444 joules into calories
Answers
hope this helps!
Answer:
106.119 calories
Explanation:
Hope this helps! If you need a step-by-step explanation feel free to ask and I'd be happy to give it to you <33
Related Questions
Calculate the molecular weight of a gas with a density of 1.524 g/L at STP. a. 16 g/mol b. 28 g/mol c. 32 g/mol d. 44 g/mol
Answers
None of the given options are correct. This calculation suggests that the molecular weight of the gas is much larger than the options provided. It is possible that there was an error in the measurement of the density or the problem was intended to be more complex.
To calculate the molecular weight of a gas with a given density at STP, we need to use the Ideal Gas Law equation PV=nRT and rearrange it to solve for the molecular weight. At STP, the pressure (P) is 1 atm and the temperature (T) is 273.15 K.
First, we need to find the molar volume of the gas at STP, which is 22.4 L/mol. Then, we can use the density (d) and the molar volume (V) to calculate the number of moles (n) using the formula n = d/V.
n = 1.524 g/L / 22.4 L/mol = 0.068 mol
Next, we can use the formula n = m/M, where m is the mass of the gas and M is the molecular weight we want to find. Since we know the density and the molar volume, we can find the mass of the gas using the formula m = dV.
m = 1.524 g/L x 22.4 L/mol = 34.13 g/mol
Now we can plug in the values for n and m in the formula n = m/M and solve for M.
0.068 mol = 34.13 g/mol / M
M = 34.13 g/mol / 0.068 mol = 501.9 g/mol
To know more about molecular weight
https://brainly.com/question/837939
#SPJ11
for benzene, c6h6, the heat of vaporization at its normal boiling point of 80 °c is 30.7 kj/mol. the entropy change when 1.67 moles of liquid c6h6 vaporizes at 80 °c, 1 atm is j/k.
Answers
The entropy change when 1.67 moles of liquid \(C_6H_6\) vaporizes at 80 °C, 1 atm is approximately 145.18 J/K.
To find the entropy change when 1.67 moles of liquid benzene (\(C_6H_6\)) vaporizes at 80°C (353.15 K) and 1 atm, you need to use the following formula:
ΔS = (ΔHvap / T) * n
Where:
ΔS is the entropy change
ΔHvap is the heat of vaporization (30.7 kJ/mol)
T is the temperature in Kelvin (353.15 K)
n is the number of moles (1.67 moles)
Step 1: Convert the heat of vaporization from kJ/mol to J/mol: 30.7 kJ/mol * 1000 J/kJ = 30700 J/mol
Step 2: Calculate the entropy change using the formula: ΔS = (30700 J/mol / 353.15 K) * 1.67 moles
Step 3: Calculate the result: ΔS = (86.94 J/mol*K) * 1.67 moles
Step 4: ΔS = 145.18 J/K
To know more about "Entropy" refer here:
https://brainly.com/question/28082783#
#SPJ11
If 40.0 grams of HCI were dissolved in enough water to make a solution with a total volume of 3.0 liters, what would be the molarity of the solution?
Answers
Answer: 0.37 M
Explanation:
HCl has a gram-formula mass of 36.46 g/mol, so 40.0 g is about 40.0/36.46=1.10 mol.
This means that since molarity = (moles of solute)/(liters of solution), the answer is 1.10/3.0 = 0.37 M
What is thermal equilibrium?
Answers
Consider the half reaction below.
Which statement best describes what is taking place?
Chlorine is losing electrons and being oxidized. Chlorine is losing electrons and being reduced. Chlorine is gaining electrons and being oxidized. Chlorine is gaining electrons and being reduced.

Answers
Answer:
balancing of charges of both sides
Answer:
A
Explanation:
A...............................
suppose both the electron affinity of and the heat of sublimation of were smaller. would be more stable? or less?
Answers
If both electron affinity and heat of sublimation are smaller, then MX would be less stable.
M²⁺ + X⁻(g) → MX(s), + Lattice energy
Therefore, from the given thermodynamic cycle,
Lattice enthalpy = -100-800 = -900kJ/mol
Lattice enthalpy MX = -900kJ/mol
Enthalpy of the formation of MX is given as follows:
M(s) + 1/2X₂(g) --------->M(g) + 1/2 X₂(g)
Enthalpy of formation = +250 kJ
M(g) + 1/2X₂(g) → M(g) +X(g)
Enthalpy of formation = +350 kJ
M (g) + X(g) ------> M²⁺(g), + X(g)
Enthalpy of formation = +400 kJ
M²⁺ (g) + X(g) 24→ M²⁺(g), + X(g)
Enthalpy of formation = +200kJ
M²⁺(g), + X⁻(g)→ MX(s)
Enthalpy of formation= +900kJ.
Enthalpy of formation of MX = 250 +350 +406-200-900 = -100 kJ
Therefore, Enthalpy of formation of MX = -100 kJ
Since electron affinities are the heat released while the heat of sublimation is the heat absorbed then if electron affinity decreases while the heat of sublimation, increases then the overall enthalpy of formation of MX will be less negative. Hence in that case MX would be less stable.
To know more about the heat of sublimation, click here:
https://brainly.com/question/14895394
#SPJ4
PLS HELP ME After completing the Gold Foil Experiment, Ernest Rutherford proposed that the positive charge of an atom was concentrated in a dense central core or
nucleus. What evidence from the experiment did he use to support this idea? Your answer should reference the image.
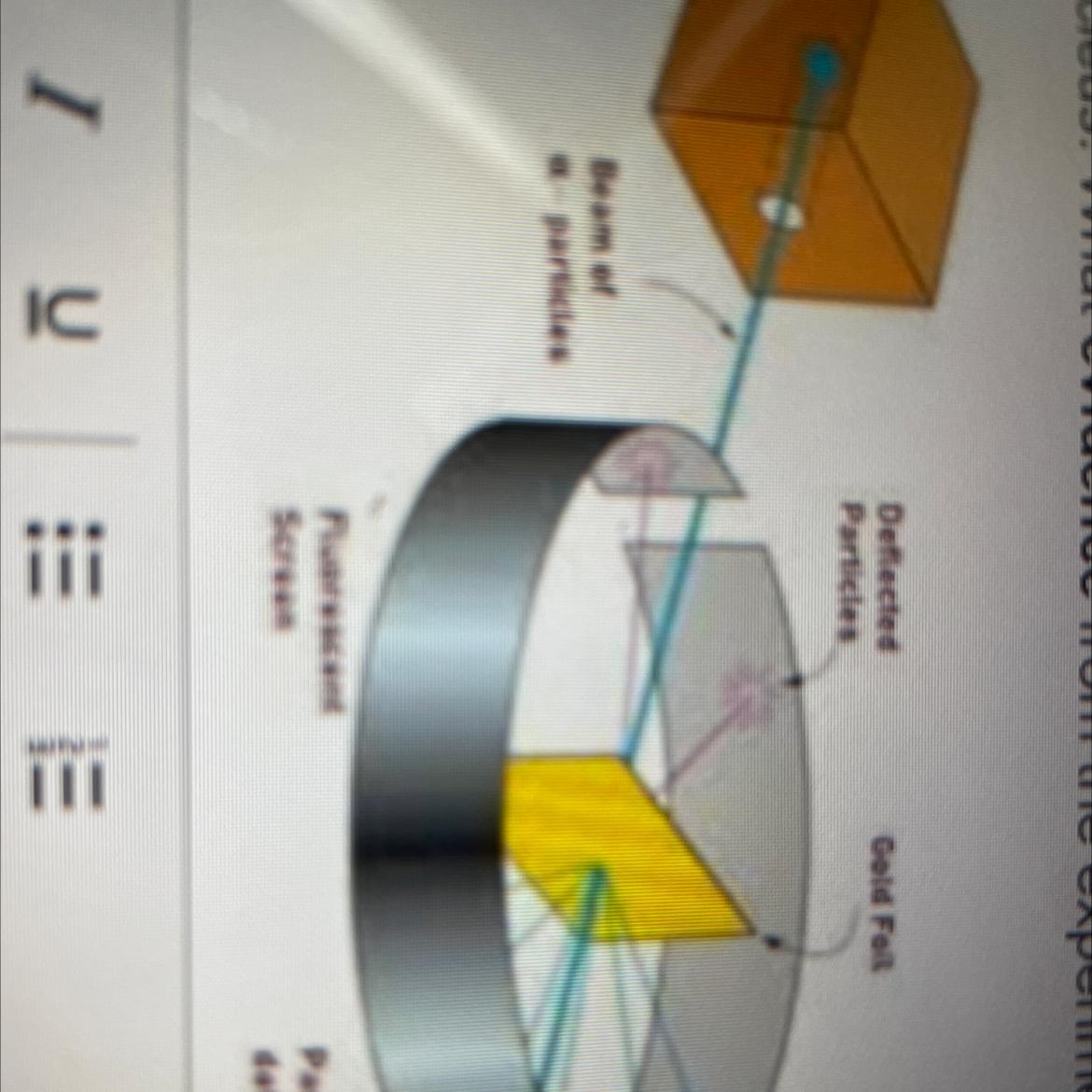
Answers
Answer:
A piece of gold foil was hit with alpha particles, which have a positive charge. Most alpha particles went right through. This showed that the gold atoms were mostly empty space. Some particles had their paths bent at large angles. A few even bounced backward. The only way this would happen was if the atom had a small, heavy region of positive charge inside it.
The half-life of 55cr is about 2. 0 hours. The delivery of a sample of this isotope from the reactor to a certain laboratory requires 12 hours. About what mass of such material should be shipped in order that 1. 0 mg of 55cr is delivered to the laboratory?.
Answers
The half-life of 55cr is about 2. 0 hours. The delivery of a sample of this isotope from the reactor to a certain laboratory requires 12 hours. The bare minimum of such material that should be shipped is 63.9 mg= 64 mg.
Given Information: 1.8 hours is the half-life. Formula: 0.693/k is the half-life.Where: k is the rate constant.k=0.693/1.8 =0.385 hr^-1
To determine the initial concentration, use the following formula: In the A/Ao=-kt
Where: A represents the final concentration.
A o stands for initial concentration.
It is now time
Using the exponential function on both sides:
A A。 A。 -kt = e A -kt = e A = 63.9mg
The bare minimum of such material that should be shipped is 63.9 mg= 64 mg.
Learn more about isotopes here:
https://brainly.com/question/12955625
#SPJ4
Which of the following materials is acidic?
A.lemon juice
B.a baking soda solution
C.drain cleaner
D.milk of magnesia
Answers
Answer:
lemon juice............
A solution prepared by dissolving 180.0 mg of a sugar (a molecular compound and a nonelectrolyte) in 1.00 g of water froze at -1.86°C. What is the molar mass of this sugar? The value of Kf is 1.86°C/m._______ g/mol
Answers
Answer:
180 g/mol.
Explanation:
What is given?
ΔT = [0 - (- 1.86 )] °C = 1.86 °C.
i = 1 (for a nonelectrolyte).
Kf = 1.86 °C/m.
Step-by-step solution:
To solve this problem, we have to use the boiling point elevation formula, which is the following:
\(\Delta T=i\cdot m\cdot K_f.\)Where ΔT is the change in boiling point, i is the Van't Hoff factor, m is the molality of solution, and Kf is the molal boiling point constant.
Let's calculate the molality with the given data:
\(m=\frac{\Delta T}{i\cdot K_f}=\frac{1.86\text{ \degree C}}{1\cdot1.86\text{ }\frac{\degree C}{m}}=1\text{ m.}\)1 m is the same that 1 mol/kg. As we have 1.00 g of water and 180.0 mg of the sugar, we can multiply 1 mol/kg by the mass of water. Remember that 1 kg equals 1000 g, so 1.00 g is the same that 0.001 kg:
\(1\text{ }\frac{mol}{kg}\cdot0.001\text{ kg=0.001 mol.}\)Remember that the units of the molar mass is in g/mol, and 1 g equals 1000 mg, so 180.0 mg is the same that 0.18 g. If we divide 0.18 g by 0.001 mol, we will obtain the molar mass of the sugar, which would be:
\(\begin{gathered} Molar\text{ mass=}\frac{0.18\text{ g}}{0.001\text{ mol}}, \\ Molar\text{ mass=180}\frac{g}{mol}. \end{gathered}\)The answer would be that the molar mass is 180 g/mol.
what mass of solute is required to produce 550.5 ml of a 0.269 m solution of kbr?
Answers
The mass of solute is required to produce 550.5 ml of a 0.269 m solution of KBr is 16.02 grams.
To calculate the mass of solute required to produce a 0.269 m solution of KBr in 550.5 mL, we need to use the formula:
m = M × V × MW
Where:
m = mass of solute (in grams)
M = molarity of solution (in moles per liter)
V = volume of solution (in liters)
MW = molecular weight of solute (in grams per mole)
First, we need to convert the volume of the solution from milliliters to liters:
550.5 mL = 0.5505 L
Next, we need to calculate the molarity of the solution:
0.269 m = 0.269 moles/L
The molecular weight of KBr is 119.0 g/mol.
Now we can substitute the values into the formula:
m = 0.269 moles/L × 0.5505 L × 119.0 g/mol
m = 16.02 g
Therefore, 16.02 grams of KBr are required to produce 550.5 mL of a 0.269 m solution.
Learn more about mass: https://brainly.com/question/29482678
#SPJ11
in the single replacement reaction AB + C → A + CB, the anion in the reactant compound AB is _______
Answers
Answer:
The anion is B.
Explanation:
Compounds are usually written as [cation][anion], and the positive charge of the cation (A) will cancel out the negative charge of the anion (B). We are reaffirmed of our answer by the product CB, which also has B as an anion.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
an element y has the ionization energy as follows:
ei1 = 578 kj/mol
ei2 = 1.817 kj/mol
ei3 = 2.745 kj/mol
ei4 = 11.575
kj/mol based on the data above, then the element is .....
Answers
The following ionization energies apply to beryllium:
e1=899.5 kj/mol
1757.1 kj/mol for ei2
14,848 kj/mol for ei3.
21,006 kj/mol for ei4.
We must examine the pattern and properties of the ionization energies in order to identify the element using the provided ionization energy data. On the periodic chart, ionization energies typically rise as we move between periods and fall as we move down groups.
The loss of a valence electron is indicated by the considerable rise in ionization energy from the first to the second ionization energy (578 kj/mol to 1.817 kj/mol), as can be seen from the supplied numbers. The sudden increase in ionization energy indicates that the element belongs to Group 2 (Group IIA) of the periodic table, where valence electrons are frequently found in pairs.
With the use of this knowledge, we may limit our search to elements in Group 2 of the periodic table. Beryllium (Be) is the sole element in Group 2 that corresponds to the given ionization energy values. The following ionization energies apply to beryllium:
e1=899.5 kj/mol
1757.1 kj/mol for ei2
14,848 kj/mol for ei3.
21,006 kj/mol for ei4.
It is likely that the element indicated in the question is an approximation or that there are additional factors affecting the ionization energies as the given ionization energy values do not exactly match those of Beryllium.
As a result, it is impossible to establish the element with certainty using the available data.
To know more about ionization energy:
https://brainly.com/question/28385102
#SPJ4
Calculate the molar solubility of BaCrO4 (Ksp = 2.1 x 10^-10) in each of the following. (a) pure water (b) 1.6 x 10^-3 M Na_2CrO_4
Answers
The molar solubility of BaCrO4 in 1.6 x 10^-3 M Na2CrO4 is 5.25 x 10^-10 M.
The solubility of BaCrO4 can be calculated using the solubility product constant (Ksp) and the stoichiometry of the balanced chemical equation for the dissolution of BaCrO4 in water.
The balanced chemical equation for the dissolution of BaCrO4 in water is:
BaCrO4(s) ↔ Ba2+(aq) + CrO42-(aq)
The solubility product constant (Ksp) expression for this reaction is:
Ksp = [Ba2+][CrO42-]
(a) To calculate the molar solubility of BaCrO4 in pure water:
Ksp = [Ba2+][CrO42-] = (x)(x) = x^2
where x is the molar solubility of BaCrO4 in pure water.
Rearranging the equation and solving for x, we get:
x = sqrt(Ksp) = sqrt(2.1 x 10^-10) = 1.45 x 10^-5 M
Therefore, the molar solubility of BaCrO4 in pure water is 1.45 x 10^-5 M.
(b) To calculate the molar solubility of BaCrO4 in 1.6 x 10^-3 M Na2CrO4:
In this case, the dissolution of BaCrO4 is affected by the common ion effect due to the presence of CrO42- ions from Na2CrO4. The balanced chemical equation for the reaction is:
BaCrO4(s) + 2Na+(aq) ↔ Ba2+(aq) + CrO42-(aq) + 2Na+(aq)
The initial concentration of CrO42- ions is 1.6 x 10^-3 M, and the concentration of BaCrO4 is x. Therefore, the equilibrium concentration of CrO42- ions is (1.6 x 10^-3 + x) M, and the equilibrium concentrations of Ba2+ and CrO42- ions are both x M.
The Ksp expression for the reaction is:
Ksp = [Ba2+][CrO42-] = (x)(1.6 x 10^-3 + x)
Substituting the value of Ksp and solving for x using the quadratic formula, we get:
x = 5.25 x 10^-10 M
Therefore, the molar solubility of BaCrO4 in 1.6 x 10^-3 M Na2CrO4 is 5.25 x 10^-10 M.
Visit here to learn more about stoichiometry brainly.com/question/28780091
#SPJ11
How to tell if a reaction is double bond or single
Answers
Answer:
Single replacement is a reaction in which one element reacts with another compund to form another compound and another element.
planation:
If the reaction is double displacement then two molecules will be displaced and if it is single displacement reaction then only one element displaces.
What is displacement reaction?Displacement reactions are those reactions in which any element of the given reactant will be displaced by any another element.
If only one element from the reactant molecules will displace then it will be known as single displacement reaction. If two elements or atoms will be displaced from the reactant molecules then it will be known as double displacement reaction.
Hence if one element displaceed then called the single displacement reaction and if two elements displaces then called as the double displacement reaction.
To know more about displacement reactions, visit the below link:
https://brainly.com/question/13328989
A student has a 0.500 m solution of hydrochloric acid (hcl) that is too concentrated for an experiment. the student needs to dilute the solution to 0.100 m. if the student needs 250 ml of the diluted solution, how much of the original solution should be used?
Answers
In order to create a total volume of 250 mL of the 0.100 M solution, the student should utilise 50 mL of the original 0.500 M solution and some solvent (water).
We must increase the solvent concentration (often water) in order to dilute the solution. The following formula can be used to determine how much original solution we need to use:
C1V1 = C2V2
where C1 denotes the starting point, V1 the starting point, C2 the ending point, and V2 the ending volume.
We are aware that C1 = 0.500 M, C2 = 0.100 M, and V2 = 250 mL in this instance. To solve for V1, we can rewrite the formula as follows:
V1 = (C2V2) / C1
V1 = (0.100 M * 250 mL) / 0.500 M
V1 = 50 mL
In order to create a total volume of 250 mL of the 0.100 M solution, the student should utilise 50 mL of the original 0.500 M solution and some solvent (water).
Learn more about M solution here:
https://brainly.com/question/26483178
#SPJ4
Select True or False.
Social Security is normally paid out in the lump payment upon  retirement
Answers
Answer:
TRUE MY DOOD
Explanation:
The sentences below are things people might say if they were planning to invest or not planning to invest Sort them into the correct categories . am thinking about buying stocks Planning to Invest Not Planning to Invest don't know much about investing can't afford to buy stocks don't really like to take risks need a way to manage my money want to save money for my future
Answers
Investing :
"I'm considering investing in equities."
"I need a system for handling my finances."
"I need to put money away for the future."
No Investment :
"My knowledge of investment is limited."
"I am unable to purchase stocks."
"I don't particularly enjoy taking chances."
Explanation:
These are accurate because I recently completed the course that taught me these things.
Learn ore about investing and no investment from here :
https://brainly.com/question/4459036?referrer=searchResults
#SPJ10
The chemical process that occurs during acidosis can be replicated in vitro by adding a strong acid to an ammonia buffer solution. How will the pH change in the solution if 1.0 mL of 0.5 M H2SO4 is added to a 100 mL solution containing 1 M NH3 and 1 M NH4+?
Answers
The pH of the solution will decrease when 1.0 mL of 0.5 M H2SO4 is added to a 100 mL solution containing 1 M NH3 and 1 M NH4+.
When H2SO4 is added to the ammonia buffer solution, it reacts with the ammonia (NH3) and forms ammonium ions (NH4+). The reaction can be represented as follows:
H2SO4 + 2NH3 → (NH4)2SO4
The addition of H2SO4 increases the concentration of NH4+ ions in the solution. As a result, the equilibrium between NH3 and NH4+ is shifted towards NH4+ to maintain the buffer capacity. This increase in NH4+ concentration leads to a decrease in pH.
Ammonium ions (NH4+) are acidic, and their presence increases the concentration of H+ ions in the solution. This increase in H+ ions lowers the pH of the solution. Therefore, the pH of the solution will decrease as a result of the acid-base reaction between H2SO4 and NH3.
The exact change in pH can be calculated using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation, which relates the pH of a buffer solution to the pKa (acid dissociation constant) and the concentrations of the acid and its conjugate base. However, without the pKa value for the ammonium ion, it is not possible to provide a precise numerical answer.
Learn more about Henderson-Hasselbalch equation here:
https://brainly.com/question/31732200
#SPJ11
Are the following chemical equations reversible or irreversible?
2H2O ←→ H3O+ + OH-
HA + H2O ←→ A- + H3O+
HA + H2O → A- + H3O+
MOH → M+ + OH-
Answers
The first two chemical equations are reversible while the other two are irreversible.
What are chemical equations?Chemical equation is a symbolic representation of a chemical reaction which is written in the form of symbols and chemical formulas.The reactants are present on the left hand side while the products are present on the right hand side.
A plus sign is present between reactants and products if they are more than one in any case and an arrow is present pointing towards the product side which indicates the direction of the reaction .There are coefficients present next to the chemical symbols and formulas .
The first chemical equation was put forth by Jean Beguin in 1615.By making use of chemical equations the direction of reaction ,state of reactants and products can be stated. In the chemical equations even the temperature to be maintained and catalyst can be mentioned.
Learn more about chemical equations,here:
https://brainly.com/question/19626681
#SPJ1
What Classification type star this?

Answers
Explanation:
The Sun is a as a G2V type star, a yellow dwarf and a main sequence star. Stars are classified by their spectra (the elements that they absorb) and their temperature.
whish this helped!
A block of wood has a mass of 180 grams it is 10.0cm long, 6.0cm wide and 4.0cm thick what is it’s volume and density
Answers
Answer:
Density = 0.75 g/cm³Explanation:
Density of a substance is given by
\(Density(\rho) = \frac{mass}{volume} \)From the question
mass of the wood = 180 g
Since the wood is a cuboid we can find the volume using the formula
Volume = length × width × height
From the question
length = 10cm
width = 6 cm
height = 4 cm
Volume = 10 × 6 × 4 = 240 cm³
Substitute the values into the above formula and solve for the Density
That's
\(Density(\rho) = \frac{180}{240} \\ = \frac{3}{4} \)We have the final answer as
Density = 0.75 g/cm³Hope this helps you
Which atom attracts electrons more strongly?
Answers
The atom that attracts electrons more strongly is fluorine (F).
Fluorine is the most electronegative element on the periodic table, meaning it has the highest tendency to attract electrons towards itself in a chemical bond. This is due to its small atomic size and high effective nuclear charge. Fluorine has a strong pull on electrons because it has seven valence electrons and only needs one more electron to achieve a stable octet. By attracting an electron from another atom, fluorine can complete its octet and become stable.
Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract electrons in a covalent bond. The higher the electronegativity, the more strongly the atom attracts electrons. Fluorine has an electronegativity value of 3.98 on the Pauling scale, which is the highest value of any element. This makes fluorine highly reactive and allows it to form strong bonds with other elements, particularly those with lower electronegativities. In compounds, fluorine often takes on a negative charge as it attracts electrons towards itself.
In summary, fluorine is the atom that attracts electrons more strongly due to its high electronegativity value and its need to complete its valence shell. Its ability to attract electrons allows it to form stable compounds and exhibit strong chemical reactivity.
for such more questions on electrons
https://brainly.com/question/26084288
#SPJ8
Answer:
Fluorine (F)
Explanation:
what does le chateliter's principle state
Answers
A sample of oxygen, O 2 , occupies 32.2 mL at 30 °C and 452 torr. What volume will it occupy at –70 °C and the same pressure?
Answers
The sample of oxygen will occupy approximately 18.5 mL at -70 °C and the same pressure.
What is the pressure of gas?The force exerted by a gas on specific area is known as gas pressure..
As we know, (P₁ V₁) /(T₁) = (P₂V₂) /(T₂)
Given, P₁ is the initial pressure (452 torr); V₁ is initial volume (32.2 mL)
T₁ is initial temperature in Kelvin (30 °C + 273.15 = 303.15 K)
P₂ is final pressure (452 torr); V₂ is final volume (what we want to find)
T₂ is the final temperature in Kelvin (-70 °C + 273.15 = 203.15 K)
Now, V2 = (P₁ V₁ T₂) / (P2 T₁)
V₂ = (452 torr x 32.2 mL x 203.15 K) / (452 torr x 303.15 K)
V₂ ≈ 18.5 mL
Therefore, the sample of oxygen will occupy approximately 18.5 mL at -70 °C and the same pressure.
To know more about pressure of gas, refer
https://brainly.com/question/24719118
#SPJ9
In calculating the equilibrium constant for a reaction, the coefficients of the chemical equation are used as exponents for the factors in the equilibrium expression. TRUE FALSE
Answers
Answer: The given statement is TRUE.
Explanation:
An equilibrium reaction is one in which rate of forward reaction is equal to the rate of backward reaction.
Equilibrium constant is defined as the ratio of the product of the concentration of products to the product of the concentration of reactants each raised to their stochiometric coefficient.
For example for the given equilibrium reaction;
\(2H_2O(g)\leftrightharpoons 2H_2(g)+O_2(g)\)
\(K_{eq}=\frac{[H_2]^2[O_2]}{[H_2O]^2}\)
Thus the given statement that in calculating the equilibrium constant for a reaction, the coefficients of the chemical equation are used as exponents for the factors in the equilibrium expression is True.
What will be the efficiency of a machine which has an energy loss of 10%
Answers
The efficiency of the machine which has an energy loss of 10% is 90%
What is efficiency?This can be defined as the capacity to achieve a given task with little or no waste. Mathematically, it can be expressed as
Efficiency = (output / input) × 100
How to determine the efficiencyWe shall assume the following:
Input = 100 JOutput = 100 – 10 = 90 JEfficiency =?Efficiency = (output / input) × 100
Efficiency = (90 / 100) × 100
Efficiency = 90%
Learn more about efficiency:
https://brainly.com/question/2009210
#SPJ1
In a synthesis reaction, two atoms of sodium (Na) combine with one molecule of chlorine gas (Cl) to produce sodium chloride (NaCl). How many molecules of
sodium chloride are produced? (1 point)
O four
two
o three
one
Answers
Answer:
3
Explanation:
- According to collision theory, what is not a factor that determines if two molecules will bind?
A. The direction the molecules are facing.
B. The speed the molecules are traveling.
C. The specific heat of the molecules.
D. What element the molecules are.
Answers
The factor which will not determines if two molecules will bind according to collision theory is the direction the molecules are facing
What is collision theory?Collision theory is a theory which describes of predicting the rate at which chemical reactions occurs between atoms and molecules of elements.
So therefore, the factor which will not determines if two molecules will bind according to collision theory is the direction the molecules are facing
Learn more about collision theory:
https://brainly.com/question/20628781
#SPJ1
how do isotopes of a given element differ?
Answers
Answer:
they have different mass numbers
Explanation: