Answers
Answer: 6.08 m/s
Explanation:
w=mg---> (9.8)(0.3)=2.94
Fc=mv^2/r ---> Fc=r(FT+w)/m
V=sqrt(r(FT+w)/m)
sqrt(2(2.6+2.94)/0.3= 6.08 m/s
hope this helps :>
Related Questions
find the rms speed of a sample of oxygen at 30° C and having a molar mass of 16 g/mol.
Answers
At 30°C, the rms speed of a sample of oxygen with a molar mass of 16 g/mol is approximately 482.34 m/s.
The root mean square (rms) speed of a gas molecule is a measure of the average speed of the gas particles in a sample. It can be calculated using the formula:
vrms = √(3kT/m)
Where:
vrms is the rms speed
k is the Boltzmann constant (1.38 x 10^-23 J/K)
T is the temperature in Kelvin
m is the molar mass of the gas in kilograms
To calculate the rms speed of oxygen at 30°C (303 Kelvin) with a molar mass of 16 g/mol, we need to convert the molar mass to kilograms by dividing it by 1000:
m = 16 g/mol = 0.016 kg/mol
Substituting the values into the formula, we have:
vrms = √((3 * 1.38 x 10^-23 J/K * 303 K) / (0.016 kg/mol))
Calculating this expression yields the rms speed of the oxygen sample:
vrms ≈ 482.34 m/s
For such more questions on speed
https://brainly.com/question/31380575
#SPJ8
How is the speed of light measured when it is light years away?
Answers
Answer:
In a vacuum, light travels at 670,616,629 mph (1,079,252,849 km/h). To find the distance of a light-year, you multiply this speed by the number of hours in a year (8,766). The result: One light-year equals 5,878,625,370,000 miles (9.5 trillion km).Need Help with this physics question, just a written response

Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
According to Newton's third law, every action has an equal and opposite reaction
so it tells us that the force exerted by the earth on the spacecraft is equal to the force exerted by the spacecraft on the earth. But we do not see the earth moving towards the spacecraft because the inertia of the spacecraft is very less than the inertia of the earth.
A flat sheet of paper of area 0.450 m2 is oriented so that the normal to the sheet is at an angle of 600 to a uniform electric field of magnitude 18 N C-1. What is the magnitude of the electric flux through the sheet? A. 3.22 N m2 C-1 B. 21.42 N m2 C-1 C. 5.04 N m2 C-1 D. 11.72 N m2 C-1 E. 4.05 N m2 C
Answers
The magnitude of the electric flux through the sheet is 4.05 N m² C⁻¹ (Option E).
The electric flux through a surface is given by the product of the electric field strength and the area of the surface projected perpendicular to the electric field.
In this case, the electric field strength is 18 N C⁻¹, and the area of the sheet projected perpendicular to the electric field is 0.450 m²
(since the normal to the sheet makes an angle of 60° with the electric field). Multiplying these values gives the electric flux:
Electric flux = Electric field strength × Area
Electric flux = 18 N C⁻¹ × 0.450 m²
Electric flux = 8.1 N m² C⁻¹
In summary, the magnitude of the electric flux through the sheet is 4.05 N m² C⁻¹. This value is obtained by multiplying the given electric field strength by the projected area of the sheet perpendicular to the electric field.
The angle of 60° is taken into account to determine the effective area for calculating the flux.(Option E).
for such more questions on electric
https://brainly.com/question/1100341
#SPJ8
Photo used to help with the question is below!! Please answer! Will mark BRAINLIEST!
⬇⬇⬇⬇⬇⬇⬇
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Chose the correct answer:
-reflection
-refraction
-absorption
-none of the above

Answers
calculate the electric potential energy in a capacitor that stores 9.40 x 10 to the negative 10 C of charge at 50.0 V
Answers
The electric potential energy stored in the capacitor is 4.70 x 10^-8 Joules.
The electric potential energy stored in a capacitor is given by the formula:
U = (1/2) * C * V^2
where U is the potential energy in Joules, C is the capacitance in Farads, and V is the voltage across the capacitor in Volts.
In this case, we are given that the capacitor stores 9.40 x 10^-10 C of charge at 50.0 V. However, we are not given the capacitance value. Therefore, we cannot calculate the potential energy directly using the above formula.
To find the capacitance value, we can use the formula:
C = Q / V
where Q is the charge stored in the capacitor and V is the voltage across the capacitor.
Substituting the given values, we get:
C = 9.40 x 10^-10 / 50.0
= 1.88 x 10^-11 F
Now we can use the formula for electric potential energy to find the energy stored in the capacitor:
U = (1/2) * 1.88 x 10^-11 * (50.0)^2
= 4.70 x 10^-8 J
Therefore, the electric potential energy stored in the capacitor is 4.70 x 10^-8 Joules.
Know more about electric potential energy here:
https://brainly.com/question/14306881
#SPJ11
Refer to the picture!
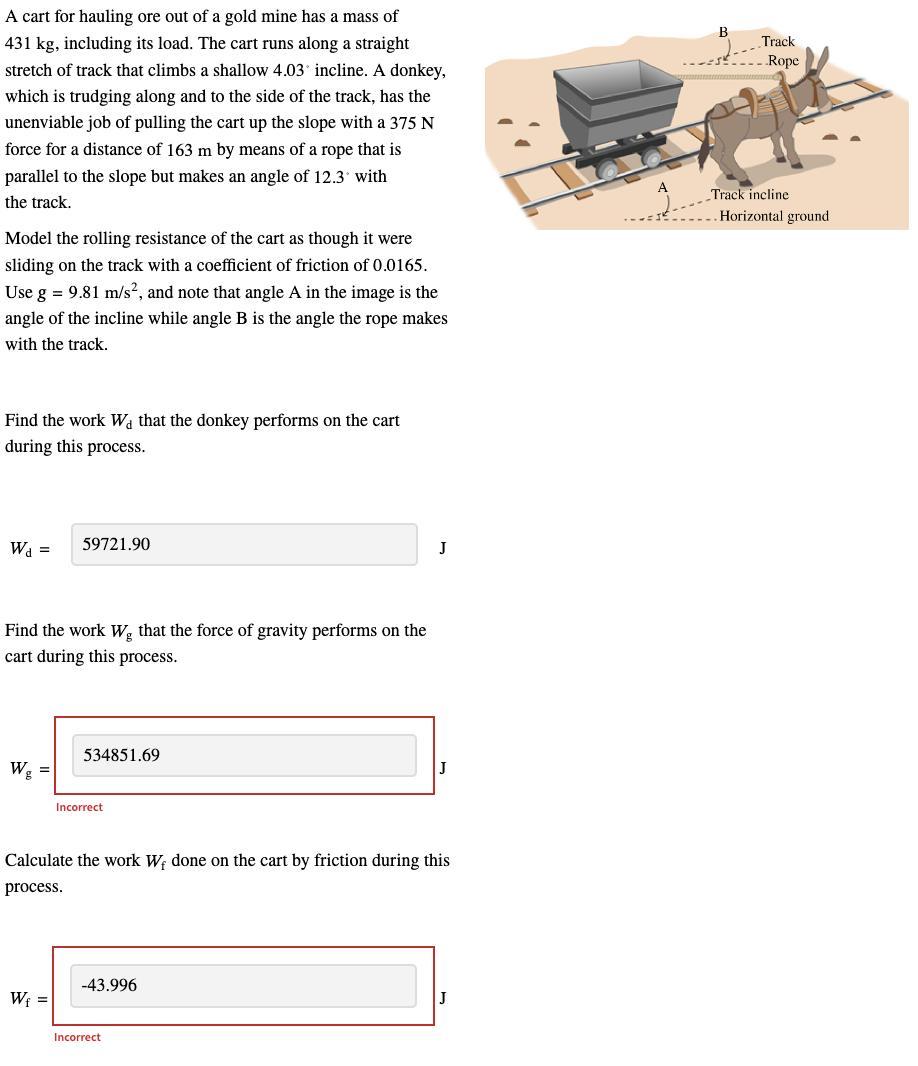
Answers
(a) The work done by the donkey on the cart is 59,721.9 J.
(b) The work done by the force of gravity on the cart is -48,434.87 J.
(c) The work done on the cart by friction during this time is 11,315.12 J.
What is the work done by the donkey on the cart?(a) The work done by the donkey on the cart is calculated as follows;
Wd = Fd cosθ
where;
F is the applied force by the donkeyd is the displacementθ is the angle of inclinationWd = 375 N x 163 m x cos(12.3)
Wd = 59,721.9 J
(b) The work done by the force of gravity on the cart is calculated as;
Wg = Fg x d x cosθ
Where;
Fg is the force of gravityd is the displacementθ is the angle between the force of gravity and displacementθ = 90⁰ + 4.03⁰ = 94.03⁰
Wg = (431 kg x 9.81 m/s²) x 163 m x cos (94.03)
Wg = -48,434.87 J
(c) The work done on the cart by friction during this time is calculated as;
Wf = Ff x d x cosθ
where;
Ff is the force of friction;Ff = μmg cosθ
Ff = 0.0165 x 431 kg x 9.81 x cos (4.03)
Ff = 69.59 N
Wf = 69.59 x 163 x cos (4.03)
Wf = 11,315.12 J
Learn more about work done by gravity here: https://brainly.com/question/15352390
#SPJ1
There are 3 resistors in series: R1=32 Ohm, R2-51 Ohm, and R3-10 Ohm.
Determine the equivalent resistance.
Answers
Answer: 93 Ohm
Explanation: The equivalent resistance of three resistors in series can be found by adding up the individual resistances.
R_total = R1 + R2 + R3
R_total = 32 Ohm + 51 Ohm + 10 Ohm
R_total = 93 Ohm
Therefore, the equivalent resistance of the three resistors in series is 93 Ohm.
Which sections does the object move in a negative direction like west?

Answers
We can elminate when the position is constant tthatis B and D
Also, we can eliminate E because it is increasing
Therefore we only have A and C that are moving in a negative direction
You go grab a car door handle in the summer (energy transfer to heat up the handle conduction) and it burns you through _____ energy transfer.
A. Radiation-transfer of energy (heat) through space by electromagnetic rays.
B. Conduction-the transfer of energy (heat) through the matter by molecules energy (touch).
C. Convection-the transfer of heat movement of mass or substance (motion).
Answers
I think the answer is A
common transparent tape becomes charged when pulled from a dispenser. if one piece is placed above another, the repulsive force can be great enough to support the top piece's weight. assuming equal point charges (only an approximation), calculate the magnitude of the charge if electrostatic force is great enough to support the weight of a 13.0 mg piece of tape held 1.30 cm above another. (the magnitude of this charge is consistent with what is typical of static electricity.)
Answers
If one piece is placed above another, the repulsive force can be great enough to support the top piece's weight.
calculate the magnitude of the charge if electrostatic force?
The magnitude of charges on the electron and proton are `1.6xx10^(-19)` C.M Mass of the electrons is `m_(e)=9.1xx10^(-31)` kg and mass of proton is `m_(p)=1.6xx10^(-27)` kg .n the equation Felect = k • Q1 • Q2 / d2 , the symbol Felect represents the electrostatic force of attraction or repulsion between objects 1 and 2.The force is perpendicular to both the velocity v of the charge q and the magnetic field B. 2. The magnitude of the force is F = qvB sinθ where θ is the angle < 180 degrees between the velocity and the magnetic field.This force emerges from the interaction between two charged objects (or point charges) and its magnitude is calculated by F=kQ1Q2r2 F = k Q 1 Q 2 r.
To learn more about magnitude of the charge refers to:
https://brainly.com/question/25316833
#SPJ4
Your lab partner tosses you a ball. As she throws the ball up in the air it follows this arc. Where is potential energy the lowest? Select all that apply.
A. point A
B. point B
C. point C
D. point D
E. They are all the same

Answers
Answer: c
Explanation:
Answer:
answer c
Explanation:
The Harrier Jump Jet is a fixed wing military jet designed for vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL). It is capable of rotating its jets from a horizontal to a vertical orientation in order to takeoff, land and conduct horizontal maneuvers. Determine the vertical thrust required to accelerate an 8600-kg Harrier upward at 0.40 m/s/s
Answers
Vertical thrust = 8600 kg x 0.40 m/s/s = 3440 N
What is the net force acting on the box?
0 285 N
0 185 N
SN
0 85 N
0 65 N
Answers
Answer:
the answer would be D 65N
Explanation:
just got it correct on EDG
A Cambra pouce car traveling at 28 m/s slow
at a rate of at 3.6 m/s every second find.
a) The time taken for the police car to come to Stop?
Answers
Answer:
t = 7.8 seconds
Explanation:
Given that,
The initial speed of the car, u = 28 m/s
Acceleration of the car, a = 3.6 m/s²
We need to find the time taken for the police car to come to Stop. When it stops, its final speed is equal to 0. So, using the equation of kinematics to find it i.e.
\(v=u+at\\\\0=28+3.6t\\\\t=\dfrac{28}{3.6}\\\\t=7.8\ s\)
So, the required time is 7.8 seconds.
What range of the electromagnetic spectrum does this wave belong to?
Answers
Answer:
please give me brainlist and follow
Explanation:
Infrared radiation
The infrared part of the electromagnetic spectrum covers the range from roughly 300 GHz to 400 THz (1 mm – 750 nm). It can be divided into three parts: Far-infrared, from 300 GHz to 30 THz (1 mm – 10 μm). The lower part of this range may also be called microwaves or terahertz waves.
The two angled ropes are used to support the crate in Figure P5.7. The tension in the ropes can have any value up to 1500 N. When the tension exceeds this value, the ropes will break. What is the largest mass the ropes can support?

Answers
Answer:
170 kg
Explanation:
Free-Body Diagram:Let's start by drawing a free body diagram for this problem. Let's call the tension in the left rope \(T_1\) and the tension in the right rope \(T_2\).
Now we can construct a free body diagram using the horizontal and vertical components of the two tension forces.
Let's start with the left tension force:
Horizontal component (x): \(T_1 \cdot cos(30)\)Vertical component (y): \(T_1 \cdot sin(30)\)The right tension force:
Horizontal component: \(T_2 \cdot cos(45)\)Vertical component: \(T_1 \cdot sin(45)\)In order to see what these forces look like on the diagram, look at the first image attached. (1)
Now, we can create the FBD using the components of the tension forces and the force of gravity pulling on the crate, known as w.
The horizontal components of \(T_1\) and \(T_2\) go on the left and right of the FBD, respectively. The two vertical components go on top, and the weight force is on the bottom. We know that weight = mg.
To see what the free body diagram should look like, see the second image attached. (2)
Now that we have the FBD, we can write a system of equations using the sum of forces in both the x- and y-direction.
Since the crate is not moving in either the horizontal or vertical direction, we can say that the net force acting on the crate is 0.
\(F_\text{net} = 0\)This means that the sum of x forces and the sum of y forces are both 0. Let's set the top and right to be the positive direction and the bottom and left to be the negative direction. Now we can write the system of equations:
\(\sum F_x = T_2 \cdot cos(45) - T_1\cdot cos(30) = 0\) \(\sum F_y = T_1 \cdot sin(30) +T_2\cdot sin(45) - mg = 0\)There are many ways to solve this system of equations, but I will be showing the top two ways that I tend to solve these types of problems.
Method 1:Solve for \(T_1 \cdot sin(30)\) and \(T_1 \cdot cos(30)\) in both equations.
\(T_1 \cdot cos(30) = T_2 \cdot cos(45)\) \(T_1\cdot sin(30) = mg - T_2 \cdot sin(45)\)We know that \(\frac{sin\theta}{cos\theta}\) = \(tan\theta\), so we can reorder both equations and divide them.
\(T_1\cdot sin(30) = mg - T_2 \cdot sin(45)\) \(T_1 \cdot cos(30) = T_2 \cdot cos(45)\) \(tan(30)=\frac{mg-T_2\cdot sin(45)}{T_2\cdot cos(45)}\)Note that \(\frac{T_1}{T_1}\) cancels, leaving us with tan(30).
Now that we have this equation, we can plug in known values. We are trying to solve for m, the largest mass of the crate that the ropes can support. We know that:
\(g=9.8\ \frac{m}{s^2}\) \(T_2=1500\ \text{N}\)Let's substitute these values into our equation:
\(tan(30)=\frac{m(9.8)-(1500)\cdot sin(45)}{(1500)\cdot cos(45)}\)Multiply 1500 * cos(45) to both sides of the equation.
\(tan(30) \cdot (1500 \cdot cos(45)) =9.8m-(1500 \cdot sin(45))\)Add 1500 * sin(45) to both sides of the equation.
\(tan(30) \cdot (1500 \cdot cos(45)) + 1500 \cdot sin(45)) =9.8m\)Divide both sides of the equation by 9.8.
\(\frac{tan(30) \cdot (1500 \cdot cos(45)) + (1500 \cdot sin(45)) }{9.8}= m\)Simplify.
\(\frac{1673.032607}{9.8}=m\) \(m=170.717613\)The largest mass the ropes can support is around 170 kg (round down, not up).
Method 2:We can use the system of equations again.
\(T_1 \cdot cos(30) = T_2 \cdot cos(45)\) \(T_1\cdot sin(30) = mg - T_2 \cdot sin(45)\)This time, let's do a little guess and check. Using the first equation, plug in 1500 N for T2 and solve for T1.
\(T_1 \cdot cos(30) = (1500) \cdot cos(45)\)Divide both sides of the equation by cos(30).
\(T_1=\frac{1500 \cdot cos(45)}{cos(30)}\)Simplify.
\(T_1=1224.744871 \ \text{N}\)Now plug in 1500 N for T1 and solve for T2.
\((1500) \cdot cos(30) = T_2 \cdot cos(45)\)Divide both sides by cos(45).
\(T_2=\frac{1500\cdot cos(30)}{cos(45)}\) \(T_2=1837.117307 \ \text{N}\)Since the tension cannot exceed 1500 N without the rope breaking, we must use the first substitution, where \(T_1=1224.744871\) and \(T_2=1500 \ \text{N}\).
Now we can use these known values and plug them into the second equation: \(T_1\cdot sin(30) = mg - T_2 \cdot sin(45)\)
Add \(T_2 \cdot sin(45)\) to both sides of the equation.
\(mg=T_1 \cdot sin(30) + T_2 \cdot sin(45)\)Divide both sides of the equation by g.
\(m=\frac{T_1 \cdot sin(30) + T_2 \cdot sin(45)}{g}\)Plug in known values and solve for m.
\(m=\frac{(1224.744871) \cdot sin(30) + (1500) \cdot sin(45)}{9.8}\)Simplify.
\(m=\frac{1673.032607}{9.8}\) \(m=170.717613\)As you can see, we get the same answer with either method. The largest mass the ropes can support is 170 kg.


2. Gerard is riding his bicycle directly east. His maximum
instantaneous velocity was 8 meters per second and his
minimum instantaneous velocity was 0 meters per second. He
covered 7.20 kilometers in 20.0 minutes. What is his average
velocity for the ride?
Answers
Gerard's average velocity for the ride is 6 meters per second.
To find Gerard's average velocity for the ride, we can use the formula:
Average velocity = Total displacement / Total time
First, we need to convert the distance traveled from kilometers to meters:
7.20 kilometers * 1000 = 7200 meters
Next, we convert the time from minutes to seconds:
20.0 minutes * 60 = 1200 seconds
Now, we can calculate the total displacement by subtracting the initial position from the final position. Since Gerard is riding directly east, there is no change in the east-west direction, so the displacement is equal to the distance traveled:
Total displacement = 7200 meters
Finally, we substitute the values into the average velocity formula:
Average velocity = 7200 meters / 1200 seconds
Average velocity = 6 meters per second
for more questions on average velocity
https://brainly.com/question/4931057
#SPJ8
Explain three ways energy moves through the water cycle.
Urgent help!!
Answers
Answer:
Liquid water evaporates into water vapor, condenses to form clouds, and precipitates back to earth in the form of rain and snow
Explanation:
its basiclly luquid, water vapor, and the form of clouds.
You are designing a machine for a space exploration vehicle. It contains an enclosed column of oil that is 1.50 m tall, and you need the pressure difference between the top and the bottom of this column to be 0.125 atm. (a) What must be the density of the oil? (b) If the vehicle is taken to Mars, where the acceleration due to gravity is 0.379g, what will be the pressure difference (in earth atmospheres) between the top and bottom of the oil column?
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
(a) To find the density of the oil, we can use the formula for pressure difference in a fluid column:
ΔP = ρgh
where ΔP is the pressure difference, ρ is the density of the fluid, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the height of the fluid column.
Plugging in the given values, we have:
0.125 atm = ρgh = ρ(9.81 m/s^2)(1.50 m)
Solving for ρ, we get:
ρ = 0.125 atm / (9.81 m/s^2 x 1.50 m) ≈ 0.00847 g/cm^3
Therefore, the density of the oil must be approximately 0.00847 g/cm^3.
(b) On Mars, the acceleration due to gravity is 0.379 times that of Earth, or g_Mars = 0.379g_Earth. The pressure difference between the top and bottom of the oil column will be:
ΔP_Mars = ρgh_Mars = ρg_Earth(0.379)(1.50 m)
Using the density we found in part (a), we have:
ΔP_Mars = (0.00847 g/cm^3)(9.81 m/s^2)(0.379)(1.50 m) / (1 atm/101325 Pa)
ΔP_Mars ≈ 0.019 atm
So, the pressure difference between the top and bottom of the oil column on Mars will be approximately 0.019 atm, or about 0.15 times the pressure difference on Earth.
Answer:
The pressure difference (in Earth's atmosphere) between the top and bottom of the oil column on Mars is 0.045 atm.
Explanation:
(a) To find the density of the oil, we can use the formula for pressure difference in a fluid column: ΔP = ρgh, where ΔP is the pressure difference, ρ is the density of the fluid, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the height of the fluid column.
We know that the pressure difference is 0.125 atm, the height of the column is 1.50 m, and the acceleration due to gravity on Earth is 9.81 m/s². Plugging in these values, we get:
0.125 atm = ρ(9.81 m/s²)(1.50 m)
Solving for ρ, we get:
ρ = 0.00803 g/cm³
Therefore, the density of the oil must be 0.00803 g/cm³.
(b) If the vehicle is taken to Mars, where the acceleration due to gravity is 0.379g, we can use the same formula to find the pressure difference:
ΔP = ρgh
We know that the height of the column is still 1.50 m, but the acceleration due to gravity is now 0.379g. Plugging in these values, we get:
ΔP = (0.00803 g/cm³)(9.81 m/s²)(0.379)(150 cm)
Solving for ΔP, we get:
ΔP = 0.045 atm
Therefore, the pressure difference (in Earth's atmosphere) between the top and bottom of the oil column on Mars is 0.045 atm.
what are the four things that affect the resistance of a wire? A. length, diameter, material, and temperature B. weight, diameter, material, and temperature C. length, height, material, temperature D. length, weight, material, and temperature
Answers
Answer:
A. length, diameter, material, temperature
Metric Conversions:
1) 5KL = ?L
2) 3L = ?KL
3) 4g = ?Kg
4) 81Kg = ?g
5) 52dg = ?g
6) 3dm = ?m
7) 14mm = ?m
Answers
The metric conversion of the given quantities is determined as
5 KL = 5,000 L3L = 0.003 KL4g = 0.004 kg81 kg = 81,000 g52 dg = 5.2 g3 dm = 0.3 m14 mm = 0.014 mWhat is metric conversion?Metric Conversion refers to the conversion of the given units to desired units for any quantity to be measured.
The metric conversion of the following quantities is calculated as follows;
5 KL = 5 x 1000 L = 5,000 L
3L = 3 x 1/1000 L = 0.003 KL
4g = 4 x 1/1000 g = 0.004 kg
81 kg = 81 x 1000 g = 81,000 g
52 dg = 52 x 1/10 g = 5.2 g
3 dm = 3 x /10 m = 0.3 m
14 mm = 14 x 1/1000 m = 0.014 m
Thus, the metric conversion of the given quantities is determined as
5 KL = 5,000 L3L = 0.003 KL4g = 0.004 kg81 kg = 81,000 g52 dg = 5.2 g3 dm = 0.3 m14 mm = 0.014 mLearn more about metric conversion here: https://brainly.com/question/26259781
#SPJ1
Define the term Distance.
Answers
Maths :
The length between 2 points.
Physics =
Distance = speed × time
Distance is defined as the space between two points in space.
What is distance?Distance is defined as the space between two points in space.
The unit of distance is metres or kilometres.
Distance can be measured directly usind instruments such as metre rule and tape rule.
The formula for calculating distance is given below:
Distnce = velocity × time.
Therefore, distance is defined as the space between two points in space.
Learn more about about distance at: https://brainly.com/question/4931057
A very long insulating cylinder of charge of radius2.40 cm carries a uniform linear density of 13.0 nC/m.
If you put one probe of a voltmeter at the surface, how far fromthe surface must the other probe be placed so that the voltmeterreads 200 V?
Answers
The distance at which the probe should be placed so that the voltmeter reads 200 V is equal to 0.216 cm.
To find the distance at which the voltmeter reads 200 V, we need to use the equation for the electric potential at a point due to a continuous distribution of charge:
V = k * ∫λ(r')/r' dr'
where V is the electric potential at a distance r from the center of the cylinder, k is the Coulomb constant (8.99 x 10^9 N*m^2/C^2), λ is the linear charge density (13.0 nC/m in this case), and r' is a dummy variable of integration.
To find the electric potential at a distance r from the surface of the cylinder, we can split the integral into two parts: one from the surface of the cylinder (r') to the point where the probe is placed (r), and one from r to the center of the cylinder (which will be a negative value since the charge density is negative):
V = k * [∫λ(r')/r' dr' from r'=r to r'=2.4 cm] + k * [∫λ(r')/r' dr' from r'=2.4 cm to r'=0]
The first term on the right hand side represents the potential at the point where the probe is placed, and the second term represents the potential at the surface of the cylinder. We are given that the potential at the surface is 200 V, so we can set the equation equal to 200 V and solve for r:
200 V = k * [∫λ(r')/r' dr' from r'=r to r'=2.4 cm] + k * [∫λ(r')/r' dr' from r'=2.4 cm to r'=0]
To solve this equation, we need to evaluate the integrals on the right hand side. The first integral is easy to evaluate:
∫λ(r')/r' dr' from r'=r to r'=2.4 cm = λ * ln(2.4 cm/r)
The second integral is a little more tricky, but we can use the fact that the charge density is uniform to simplify it:
∫λ(r')/r' dr' from r'=2.4 cm to r'=0 = λ * ∫1/r' dr' from r'=2.4 cm to r'=0
= λ * [ln(r')] from r'=2.4 cm to r'=0
= λ * [-ln(2.4 cm)]
Substituting these values back into the original equation and solving for r, we find that the distance at which the voltmeter reads 200 V is:
r = 2.4 cm * exp(-200 V / (k * λ))
r = 0.216 cm
Learn more about Voltmeter at:
brainly.com/question/28236233
#SPJ4
Two identical loudspeakers 2.00 m apart are emitting sound waves into a room where the speed of sound is 340 m/s. Abby is standing 5.00 m in front of one of the speakers, perpendicular to the line joining the speakers, and hears a maximum in the intensity of the sound.
Required:
What is the lowest possible frequency of sound for which this is possible?
Answers
Answer:
The lowest possible frequency of sound for which this is possible is 1307.69 Hz
Explanation:
From the question, Abby is standing 5.00m in front of one of the speakers, perpendicular to the line joining the speakers.
First, we will determine his distance from the second speaker using the Pythagorean theorem
l₂ = √(2.00²+5.00²)
l₂ = √4+25
l₂ = √29
l₂ = 5.39 m
Hence, the path difference is
ΔL = l₂ - l₁
ΔL = 5.39 m - 5.00 m
ΔL = 0.39 m
From the formula for destructive interference
ΔL = (n+1/2)λ
where n is any integer and λ is the wavelength
n = 1 in this case, the lowest possible frequency corresponds to the largest wavelength, which corresponds to the smallest value of n.
Then,
0.39 = (1+ 1/2)λ
0.39 = (3/2)λ
0.39 = 1.5λ
∴ λ = 0.39/1.5
λ = 0.26 m
From
v = fλ
f = v/λ
f = 340 / 0.26
f = 1307.69 Hz
Hence, the lowest possible frequency of sound for which this is possible is 1307.69 Hz.
In some areas, hydroelectric power is not geographically appropriate and a different renewable energy source would be a better option. A conservation group is looking for renewable energy sources other than hydroelectric energy that could be used to generate electricity in grassland ecosystems, such as in the midwestern United States or in a savanna in Africa.
Required:
a. Propose a different renewable resource to use that would be a realistic solution to generating electricity without using fossil fuels or hydroelectric power in a grassland ecosystem.
b. Justify the solution proposed above by explaining a potential advantage of using a different renewable resource to generate electricity.
Answers
Answer:
a) wind power system, turbines powered, solar power system
b) the possibility of creating jobs for the local workforce and of maintaining the environment without damaging it.
Explanation:
In a grassland system it may not have great changes in height or mountain system where it is easy to represent a river, therefore a hydroelectric power system is not very feasible.
a) You can have several alternative energy systems.
* If there is a fairly constant air current, a wind power system could be implemented.
* If there is a river with an acceptable flow, a generation system can be implemented with turbines powered by the river flow.
* Another system is a solar power system
b) To select any of the possible systems proposed, the current and future energy requirements of the region must be analyzed.
The amount of energy that each proposal can supply
Analyze the installation costs and the economic benefits of a given system.
Study the possible problems for the maintenance of each system.
A great advantage of these systems is the possibility of creating jobs for the local workforce and of maintaining the environment without damaging it.
The most plausible renewable energy source in a grassland is wind energy.
Renewable energy refers to energy that is obtained from wind, water biomass or underground heat. All of these sources of energy are inexhaustible and hold great prospect to solving the current energy deficit is many parts of the world.
In grasslands, the most plausible renewable source of energy is wind. Winds are abundant in grasslands . It is more plausible than hydroelectric power because it does not create any adverse environmental impact. It is the cleanest energy source.
Learn more about renewable energy: https://brainly.com/question/4038933
A 500 grams ball is thrown vertically upwards with a speed of 20 metres per seconds. what is the kinetic energy of the ball at the height of 5 metres?
Answers
Answer:
Ek = 24.5 [J]
Explanation:
To solve this problem we must use the theorem of work and energy which tells us that potential energy is transformed into kinetic energy or vice versa.
In this way, the kinetic energy will be equal to the potential energy at each moment.
Ep = Ek
With the height and mass data, we can find the potential energy.
Ep =m*g*h
where:
Ep = potential energy [J] (energy in Joules)
m = mass = 500 [gr] = 0.5 [kg]
g = gravity acceleration = 9.81 [m/s²]
h = elevation = 5 [m]
Ep = 0.5*9.81*5
Ep = 24.5 [J]
So the kinetic energy is the same that the potential energy.
Ek =24.5 [J]
please help me out with these !! 50 points would greatly appreciate it.





Answers
Answer:
Its nymber 2
Explanation:
What is the average velocity of a car that travels 12 kilometers in 0.20 hours?
Answers
Answer:
60 km/hr
Explanation:
Looking for km / hr
12 km / (.20 hr) = 60 km/hr
SOMEONE PLEASE HELP ASAP?!
A neutron and a proton combine to form a nucleus. How does the sum of the masses of the nucleons that make up the nucleus compare with the mass of the nucleus itself?

Answers
The nucleons have less mass, because matter is converted into binding energy. Option D is correct.
During the process of combining a neutron and a proton to form a nucleus, a small amount of mass is converted into binding energy. This is due to the strong nuclear force that holds the nucleus together. The mass of the nucleus is slightly less than the sum of the masses of the individual nucleons, and the difference in mass is referred to as the mass defect.
This mass defect is related to the binding energy of the nucleus through Einstein's famous equation E=mc², where E is energy, m is mass, and c is the speed of light. The mass defect represents the amount of mass that is converted into binding energy to hold the nucleus together. Option D is correct.
To know more about nucleons, here
brainly.com/question/17116720
#SPJ1