A negative charge -Q is placed inside the cavity of a hollow metal solid. The outside of the solid is grounded by connecting a conducting wire between it and the earth. Is any excess charge induced on the inner surface of the metal? Is there any excess charge on the outside surface of the metal? Why or why not? Would someone outside the solid measure an electric field due to the charge -Q? Is it reasonable to say that the grounded conductor has shielded the region outside the conductor from the effects of the charge -Q? In principle, could the same thing be done for gravity? Why or why not?
Answers
Answer:
a) + Q charge is inducce that compensates for the internal charge
b) There is no excess charge on the external face q_net = 0
c) E=0
Explanation:
Let's analyze the situation when a negative charge is placed inside the cavity, it repels the other negative charges, leaving the necessary positive charges to compensate for the -Q charge. The electrons that migrated to the outer part of the sphere, as it is connected to the ground, can pass to the earth and remain on the planet; therefore on the outside of the sphere the net charge remains zero.
With this analysis we can answer the specific questions
a) + Q charge is inducce that compensates for the internal charge
b) There is no excess charge on the external face q_net = 0
c) If we create a Gaussian surface on the outside of the sphere the net charge on the inside of this sphere is zero, therefore there is no electric field, on the outside
d) If it is very reasonable and this system configuration is called a Faraday Cage
e) We cannot apply this principle to gravity since there are no particles that repel, in all cases the attractive forces.
Related Questions
Descriptions of the sky at various locations on Earth
Answers
Sulfur bonds with Beryllium in an ionic bond to create the stable compound Beryllium Sulfide. After the bond occurs, what is the charge of the Sulfur ion?
Answers
Answer:
S²⁺
Explanation:
Beryllium is in group 2, so it has a charge of 2+. So the S ion has to have a charge of 2-.
3. An object of mass 8 kg is sliding down a friction lessinclined plane of length 11 m that makes an angleof 70 deg with the horizontal. Calculate thework done by gravitational force as the objectslides from the top of the inclined plane to theground. (1 point)A. 099.045 JB. O1135.872 JC.810.391 JD.499.917

Answers
Given
Mass of the object, m=8 kg
Length of the inclined plane, l=11 m
Angle of inclination,
\(\theta=70^o\)To find
Calculate the work done by gravitational force as the object slides from the top of the inclined plane to the
ground.
Explanation
The height of the ramp
\(h=lsin\theta=11sin70^o\)The work done by gravitational force,
\(\begin{gathered} W=mgh \\ \Rightarrow W=8\times9.8\times11sin70^o \\ \Rightarrow W=810.390J \end{gathered}\)Conclusion
The work done is C.810.391
What is the difference between classical mechanics and quantum mechanics?
Answers
Classical mechanics describes the motion of objects on a macroscopic scale, while quantum mechanics deals with the behavior of particles on a microscopic scale. Classical mechanics is deterministic, meaning that it predicts precise outcomes based on initial conditions, while quantum mechanics is probabilistic, providing probabilities of different outcomes. Classical mechanics follows the principle of causality, where every effect has a specific cause, whereas quantum mechanics introduces inherent uncertainty and wave-particle duality. Classical mechanics is well-suited for describing everyday objects, while quantum mechanics is necessary to explain the behavior of particles at the atomic and subatomic levels.
~~~Harsha~~~
classical mechanics is the branch of physics that deals with the motion of everyday objects like balls, cars, and planets.
quantum mechanics is a branch of physics that focuses on the behavior of very small particles, such as atoms and subatomic particles like electrons.
Calculate the potential difference across a 25-Ohm. resistor if a 0.3-A current is flowing through it.
V
Answers
Answer:7.5V
Explanation:
Ohm's law, V=IR
so, V=0.3×25
V=7.5V
Answer:
7.5 V
Explanation:
Rubbing glass and silk together is an example of applying a charge throughA. Friction B. Translation C. Induction D. Conduction
Answers
Answer: A. Friction
Explanation:
When glass is rubbed against silk, there is friction between both materials. Thus, the charge acquired is through friction. The correct option is
A. Friction
PLEASEEEEE THIS A TIMED TESTTTTTTTTT
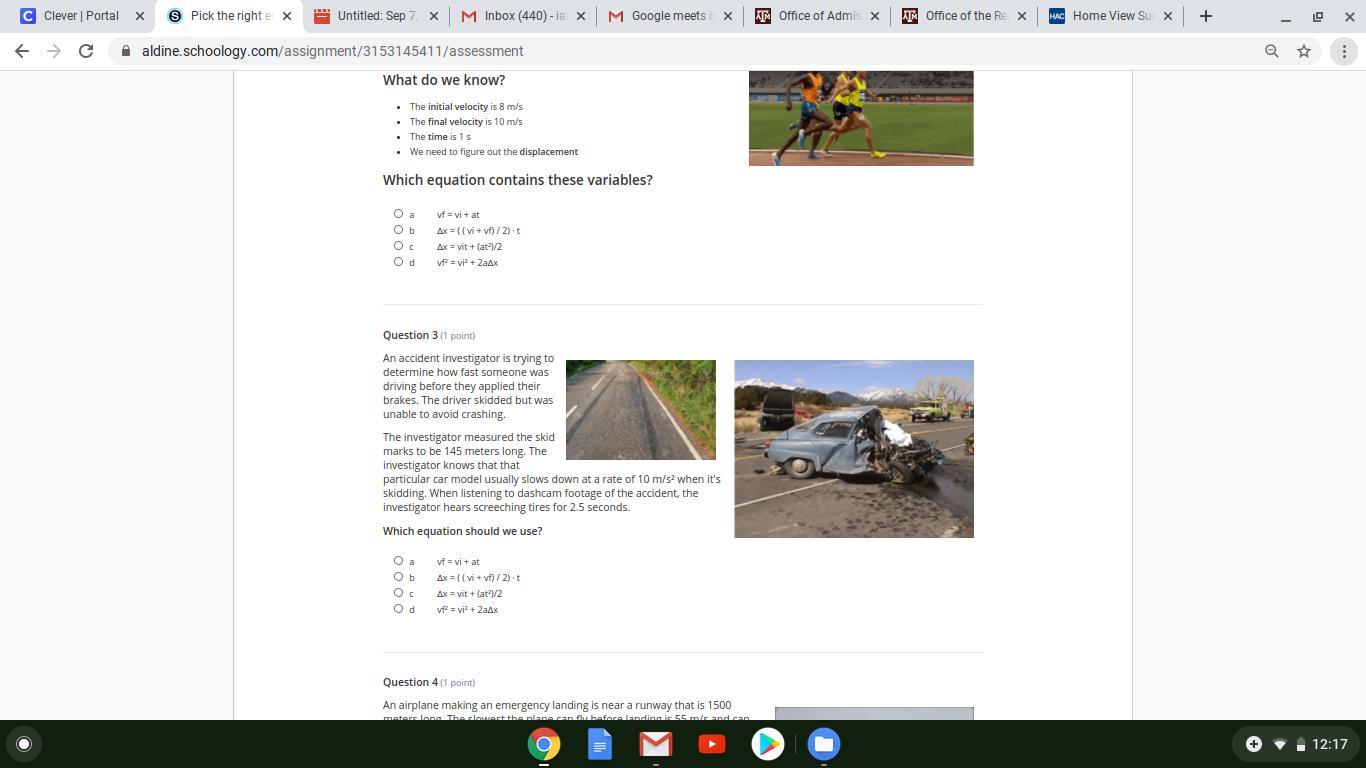

Answers
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Answer:
that car got obliterated almost like the day my uncle said come with me
Explanation:
the outcome was not good
What is the density of a sample of charcoal with a mass of 3.0 g and a volume of 10 cm³?
A. 0.3 g/cm³
B. 3.3 g/cm³
C. 7 g/cm³
D. 30 g/cm³
Answers
The carbon has a mass of 3.0 g and a volume of 10 cm³. So we will calculate the density. The formula to calculate its density is:
d = m/v
We substitute the data in the formula and solve:
d = 3.0 g/10 cm³
d = 0.3 g/cm³
Therefore the density of the carbon sample is 0.3 g/cm³. Opction "A".
Skandar
PLEASE ANSWER FASG I WILL MARK BRAINELIST PLEASEEEEE
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom determines the species of the atom, i.e., the element to which the atom belongs. An atom has the same number of protons and neutrons. But the electron number cannot be used instead because (5 points)
a. electrons are not within the nucleus
b. electrons are negatively charged
c. electrons can be removed from or added to an atom
d. electrons are lighter than protons
Answers
The electron number cannot be used instead because electrons can be removed from or added to an atom (option C)
Why the electron number cannot be used instead?The element of an atom is determined by its proton count, while the electron count can exhibit variability. Take, for instance, a sodium atom, which encompasses 11 protons and 11 electrons. However, it has the capacity to relinquish one electron, transforming into a sodium ion housing only 10 electrons.
This occurs due to the relatively loose binding of electrons to the nucleus, enabling their removal through the influence of an electric field or alternative mechanisms.
Learn about electron here https://brainly.com/question/13998346
#SPJ1
Compare the weight of a 60 kg person on the earth with the weight of the same person on
the moon. Then, describe a quick (but very costly) way for dieters
at NASA to lose weight.
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
The formula for weight is
W = mg, where
W = the weight of the object or person
m = mass of the object or person
g = acceleration due to gravity
Now, we're given the mass of the person to be 60 kd, and thus, the weight of that person would be
W = 60 * 9.81
W = 588.6 N
On the surface of the moon, the weight of the person would be
W = 60 * 1.625
W = 97.5 N
Therefore, the weight of the person on both surfaces are 588.6 and 97.5 respectively
Ayudaaa :(
Calcula la resistencia total del siguiente circuito eléctrico.

Answers
817 cm3 at 80.8 kPa to 101.3 kPa: __________ cm3 (No temp. change)
Answers
The final volume of the gas, when the pressure changes from 80.8 kPa to 101.3 kPa at constant temperature, is approximately 652.9 cm³.
To solve this problem, we can use Boyle's Law, which states that the pressure and volume of a gas are inversely proportional at constant temperature.
Boyle's Law can be represented by the equation: P₁V₁ = P₂V₂
Where P₁ and V₁ are the initial pressure and volume, and P₂ and V₂ are the final pressure and volume.
Given:
Initial volume, V₁ = 817 cm³
Initial pressure, P₁ = 80.8 kPa
Final pressure, P₂ = 101.3 kPa
We need to find the final volume, V₂.
Using Boyle's Law equation, we can rearrange it to solve for V₂:
V₂ = (P₁V₁) / P₂
Plugging in the given values:
V₂ = (80.8 kPa * 817 cm³) / 101.3 kPa
Simplifying the expression:
V₂ ≈ 652.9 cm³
Therefore, the final volume of the gas, when the pressure changes from 80.8 kPa to 101.3 kPa at constant temperature, is approximately 652.9 cm³.
for more questions on volume
https://brainly.com/question/14197390
#SPJ8
In a nuclear power plant, the nuclear reaction is kept from going critical by keeping the rate of reaction safe.
How do the control rods figure into this?
A. The control rods absorb the excess heat produced in the reaction.
B. The control rods absorb excess neutrons, keeping them from causing too many uranium atoms to split too quickly.
C. The control rods absorb excess uranium atoms so that the reaction doesn't happen too quickly.
D. The control rods provide additional neutrons to keep the reaction going.
Answers
Answer:
B. The control rods absorb excess neutrons, keeping them from causing too many uranium atoms to split too quickly
Answer:
The control rods absorb excess neutrons, keeping them from causing too many uranium atoms to split too quickly.
Explanation:
I took the test before.
You can see my other article just search in search engine with: Learningandassignments diy4pro
Click on my site and find these related article post:
Nuclear Energy- Quiz
Hope it helps.
#diy4pro
A 148 g ball is dropped from a tree 11.0 m above the ground. With what speed would it hit the ground
Answers
Answer:
14.68m/s
Explanation:
As per the question, the data provided is as follows
Mass = M = 0.148 kg
Height = h = 11 m
Initial velocity = U = 0 m/s
Final velocity = V
Gravitational force = F
Mass = M
Based on the above information, the speed that hit to the ground is
As we know that
Work to be done = Change in kinetic energy
\(F ( S) = (\frac{1}{2} ) M ( V^2 - U^2 )\)
\(M g h = (\frac{1}{2} ) M ( V^2 - U^2 )\)
\(g h = (\frac{1}{2} ) ( V^2 - U^2 )\)
\(V^2 - U^2 = 2gh\)
\(V^2 - 0 = 2gh\)
\(V = \sqrt{2 g h}\)
\(= \sqrt{2\times9.8\times11}\)
= 14.68m/s
The mass of Saturn is 5.68 x 1026 kg, and use an orbital radius of 3.00 x 105 km. (G = 6.67 × 10-11 N ∙ m2/kg2). Find the orbital speed of an ice cube in the rings of Saturn.
Answers
The orbital speed of an ice cube in the rings of Saturn is determined as 355,366.5 m/s.
What is orbital speed?
The orbital speed of an astronomical body or object is the speed at which it orbits around the center of mass of the most massive body.
Orbital speed of ice cube in the rings of SaturnThe orbital speed of ice cube in the rings of Saturn is calculated as follows;
v = √GM/r
where;
G is universal gravitation constantM is mass of Saturnr is the distance of the ice cubev = √(6.67 x 10⁻¹¹ x 5.68 x 10²⁶)/(3 x 10⁵)
v = 355,366.5 m/s
Thus, the orbital speed of an ice cube in the rings of Saturn is determined as 355,366.5 m/s.
Learn more about orbital speed here: https://brainly.com/question/22247460
#SPJ1
Which value is equivalent to 178 centimeters?
Answers
Answer:
5.8399
Explanation
work:
176cm
1cm=0.39 in
1cm=0.39x178=178cm=70.07in
70.0787/12=5.8399
Answer:
1.78 meters
Explanation:
It's what you get when you convert it to meters in search
An aeroplaneflying above groundnd490m with 100 meterpersecond how far on ground it will strike
Answers
The airplane will strike the ground at a horizontal distance of 490 meters.
To determine how far the airplane will strike on the ground, we need to consider the horizontal distance traveled by the airplane during its flight.
The horizontal distance traveled by an object can be calculated using the formula:
Distance = Speed × Time
In this case, the speed of the airplane is given as 100 meters per second and the time it takes to cover the distance of 490 meters is unknown. Let's denote the time as t.
Distance = 100 m/s × t
Now, to find the value of time, we can rearrange the equation as follows:
t = Distance / Speed
t = 490 m / 100 m/s
t = 4.9 seconds
Therefore, it takes the airplane 4.9 seconds to cover a horizontal distance of 490 meters.
Now, to calculate the distance on the ground where the airplane will strike, we can use the formula:
Distance = Speed × Time
Distance = 100 m/s × 4.9 s
Distance = 490 meters
It's important to note that this calculation assumes a constant speed and a straight flight path. In reality, various factors such as wind conditions, changes in speed, and maneuvering can affect the actual distance traveled by the airplane.
for more questions on horizontal distance
https://brainly.com/question/29147679
#SPJ8
Now attach the 100 g mass to spring 1. Play the simulator. Using the stopwatch, measure the time for 10 complete cycles, (starting from down, lowest position, and then up, then hitting down again: is an example of one complete cycle). Calculate the measured period by dividing the total time by 10. We will call this value Tz. Pause the simulator. Remove the 100 grams mass from the hook of the spring.
Answers
By attaching a mass of 100 g too spring 1. Play the simulator. Measure the duration of the stopwatch for 10 full cycles. The measured period by dividing the total time by 10 is 2 seconds.
The period of oscillation of the mass on spring 1, you would need to measure the time it takes for the mass to complete 10 complete cycles. You can do this by starting a stopwatch when the mass is in the down position and stopping the stopwatch when the mass returns to the down position after completing 10 cycles. Once you have measured the total time for 10 complete cycles, you can calculate the period by dividing the total time by 10. For example, if the total time for 10 complete cycles is 20 seconds, then the period would be 20 seconds / 10 = 2 seconds. We will call this value Tz.
After measuring the period of oscillation of the mass on spring 1, you should pause the simulator and remove the mass from the hook of the spring. This will allow you to perform any additional measurements or calculations without interference from the mass.
To know more about period please refer: https://brainly.com/question/12421962
#SPJ4
A cylinder of metal has the weight of 20 N hanging from a spring scale. Upon being submerged in water, the cylinder now has an apparent weight on the spring scale of 12 N. What is the buoyant force on the piece of metal?
Answers
This question involves the concepts of buoyant force and the weight of an object.
The buoyant force on the piece of metal is "8 N".
The apparent weight of the piece of metal is given by the following formula:
Apparent Weight = Actual Weight - Buoyant Force
Buoyant Force = Actual Weight - Apparent Weight
Buoyant Force = 20 N - 12 N
Buoyant Force = 8 N
Learn more about buoyant force here:
brainly.com/question/21990136?referrer=searchResults
The attached picture illustrates the buoyant force.

Refer to the picture!
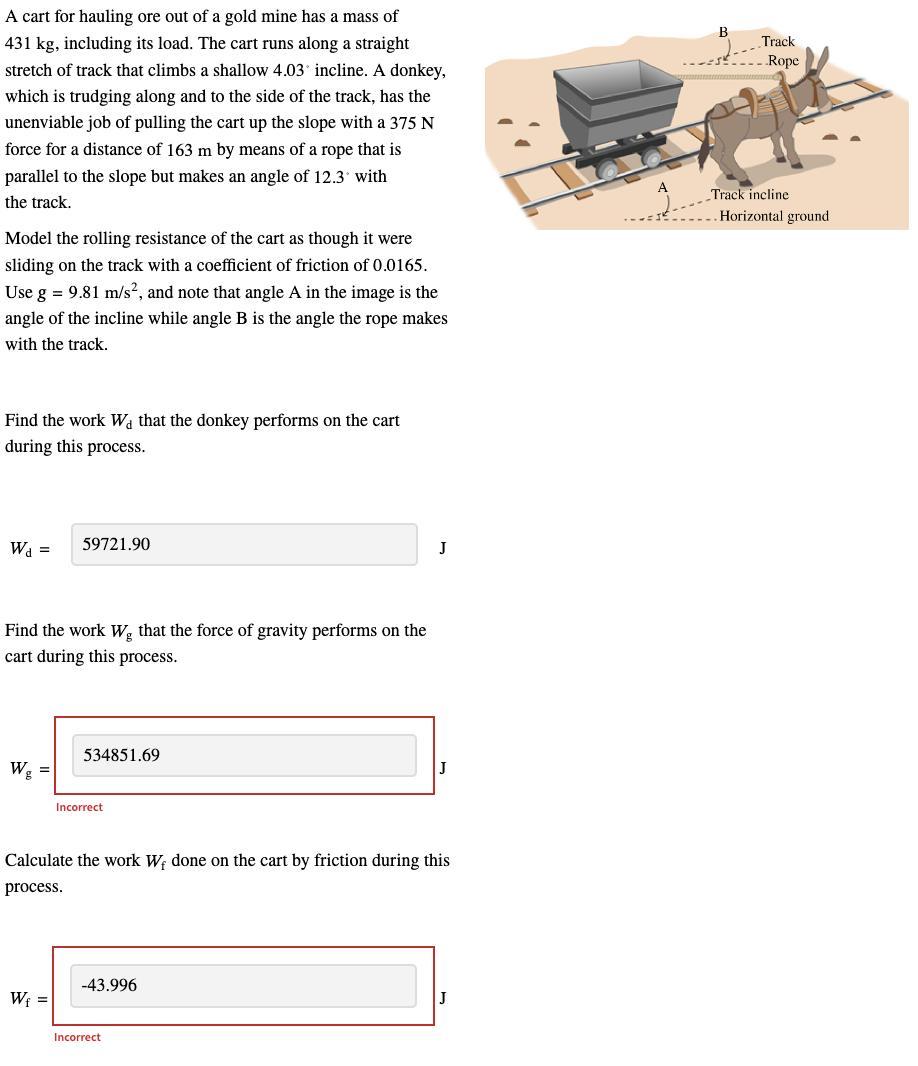
Answers
(a) The work done by the donkey on the cart is 59,721.9 J.
(b) The work done by the force of gravity on the cart is -48,434.87 J.
(c) The work done on the cart by friction during this time is 11,315.12 J.
What is the work done by the donkey on the cart?(a) The work done by the donkey on the cart is calculated as follows;
Wd = Fd cosθ
where;
F is the applied force by the donkeyd is the displacementθ is the angle of inclinationWd = 375 N x 163 m x cos(12.3)
Wd = 59,721.9 J
(b) The work done by the force of gravity on the cart is calculated as;
Wg = Fg x d x cosθ
Where;
Fg is the force of gravityd is the displacementθ is the angle between the force of gravity and displacementθ = 90⁰ + 4.03⁰ = 94.03⁰
Wg = (431 kg x 9.81 m/s²) x 163 m x cos (94.03)
Wg = -48,434.87 J
(c) The work done on the cart by friction during this time is calculated as;
Wf = Ff x d x cosθ
where;
Ff is the force of friction;Ff = μmg cosθ
Ff = 0.0165 x 431 kg x 9.81 x cos (4.03)
Ff = 69.59 N
Wf = 69.59 x 163 x cos (4.03)
Wf = 11,315.12 J
Learn more about work done by gravity here: https://brainly.com/question/15352390
#SPJ1
Guys pls I need help with this question anyone plsss help it will be appreciated

Answers
Answer:
I think it is A.
Explanation:
Word has a meaning similar to obesity?
Fatness
Best definition for corpulence.
The state of being fat
A condition characterized by abnormal or excessive fat accumulation.
Treatable by a medical professional
Does diagnosis require lab test or imaging?
Doesn't require lab test or imaging
Time taken for recovery
Can last several years or be lifelong
Condition Highlight
Family history may increase likelihood for some types
The energy in electron-volts) for a photon with awavelength 724.4 nm is:
Answers
Use the Planck expression to find the energy of a photon.
\(E=hf\)Where h = 6.63x10^-34 J*s and f = c/lambda.
\(\begin{gathered} E=6.63\times10^{-34}J\cdot s\cdot\frac{c}{\lambda}=6.63\times10^{-34}J\cdot s\cdot\frac{3\times10^8\cdot\frac{m}{s}}{724.4\times10^{-9}m} \\ E=2.75\times10^{-19}J \end{gathered}\)Now, transform the energy from Jules to electron-volts. We know that 1 electron-volt equals 1.60x10^-9 J.
\(E=2.75\times10^{-19}J\cdot\frac{1eV}{1.6\times10^{-19}J}=1.72eV\)Therefore, the energy of the photon with the given wavelength is 1.72 eV.
6. An object accelerates from rest to 70 m/s in 3.5 s. What is the acceleration of the object?
Answers
Answer:
The acceleration of the object is 20 meters per second square = 20 m/s^2
Explanation:
Recall that acceleration is defined as the change in velocity divided the time it takes for the change. Therefore , if the object accelerates from rest (zero velocity) to 70 m/s , the change in velocity is (70 m/s - 0 m/s = 70 m/s)
which divided by the 3.5 seconds it took for the change, gives:
acceleration = (70 m/s / 3.5 s ) = 20 m/s^2
the temperature at which the velocity of sound in air is twice its velocity at 15°C
Answers
With the use of below formula, at 879 °C, velocity will be double the velocity at 15 °C.
What is the relationship between Velocity and sound ?The velocity of sound waves in air is proportional to the square root of Thermodynamic temperature. That is, V = K\(\sqrt{T}\)
Given that the temperature at which the velocity of sound in air is twice its velocity at 15°C, Let us make use of the formula;
(v2/v1) = √(T2 / T1)
Where
v2 = final velocityv1 = initial velocityT2 = final absolute temperatureT1 = initial temperature.Recall that absolute temperature = °C + 273.
If v2 = 2 × v1 and temperature in degree Celsius = 15°C, then,
Temperature in Kelvin K = 15 + 273 = 288
Substitute all the parameters into the formula
(2 × v1)/v1 = √(T2/288)
2 = √ (T2 /288)
Square both sides
4 = (T2/288)
T2 = 4 × 288
T2 = 1152K
Temperature in degrees Celsius = 1152 - 273 = 879 °C.
Therefore, at 879 °C, velocity will be double the velocity at 15 °C.
Learn more about sound waves here: https://brainly.com/question/13105733
#SPJ1
A car weighing 12,000N12,000N is raised using a hydraulic lift, which consists of a U-tube with arms of unequal areas, filled with incompressible oil with a density 800 kg/m^3800kg/m 3 and capped at both ends with tight-fitting pistons. The car rests on the piston on the wider arm of the U-tube that has a radius of 18.0cm18.0cm, and the narrower arm has a radius of 5.00cm5.00cm. The pistons are initially at the same level. The pistons are initially at the same level. What is the initial force that must be applied to the smaller piston in order to start lifting the car
Answers
A force of magnitude F applied to the smaller piston exerts a pressure of
P = F / (π (0.0500 m)²)
while the 12 kN car exerts the same pressure at the other piston of
P = (12,000 N) / (π (0.180 m)²)
Solve for F :
F / (π (0.0500 m)²) = (12,000 N) / (π (0.180 m)²)
F = (12,000 N) (0.0500 m)² / (0.180 m)²
F = 925.926 N ≈ 930 N
Then a minimum force of 930 N must be applied in order to start lifting the car.
The radius of curvature of both sides of a converging lens is 18 cm. One side of the lens is coated withsilver so that the inner surface is reflective. When light is incident on the uncoated side it passes throughthe lens, reflects off the silver coating, and passes back through the lens. The overall effect is that of amirror with focal length 5.0 cm. What is the index of refraction of the lens material
Answers
Answer:
n = 1.4
Explanation:
Given,
R1 = 18 cm, R2 = -18 cm
From lens makers formula
1/f = (n - 1)(1/18 + 1/18) = (n-1)/9
f = 9/(n-1)
Power, P = 1/f ( in m) = (n-1)/0.09
Now, this lens is in with conjunction with a concave mirror which then can be thought of as to be in conjunction with another thin lens
Power of concave mirror = P' = 1/f ( in m) = 2/R = 2/0.18 = 1/0.09
Net power of the combination = 2P + P' = 2(n-1)/0.09 + 1/0.09 = 1/0.05
n = 1.4
Calculate how much energy is produced by a human heart over an 94-year lifetime in GigaJoules or GJ (1GJ= 109 Joules), assuming 365 days per year. The average output power of the heart is 1.33 Watts (J/s).
Answers
94 years x 365 days/year x 24 hours/day x 60 minutes/hour x 60 seconds/minute x 1.33 Watts = 2.4 GigaJoules (GJ)
What is Watts ?Watts are a unit of power, measured in joules. It is a measure of the rate of energy transfer, or the amount of energy used in a given amount of time. Watts are typically used to measure the electrical power of an appliance, the power output of a motor, or the power being transmitted over a power line. Watts are often used to describe the rate of energy consumption for an appliance or device, such as a light bulb or a heater. The higher the wattage, the more power the appliance or device requires. Watts are also sometimes used to describe the power output of a generator, or the amount of energy produced by a solar panel.
To learn more about Watts
https://brainly.com/question/1446143
#SPJ1
A 0.0300-kg bullet is fired vertically at 200.0 m/s into a 0.159-kg baseball that is initially at rest. The bullet lodges in the baseball and, after the collision, the baseball/bullet rise to a height of 37.0 m. Assume up to be the positive direction. What was the average force of air resistance while the baseball/bullet was rising? If the force is upward, enter a positive answer and if the force is downward, enter a negative answer.
Answers
The average force of air resistance while the baseball/bullet was F=-0.94N
Given:
mbullet=0.030 kg
vbullet=200m/s
mbasketball=0.15kg
To solve the velocity after collision, we will use the conversation of momentum
m₁v₁=m₂v₂
\(v_{2} =\frac{m_{1}v_{1} }{m_{2} }\)
since the baseball is at rest before the collision, the initial momentum can be calculated purely from the bullet
m₁=mbullet=0.030kg.
v₁=vbullet=200m/s
However, since the bullet lodges to the baseball after the collision, the mass after the collision should be
m₂=mbullet+mbaseball
m₂=0.030kg+0.15kg
m₂=0.18kg
plugging in the values to the equation of v₂
v₂=(0.030)(200)/0.18
v₂=33m/s
To calculate the average force air resistance, we must first determine the work done by the air on the bullet and baseball
-Wair=Wbullet+baseball-Wgravity
Since work done by the bullet and baseball is purely kinetic energy, it can be expressed as
\(Wbullet+baseball=\frac{1}{2}mv^2\)
On the other hand, the work done by gravity is purely potential thus
Wgravity=mgh
we can now express the work done on the air as follows
\(Wair=\frac{1}{2} mv^2+mgh\)
plugging the given values
\(Wair=\frac{1}{2} (0.18)(33.333)^2+(0.18)(9.8)(37)\)
Wair=-34.73J
We will now use the work equation to calculate the average force of air resistance:
W=Fd
\(F=\frac{W}{d} \\\\F=\frac{-34.73}{37}\)
F=-0.97N
To know more about Average force:
https://brainly.com/question/16200276
#SPJ4
Which of the following is a reason Pluto was demoted to a dwarf planet?A. orbits the sunB. cleared debris in its orbital pathwayC. round shape
Answers
Answer:
B. cleared debris in its orbital pathway
Explanation:
Pluto orbit the sun and it has a round shape, however, it is not big enough to clear debris in its orbital pathway, so the reason Pluto was demoted to a dwarf planet is
B. cleared debris in its orbital pathway
6° with the horizontal) at a steady speed of 4.0 m/s. Assuming a total mass of 75 kg (bicycle and Kasek), what must be Kasek's power output to climb the same hill at the same speed?
Answers
Answer:
Power, P = 307.31 W
Explanation:
It is given that,
Kasek climb at an angle of 6° with the horizontal at a steady speed of 4.0 m/s.
The total mass of bicycle and Kasek is 75 kg
We need to find the Kasek's power output to climb the same hill at the same speed. The angle is made with the horizontal. It means that,
F = F sinθ
So,
Power output is given by :
\(P=mg\sin\theta\times v\\\\P=75\times 9.8\times \sin(6)\times 4\\\\P=307.31\ W\)
So, Kasek's power output to climb the same hill is 307.31 W.