A baby's mouth is a distance of 35 cm from her father's ear and a distance of 1.60 m from her mother's ear. What is the difference between the sound intensity levels heard by the father and by the mother? Express your answer using two significant figures. βfather−βmother=?
Answers
The difference between the sound intensity levels heard by the father and the mother is approximately -16 dB. This means that the sound is approximately 16 dB louder at the baby's mouth compared to the mother's ear.
The difference in sound intensity levels between two points can be calculated using the formula:
Δβ = 10 log10(I2/I1)
Where Δβ is the difference in sound intensity levels, I2 is the sound intensity at the second point, and I1 is the sound intensity at the first point.
Let's assume that the sound intensity at the baby's mouth is I1, the sound intensity at the father's ear is I2, and the sound intensity at the mother's ear is I3.
We can use the inverse square law of sound propagation to relate the sound intensities at different distances:
I2/I1 = (r1/r2)^2
I3/I1 = (r1/r3)^2
Where r1 is the distance from the baby's mouth to her father's ear (35 cm = 0.35 m) and r3 is the distance from the baby's mouth to her mother's ear (1.60 m).
Let's substitute the given values into the equations:
I2/I1 = (0.35/0.35)^2 = 1
I3/I1 = (0.35/1.60)^2 ≈ 0.0625
Now we can calculate the difference in sound intensity levels:
Δβ = 10 log10(I2/I1) = 10 log10(1) = 0 dB (difference between father's ear and baby's mouth)
Δβ = 10 log10(I3/I1) ≈ 10 log10(0.0625) ≈ -16 dB (difference between mother's ear and baby's mouth)
The difference between the sound intensity levels heard by the father and the mother is approximately -16 dB. This means that the sound is approximately 16 dB louder at the baby's mouth compared to the mother's ear.
To know more about sound, visit;
https://brainly.com/question/1199084
#SPJ11
Related Questions
the unit of energy is a derived unit
Answers
Explanation:
Hi, there!!
Energy is defined as the capacity or ability to do work. It's SI unit is Joule.
here,
Joule = (kg×m×m)/(s×s)
= kg×m^2/s^2.
Therefore, the derived unit is kg.m^2 by s^2.
Hope it helps...
a hot-air balloon is accelerating upward under the influence of several forces. the hot air inside the balloon has a density of 0.930 kg/m3, and the density of the cool air outside is 1.29 kg/m3. the mass of the balloon fabric and basket is negligible. find the acceleration of the rising balloon. include in your solution a free-body diagram for the balloon.
Answers
Explanation:
0.930kg/m^3+1.29kg/m^3=2.220kg/m^3
Given the electric flux density determine a) rhov using the differential form of Gauss's Law. b) The total charge Q enclosed in a cube 2 m located in the first quadrant with one of its corners at the origin using the results of part a), and c) The total charge Q in the cube using the integral form of Gauss's Law. Dx(x,y):=4⋅(x+y)⋅C/m^2
Dy(x,y):=(3⋅x−1⋅y)⋅C/m^2
Answers
The electric flux density is given as Dx(x, y) = \(4(x + y) C/m^2$ and Dy(x, y) = (3x - y) C/m^2.\) Using Gauss's Law, the price density ρv is discovered to be ε * 3.
The general charge enclosed in a cube may be calculated by integrating ρv over the quantity of the cube. The critical form of Gauss's Law relates the electric flux Φ thru a closed surface to the overall charge Q enclosed.
To clear up the hassle, we will use the differential and indispensable varieties of Gauss's Law. Let's pass step by step:
a) Using the differential form of Gauss's Law, which states that the divergence of the electric flux density (D) is identical to the charge density (ρv) divided by using the permittivity of the medium (ε):
∇ · D = ρv / ε
Given the electric flux density components:
\(Dx(x, y) = 4(x + y) C/m^2\\Dy(x, y) = (3x - y) C/m^2\)
We can discover the fee density ρv by means of taking the divergence of D:
∇ · D = ∂Dx/∂x + ∂Dy/∂y
∂Dx/∂x = 4
∂Dy/∂y = -1
∇ · D = 4- 1 = 3
Therefore, ρv = ε * (∇ · D) = ε * 3
b) To discover the whole fee Q enclosed within the dice, we want to integrate the fee density ρv over the volume of the dice. Since the cube has a side length of 2 m and is placed in the first quadrant with one nook at the foundation, its volume is \((2 m)^3= 8m^3\). Thus:
Q = ∫∫∫ ρv dV
Q = ∫∫∫ ε * 3 dV
Q = ε * 3 * ∫∫∫ dV
Q = ε * 3* (extent of the cube)
Q = ε * 3* 8m³
c) Using the fundamental form of Gauss's Law, which states that the electrical flux (Φ) through a closed floor is equal to the entire charge (Q) enclosed divided with the aid of the permittivity of the medium (ε):
Φ = Q / ε
We can rewrite this equation as:
Q = Φ * ε
To discover the electric flux Φ, we want to assess the floor essential of the electric flux density (D) over a closed surface enclosing the dice. Since the electric flux density is given, we are able to calculate:
Φ = ∫∫ D · dA
wherein dA is a vector detail of the floor place.
Finally, we can calculate the total charge Q the usage of Q = Φ * ε.
To know more about integration,
https://brainly.com/question/30215870
#SPJ4
the speed of light in sapphire is 1.69 x 10^8 m/s. determine the index of refraction for sapphire.
Answers
Answer:
1.775 is the answer
Explanation:
We can figure out the index of refraction of the sapphire by using the following equation n = c/v
n = index of refraction
c = speed of light in a vacuum
v = speed of light traveling in medium
Step 1 :
v = 1.69 × 10^8
c = 3 × 10^8
Step2: Substitute values
n = c/v -----> n = 3 × 10^8 / 1.69 × 10^8 = 3/1.69 = 1.775
Index of refraction of sapphire is 1.775
Classify each process according to whether it does or does not produce a new substance.
cooking an egg
melting ice
fireworks exploding
evaporating puddle of water
rusting of a metal tool
dissolving of salt in water
Produces a New Substance
Does Not Produce a New
Substance
Resul
Glosse
Save
Submit
Аа
Langur

Answers
The processes under chemical change are: cooking an egg, fireworks exploding, and rusting of a metal tool.
The processes under physical change are: melting ice, evaporating puddle of water, and dissolving of salt in water.
Given:
The following process:
cooking an eggmelting icefireworks explodingevaporating puddle of waterrusting of a metal toolDissolving of salt in waterTo find:
The classify the processes in whether it does or does not produce a new substance.
Solution:
Chemical change is the change when a new substance is formed due to a change in the chemical composition of the substance.Physical change is the change in which no change in chemical composition takes place and the identity of the substance remains the same.Cooking an eggChemical change, due to change in atomic arrangement egg get solidified on cooking, a new substance is formed.
Melting icePhysical change, change in the state of matter is taking from solid to liquid, no new substance is formed.
Firework explodingChemical change. formation of carbon dioxide gas and sound energy, anew substance formed
Evaporating puddle of waterPhysical change, change in the state of matter is taking from liquid to gas, no new substance is formed.
Rusting of metal toolChemical change, formation of oxides on the surface of the metal tool due to reaction between air and metal, a new substance is formed.
Dissolving of salt in waterPhysical change, ions of salt in the solid state are changing into aqueous ions with no formation of new substance, no new substance is formed.
The processes under chemical change are: cooking an egg, fireworks exploding, and rusting of a metal tool.
The processes under physical change are: melting ice, evaporating puddle of water, and dissolving of salt in water.
Learn more about physical change and chemical change here:
brainly.com/question/864557?referrer=searchResults
brainly.com/question/13316655?referrer=searchResults
The density of iron is 14.0 g/cm³. A worker in a science lab calculates the density of iron as 4.5
g/cm³. What is the percent error of the worker's measurement?
Answers
Answer:
Percent Error = 67.86%
Explanation:
The percent error can be calculated using the following equation:
| measured value - true value |
Percent Error = ------------------------------------------------- x 100%
true value
In this equation,
---> The "measured value" is the value found after performing an experiment.
---> The "true value" is the value you expect to find after performing an experiment.
In this case,
---> measured value = 4.5 g/cm³
---> true value = 14.0 g/cm³
| 4.5 g/cm³ - 14.0 g/cm³ |
Percent Error = ---------------------------------------- x 100% <----- Insert values
14.0 g/cm³
| -9.5 g/cm³ |
Percent Error = ------------------------ x 100% <----- Subtract
14.0 g/cm³
9.5 g/cm³
Percent Error = ------------------------ x 100% <----- Take absolute value
14.0 g/cm³
Percent Error = 0.6786 x 100% <----- Divide
Percent Error = 67.86% <----- Multiply
an electric lamp is marked 240 volt 60 watt what is the resistor when it is operated at the correct voltage.b A. 1/960. B. 1/4 C. 4. D. 960. E. 14.400
Answers
The resistor of the electric lamp is marked at 240 volts and 60 watts is 960 ohms. Thus, option D is correct.
The resistance is a property that gives obstruction the current flow. It blocks the current flow in the circuit. The unit of resistance is the ohm.
From the given,
The voltage of the electric lamp (E) = 240 volt
Power in the circuit (P) = 60 watt
Resistance =?
Power (P) = E² / R
R = E²/P
= 240×240/60
= 960 Ω
The resistance of the electric lamp with a given voltage and power is 960 Ω. Thus, the ideal solution is D.
To learn more about resistance and power:
https://brainly.com/question/14856965
#SPJ1
Consider an ideal spring that has an unstretched length l_0. Assume the spring has a constant k. Suppose the spring is attached to an cart of mass m that lies on a frictionless plane that is inclined by an angle theta from the horizontal. Let g denote the gravitational constant The given quantities in this problem are l_0, m, k, theta, and g. a) The spring stretches slightly to a new length l>l_0 to hold the cart in equilibrium. Find the length l in terms of the given quantities. b) Now move the cart up along the ramp so that the spring is compressed a distance x from the unstretched length l_0. Then the cart is released from rest What is the velocity of the cart when the spring has first returned to its unstretched length l_0? c) What is the period of oscillation of the cart?
Answers
The length of the spring in equilibrium is l = l0 +(mgsin(theta)/k in terms of the given quantities
a) The length of the spring in equilibrium can be calculated using the spring's force equation, F = -k(l-l0).The force exerted by gravity on the cart is mgsin (theta), which must be equal to the force exerted by the spring in order to achieve equilibrium. Setting these two forces equal to each other and solving for l gives:
l = l0 +(mgsin(theta)/k
b) When the cart is released from rest, it will have potential energy stored in the spring. This potential energy can be converted into kinetic energy as the spring expands. The velocity of the cart when the spring has first returned to its unstretched length can be found using the conservation of energy. The potential energy stored in the spring when the cart is released is (1÷2) kx2, and the kinetic energy at the point when the spring returns to its unstretched length is (1÷2) mv². Setting these two equal to each other and solving for v gives:
sqrt(2kx÷m) = v
c) The period of oscillation of the cart is the time it takes for the cart to complete one full oscillation. T = 2pisqrt(m/k) can be used to calculate it.
2pisqrt(m÷k) = T
Learn more about spring:
https://brainly.com/question/29975736
#SPJ4
Light travels in a straight line at a constant speed of 300000 m/s. What is the acceleration of light?
Answers
Answer:
As light travels in a straight line at a constant speed, it's acceleration is 0 m/s².
There is no rate of change of speed, so there is no acceleration.
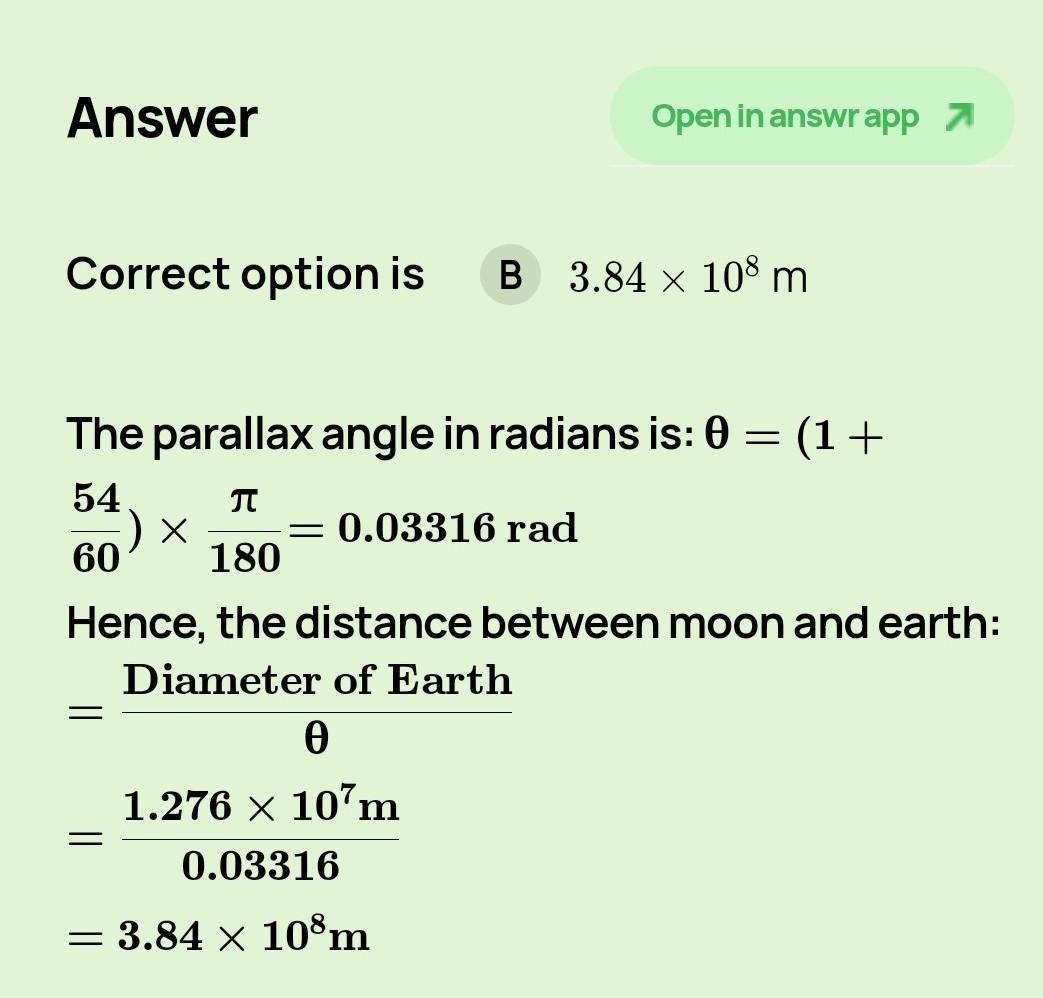
0 m/s² is the right answer.Example 2.3 The moon is observed from
two diametrically opposite points A and B
on Earth. The angle o subtended at the
moon by the two directions of observation
is 1°54'. Given the diameter of the Earth to
be about 1.276 x 107 m, compute the
distance of the moon from the Earth.
Answers
Explanation:
you can see this example to undersranding the question
The scattering of dissolved particles evenly is called
Answers
Answer:
the process of that happening is called Dissolving
the substance that is dissolved is called
Solute
How many electrons have a +1/2 spin in the 3d, 4d and 5d orbits combined?
O 15
30
O 5
O 10
Answers
Hund's rule allows us to find that the number of combined mismatched electrons is 12
Hund's rule is which configuration has the lowest energy in a system, so this must be met
Electrons spin are distributed in a parallel configuration to decrease energy For a given total spin, the lowest energy value is when the angular momentum is maximum.In this case the number of sublevel of the d orbital where they fit
# sublevels = 2 d + 1
# sublevels = 2 2 +1
# sublevels = 5
Each sublevel fits two electrons according to the Pauli principle, which establishes that all quantum numbers in a novel cannot be the same.
Let's distribute the electrons at each level
level electrons
3d ½ ½ ½
4d ½ ½ ½ ½
5d ½ ½ ½ ½ ½
Where there is a single electron in each sublevel according to Hund's principle
The number of unpaired electrons combined is 12In conclusion using Hund's rule we can find that the number of combined unpacked electrons is 12
Learn more about Hund's rule here:
brainly.com/question/13115697
Answer:15
Explanation: I have the same college class is based on hunds rule
heat always flows up.
true or false?
Answers
Answer:
true
Explanation:
you don't need an explanation
1) A negative charge of 6C exerts an attractive force of 65N on a second
charge that is 0.005 m away. What is the strength of the second charge?
Answers
Answer: \(30.09\times 10^{-15}\ C\)
Explanation:
Given
The first charge is \(q_1=-6\ C\)
Attraction force \(F=65\ N\)
the second charge is at \(0.005\ m\) away
Suppose the second charge is \(q_2\)
The electrostatic force is given by
\(F=\dfrac{kq_1q_2}{r^2}\)
Insert the values
\(65=\dfrac{9\times 10^9\times 6\times q_2}{[5\times 10^{-3}]^2}\\\\\Rightarrow q_2=\dfrac{65\times 25\times 10^{-6}}{54\times 10^9}\\\\\Rightarrow q_2=\dfrac{1625\times 10^{-6-9}}{54}\\\\\Rightarrow q_2=30.09\times 10^{-15}\ C\)
3. How do the individual forces compare when the rider experiences a sensation of
being heavier than his normal weight? What is the acceleration direction when this
occurs?
Answers
Answer:
When the acceleration of the elevator is going upward, the rider experiences a sensation of being heavier than his normal weight due to the upward normal force being more than the rider's weight.
When the elevator is accelerating downward, the person feels lighter due to the downward normal force being less than the person's weight.
What are the characteristics of elevator?A person riding in an elevator subjected to a series of unbalanced forces depending on the direction the elevator is travelling.
Two forces are acting on the person, the force of gravity and the upward normal force from the elevator.
When the elevator is going upwards with acceleration a, the person feels heavier than his normal weight, due to the upward normal force being greater than the person's weight.
N = mg + ma
When the elevator is moving downwards with acceleration a, the person feels lighter due to the downward normal force being less than the person's weight.
N = mg - ma
However, when the elevator is moving up or down at constant velocity ie. acceleration a = 0, the person experience a normal force equal to weight.
N = mg
When the elevator is moving downwards with acceleration a = g, the person experiences weightlessness.
N = (mg - mg) = 0
When the elevator is accelerating downward, the person feels lighter due to the downward normal force being less than the person's weight.
Learn more about elevator,
https://brainly.com/question/481548
#SPJ5
I WILL GIVE BRAINLIEST
This is science but there’s no science category
When does a solar eclipse occur?
When an object in space comes close to Earth's orbit
When an object in space gets too close to the sun
When an object in space comes between two planets
When an object in space comes between the sun and Earth
Answers
Hope this helps
An object with a mass of 10 kg is moving with a speed of 12 km/h. What is the kinetic energy of the object?
Answers
The Kinetic Energy of the object of mass 10 kg and is moving with a speed of 12 km/h is 55.44 joules.
What is Kinetic Energy of a body?The energy of a body by due to its motion is called kinetic energy. Mathematically -
E[K] = 1/2mv²
Given is an object with a mass of 10 kg is moving with a speed of 12 km/h.
We can calculate the kinetic energy from the formula discussed above as -
E[K] = 1/2mv²
Velocity of object = [v] = 12 km/h = 12000/3600 m/s = 3.33 m/s
Substituting the values, we get -
E[K] = 1/2 x 10 x 3.33 x 3.33 = 55.44 joules
Therefore, the Kinetic Energy of the object of mass 10 kg and is moving with a speed of 12 km/h is 55.44 joules.
To solve more questions on Kinetic energy, visit the link below-
https://brainly.com/question/10703924
#SPJ2
is it true that scientific theories and scientific laws both describe observed events??? provide evidence!!!!! only 2 people could answer so if you can't then comment and provide evidence thank you very much!!!!!!
Answers
Answer:
I'm not positive but I think the answer is Yes, because both scientific laws and theories are based on evidence.
Explanation:
Sorry I don't have notes on this, hope this helps! :)
Use the universal law of gravitation to solve the following problem.
The force of gravity between Jake and his daughter Annika is 1.67 × 10–9 N. If they are 11 m apart and Jake has a mass of 110 kg, what is Annika's mass?
a. Write out the formula for this problem.
b. Plug in the values from this problem into the formula.
c. Solve the problem, writing out each step.
d. Correct answer
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
Formula
Force = G * m1 * m2 / r^2
Givens
F = 1.67 * 10 - 9 NG = 6.67 × 10-11 Newtons kg-2 m2.m1 = 110 kgm2 = ?r = 11 meters.Solution
1.67 * 10^-9 = 6.67 * 10^-11 * 110 * m2/(11)^2 Divide both sides by 10^-9
1.67 * 10^-9/10^-9 = 6.67*10^-11/(10^-9 *110*m2/121
1.67 = 6.67 * 110 * 10^-2 * m2 / 121 Multiply both sides by 121
1.67 * 121 = 6.67 * 10 ^-2 * 110 * m2 * 121/121 Combine
202.07 = 7.337 * m2 Divide both sides by 7.337
202.07/7.337 = m2
m2 = 27.54 kg
being able to detect the origin of a sound is called
Answers
Detailed explanation of sound localization:
1. Binaural Hearing: One of the primary mechanisms of sound localization is binaural hearing, which involves using both ears to perceive sound. Each ear receives sound waves at slightly different times and with slightly different intensities and frequencies, depending on the sound source's location relative to the listener.
2. Interaural Time Difference (ITD): The time difference between when a sound reaches one ear compared to the other ear provides information about the sound source's horizontal position. If a sound is coming from the right side, it will reach the right ear slightly before reaching the left ear. The brain processes this time delay to determine the direction of the sound source.
3. Interaural Level Difference (ILD): The intensity or volume of a sound can also differ between the ears due to the distance between the sound source and each ear. The brain analyzes these intensity differences to help determine the sound source's lateral position.
4. Head-Related Transfer Function (HRTF): The unique shape of our ears and the structure of our head create subtle modifications to the sound waves as they enter our ears. These modifications, known as the head-related transfer function, provide additional cues for sound localization. They help us perceive the elevation or vertical position of a sound source.
5. Auditory Processing: The brain integrates the inputs from both ears, along with other contextual cues, to accurately determine the direction and location of a sound source. It combines the information from ITD, ILD, and HRTF to create a spatial map of sound in our auditory perception.
Overall, sound localization is a remarkable ability that allows us to identify the direction and location of sounds in our environment. It relies on the complex interplay between our ears, brain processing, and contextual cues to provide us with a rich auditory experience and helps us navigate our surroundings and respond to auditory stimuli effectively.
To know more about sound localization refer here
https://brainly.com/question/13044885#
#SPJ11
Wolves, which are top predators, were eliminated from Yellowstone National Park in the 1930s. In 1995, wolves were reintroduced into Yellowstone. During the period in which wolves were absent from Yellowstone, which MOST likely occurred?
A. an increase in competition for food resources among small prey
B. a greater opportunity for primary producers to flourish
C. an increase in the population of tertiary consumers
D. a greater balance of predator-prey relationships
Answers
Answer:
The answer is E
Explanation:
Wolves died off from the rona virus back in the 1930s so when they came back they brought C- 19 with them
How many ways (directions) can an object move in 1 Dimension? Can it be still? Can it speed up or slow down?
Answers
Explanation:
Let's assume the 1D is along x - axis.
Then, the object can move in two directions, along +x axis or - x axis, depending upon reference point .
Yes, it can be still, speed up and slow down.
Which of the following pairs of forces is balanced?
a) 5 N to the West and 5 N to the North b) 5 N to the West and 5 N to the South
c) 5 N to the West and 5 N to the East d) 5 N to the West and 5 N to the West
Answers
Answer:
I guess the answer is c the f am not wrong
Why is tungsten used as a filament in a bulb?
Answers
Answer:
because of tungsten's high melting point
Explanation:
estimate the moment of inertia of a bicycle wheel 65 cm in diameter. the rim and tire have a combined mass of 1.1 kg .
Answers
The moment of inertia of a bicycle wheel of 65cm diameter and mass 1.1 kg is 0.116 Kg m^2.
What is moment of inertia?
Moment of inertia can be defined as the tendency of any object to remain in the state of rest or a constant rotational velocity which can be calculated by I = mr^2, where I is moment of inertia, m is mass and r is radius.
The moment of inertia of the bicycle wheel can be calculated as,
diameter of the bicycle wheel = 65 cm = 0.65 m
radius = d/2 = 0.65 m / 2 = 0.325 m
I = mr^2 = 1.1 Kg x (0.325m)^2 = 0.116 Kg m^2
Therefore the moment of inertia of the bicycle wheel is 0.116 Kg m^2.
To learn more about moment of inertia click on the given link https://brainly.com/question/14460640
#SPJ4
a method for developing questionnaire items that focuses on including questions that characterize the group the questionnaire is intended to distinguish
Answers
A method for developing questionnaire items that focuses on including questions that characterize the group the questionnaire is intended to distinguish is known as "differentiation sampling."
Differentiation sampling is a method used in questionnaire development to ensure that the questionnaire items effectively capture the characteristics that distinguish the target group from others. This approach involves selecting or generating questionnaire items that have the potential to discriminate between the target group and other groups.
To develop questionnaire items using differentiation sampling, researchers typically consider the unique attributes, behaviors, or experiences of the target group. Exothermic reaction attributes can be identified through prior research, expert knowledge, or insights gained from qualitative studies. The goal is to create items that are specific to the target group, effectively capturing their distinct characteristics.
This method enhances the precision and effectiveness of the questionnaire in assessing the intended group and its unique characteristics.
Learn more about Exothermic reaction here
https://brainly.com/question/29575731
#SPJ11
A ball that has a mechanical energy of 65 J has 12 J of kinetic energy. The ball has
J of potential energy
Answers
Answer:
The ball has a potential energy of 53 J.
Explanation:
Mechanical energy, E = Kinetic energy + Potential energy
E = K.E + P.E
65 = 12 + P.E
P.E = 65 – 12
P.E = 53 J
Therefore the potential energy of the ball is 53 J
Answer:
53
Explanation:
on e2021
by amplifying soft sounds but not loud sounds, digital hearing aids produce:
Answers
Digital hearing aids are designed to amplify soft sounds while suppressing loud sounds. This is achieved through advanced signal processing capabilities and adjustable gain settings.
Soft sounds typically have low amplitudes and may be difficult for individuals with hearing loss to perceive. Digital hearing aids use their microphone to capture these soft sounds and convert them into digital signals. The digital signal processor in the hearing aid analyzes and amplifies these signals selectively, boosting their amplitudes to make them more audible to the wearer.
On the other hand, loud sounds can be uncomfortable or even painful for individuals with hearing loss. To ensure listening comfort and protect against further damage, digital hearing aids incorporate compression algorithms. These algorithms automatically detect and limit the amplification of loud sounds, preventing them from reaching uncomfortable or harmful levels.
By differentiating between soft and loud sounds and applying appropriate amplification techniques, digital hearing aids provide a more balanced and comfortable listening experience. They enhance the audibility of soft sounds, helping individuals with hearing loss regain clarity and understanding in quieter environments while maintaining a safe and comfortable listening level in the presence of loud sounds.
Know more about amplitudes here:
https://brainly.com/question/29982197
#SPJ8
A battery with an emf of 120 V, an 80-22 resistor, and a 4-µF capacitor are connected in series such that the capacitor is being charged up. When the current in the resistor is 1 A, what is the magnitude of the charge on the capacitor? Assume that the battery has no internal resistance. 80 μC A. Β. 240 μC C. 480 μC D. 160 μC E. 320 μC
Answers
The expression for the charge on a capacitor can be expressed as Q = C × V, where Q is the charge, C is the capacitance, and V is the potential difference. A capacitor is charged to a potential difference V when a charge Q is stored on its plates.
Let’s solve this problem using the above equation. We can calculate the charge on the capacitor in the given problem using the below equation Q = C × V Where Q = charge on the capacitor = ?C = capacitance = 4 µF = 4 × 10⁻⁶FV = potential difference across the capacitor = emf of battery = 120 VQ = C × V = 4 × 10⁻⁶ × 120= 0.00048 C or 480 µC Therefore, the magnitude of the charge on the capacitor is 480 μC.Option C is correct.
To know more about potential difference visit
https://brainly.com/question/23716417
#SPJ11
The reason padded dashboards are used in cars is that they _____.
a. change the impulse in a collision
b. increase the time it takes the person to come to a complete stop
c. change the momentum of a collision
d. increase the force on the person as they come to a final stop
Answers
The reason padded dashboards are used in cars is that they a.) change the impulse in a collision. Therefore option a) is correct.
Why are padded dashboards used in cars?Padded dashboards make automobiles safer as they increase the time taken to decrease the momentum of impacting body to zero, which also decreases the impact. Therefore, force acting on the padded dashboards is small.
If the driver or passenger hits the dashboard, then the force and time required to stop the momentum is exerted by the dashboard. Padded dashboards serve to extend the time duration of the impact, hence minimizing the effect of the force.
To know more about padded dashboard, refer
https://brainly.com/question/22099771
#SPJ1