7. Determine the de Broglie wavelength of a proton that has 1.2 x 10 eV of kinetic energy.
Answers
The de Broglie wavelength of a proton with 1.2 x 10 eV of kinetic energy is approximately 1.14 x \(10^-^1^0\) meters.
To determine the de Broglie wavelength of a proton, we can use the de Broglie wavelength equation:
λ = h / p
where λ is the de Broglie wavelength, h is Planck's constant (6.626 x \(10^-^3^4\)J*s), and p is the momentum of the proton.
The momentum of a proton can be calculated using the equation:
p = (\(\sqrt{2mK)}\)
where p is the momentum, m is the mass of the proton (1.67 x \(10^-^2^7\) kg), and K is the kinetic energy of the proton.
Given the kinetic energy of the proton as 1.2 x 10 eV, we need to convert it to joules before proceeding with the calculation. The conversion factor is 1 eV = 1.6 x \(10^-^1^9\) J. Therefore, the kinetic energy of the proton is:
K = 1.2 x 10 eV * (1.6 x \(10^-^1^9\) J/eV)
K = 1.92 x \(10^-^1^9\) J
Next, we can calculate the momentum of the proton:
p = \(\sqrt{(2 * 1.67 x 10^-^2^7 kg * 1.92 x J)}\)
p =\(\sqrt{ (3.3648 x 10^-^4^6 kg }\)* J)
p = 5.8 x \(10^-^2^4\)kg*m/s
Finally, we can substitute the momentum into the de Broglie wavelength equation to find the de Broglie wavelength of the proton:
λ = (6.626 x \(10^-^3^4\)J*s) / (5.8 x\(10^-^2^4\) kg*m/s)
λ = 1.14 x \(10^-^1^0\) m
For more such information on: wavelength
https://brainly.com/question/10750459
#SPJ8
Related Questions
Can someone help me with this? It's on the Kepler's Second Law experiment. These two questions are the same for all the planets.
(You can prob look up the photo for them, but I don't fully get it)
Mercury:
1. What do you notice about each area?
2. Record any observation regarding the perihelion distance (Rp) and the aphelion distance (Ra).
Earth:
1. What do you notice about each area?
2. Record any observation regarding the perihelion distance (Rp) and the aphelion distance (Ra).
Mars:
1. What do you notice about each area?
2. Record any observation regarding the perihelion distance (Rp) and the aphelion distance (Ra).
Saturn:
1. What do you notice about each area?
2. Record any observation regarding the perihelion distance (Rp) and the aphelion distance (Ra).
Neptune:
1. What do you notice about each area?
2. Record any observation regarding the perihelion distance (Rp) and the aphelion distance (Ra).
Comet:
1. What do you notice about each area?
2. Record any observation regarding the perihelion distance (Rp) and the aphelion distance (Ra).
can anyone fully help me with Neptune?
1. What is the orbit of the Neptune?
2. Is the Sun at the center of the Nepturn’s orbit?
3. Describe the motion of Neptune throughout its orbit? Does it move at constant speed?
4. What do you notice about each area?
5. Record any observation regarding the perihelion distance (Rp) and the aphelion distance (Ra).
Answers
According to Kepler's Second Law, as a planet orbits the Sun, an imaginary line connecting them sweeps across the same amount of area at the same rate.
Mercury's orbit is shaped like an egg, and the Mercury, orbits the Sun within Earth's orbit as an inferior planet; from Earth, Mercury's apparent distance from the Sun never exceeds 28°.
Due to its close proximity to the Sun, the planet may only be seen around the horizons of the western and eastern hemispheres, typically in the twilight hours.
To learn more about Kepler's Second Law, click:
https://brainly.com/question/30767101
#SPJ1
An entertainer pulls a table cloth off a table leaving behind the plates and sliverware undisturbed is an example of
A.
the law of balanced forces
B.
Newton's second law
C.
Newton's third law
D.
Newton's first law
Answers
Answer:
d.) Newton's first law
Explanation:
This is also called the law of inertia, which means that an object in motion will not stop unless a force is acted upon it, and vice versa. Try this out with a piece of paper and a quarter. Pull the paper from under the quarter slightly quick, and the quarter will stay on the table. Hope i helped you.
Identify all the forms of energy in the picture below
identify thermal energy, mechanical energy, radiant energy, electrical energy, sound energy, and chemical energy

Answers
Answer:
we are going to focus on just a few. • Heat energy ( Thermal). • Mechanical energy. • Light (Radiant) energy. • Electrical energy. • Sound energy. • Chemical energy
Please do all of i will give you brainlest and thanks to best answer plz do it right

Answers
Answer:
the answer is B
Explanation:
because i had this question in 8th grade
please answer withhin 400 words
Question 52 (8 points) Using schematics, draw and fully describe with labels and descriptive text a horizontal cross section of a warm front and a cold front for a mid-latitude low pressure system at
Answers
The slope of a cold front is steeper than that of a warm front.
A warm front and a cold front are two different fronts associated with a mid-latitude low-pressure system. A cross-sectional view of these fronts can be helpful in better understanding their characteristics and structure. Let's take a look at the horizontal cross-section of these fronts:
Image showing the Horizontal Cross section of a warm front and a cold front for a mid-latitude low pressure system:
The 150 isobar is shown in bold.
The vertical structure of a warm front:
In a mid-latitude low-pressure system, a warm front represents the leading edge of a warm, moist air mass as it approaches a region of cold, dry air. In general, the warm air moves toward the cold air in the form of a low-level wedge. The warm front is associated with a gradual decrease in temperature and pressure as one moves from the warm side to the cold side of the front. The steepness of the frontal slope is gradual. The slope is gradual because the warm air rises over the cool air.
The vertical structure of a cold front:
A cold front represents the leading edge of a cold, dry air mass as it advances toward a region of warm, moist air. It is usually associated with a line of clouds, precipitation, and thunderstorms. The frontal slope is steeper than that of a warm front, with a temperature drop of several degrees Celsius per kilometer of ascent. The cold air moves in a downward motion to the ground and forces the warm air up. This motion creates clouds, precipitation, and sometimes thunderstorms. Therefore, the slope of a cold front is steeper than that of a warm front.
learn more about cold front on
https://brainly.com/question/24261973
#SPJ11
Carter is going camping outside he wants to bring a frying pan that will heat up and cool down quickly Which frying pan should carter use that will heat up and cool down the fastest
A copper
B iron
C glass
D steel
Plz help

Answers
The specific heat of the copper pan is the lowest among the other given pans. Therefore, a copper pan should carter used that will heat up and cool down the fastest. Therefore, option (A) is correct.
What is the specific heat?Specific heat of a substance can be described as the heat energy required to raise the temperature of one unit mass of a material by 1 °C. The S.I. unit of the specific heat capacity of a material is J/g°C.
The thermal capacity of a substance is a physical characteristic of a substance so it depends upon the nature of the material.
The mathematical expression of specific heat can be represented as :
Q = m×C× ΔT Where C is the specific heat.
The specific heat is an intensive characteristic of a material and does not depend upon the shape or size of the quantity.
As given the values of the specific heat of metals of the frying pans, the highest specific heat means that the pan will take more heat to increase just one-degree temperature. As copper has the lowest specific heat so it can easily heat up in comparison to other pans.
Learn more about specific heat, here:
brainly.com/question/11297584
#SPJ2
Systems in the body interact to carry out life functions. The muscles of the body are part of the musculoskeletal system. Which system provides the impulses that cause the muscles to contract?
A.
circulatory
B.
integumentary
C.
respiratory
D.
nervous
Answers
Ayla hangs a 7.5 kg bowling ball from the ceiling by a rope of negligible mass. The rope will break if the tension in the rope exceeds 115 N. What minimum force must Ayla's dog Rufus exert on the bowling ball to break the rope.
Answers
Answer: >41.5N
Explanation:
Mass of bowling ball = 7.5kg
Breaking point of rope = T > 115N
Where T = Tension on the rope
Since the bowling ball is hung by a rope :
Tension (T) = mg = 7.5 kg × 9.8m/s^2 = 73.5kgm/s^2
T = mg + ma
F = ma
T = mg + F
>115 = 73.5 + F
F = 115 - 73.5
F = 41.5N
Force >41.5N
the arrow maintains a constant horizontal velocity while its vertical velocity increases steadily because blank .
Answers
The arrow maintains a constant horizontal velocity while its vertical velocity increases steadily due to the force of gravity.
The reason why the arrow maintains a constant horizontal velocity while its vertical velocity increases steadily is due to the force of gravity acting upon it.
When an arrow is shot horizontally, it experiences no horizontal forces, such as air resistance, to change its velocity. As a result, the horizontal velocity remains constant throughout its flight.
However, the force of gravity acts vertically downwards on the arrow, causing it to accelerate in the downward direction. This acceleration results in an increase in the arrow's vertical velocity over time.
The arrow's vertical velocity increases steadily because the force of gravity is constantly acting upon it, causing it to fall towards the ground at an increasing rate.
It's important to note that the horizontal and vertical motions of the arrow are independent of each other. The arrow's horizontal velocity remains unchanged because there is no force acting in the horizontal direction.
Meanwhile, its vertical velocity increases due to the force of gravity acting vertically downwards. This combination of motions results in the arrow following a curved trajectory known as a parabola.
To know more about "Velocity " refer here:
https://brainly.com/question/31479424#
#SPJ11
Projectile Motion
a. Identify the variables (givens and unknown.) Remember to include the units.
B. Which kinematic formula should you use to solve?
C. Solve the problems.
An egg is thrown horizontally off the roof.
Which is 70 meters high, with an
initial velocity of 5.5 m/s. How long does it take to hit the ground? How far
does it go in the x direction?
3 variable
Variable Chart Given and Unknown?
PLEASE HELP ME FAST ITS 25 POINTS

Answers
Answer:thx
Explanation:
Homework Help!! Thsnkyouu

Answers
A. The frisbee will remain in the air for 5.88 s
B. The horizontal distance the frisbee will go is 29.4 m
A. How to determine the time the frisbee will remain in the airThe time the frisbee will spend in the air can be obtained as illustrated below:
Height (h) = 169.2 mAcceleration due to gravity (g) = 9.8 m/s²Time (t) =?169.2 = ½gt²
169.2 = ½ × 9.8 × t²
169.2 = 4.9 × t²
Divide both side by 4.9
t² = 169.2 / 4.9
Take the square root of both side
t = √(169.2 / 4.9)
Time = 5.88 s
How to determine the horizontal distanceThe horizontal distance travelled by the frisbee can be obtained as follow:
Initial velocity (u) = 5 m/sTime (t) = 5.88 sHorizontal distance (s) =?s = ut
s = 5 × 5.88
Horizontal distance = 29.4 m
Learn more about motion under gravity:
https://brainly.com/question/22719691
#SPJ1
In a galvanic cell, electrons move a) along the wire in the external circuit from the anode to the cathode b) along the wire in the external circuit from the cathode to the anode c) through the salt bridge from the anode to the cathode d) through the salt bridge from the cathode to the anode
Answers
In a galvanic cell electrons move a) along the wire in the external circuit from the anode to the cathode.
In a galvanic cell, electrons move along the wire in the external circuit from the anode to the cathode (option a). This flow of electrons constitutes an electric current, which is generated by the redox reaction occurring within the cell.
At the anode, oxidation takes place, and the electrode loses electrons. These electrons are released into the wire, creating a buildup of negative charge at the anode. Simultaneously, at the cathode, reduction occurs, and the electrode gains electrons, leading to a buildup of positive charge. This charge separation establishes an electric potential difference between the anode and the cathode, creating an electromotive force (emf).
The movement of electrons through the wire is driven by this potential difference. Electrons naturally flow from areas of higher potential (anode) to areas of lower potential (cathode), which establishes the direction of electron flow from the anode to the cathode.
In contrast, the salt bridge plays a different role in the galvanic cell. It serves to maintain charge balance within the cell by allowing the flow of ions. As electrons leave the anode, cations from the salt bridge migrate to the anode, balancing the negative charge. Likewise, anions from the salt bridge move to the cathode, balancing the positive charge. This movement of ions through the salt bridge ensures that the overall cell remains electrically neutral.
Therefore, while the salt bridge facilitates the flow of ions for charge balance, it is the wire in the external circuit where the primary movement of electrons occurs, from the anode to the cathode, generating the electric current in a galvanic cell.
To know more about galvanic cell refer here: https://brainly.com/question/30268944#
#SPJ11
What is the equivalent resistance (total resistance) of the series circuit shown?
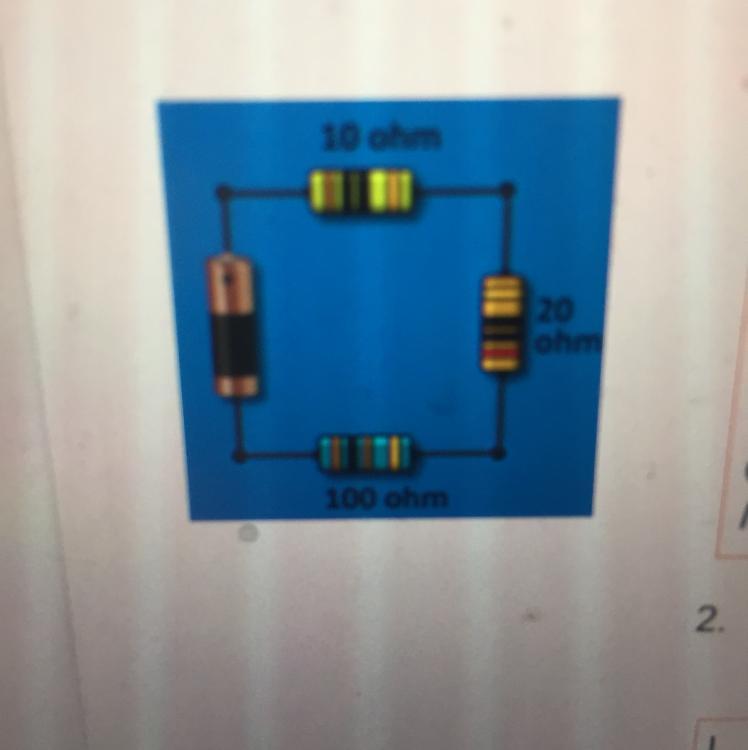
Answers
You can use _______________ to change a liquid into a gas.
Answers
Answer:
below
Explanation: When a liquid changes into a gas vaporization has occurred. The process can either occur due to boiling or evaporation. Boiling occurs when the vapor pressure of the liquid is raised (by heating) to the point where it is equal to the atmospheric pressure.
You can use thermal energy to change a liquid into a gas.
What is thermal energy?By virtue of its temperature, a system in a condition of thermodynamic equilibrium has thermal energy, or internal energy. Unlike the energy of systems that are not in a state of thermodynamic equilibrium, thermal energy cannot be transformed into meaningful work as quickly.
For instance, the same fluid or solid in a thermodynamic equilibrium state with the same energy (as thermal energy) cannot do work unless it is combined with another substance at a different temperature, as in a heat engine. However, the same fluid or solid in a moving state with the same energy (as mechanical energy) can be converted to work in some mechanical device, such as a windmill or a waterwheel.
Learn more about thermal energy here:
https://brainly.com/question/11278589
#SPJ2
A boy pushes forward a cart of groceries with a total mass of 40.0 kg. What is the acceleration of the cart if the net force on the cart is 60.0 N?
Answers
1.5m/s2
F=ma
a=F/m
a=60/40
a=1.5m/s2
The acceleration of the cart is 1.5 meter per seconds square.
Given the following data:
Mass of groceries = 40.0 kgNet force = 60.0 NewtonTo find the acceleration of the cart, we would use Newton's Second Law of Motion.
Mathematically, Newton's Second Law of Motion is given by the formula;
\(Acceleration = \frac{Net\; Force}{Mass}\)
Substituting the given parameters into the formula, we have;
\(Acceleration = \frac{60}{40}\)
Acceleration = 1.5 meter per seconds square.
Therefore, the cart's acceleration is 1.5 meter per seconds square.
Read more here: https://brainly.com/question/24029674
Helpppp helppp I will make you a brainlist!!
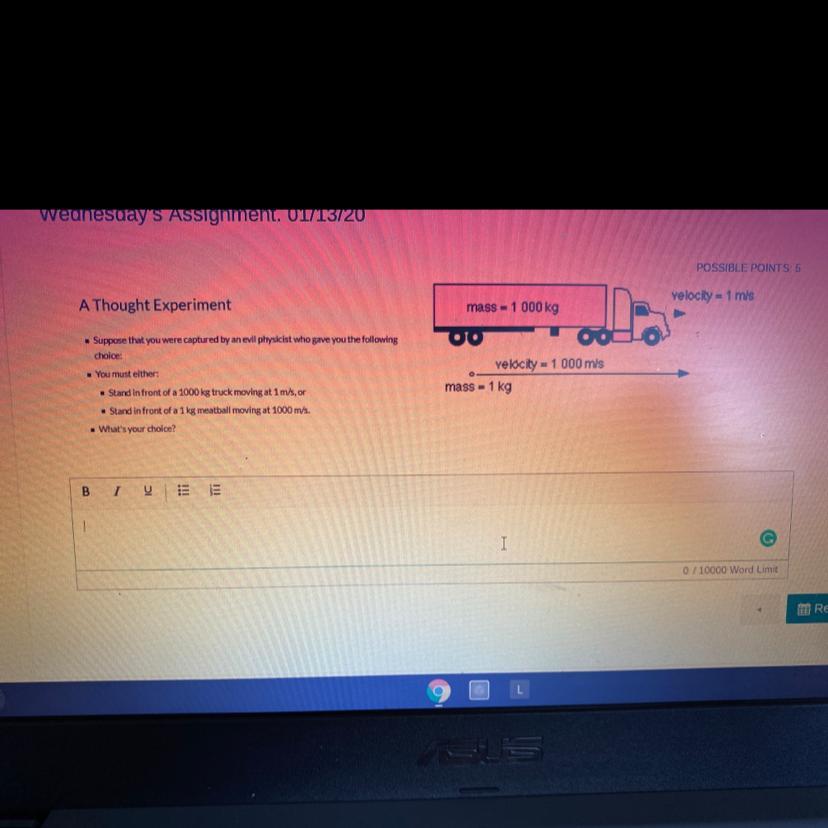
Answers
Answer:
The answer is that the evil psychic is merciless, see the explanation below:)
Explanation:
When a body is about to receive an impact or collision, two important factors should be taken into consideration; the mass of the body and the velocity with which it moves. The product of mass by velocity is defined as momentum.
Therefore:
\(P=m*v\\\)
where:
P = momentum [kg*m/s]
m = mass [kg]
v = velocity [m/s]
That is, is we are standing in front of the truck:
\(P_{truck}=1000*1\\P_{truck}=1000[kg*m/s]\)
Or in front of the meatball:
\(P_{meatball}=1*1000\\P_{meatball}=1000[kg*m/s]\)
A race car travels at 33m/s slows at a constnt rate to a velocity of 22 m/s over 112. How far does it move during this time
Answers
If a race car travels at 33m/s slows at a constant rate to a velocity of 22 m/s over 112s, then distance travel by the race car is 3361.1 m.
How to calculate the Acceleration ?From Newton's first equation of motion
a = (v-u) /t
Given,
Initial velocity = u = 33m/s
Final velocity = v = 22m/s
Time = t = 112s.
Now,
a = (v-u) /t
a = (22-33) / 112
a = -11/112
a = - 0.09m/s²
How to calculate the Distance ?This can be calculated by using second law of equation or by the third law of equation.
From third equation of motion,
v² − u² = 2as
484 - 1089= 2(0.09) s
605 = 0.18 s
s = 3361.1m.
Thus, we calculated that if a race car travels at 33m/s slows at a constant rate to a velocity of 22 m/s over 112s, then distance travel by the race car is 3361.1 m.
learn more about Newton's equation of motion:
https://brainly.com/question/8898885
#SPJ9
A car traveled 1 hour at a contanst velocity of 65 mph west with cruise control. The acceleration is
Answers
Hope that helps, have a good day :)
How do you find distance from average velocity and time
Answers
Answer:
Calculate the total distance travelled by the object - its motion is represented by the velocity-time graph below.
Here, the distance travelled can be found by calculating the total area of the shaded sections below the line.
½ × base × height.
½ × 4 × 8 = 16 m 2
(10 – 4) × 8 = 48 m 2
Explanation:
Question 12 of 20
Which force holds distant stars and other matter together in a galaxy?
A. Electromagnetic
B. Weak nuclear
C. Gravitational
O D. Strong nuclear
PLEASE HELP.
Answers
Answer:
C. gravity
Explanation:
Answer:
Gravitational
Hope this helps :)
How does the Coriolis effect impact the Gulf Stream and the Brazil Current?
Answers
Answer: The Coriolis effect results in bending the direction of surface currents to the right in the Northern Hemisphere and left in the Southern Hemisphere. The Coriolis effect causes winds and currents to form the circular patterns. The direction in which they spin depends upon the hemisphere in which they are present.Coriolis Effect is named after the French mathematician and physicist Gaspard-Gustave de Coriolis. It affects the weather patterns of an area, it affects the ocean currents, and it also affects air quality.
What is definition of surface tension
Answers
Surface tension is defined as the force per unit length required to break the surface film of a liquid and is commonly measured in units of Newtons per meter (N/m).
The molecules of a liquid are held together by attractive forces known as intermolecular forces. At the surface of the liquid, the molecules are subjected to unbalanced intermolecular forces that pull them inward, causing the surface to behave as if it were under tension.
This tension is what causes liquid surfaces to form into a distinct shape, such as a droplet, and to resist external forces that try to deform or break the surface. Surface tension is a physical property of a liquid that arises from the cohesive forces between the molecules at the surface of the liquid.
The magnitude of the surface tension depends on the nature of the liquid and the surrounding environment, such as temperature and pressure. It can also be affected by the presence of impurities or surfactants, which can alter the intermolecular forces at the surface.
Surface tension has important practical applications, such as in the formation of bubbles and the behavior of fluids in capillary tubes. It is also a key factor in the wetting and spreading of liquids on surfaces, as well as in the formation of emulsions and foams.
To know more about surface tension here
https://brainly.com/question/11348644
#SPJ4
Squeezing due to differences in the gravitational force of the moon at different points on earth causes
Answers
Answer:
the most important effect of the gravitational force is the change in the tide.
Explanation:
The gravitational force between the Moon and the Earth is given by
F = G m M / r2
where m is the mass of the Moon, M the mass of the Earth, and r the distance between the two.
The magnitude that changes in this formula is the distance between the Moon and the Earth, due to the lunar rotation, at the points of maximum approach in the periods of high tide and in the periods of greater distance the tide is low.
It should be mentioned that the earth's crust is also affected, but its movement is much less than that of water, which is why in almost all cases it is taken as fixed.
Lately it has also been analyzed that the Earth-Moon structure creates greater stability in the rotation of the two bodies.
Consequently the most important effect of the gravitational force is the change in the tide.
A small convex mirror is placed 60 cm from the pole and on the axis of a large concave mirror of radius of curvature 200 cm. The position of the convex mirror is such that a real image of distant object is formed on the plane of a hole drilled through the concave mirror at its pole. Calculate 'R' of convex mirror and height of the real image if distant object forms 0.5 degree angle at the pole of the concave mirror.
Answers
Answer:
Calculate 'R' of convex mirror and height of the real image
the radius of the convex mirror is 48cm
Explanation:
Distance between convex and concave mirror is =60cm
Radius of the concave mirror (R) = 200cm
For the concave mirror, u = ∞
V = {R}/{2}=100cm
The object for the convex mirror and the final image is on the pole of the concave mirror, and distance between convex and concave mirror is 60cm
u_1=60-100 =-40cm
Object will be behind the convex mirror
1/f=1/40+1/60
f=24cms
the radius of the convex mirror is 48cm
g how does the pressure at each of the five points change if the tank and its previous contents were buried an extra 1 meter below the current level such that the pipe to the surface is now 3 meters long?
Answers
The pressure at each of the five points would increase by ρg × 1 Pa.
The pressure at each of the five points would increase if the tank and its previous contents were buried an extra 1 meter below the current level. The pressure at a point in a fluid is proportional to the height of the fluid column above that point. Since the pipe to the surface is now 3 meters long, the height of the fluid column above each of the five points has increased by 1 meter. Hence, the pressure at each of the five points would increase by an amount proportional to the height of the fluid column, or P2 = P1 + ρgh, where P1 is the original pressure, P2 is the new pressure, ρ is the density of the fluid, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the increase in height. As a result, the pressure at each of the five points would increase by ρg × 1 Pa.
Learn more about pressure:
brainly.com/question/12971272
#SPJ4
the distance between slits on a diffraction grating is 0.60 mm, and one of the angles of diffraction is 0.30°. the light forms a second-order bright band.
Answers
The distance between slits on a diffraction grating is 0.60 mm: The path difference for the second-order bright band is 0.12 mm.
In a diffraction grating, when light passes through the slits, it diffracts and creates interference patterns. The path difference is the difference in the distance traveled by light from two adjacent slits to a specific point on the screen.
To calculate the path difference, we can use the formula:
Path Difference = d * sin(θ)
where d is the distance between slits (also known as the slit spacing) and θ is the angle of diffraction.
In this case, the distance between slits is given as 0.60 mm, and the angle of diffraction is 0.30°. Since it is mentioned that the light forms a second-order bright band, we need to consider the path difference corresponding to the second-order interference.
Using the formula, we can calculate the path difference as follows:
Path Difference = (0.60 mm) * sin(0.30°)
Calculating the value, we find:
Path Difference = 0.60 mm * 0.0052359 ≈ 0.0031416 mm ≈ 0.12 mm
Therefore, the path difference for the second-order bright band is approximately 0.12 mm.
To know more about diffraction, refer here:
https://brainly.com/question/12290582#
#SPJ11
are zebra fish schooling fish?
Answers
Answer:
they r schooling fish
Explanation:
they need to be kept in groups of 5.
Answer:
yes thwy are schooling fish
An astronaut landed on the moon. He decided to test Newton's Laws of Motion by playing golf on the moon.
The golf ball was hit. The ball traveled much farther on the moon than a golf ball that is hit with the same force on the Earth. Which statement BEST explains this phenomenon?
Select TWO correct answers.
The unbalanced force of friction from Earth's atmosphere slows the ball down, causing the ball not to travel as far.
The moon's gravitational pull is greater than the pull of the Earth, causing the ball to travel farther.
The ball's inertia is greater on the moon because of the space, causing it to travel farther.
The mass of the ball is the same on the Earth and the moon, so the ball will travel farther on the moon.
The moon's gravitational pull is not as strong as the Earth's gravitation pull, causing the ball to travel a greater distance.
Answers
Here are the two claims: Because of the moon's weaker gravity, the ball has a higher inertia and moves farther. As the moon has no atmosphere, there is no air resistance to cause the ball to slow down.
What happens if a golf ball is struck on the moon?The ball would fly six times further and land about 2 km (or 1.25 miles) further on the moon, where the gravity acceleration is six times smaller. A professional golfer could hit a drive on the moon this far if they had the right equipment.
On the moon, did astronauts play golf?On the moon, Alan Shepard of Apollo 14 played golf. He held a contingency sample extension handle with a no. 6 iron head in his hand as his "club." For personal things, each astronaut was given a set amount of weight. Shepard took the club head and three golf balls with his.
To learn more about golf on moon visit:
brainly.com/question/12463090
#SPJ1
ham radio operators sometimes operate receivers for the 2 meter wavelength band. the 2 meters refers to the
Answers
The 2 meters refers to the wavelength of the radio signals.
In ham radio, the 2-meter wavelength band refers to the portion of the radio spectrum that has a wavelength of approximately 2 meters (roughly 144-148 MHz). This is a popular frequency range for amateur radio operators, as it allows for both local and long-distance communication, depending on the specific mode and equipment used.
The 2-meter band is part of the VHF (Very High Frequency) spectrum, which has various applications such as FM radio, television broadcasts, and amateur radio. Ham radio operators use the 2-meter band for different modes of communication, including voice, digital, and Morse code. The 2-meter wavelength enables them to establish a connection with other radio operators locally, regionally, or even internationally via satellite or other propagation methods, such as tropospheric ducting or sporadic E propagation.
To know more about wavelength visit:-
https://brainly.com/question/31322456
#SPJ11
WHAT IS NUMBER OF TICKS? IN FINDING APPROXIMATE AREA OF YOUR PALM? IMPORTANT PLZ ANSWER QUICK
Answers
Answer:
idk
Explanation: