efficient ways of using electricity in residential, commercial and industrial settings—as well as in the transportation sector
a device that spreads light into different wavelengths is a what?
Answers
maybe a spectrograph ?
 A penny is dropped off of the top of the Statue of Liberty, which is 93 meters tall. How long will it take for the penny to hit the ground?
Answers
Answer:
About 4.4 seconds
Explanation:
\(h=1/2(gt^{2} )\)
\(t^{2} =\frac{2h}{g}\)
\(t=\sqrt{\frac{2h}{g} }\)
\(t=\sqrt{\frac{2(93)}{9.8} } =\sqrt{18.98} =4.36\)
Hope this helps
A camera takes a properly exposed photo at f/5.6 and 1/250 s. What shutter speed should be used if the lens is changed to f/4.0?
a.1/65 s
b.1/125 s
c.1/250 s
d.1/500 s
e.1/1000 s
Answers
The shutter speed that should be used if the lens is changed to f/4.0 is; Choice D: 1/500 s.
The relationship between the shutter speed and the focal ratio is an inverse relationship.
Ratio of Areas = 5.6²/4²
A1/A2 = 1.96 = 2Since; T1A1 = T2A2
T2 = T1(A1/A2)T2 = 250 × 2 = 500 secondsIn essence; when the focal ratio is reduced as in this case; from f/5.6 to f/4.0; the shutter speed is increased.
Ultimately, the shutter speed of the camera in discuss increases to; 1/500 s.
Read more:
https://brainly.com/question/13083614
As a capacitor is being charged, current flowing into the capacitor will?
Answers
Answer:
the curring flowing into the capracitor will get "stuck" on the plates because they can't get past the insulating dielectric.
Explanation:
You have discovered a planet that is one-quarter the radius of Earth (Rp = 1/4R⊕) and one-half as massive (Mp = 1/2M⊕). How does the gravity on the surface of this planet compare to the gravity on the surface of Earth (Fgp = XFg⊕)?
Answers
The new planet has the radius of only 1/4th of earth and mass of half that of earth. Then , the gravity on the surface of the new planet will be8 times higher than that of earth.
What is gravitational force?The gravitational force is the force by which an object attracts other object into its center of mass. Earth attracts every objects on ots surface to the ground by gravitation.
The force of gravitation is directly proportional to the mass and inversely proportional to the distance or radius of the planet.
g = G m/r²
Where G is the universal gravitational constant.
The new planet has the mass half of that of earth (me) and radius 1/4th of earth.
gn = G me/2 (re/4)²
= G 16 me/2
= 8 ge
Where ge is the gravity by earth and gn that of new planet. The gravitational force of the new planet will be 8 times greater than that of earth.
Find more on gravitational force:
https://brainly.com/question/12528243
#SPJ2
HELPPPPPP!!!! Jupiter has a gravity that is 2.4 times that of Earth. A person has a mass of 60kg. What is the mass of this person on Jupiter?
60 kg
144 kg
600N
1440N
Answers
60
because mass of an object never change
but weight can change for example if it's
mass is 60kg 5he wieght will be 60kg * 9.8m/s²
=588N
HELP ME ASAPPPPPPPPPPP
A penny sinks to the bottom of a wishing well
What type of frictional force is that?
Answers
The frictional force involved when a penny sinks to the bottom of a wishing well is primarily due to viscous drag or fluid friction. As the penny moves through the water, it experiences resistance from the surrounding fluid. This resistance is caused by the frictional forces between the water molecules and the penny's surface.
Which law of thermodynamics does each of the following scenarios violate (if any)?
A machine that can turn 1000J of heat directly into 1000J of electricity
1.
The first law of thermodynamics
2.
The second law of thermodynamics
3.
The third law of thermodynamics
4.
It is allowed
Answers
Answer: The scenario violates the second law of thermodynamics.
Explanation: The second law states that heat cannot be converted into work without some loss of usable energy, and that the amount of usable energy in a closed system will always decrease over time. Therefore, the machine described in the scenario cannot exist because it would violate the second law by converting all of the heat into electricity without any loss of usable energy.
please help me
7. If microsecound = 0.5, how much force must be applied to a spring (spring constant of 0.8 N/m) which is attached to a block of wood (mass = 4.0 kg) in order to just begin to move the block?
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
Your question is quite confusing, particularly the information about microsecond = 0.5.
I'm going to ASSUME that you mean coefficient of static friction μs = 0.5
unfortunately typing a subscript "s" is very difficult and probably leads to such confusion.
I will also ASSUME that the block, and spring, and force vector are all horizontal.
If the force is slowly increased until the block slips, the spring will compress until the force on each end equals the maximum static friction force. As we are not concerned with the compression distance, only the force, we can ignore the spring constant information and simply find the maximum available static friction force.
F = μN
F = μmg
F = 0.5(4.0)(9.8)
F = 19.6 N
Not that it matters, but the spring will have extended or compressed 19.6/0.8 = 24.5 m, which is a very long and very light spring
The highness or lowness of a sound is perceived as
a.
compression.
c.
ultrasound.
b.
wavelength.
d.
pitch.
Answers
Answer:
i think its D
Explanation:
Answer:
The highness or lowness of a sound is perceived as pitch. Pitch is a perceptual property of sound that allows us to distinguish between sounds that have the same loudness and duration, but differ in their frequency content. The pitch of a sound is determined by the frequency of the sound wave, with higher frequencies producing higher pitches and lower frequencies producing lower pitches. The pitch is what makes a sound distinguishable and is important in music, language, and communication.
Which of the following has the greatest momentum? *
(20 Points)
tortoise with a mass of 270 kg moving at a velocity of 0.5 m/s
hare with a mass of 2.7 kg moving at a velocity of 7 m/s
turtle with a mass of 91 kg moving at a velocity of 1.4 m/s
roadrunner with a mass of 1.8 kg moving at a velocity of 6.7 m/s
Answers
Answer:
Tortoise with a mass of 270 kg moving at a velocity of 0.5 m/s
Explanation:
From the question above,
(1) tortoise with a mass of 270 kg moving at a velocity of 0.5 m/s
Mometum = mass×velocity
Momentum = 270×0.5
Momentum = 135 kgm/s
(2) hare with a mass of 2.7 kg moving at a velocity of 7 m/s
Mementum = mass × velocity
Momentum = 2.7×7
Momentum = 18.9 kgm/s
(3) turtle with a mass of 91 kg moving at a velocity of 1.4 m/s
Momentum = mass × velocity
Momentum = 91×1.4
Momentum = 127.4 kgm/s
(4) roadrunner with a mass of 1.8 kg moving at a velocity of 6.7 m/s
Momentum = mass × velocity
Momentum = 1.8×6.7
Momentum = 12.06 kgm/s
From the above, the one with the greatest momentum is tortoise with a mass of 270 kg moving at a velocity of 0.5 m/s
Please help It is Anatomy and Phys
Think about the last time you had your temperature taken. Describe the circumstances that led you to have your temperature taken, including the mechanism by which your temperature was measured (oral thermometer, ear thermometer, etc.), so that given the right equipment, you could demonstrate the technique yourself to another person. What would have been considered an abnormal temperature in that situation?
Answers
Answer:
the last time i had my tempature taken was at disney prings about a week ago -_- they used one of those gun things that dont touch u and the SHOVED me forward so i guess i was fine
Explanation:
Answer:
thermometer
Explanation:
Tim, with mass 73.1 kg, climbs a gymnasium rope a distance of 4.6 m. The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s 2 . How much potential energy does Tim gain? Answer in units of J.
Answers
Answer:
3,295.348Joules
Explanation:
Potential Energy = mass * acceleration due to gravity * height
Given the following
Mass = 73.1kg
Acceleration due to gravity = 9.8m/s²
Distance (Height) = 4.6m
Substitute into the formula;
Potential Energy = 73.1 * 9.8 * 4.6
Potential Energy = 3,295.348Joules
Hence Tim gain 3,295.348Joules of energy
A block of weight 5 N is placed on a horizontal turntable. The maximum friction that can be developed between the block and the turntable is 2 N. If the turntable is rotating at 0.6 revolution per second, what is the greatest distance of the block from the center of rotation so that it does not slip?
Answers
The greatest distance of the block from the center of rotation so that it does not slip is approximately 0.089 meters or 8.9 centimeters.
In order for the block to remain on the turntable without slipping, the frictional force between the block and the turntable must be equal to or less than the maximum friction that can be developed, which is 2 N in this case. The maximum frictional force is given by the product of the coefficient of friction and the normal force.The normal force is equal to the weight of the block, which is 5 N. Therefore, the maximum frictional force is 2 N.
To find the greatest distance of the block from the center of rotation without slipping, we need to consider the centrifugal force acting on the block due to the rotation of the turntable. The centrifugal force is given by the product of the mass of the block, the acceleration due to the rotation (which is equal to the square of the angular velocity times the radius), and the coefficient of friction.
Since the weight of the block is 5 N, the mass can be calculated as 5 N divided by the acceleration due to gravity (approximately 9.8 m/s^2), which gives us a mass of approximately 0.51 kg.
Given that the turntable is rotating at 0.6 revolution per second, the angular velocity can be calculated as 2π times the frequency, which gives us approximately 3.77 rad/s.
Let's assume the greatest distance of the block from the center of rotation is "r" meters.
The centrifugal force is then given by m * (ω^2) * r, and this force must be equal to or less than the maximum frictional force, which is 2 N.
Therefore, we can write the equation:
m * (ω^2) * r ≤ 2 N
Substituting the values we calculated:
0.51 kg * (3.77 rad/s)^2 * r ≤ 2 N
Simplifying the equation, we find:
r ≤ 0.089 m
For more such questions on distance
https://brainly.com/question/26550516
#SPJ8
what country is this
Answers
Answer:
USA
NAMELY UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
america
Explanation:
because why not
A shell is fired from a mortar over level terrain. The firing speed is 59 m/s and the mortar is aimed 70° above the horizontal. Find the range of the shell.
Answers
Answer:
228.23m
Explanation:
Vy=59sin70=55.44m/s
x=V0t+1/2at^2
0=55.44t-4.9t^2
t=11.31s
Vx=59cos70=20.18m/s
Range=20.18*11.31=228.23m
given an angle of incidence of ice as 40 degree and angle of refraction of 25.9 degree what is the refractive index of the ice
Answers
Answer:sin40∘=0.643) Hint: The relationship of angle of incidence and angle of refraction at interface of two media is given by Snell's law.
Explanation:
A wave with a frequency of 17 Hz has a wavelength of 5 meters. At what speed will this wave travel?
Answers
Answer:
85
Explanation:
soln
given that;
frequency=17Hz
wavelength=5m
speed?
formula for wavelength is;
wavelength= speed/frequency
then ; making v the subject formula
we have that v=wavelength*frequency
v=17*5=>85ms
ball is dropped from a height of 45 m on a floor. If at each collision with the floor the ball loses the nineteen percent of kinetic energy then the speed of the ball just after striking the floor second time, is (g = 10 m s–2)
Answers
The speed of the ball just after striking the floor a second time, is 30.0 m/s.
Initial height (h) = 45 m
Acceleration due to gravity (g) = 10 m/s²
Energy loss per collision (k) = 19% = 0.19
At each collision with the floor, the ball loses 19% of its kinetic energy, which means the remaining kinetic energy is 81% (100% - 19%).
When the ball reaches the floor for the first time, it has converted all its potential energy into kinetic energy. So, the initial kinetic energy (K₁) is equal to the potential energy (PE) at the initial height:
K₁ = PE = mgh
Now, let's consider the ball's motion from the initial height to the first collision point. The ball undergoes free fall, so we can use the equations of motion:
h = (1/2)gt²
t = sqrt(2h/g)
Using this time, we can calculate the initial kinetic energy (K₁):
K₁ = mgh = m * 10 m/s² * 45 m
Since the ball loses 19% of its kinetic energy at each collision, the remaining kinetic energy is 81%:
K₂ = K₁ * 0.81
The ball then rebounds elastically from the floor, conserving both kinetic energy and speed. Therefore, the speed just after striking the floor for the second time (v₂) is equal to the speed just before the first collision (v₁):
v₂ = v₁
To find the speed just before the first collision (v₁), we can use the equation of motion:
v = gt
Substituting the time (t) we found earlier, we have:
v₁ = g * sqrt(2h/g)
Now, we can substitute the known values and calculate the speed just after striking the floor for the second time:
v₁ = 10 m/s² * sqrt(2 * 45 m / 10 m/s²)
v₂ = v₁
By evaluating the expression, we find:
v₁ ≈ 30.0 m/s
v₂ ≈ 30.0 m/s
Therefore, the speed of the ball just after striking the floor for the second time is 30.0 m/s.
For more such questions on kinetic energy:
https://brainly.com/question/20658056
##SPJ8
An air puck of mass 0.030 kg is tied to a string
and allowed to revolve in a circle of radius 1.2
m on a frictionless horizontal surface. The
other end of the string passes through a hole
in the center of the surface, and a mass of
2.7 kg is tied to it, as shown. The suspended
mass remains in equilibrium while the puck
revolves on the surface. What is the magnitude of the force that
maintains circular motion acting on the puck?
The acceleration due to gravity is 9.81 m/s^2 answer in Newtons.
Part 2: What is the linear speed of the puck?
Answer in units of m/s.
Answers
9.8 N is the magnitude of the force that maintains circular motion acting on the puck.
32.53 m/sec is the linear speed of the puck.
What is force?The term "force" has a specific meaning in science. At this level, it is quite acceptable to refer to a force as a push or a pull. An item does not have a force inside of it or within it. Another item applies a force to another. The concept of a force is not restricted to living or non-living entities. An external force is an agent that has the power to alter the resting or moving condition of a body. It has a direction and a magnitude.
As we know, from free body diagram, when the system is in equillibrium, the force acting on the puck on the table is as follows:
When the air puck of mass is revolving round the circle, then the tension (T) in the top string and the bottom of the string is same.
F = T
F = 9.8 N
Now, calculate the velocity of the puck:
From the given data, the air puck moves in a circular path. Hence, the tension in the top string is equal to the centripetal force acting on the puck.
Thus, the expression for the tension in the top string is as follows:
T = mv² / R
The velocity of the puck is as follows:
Mg = mv² / R
v² = MgR / m
v² = (2.7 × 9.8 × 1.2 ) / 0.030
v² = 1058.4
v = \(\sqrt{1058.4}\)
v = 32.53 m/sec
To know more about force refer to:
https://brainly.com/question/12785175
#SPJ1
HELP ME PLS THIS IS 8th grade science due TOMORROW

Answers
library to coffee shop - 10 km west
mall to library- 40 km east
post office to coffee - 30 km west
Forgetting takes place only in short-term memory. Please select the best answer from the choices provided T F
Answers
Answer:
false
Explanation:
Answer:
false
Explanation:
edge
I have two problems and i need help please..
First one: A mass of 0.05KG of the air is heated at constant pressure of 2 bar until the volume is occupied is 0.0658 m^3. Calculate the supplied heat and the workdone if the initially temperature of the air is 130 C.?
The second and the last one: 1 KG of nitrogen is compressed reversibly and isothermally from 1.01 bar, 20 C to 4.2 bar. Calculate the workdone and the heat Flow during the process Assuming nitrogen to be a perfect gas and molar mass 28kg/kmol
Answers
For the first one, W = 7.3 kJ, Q = 25.83kJ
For the second one, W = Q = 124KJ
First One:
Parameters given are:
Mass m = 0.05kg
\(V_{2}\) = 0.0658 \(m^{3}\)
Since the pressure is constant, \(P_{1} = P_{2} = 2bar\)
While \(T_{1} = 130\)°C
Convert degree Celsius to degree kelvin
Temperature = 273 + 130 = 403 K
Before we can get the work done, we need to calculate the initial volume \(V_{1}\) by using Ideal gas general formula.
\(P_{1}V_{1} = mRT_{1}\)
Make \(V_{1}\) the subject of formula
\(V_{1}\) = \(mRT_{1}\) / \(P_{1}\)
\(V_{1}\) = (0.05 x 287 x 403) / (2 x \(10^{5}\))
\(V_{1}\) = 0.0289\(m^{3}\)
From the table, specific volumes are:
\(u_{1}\) = 0.578\(m^{3}\)kg
\(u_{2}\) = 1.316\(m^{3}\)kg
Work done can be calculated by using the below formula
W = P( \(u_{2}\) - \(u_{1}\) )
W = 2 x \(10^{5}\)( 1.316 - 0.578)
W = 147600 J/kg
The Total work done = 147600 x 0.05 = 7380J = 7.3 kJ
To calculate the heat supplied by using the heat formula
Q = m\(C_{p}\)( \(T_{2} - T_{1}\)), we need to calculate for final temperature \(T_{2}\) and also check the table for
where \(C_{p}\) = 1.005
we can calculate for \(T_{2}\) by using Ideal gas formula
\(P_{2}V_{2} = mRT_{2}\)
make \(T_{2}\) the subject of formula
\(T_{2}\) = PV/mR
\(T_{2}\) = (2 x \(10^{5}\) x 0.0658) / (0.05 x 287)
\(T_{2}\) = 917 K
Substituting \(T_{2}\) and other parameters into the formula
Q = m\(C_{p}\)(\(T_{2} - T_{1}\))
Q = 0.05 x 1.005 ( 917 - 403)
Q = 25.83 KJ
Second one
From the question, the following parameters are given
mass m = 1kg
Molar M = 28kg/mol
Since the system is compressed reversibly and isothermally,
\(T_{2}\) = T = 20°C
\(P_{1}\) = 1.01 bar
\(P_{2}\) = 4.2 bar
To calculate both heat and work done, we will use the formula below
W = RTln\(P_{1}\)/\(P_{2}\)
But R = Ro/M
R = 8314/28
R = 297 J/kg.k
W = 297 x 293 x ln(1.01/4.2)
W = - 124kJ / kg
We can therefore conclude that the work input during the process is
124 KJ While the heat produced is also 124 KJ because W = Q
Learn more Here: https://brainly.com/question/20382572
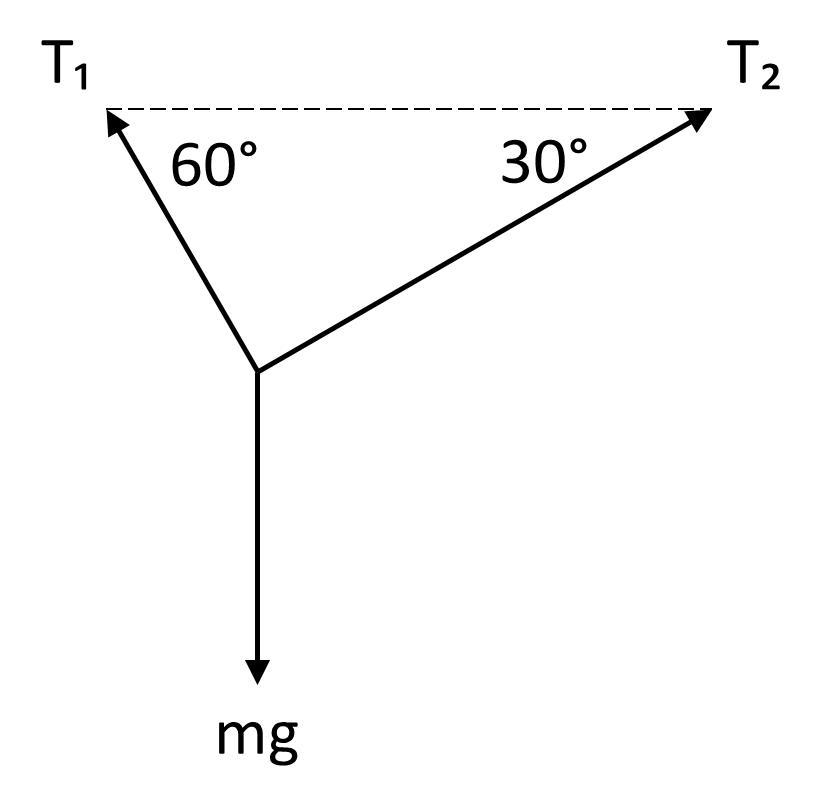
A body weighing 8 N is supported by two cables whose voltages T1 and T2 form angles of 60 ° and 30 ° with the ceiling. How much are these tensions worth? Choose the correct option. Select one: a. 4N and 7N b. 5N and 7N c. 4N and 10N
Answers
Answer:
a. 4N and 7N
Explanation:
Draw a free body diagram.
Sum of the forces in the x direction:
∑F = ma
T₂ cos 30° − T₁ cos 60° = 0
T₂ cos 30° = T₁ cos 60°
T₂ (½√3) = T₁ (½)
T₁ = T₂ √3
Sum of the forces in the y direction:
∑F = ma
T₂ sin 30° + T₁ sin 60° − mg = 0
T₂ sin 30° + (T₂ √3) sin 60° − mg = 0
½ T₂ + 1.5 T₂ − mg = 0
2 T₂ = mg
T₂ = 4 N
T₁ = 4√3 N
T₁ ≈ 7 N
velocity equations solve:
15, km over second
find the m/s
and find the km/h
Answers
The 15 km/s velocity is equivalent to 15000 m/s and 54000 km/h.
Velocity is a vector quantity. It consist both a direction and a magnitude. The magnitude of velocity is called speed. Its S.I. unit is a meter/second. It also has other units like Km/h and Km/s. Its dimensional formula is [\(LT^{-1}\)].
Given in the question
Velocity is 15 Km over a second
We can infer from the given value that the body moves 15 km per second.
1 Km = 1000 m
1 Km × 15 = 15 × 1000 m
So 15 Km = 15000 m
Hence we can say that the body travels 15000 meters in a second.
As a result, its velocity in m/s is 15000 m/s.
Now
15 kilometers can be covered in 1 second.
Distance traveled in 3600 seconds = 3600 × 15 Km
So the total distance traveled in 3600 seconds is 54000 kilometers.
Also 3600 seconds = 1 hour
In other words, The body travels 54000km in 1 hour, hence its velocity is 54000 km/h.
Therefore, the 15 km/h velocity is equal to 15000 m/s and 54000 km/h.
LEARN MORE ABOUT VELOCITY HERE:
https://brainly.com/question/6504879
#SPJ9
6.
A runner completed the 100.-meter dash in
10.0 seconds. Her average speed was
A) 10.0 m/s
B) 1,000 m/s
C) 0.100 m/s
D) 100 m/s
Answers
Answer:
A) 10.0 m/s
Explanation:
the formula for average speed is v=d/t
the distance is 100 meters
The time is 10.0 seconds
so v=100m/10.0s
= 10.0m/s
so the runners average speed was 10.0m/s
The average speed of the runner is equal to 10.0 m/s. Therefore, option (A) is correct.
What is speed?The speed of a body can be described as the distance covered in a definite time interval. The average speed can be defined as a scalar parameter as it possesses magnitude with no direction.
The speed can be determined from the ratio of the distance traveled by the object to the time taken to travel that distance.
The speed of any object can be calculated from the formula equation mentioned below:
Speed = total distance /time taken
Given, the distance covered by the runner = 100 m
The time taken by the runner, t = 10.0 s
The average speed of the runner can be calculated from the formula as shown below:
Speed = 100/10 = 10 m/s
Therefore, the average speed of the runner is 10.0 m/s.
Learn more about the speed, here:
brainly.com/question/12322912
#SPJ2
How much potential energy is stored in a spring that is stretched 15 cm by a force of 72 N?
Answers
Answer:
10,800
Explanation:
The formula is MGH I hop this helps